sklearn学习01——LinearRegression / LogisticRegression
sklearn学习01——LinearRegression / LogisticRegression
- 前言
- 一、一/多元线性回归
-
- 1.1、数据生成
- 1.2、得到模型
- 1.3、模型测试和比较
- 1.4、多元线性回归
- 1.5、训练一元线性模型常用方法——梯度下降法
- 二、多项式线性回归
- 三、逻辑(Logistic)回归
-
- 3.1、损失函数
- 3.2、梯度下降法
- 3.3、代码实现
- 总结
前言
在学习了机器学习(周志华)的一系列的模型和学习算法之后,我们也需要使用python实际操作,实现它的效果,进而深入理解这些模型的原理。本篇讲解 几种线性回归 的sklearn实现。一、一/多元线性回归
1.1、数据生成
仅为了更加方便直观的理解机器学习算法,这里使用人工生成的简单数据。生成数据的思路是:设定一个二维的函数(维度高了没办法在平面上画出来),根据这个函数生成一些离散的数据点,对每个数据点我们可以适当的加一点波动,也就是噪声。代码如下:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def true_fun(X): # 这是我们设定的真实函数,我们的模型越接近它越好
return 1.5*X + 0.2
np.random.seed(0) # 设置随机种子
n_samples = 30 # 设置采样数据点的个数
'''生成随机数据作为训练集,并且加一些噪声'''
X_train = np.sort(np.random.rand(n_samples))
y_train = (true_fun(X_train) + np.random.randn(n_samples) * 0.05).reshape(n_samples,1)
30个样本,每个样本都只有一个特征(因为是一维的)。
注意:噪声是按照正态分布随机生成的30个数,附加到每个样本的 y 上,因此 y 也是符合正态分布的了。
1.2、得到模型
第一步生成好了数据,即有了训练集。接下来可以定义我们的算法模型,因为sklearn库中有类LinearRegression,所以直接调用它作为我们的线性模型即可。我们要做的就是:将训练集放入该LinearRegression模型中,然后等待它调用自己内部的方法求得最优解。代码如下:
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression # 导入线性回归模型
model = LinearRegression() # 定义模型
model.fit(X_train[:,np.newaxis], y_train) # 训练模型
print("输出参数w:",model.coef_) # 输出模型参数w
print("输出参数b:",model.intercept_) # 输出参数b
输出参数w: [[1.4474774]]
输出参数b: [0.22557542]
1.3、模型测试和比较
第二步我们根据训练集和 sklearn 库中的模型算法得到一组解,写成方程形式为:y = 1.4474774 * x + 0.22557542,而真实的函数为:y = 1.5*x + 0.2,相比来说还是非常接近的。下面使用python代码将训练集(30个样本点)、我们学得的模型、真实模型都可视化出来:
X_test = np.linspace(0, 1, 100)
plt.plot(X_test, model.predict(X_test[:, np.newaxis]), label="Model")
plt.plot(X_test, true_fun(X_test), label="True function")
plt.scatter(X_train,y_train) # 画出训练集的点
plt.legend(loc="best")
plt.show()
1.4、多元线性回归
多元的线性回归,思路与一元是一样的。使用sklearn库来实现的话,我们只需要准备一组 多元的训练集 即可,依旧调用 内部的LinearRegression类 实现模型的训练,代码如下:
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
X_train = [[1,1,1],[1,1,2],[1,2,1]] # 以三元为例
y_train = [[6],[9],[8]]
model = LinearRegression()
model.fit(X_train, y_train)
print("输出参数w:",model.coef_) # 输出参数w1,w2,w3
print("输出参数b:",model.intercept_) # 输出参数b
test_X = [[1,3,5]]
pred_y = model.predict(test_X)
print("预测结果:",pred_y)
1.5、训练一元线性模型常用方法——梯度下降法
梯度下降法大致流程如下图:
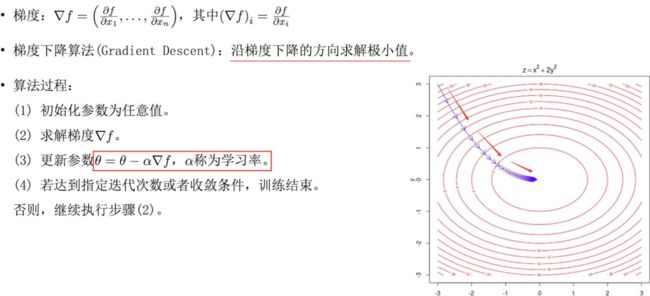
首先先假定我们的线性模型为:
那么损失函数为:
![]()
要求损失函数最小值,我们对其求梯度:
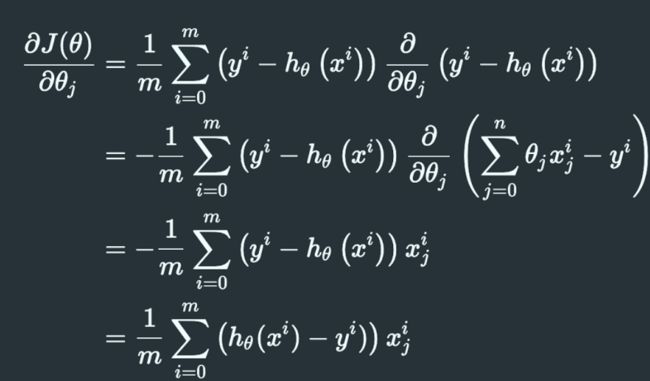
上述梯度使用矩阵形式表示:
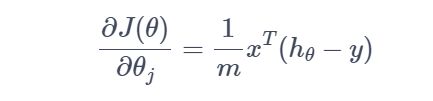
在使用梯度下降算法更新我们线性模型的参数时,先初始化这些参数为全 1,然后按照梯度下降的方向更新所有的参数(批量梯度下降),达到迭代次数或者达到精度即可停止更新。代码如下:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 梯度下降方法 实现一元线性回归模型
def true_fun(X):
return 1.5 * X + 0.2
np.random.seed(0) # 随机种子
n_samples = 30
'''生成随机数据作为训练集'''
X_train = np.sort(np.random.rand(n_samples))
y_train = (true_fun(X_train) + np.random.randn(n_samples) * 0.05).reshape(n_samples, 1)
# 添加一维数据
data_X = []
for x in X_train:
data_X.append([1, x])
print(data_X)
data_X = np.array((data_X))
print(data_X)
m,p = np.shape(data_X) # m, 数据量 p: 特征数
max_iter = 1000 # 迭代数
weights = np.ones((p,1)) # 初始权重:设置为 1
print(weights)
alpha = 0.1 # 学习率
for i in range(0,max_iter):
error = np.dot(data_X,weights)- y_train
gradient = data_X.transpose().dot(error)/m
weights = weights - alpha * gradient
print("输出参数w:",weights[1:][0]) # 输出模型参数w
print("输出参数b:",weights[0]) # 输出参数b
X_test = np.linspace(0, 1, 100)
plt.plot(X_test, X_test*weights[1][0]+weights[0][0], label="Model")
plt.plot(X_test, true_fun(X_test), label="True function")
plt.scatter(X_train,y_train) # 画出训练集的点
plt.legend(loc="best")
plt.show()
输出参数w: 1.4454389990357697
输出参数b: 0.2268326207539249
二、多项式线性回归
- 训练集
用来训练模型内参数的数据集 - 验证集
用于在训练过程中检验模型的状态,收敛情况,通常用于调整超参数,根据几组模型验证集上的表现决定哪组超参数拥有最好的性能。
同时验证集在训练过程中还可以用来监控模型是否发生过拟合,一般来说验证集表现稳定后,若继续训练,训练集表现还会继续上升,但是验证集会出现不升反降的情况,这样一般就发生了过拟合。所以验证集也用来判断何时停止训练 - 测试集
测试集用来评价模型泛化能力,即使用训练集调整了参数,之前模型使用验证集确定了超参数,最后使用一个不同的数据集来检查模型。
这里我们使用 交叉验证方法来获得多组的 训练集/测试集,求得每组的模型评估(回归的评估度量手段一般为均方误差)然后求平均,作为评估此模型的标准。

多项式回归代码如下(这里尝试了三个最高次 1、4、15):
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.pipeline import Pipeline
from sklearn.preprocessing import PolynomialFeatures
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score
def true_fun(X):
return np.cos(1.5 * np.pi * X)
np.random.seed(0)
n_samples = 30
degrees = [1, 4, 15] # 多项式最高次
X = np.sort(np.random.rand(n_samples))
y = true_fun(X) + np.random.randn(n_samples) * 0.1
plt.figure(figsize=(14, 5))
for i in range(len(degrees)):
ax = plt.subplot(1, len(degrees), i + 1)
plt.setp(ax, xticks=(), yticks=())
polynomial_features = PolynomialFeatures(degree=degrees[i],
include_bias=False)
linear_regression = LinearRegression()
pipeline = Pipeline([("polynomial_features", polynomial_features),
("linear_regression", linear_regression)]) # 使用pipline串联模型
pipeline.fit(X[:, np.newaxis], y)
# 使用交叉验证
scores = cross_val_score(pipeline, X[:, np.newaxis], y,
scoring="neg_mean_squared_error", cv=10)
X_test = np.linspace(0, 1, 100)
plt.plot(X_test, pipeline.predict(X_test[:, np.newaxis]), label="Model")
plt.plot(X_test, true_fun(X_test), label="True function")
plt.scatter(X, y, edgecolor='b', s=20, label="Samples")
plt.xlabel("x")
plt.ylabel("y")
plt.xlim((0, 1))
plt.ylim((-2, 2))
plt.legend(loc="best")
plt.title("Degree {}\nMSE = {:.2e}(+/- {:.2e})".format(
degrees[i], -scores.mean(), scores.std()))
plt.show()
三、逻辑(Logistic)回归
3.1、损失函数
我们知道,在线性模型上套一个Sigmoid函数就成了对数几率回归(具体参考西瓜书),假设此模型为:
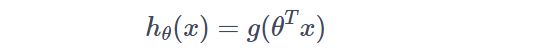

再参考西瓜书得到其损失函数,这里直接写出来:
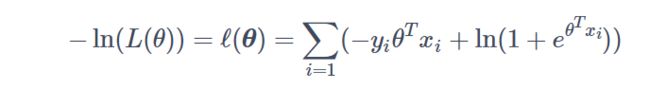
3.2、梯度下降法
3.3、代码实现
import sys
from pathlib import Path
curr_path = str(Path().absolute())
parent_path = str(Path().absolute().parent)
sys.path.append(parent_path) # add current terminal path to sys.path
import numpy as np
from Mnist.load_data import load_local_mnist
(x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test) = load_local_mnist(one_hot=False)
# print(np.shape(x_train),np.shape(y_train))
ones_col=[[1] for i in range(len(x_train))] # 生成全为1的二维嵌套列表,即[[1],[1],...,[1]]
x_train_modified=np.append(x_train,ones_col,axis=1)
ones_col=[[1] for i in range(len(x_test))]
x_test_modified=np.append(x_test,ones_col,axis=1)
# print(np.shape(x_train_modified))
# Mnsit有0-9十个标记,由于是二分类任务,所以可以将标记0的作为1,其余为0用于识别是否为0的任务
y_train_modified=np.array([1 if y_train[i]==1 else 0 for i in range(len(y_train))])
y_test_modified=np.array([1 if y_test[i]==1 else 0 for i in range(len(y_test))])
n_iters=10
x_train_modified_mat = np.mat(x_train_modified)
theta = np.mat(np.zeros(len(x_train_modified[0])))
lr = 0.01 # 学习率
def sigmoid(x):
'''sigmoid函数
'''
return 1.0/(1+np.exp(-x))
小批量梯度下降法
for i_iter in range(n_iters):
for n in range(len(x_train_modified)):
hypothesis = sigmoid(np.dot(x_train_modified[n], theta.T))
error = y_train_modified[n]- hypothesis
grad = error*x_train_modified_mat[n]
theta += lr*grad
print('LogisticRegression Model(learning_rate={},i_iter={})'.format(
lr, i_iter+1))
总结
本文对一元线性回归、多元线性回归、多项式线性回归以及逻辑回归进行了算法分析和代码实现,梯度下降法也是求凸函数最优解常用的方法;同时,sklearn相关库、函数的调用掌握不足,需要多加学习。另外,本文参考了下述链接:
机器学习算法实现。