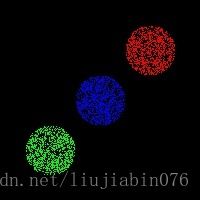
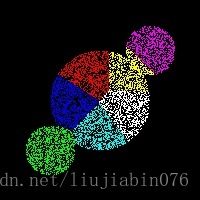
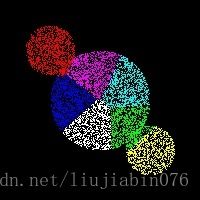
【聚类】ISODATA使用示例
Kmeans在进行样本聚类时,需要设定样本类别。ISODATA算法是在k-均值算法的基础上,增加对聚类结果的“合并”和“分裂”两个操作,并设定算法运行控制参数的一种聚类算法。因此,ISODATA是一种自适应聚类的算法。算法原理见聚类算法:ISODATA算法。
这里给出ISODATA使用示例。
首先,利用随机数生成待分类样本。给定一个圆的中心与半径,并设定样本点规模,生成二值样本。
void genDataPoints(int width, int height, cv::Mat& image, cv::Point center, int radius)
{
if (image.empty())
image = cv::Mat(height,width,CV_8U,cv::Scalar::all(0));
int total_count = (int)( 0.5+ CV_PI*radius*radius);
std::random_device rd;
std::mt19937 mt(rd());
std::uniform_int_distribution<> d(-radius,radius );
std::map<int, int> hist;
for (int n = 0; n < total_count*0.8; ++n) {
int rand1 = d(mt);
int rand2 = d(mt);
float distance = sqrt(rand1*rand1 + rand2*rand2);
int x = center.x + rand1;
int y = center.y + rand2;
if (x < 0 || x >= width || y < 0 || y >= height || distance >= radius)
continue;
image.ptr(y)[x] = 255;
++hist[rand1];
++hist[rand2];
}
for (auto p : hist) {
std::cout << std::fixed << std::setprecision(1) << std::setw(2)
<< p.first << ' ' << std::string(p.second / 20, '*') << '\n';
}
} int width = 200, height = 200;
int radius = 25;
Mat genMask;
genDataPoints(width, height, genMask,cv::Point(width/2,height/2) ,radius);
genDataPoints(width, height, genMask, cv::Point(width / 4, height / 4),
radius);
genDataPoints(width, height, genMask, cv::Point(3*width / 4, 3*height / 4),
radius);
genDataPoints(width, height, genMask, cv::Point(width / 4, 3*height / 4),
radius);
genDataPoints(width, height, genMask, cv::Point(3*width / 4, height / 4),
radius);
其次,利用ISODATA算法进行分类:
bool autoCluster(cv::Mat mask)
{
//1. prepare data
int sampleCount = countNonZero(mask);
if (sampleCount < 2500)
return false;
int w = mask.cols, h = mask.rows;
int NUMBANDS = 2;
int SAMPRM = 500;
int NUMCLUS = 3;
KMpointArray points = AllocPts(sampleCount, NUMBANDS); // (x,y)
int ncount = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < h; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < w; j++)
{
int mask_val = mask.ptr(i)[j];
if (0 == mask_val)
continue;
points[ncount][0] = 1.0*j / w; // x ->j
points[ncount][1] = 1.0*i / h; // x->i
ncount++;
}
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//2.cluster
int iter = 0;
double exec_time = 0;
int MAXITER = 20;
int MAXPAIR = 5; // maximum number of pairs to lump
double LUMP = 0.1;
double std_m = 1.0 / pow(NUMCLUS, 1 / (double)NUMBANDS);
double STDV = std_m*0.1;
Image IMG = Image(sampleCount, 1, NUMBANDS, NUMCLUS, SAMPRM);
IMG.setPoints(points);
IMG.sampleCenters();
IMG.samplePoints(sampleCount);
clock_t start = clock(); // start the clock
for (iter = 1; iter <= MAXITER; iter++)
{
LOG(INFO) << " Iteration Number " << iter << " :";
if (iter == MAXITER)
{
LOG(INFO) << "\tPerform the last iterative clustering on all points";
IMG.preFinalClustering();
}
do
{
IMG.CalculateDistances();
LOG(INFO) << "\tPut points into clusters.";
IMG.PutInCluster();
//STEP 3:
IMG.PostAnalyzeClusters();
//STEP 4:
LOG(INFO) << "\tUpdate centers by calculating the average point in each cluster.";
IMG.UpdateCenters();
} while (IMG.WasDeleted());
//need to update distances since in the last iteration centers have modified.
IMG.CalculateDistances();
IMG.PutInCluster();
//STEP 5:
IMG.CalculateAverageDistances();
//STEP 6:
IMG.OverallAverageDistances();
//STEP 7:
int next_step = 8;
if (iter == MAXITER)
{
LUMP = 0;
next_step = 11;
}
else if (IMG.getNumCenters() <= (NUMCLUS / 2))
{
next_step = 8;
}
else if ((iter % 2 == 0) || (IMG.getNumCenters() >= 2 * NUMCLUS))
{
next_step = 11;
}
switch (next_step)
{
case 8:
{
//STEP 8:
IMG.CalculateSTDVector();
//STEP 9:
IMG.CalculateVmax();
//STEP 10:
// the vector to_split will contain integers that represent the cluster numbers
// that need to be split.
std::vector<int> to_split = IMG.ShouldSplit(STDV);
if (to_split.size() != 0)
{
IMG.Split(to_split);
//we need to substract one if it was the last iteration because otherwise we
//we will exit the loop without updating clusters.
if (iter == MAXITER)
iter = iter - 1;
break; //go to step 2
}
} //CASE 8
case 11:
{
//STEP 11:
IMG.ComputeCenterDistances();
//STEP 12:
std::vector to_lump = IMG.FindLumpCandidates(LUMP, MAXPAIR);
//STEP 13:
if (to_lump.size() != 0)
IMG.Lump(to_lump);
} //CASE 11
} // SWITCH
// LOG(INFO) << "total overall dist " << IMG.getDistortions();
if (IMG.getDistortions() < 0.005)
break;
} // for LOOP
exec_time = elapsedTime(start); // get elapsed time
LOG(INFO) << "Algorithm's run time: " << exec_time << " CPU seconds.";
LOG(INFO) << "total overall dist " << IMG.getDistortions();
LOG(INFO) << "cluster number " << IMG.getNumCenters();
DeallocPts(points);
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//3. return result
int* label = new int[sampleCount];
if (!label)
{
LOG(ERROR) << "Memory Allocation for 'label' Failed.";
return false;
}
int num_cluster = IMG.getNumCenters();
if (num_cluster > 6)
{
LOG(ERROR) << "points cluster more than 6 : num_cluster = " << num_cluster;
return false;
}
IMG.getClusterLabel(label);
std::vector< std::vector > clustered_points(num_cluster);
ncount = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < h; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < w; j++)
{
int mask_val = stamp_text_mask.ptr(i)[j];
if (0 == mask_val)
continue;
int cluster_id = label[ncount];
if (0 == cluster_id)
{
ncount++;
continue;
}
clustered_points[label[ncount] - 1].push_back(cv::Point(j, i));
ncount++;
}
delete[] label;
label = NULL;
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// 4. draw result
cv::Vec3b colors[8] = { cv::Vec3b(0, 0, 255),
cv::Vec3b(0, 255, 0),
cv::Vec3b(255, 0, 0),
cv::Vec3b(255, 0, 255),
cv::Vec3b(255, 255, 0),
cv::Vec3b(0, 255, 255),
cv::Vec3b(255, 255, 255) };
Mat drawImg;
cvtColor(mask, drawImg, CV_GRAY2BGR);
drawImg.setTo(cv::Scalar::all(0));
std::random_device rd;
for (int i = 0; i < num_cluster; i++)
{
std::mt19937 mt(rd());
std::uniform_int_distribution<> d(0, 255);
std::vector points = clustered_points[i];
cv::Vec3b color = colors[i%8];
for (int j = 0; j < points.size(); j++)
{
int px = points[j].x, py = points[j].y;
drawImg.ptr(py)[px] = color;
}
}
cv::namedWindow("Cluster", 0);
cv::imshow("Cluster", drawImg);
cv::waitKey();
cv::imwrite("cluster.jpg", drawImg);
return true;
}
接着,对应分类关键参数说明如下,注意输入样本数据均作归一化处理。
int MAXITER = 20;// 算法最大迭代次数
int MAXPAIR = 5; // 单次不同类别进行合并时的最大类别数
double LUMP = 0.1; // 不同类别进行合并时的最大中心距离,大于该值则不进行合并
double std_m = 1.0 / pow(NUMCLUS, 1 / (double)NUMBANDS);
double STDV = std_m*0.1; // 同一类别样本方差的最大值,大于该值则进行分裂最后,给出其他数据聚类结果。针对不同样本数据,类别合并与分裂的参数(LUMP , STDV)需要进行对应的调整。 关于如何设置这两个参数,我的个人思路是,针对数据样本集合,选择有代表性的几个不同类型样本,由于已知样本类别数量,可通过Kmeans方法计算出正确分类,然后得出不同类别中心之间的距离以及单个类别的数据样本方差。通过多组数据的分析与总结,从而得出整个样本集合中,什么情况下样本实例的类别需要合并或者分裂。
总结,针对数据集不同类别其样本数量有较大差别时,在进行自适应聚类时,将很难设定一个有效参数,获得样本数据的准确类别。上图数据中,中心类别的数据样本数量远大于两侧类别的样本数量(4倍),因此分类结果有误,此时一个较好的思路是,通过类别中心位置等先验信息有差别地设置样本合并与聚类参数。
完整代码见 GitHub。