图像语义分割网络FCN(32s、16s、8s)原理及MindSpore实现
一、FCN网络结构
全卷积网络(Fully Convolutional Networks),是较早用于图像语义分割的神经网络。根据名称可知,FCN主要网络结构全部由卷积层组成,在图像领域,卷积是一种非常好的特征提取方式。本质上,图像分割是一个分类任务,需要做的就是对图像上每一个像素按照人工标注进行分类。
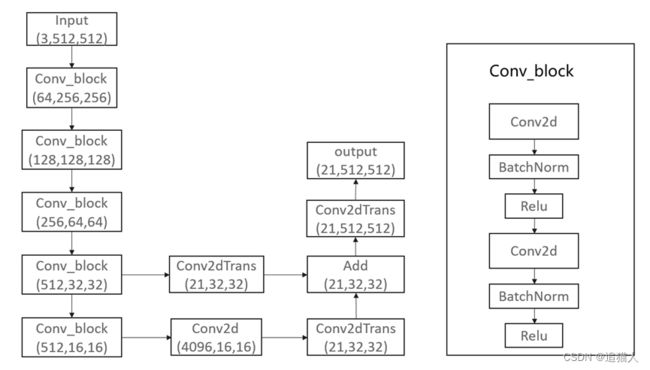
FCN大致网络结构如下:
上图模型结构为针对VOC数据集的21个语义分割,即数据集包含21种不同分割类型。当图像进入神经网络,第一个卷积层将图像由三通道转换为96通道featuremap,第二个卷积层转换为256个通道,第三个卷积层384个通道,直到最后一个卷积层变为21个通道,每个通道对应不同分割类型。实际上,卷积层整个网络结构中卷积层的通道数可以根据不同任务进行调整,前面每经过一层会对图像进行一次宽高减半的下采样,经过5个卷积层以后,featuremap为输入的1/32,最后通过反卷积层将featuremap宽高恢复到输入图像大小。
二、FCN模型结构实现
FCN模型结构可以根据分割细粒度使用FCN32s、FCN16s、FCN8s等结构,32s即从32倍下采样的特征图恢复至输入大小,16s和8s则是从16倍和8倍下采样恢复至输入大小,当然还可以使用4s、2s结构,数字越小使用的反卷积层进行上采样越多,对应模型结构更加复杂,理论上分割的效果更精细。这里采用深度学习框架MindSpore来搭建模型结构。
FCN32s模型结构示意图:
模型构建脚本:
class FCN32s(nn.Cell):
def __init__(self, n_class=21):
super(FCN32s, self).__init__()
self.block1 = nn.SequentialCell(
nn.Conv2d(3, 64, 3),
nn.BatchNorm2d(64),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(64, 64, 3),
nn.BatchNorm2d(64),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(2, stride=2)
)
self.block2 = nn.SequentialCell(
nn.Conv2d(64, 128, 3),
nn.BatchNorm2d(128),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(128, 128, 3),
nn.BatchNorm2d(128),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(2, stride=2)
)
self.block3 = nn.SequentialCell(
nn.Conv2d(128, 256, 3),
nn.BatchNorm2d(256),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(256, 256, 3),
nn.BatchNorm2d(256),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(256, 256, 3),
nn.BatchNorm2d(256),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(2, stride=2)
)
self.block4 = nn.SequentialCell(
nn.Conv2d(256, 512, 3),
nn.BatchNorm2d(512),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(512, 512, 3),
nn.BatchNorm2d(512),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(512, 512, 3),
nn.BatchNorm2d(512),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(2, stride=2)
)
self.block5 = nn.SequentialCell(
nn.Conv2d(512, 512, 3),
nn.BatchNorm2d(512),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(512, 512, 3),
nn.BatchNorm2d(512),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(512, 512, 3),
nn.BatchNorm2d(512),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(2, stride=2)
)
self.block6 = nn.SequentialCell(
nn.Conv2d(512, 4096, 7),
nn.BatchNorm2d(4096),
nn.ReLU()
)
self.block7 = nn.SequentialCell(
nn.Conv2d(4096, 4096, 1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(4096),
nn.ReLU()
)
self.upscore = nn.SequentialCell(
nn.Conv2d(4096, n_class, 1),
nn.Conv2dTranspose(n_class, n_class, 4, 2, has_bias=False),
nn.Conv2dTranspose(n_class, n_class, 32, 16, has_bias=False)
)
def construct(self, x):
x = self.block1(x)
x = self.block2(x)
x = self.block3(x)
x = self.block4(x)
x = self.block5(x)
x = self.block6(x)
x = self.block7(x)
x = self.upscore(x)
return x
FCN16s模型结构示意图:
FCN16s模型脚本:
class FCN16s(nn.Cell):
def __init__(self, n_class=21):
super(FCN16s, self).__init__()
self.block1 = nn.SequentialCell(
nn.Conv2d(3, 64, 3),
nn.BatchNorm2d(64),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(64, 64, 3),
nn.BatchNorm2d(64),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(2, stride=2)
)
self.block2 = nn.SequentialCell(
nn.Conv2d(64, 128, 3),
nn.BatchNorm2d(128),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(128, 128, 3),
nn.BatchNorm2d(128),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(2, stride=2)
)
self.block3 = nn.SequentialCell(
nn.Conv2d(128, 256, 3),
nn.BatchNorm2d(256),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(256, 256, 3),
nn.BatchNorm2d(256),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(256, 256, 3),
nn.BatchNorm2d(256),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(2, stride=2)
)
self.block4 = nn.SequentialCell(
nn.Conv2d(256, 512, 3),
nn.BatchNorm2d(512),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(512, 512, 3),
nn.BatchNorm2d(512),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(512, 512, 3),
nn.BatchNorm2d(512),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(2, stride=2)
)
self.block5 = nn.SequentialCell(
nn.Conv2d(512, 512, 3),
nn.BatchNorm2d(512),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(512, 512, 3),
nn.BatchNorm2d(512),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(512, 512, 3),
nn.BatchNorm2d(512),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(2, stride=2)
)
self.block6 = nn.SequentialCell(
nn.Conv2d(512, 4096, 7),
nn.BatchNorm2d(4096),
nn.ReLU()
)
self.block7 = nn.SequentialCell(
nn.Conv2d(4096, 4096, 1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(4096),
nn.ReLU()
)
self.upscore_pool5 = nn.SequentialCell(
nn.Conv2d(4096, n_class, 1),
nn.Conv2dTranspose(n_class, n_class, 4, 2)
)
self.score_pool4 = nn.Conv2dTranspose(512, n_class, 1, has_bias=False)
self.add = op.Add()
self.upscore_pool = nn.Conv2dTranspose(n_class, n_class, 32, 16, has_bias=False)
def construct(self, x):
x1 = self.block1(x)
x2 = self.block2(x1)
x3 = self.block3(x2)
x4 = self.block4(x3)
x5 = self.block5(x4)
x6 = self.block6(x5)
x7 = self.block7(x6)
pool5 = self.upscore_pool5(x7)
pool4 = self.score_pool4(x4)
pool = self.add(pool4, pool5)
pool = self.upscore_pool(pool)
return pool
FCN8s模型结构示意图:
FCN8s模型脚本:
class FCN8s(nn.Cell):
def __init__(self, n_class=21):
super(FCN8s, self).__init__()
self.block1 = nn.SequentialCell(
nn.Conv2d(3, 64, 3),
nn.BatchNorm2d(64),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(64, 64, 3),
nn.BatchNorm2d(64),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(2, stride=2)
)
self.block2 = nn.SequentialCell(
nn.Conv2d(64, 128, 3),
nn.BatchNorm2d(128),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(128, 128, 3),
nn.BatchNorm2d(128),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(2, stride=2)
)
self.block3 = nn.SequentialCell(
nn.Conv2d(128, 256, 3),
nn.BatchNorm2d(256),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(256, 256, 3),
nn.BatchNorm2d(256),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(256, 256, 3),
nn.BatchNorm2d(256),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(2, stride=2)
)
self.block4 = nn.SequentialCell(
nn.Conv2d(256, 512, 3),
nn.BatchNorm2d(512),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(512, 512, 3),
nn.BatchNorm2d(512),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(512, 512, 3),
nn.BatchNorm2d(512),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(2, stride=2)
)
self.block5 = nn.SequentialCell(
nn.Conv2d(512, 512, 3),
nn.BatchNorm2d(512),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(512, 512, 3),
nn.BatchNorm2d(512),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(512, 512, 3),
nn.BatchNorm2d(512),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(2, stride=2)
)
self.block6 = nn.SequentialCell(
nn.Conv2d(512, 4096, 7),
nn.BatchNorm2d(4096),
nn.ReLU()
)
self.block7 = nn.SequentialCell(
nn.Conv2d(4096, 4096, 1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(4096),
nn.ReLU()
)
self.upscore_pool5 = nn.SequentialCell(
nn.Conv2d(4096, n_class, 1),
nn.Conv2dTranspose(n_class, n_class, 4, 2, has_bias=False)
)
self.score_pool4 = nn.Conv2dTranspose(512, n_class, 1, has_bias=False)
self.score_pool3 = nn.Conv2dTranspose(256, n_class, 1, has_bias=False)
self.add = op.Add()
self.upscore_pool4 = nn.Conv2dTranspose(n_class, n_class, 4, 2, has_bias=False)
self.upscore_pool = nn.Conv2dTranspose(n_class, n_class, 16, 8, has_bias=False)
def construct(self, x):
x1 = self.block1(x)
x2 = self.block2(x1)
x3 = self.block3(x2)
x4 = self.block4(x3)
x5 = self.block5(x4)
x6 = self.block6(x5)
x7 = self.block7(x6)
pool5 = self.upscore_pool5(x7)
pool4 = self.score_pool4(x4)
pool3 = self.score_pool3(x3)
pool4 = self.add(pool4, pool5)
pool4 = self.upscore_pool4(pool4)
pool = self.add(pool3, pool4)
pool = self.upscore_pool(pool)
return pool
三、数据集
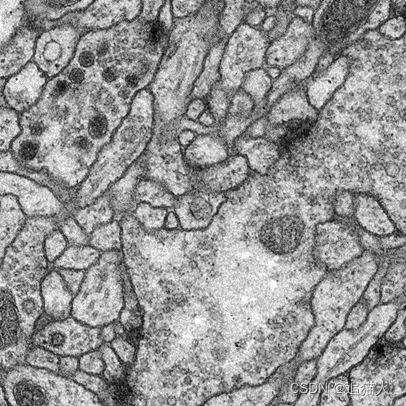
模型结构定义好后,我们需要通过对数据集的训练来检验模型性能。这里使用开源的细胞分割数据集:https://www.kaggle.com/code/kerneler/starter-isbi-challenge-dataset-21087002-9/data。数据集包含30张果蝇一龄幼虫腹神经索(VNC)的连续透射电子显微镜图像数据。
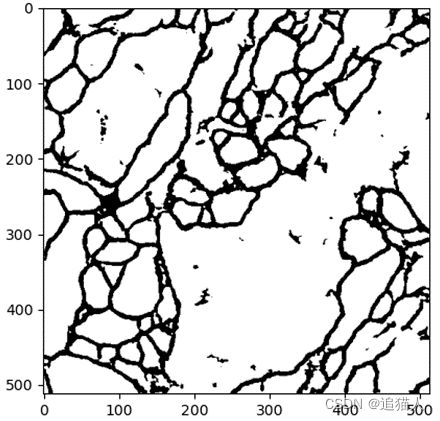
首先通过数值替换对分割标签图像进行转换,将白色背景替换为1。
标签图像预处理:
def convert(path, outpath):
files = os.listdir(path)
for i in range(len(files)):
file = files[i]
img_path = os.path.join(path, file)
img = cv2.imread(img_path)
img[img==255] = 1
out = os.path.join(outpath, file)
cv2.imwrite(out, img)
定义数据集:
class Cell_seg_dataset:
def __init__(self, root_path):
img_path = os.path.join(root_path, 'images')
label_path = os.path.join(root_path, 'labels')
self.img_list = []
self.label_list = []
img_names = os.listdir(img_path)
label_names = os.listdir(label_path)
self.img_index = np.array(range(len(img_names)))
self.label_index = np.array(range(len(label_names)))
for i in range(len(img_names)):
self.img_list.append(os.path.join(img_path, img_names[i]))
self.label_list.append(os.path.join(label_path, label_names[i]))
self.img_index[i] = i
self.label_index[i] = i
if len(img_names) != len(label_names):
raise 'images is not equal to labels !'
def __getitem__(self, index):
return self.img_index[index], self.label_index[index]
def __len__(self):
return len(self.img_list)
数据预处理:
def _preprocess(dataset, images, labels, classes, batch_size, img_channel, img_shape, label_shape):
img_path = []
label_path = []
for i in range(batch_size):
img_path.append(dataset.img_list[images[i]])
label_path.append(dataset.label_list[labels[i]])
one_hot = ops.OneHot()
transpose = ops.Transpose()
img_out = np.zeros((batch_size, img_channel, img_shape, img_shape))
label_out = np.zeros((batch_size, label_shape, label_shape, classes))
for i in range(len(images)):
img = cv2.imread(img_path[i])
img = img / 255.0
img = Tensor(img, dtype=mindspore.float32)
img = transpose(img, (2, 0, 1))
label = cv2.imread(label_path[i])
label = cv2.cvtColor(label, cv2.COLOR_RGB2GRAY)
label = one_hot(Tensor(label, dtype=mindspore.int32), classes,
Tensor(1, dtype=mindspore.float32),
Tensor(0, dtype=mindspore.float32))
img_out[i] = img.asnumpy()
label_out[i] = label.asnumpy()
img_out = Tensor(img_out, dtype=mindspore.float32)
label_out = Tensor(label_out, dtype=mindspore.float32)
return img_out, label_out
四、模型训练
首先需要根据模型输出结果结合标签数据进行损失计算,这里使用的数据集为二分类图像分割数据,通过onehot将标签图像转换为2通道的featuremap,将网络输出结果与标签featuremap进行逐像素计算loss,通过反向传播更新模型。
优化器:Adam
损失函数:交叉熵损失
计算loss:
class MyWithLossCell(nn.Cell):
def __init__(self, backbone, loss_func, batch_size, classes, label_shape):
super(MyWithLossCell, self).__init__()
self._backbone = backbone
self._loss_func = loss_func
self.transpose = ops.Transpose()
self.shape = (batch_size * label_shape * label_shape, classes)
self.reshape = ops.Reshape()
self.sum = ops.ReduceSum(False)
def construct(self, inputs, labels):
logits = self._backbone(inputs)
logits = self.transpose(logits, (0, 2, 3, 1))
logits = self.reshape(logits, self.shape)
labels = self.reshape(labels, self.shape)
loss = self._loss_func(logits, labels)
loss = self.sum(loss)
return loss
定义训练脚本:
def train():
train_data_path = config.train_data
dataset = Cell_seg_dataset(train_data_path)
train_data = ds.GeneratorDataset(dataset, ["data", "label"], shuffle=True)
train_data = train_data.batch(config.batch_size)
if config.backbone == 'FCN8s':
net = FCN8s(config.num_classes)
elif config.backbone == 'FCN16s':
net = FCN16s(config.num_classes)
else:
net = FCN32s(config.num_classes)
if config.use_pretrain_ckpt:
ckpt_file = config.pretrain_ckpt_path
param_dict = load_checkpoint(ckpt_file)
load_param_into_net(net, param_dict)
opt = nn.Adam(params=net.trainable_params(), learning_rate=config.lr, weight_decay=0.9)
loss_func = nn.SoftmaxCrossEntropyWithLogits()
loss_net = MyWithLossCell(net, loss_func, config.batch_size, config.num_classes, config.label_shape)
train_net = nn.TrainOneStepCell(loss_net, opt)
train_net.set_train()
for epoch in range(config.epochs):
train_loss = 0
step = 0
for data in train_data.create_dict_iterator():
images, labels = _preprocess(dataset, data['data'], data['label'], config.num_classes, config.batch_size,
config.input_channel, config.input_shape, config.label_shape)
loss = train_net(images, labels)
step += 1
print(f'step:{step},loss:{loss}')
train_loss += loss
iter = epoch + 1
print(f'epoch:{iter}, train loss:{train_loss}')
if iter % 10 == 0:
save_checkpoint(net, f'{iter}.ckpt')
五、推理验证
训练完成后,通过加载保存的ckpt文件,在测试数据上进行推理验证。
推理脚本:
import mindspore
from mindspore import load_checkpoint, load_param_into_net, Tensor, ops
from src.model import FCN8s
import numpy as np
import cv2
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def main(ckptPath, imagePath, classes):
img = cv2.imread(imagePath)
img = img / 255.0
img = Tensor(img, dtype=mindspore.float32)
transpose = ops.Transpose()
img = transpose(img, (2, 0, 1))
expand_dim = ops.ExpandDims()
img = expand_dim(img, 0)
net = FCN8s(classes)
param_dict = load_checkpoint(ckptPath)
load_param_into_net(net, param_dict)
net.set_train(False)
result = net(img)
result = np.squeeze(result.asnumpy())
return result
if __name__ == '__main__':
img_path = '0.jpg'
ckpt_path = '800.ckpt'
num_classes = 2
result = main(ckpt_path, img_path, num_classes)
print(result.shape)
img_rgb = [[0, 0, 0], [255, 255, 255]]
img = np.ones((512, 512, 3))
for i in range(512):
for j in range(512):
max_value = 0
max_index = 0
for k in range(num_classes):
value = result[k, i, j]
if value > max_value:
max_value = value
max_index = k
img[i][j] = img_rgb[max_index]
plt.figure('image')
plt.imshow(img)
plt.show()