Yolov3中部分算法及函数
0、解析xml文件中的标注信息转化为中心点及宽高并归一化
def load_dataset(path):
dataset = []
# print(path)
print(listdir(path))
for xml_file in glob.glob("{}/*xml".format(path)):
# print(xml_file)
tree = ET.parse(xml_file)
# print('tree')
height = int(tree.findtext("./size/height"))
width = int(tree.findtext("./size/width"))
# print(height)
# print(tree.iter("object"))
for obj in tree.iter("object"):
# print(obj.findtext("bndbox/xmin"))
xmin = int(obj.findtext("bndbox/xmin")) / width
ymin = int(obj.findtext("bndbox/ymin")) / height
xmax = int(obj.findtext("bndbox/xmax")) / width
ymax = int(obj.findtext("bndbox/ymax")) / height
dataset.append([xmax - xmin, ymax - ymin])
return np.array(dataset)1、k-means
算法思想:
(1)随机选取k个聚类中心(一般在样本集中选取,也可以自己随机选取);
(2)计算每个样本与k个聚类中心的距离,并将样本归到距离最小的那个类中;
(3)更新中心,计算属于k类的样本的均值作为新的中心。
(4)反复迭代(2)(3),直到聚类中心不发生变化,后者中心位置误差在阈值范围内,或者达到一定的迭代次数。
import numpy as np
"""K-mean算法的函数"""
def iou(box, clusters):
"""
Calculates the Intersection over Union (IoU) between a box and k clusters.
:param box: tuple or array, shifted to the origin (i. e. width and height)
:param clusters: numpy array of shape (k, 2) where k is the number of clusters
:return: numpy array of shape (k, 0) where k is the number of clusters
"""
# print("box:",box,"cls",clusters)
x = np.minimum(clusters[:, 0], box[0])
y = np.minimum(clusters[:, 1], box[1])
# print(x)
# print(np.count_nonzero(x == 0))
# print(np.count_nonzero(y == 0))
if np.count_nonzero(x == 0) > 0 or np.count_nonzero(y == 0) > 0:
raise ValueError("Box has no area")
intersection = x * y
box_area = box[0] * box[1]
cluster_area = clusters[:, 0] * clusters[:, 1]
iou_ = intersection / (box_area + cluster_area - intersection)
return iou_
def avg_iou(boxes, clusters):
"""
Calculates the average Intersection over Union (IoU) between a numpy array of boxes and k clusters.
:param boxes: numpy array of shape (r, 2), where r is the number of rows
:param clusters: numpy array of shape (k, 2) where k is the number of clusters
:return: average IoU as a single float
"""
return np.mean([np.max(iou(boxes[i], clusters)) for i in range(boxes.shape[0])])
def translate_boxes(boxes):
"""
Translates all the boxes to the origin.
:param boxes: numpy array of shape (r, 4)
:return: numpy array of shape (r, 2)
"""
new_boxes = boxes.copy()
for row in range(new_boxes.shape[0]):
new_boxes[row][2] = np.abs(new_boxes[row][2] - new_boxes[row][0])
new_boxes[row][3] = np.abs(new_boxes[row][3] - new_boxes[row][1])
return np.delete(new_boxes, [0, 1], axis=1)
def kmeans(boxes, k, dist=np.median):
"""
Calculates k-means clustering with the Intersection over Union (IoU) metric.
:param boxes: numpy array of shape (r, 2), where r is the number of rows
:param k: number of clusters
:param dist: distance function
:return: numpy array of shape (k, 2)
"""
rows = boxes.shape[0]
distances = np.empty((rows, k))
last_clusters = np.zeros((rows,))
np.random.seed()
# the Forgy method will fail if the whole array contains the same rows
clusters = boxes[np.random.choice(rows, k, replace=False)]
while True:
for row in range(rows):
# print(row)
# print(boxes[row])
# if boxes[row][0]==0 :
# print('------',row)
# continue
distances[row] = 1 - iou(boxes[row], clusters)
nearest_clusters = np.argmin(distances, axis=1)
if (last_clusters == nearest_clusters).all():
break
for cluster in range(k):
clusters[cluster] = dist(boxes[nearest_clusters == cluster], axis=0)
last_clusters = nearest_clusters
return clusters, last_clusters
2、NMS
在测试和检测过程中经模型得出的所有box进行非极大值抑制:
若只有13*13和26*26两种尺度,N个类,预测共有13*13*3+26*26*3=2535个box
prediction的形式为(2535,5+N),5+N为中心坐标、宽高、置信度及每类预测的概率
①筛选出满足置信度阈值(conf_thres)条件的box
②在从①中筛选出每个box中概率最大的作为该box预测最有可能的类别
③坐标转换:bbox(x, y, w, h)->bbox(x1,y1,x2,y2)
④整理筛选后剩余box的信息(x1,y1,x2,y2,置信度,概率,类别(列号)),统计所有box中不重复的类别
⑤遍历类别,取出每次遍历类别的对应的box(即相同类别的box),
计算这些box的score=置信度*概率,然后对score进行排序,记录排序后原有的box位置(行号)
重新获取已排序后的box
⑥NMS处理(3种方式选择or):首先以最大score对应的box进行保存,然后计算该box与之后所有box的iou(同一类别两个box)
⑦满足iou>nms_thres(即表明同一位置预测到多个box,我们要剔除,只保留一个),记录该box的序号,暂时剔除这些box(也包括自己),然后再对剩余的box进行⑥⑦操作,最后会获得不同位置(这些位置预测都是同一类)有唯一的box
⑧遍历下一个类即重复⑤⑥⑦即可,最终筛选出不同位置预测出同类或不同类的唯一box(类别可能相同但是位置绝对不能相同这就是非极大值抑制作用)
def non_max_suppression(prediction, conf_thres=0.5, nms_thres=0.4):
"""
非极大值抑制 NMS
Removes detections with lower object confidence score than 'conf_thres'
Non-Maximum Suppression to further filter detections.
Returns detections with shape:
(x1, y1, x2, y2, object_conf, class_score, class_pred)
"""
output = [None for _ in range(len(prediction))]
for image_i, pred in enumerate(prediction):
# Experiment: Prior class size rejection
# x, y, w, h = pred[:, 0], pred[:, 1], pred[:, 2], pred[:, 3]
# a = w * h # area
# ar = w / (h + 1e-16) # aspect ratio
# n = len(w)
# log_w, log_h, log_a, log_ar = torch.log(w), torch.log(h), torch.log(a), torch.log(ar)
# shape_likelihood = np.zeros((n, 60), dtype=np.float32)
# x = np.concatenate((log_w.reshape(-1, 1), log_h.reshape(-1, 1)), 1)
# from scipy.stats import multivariate_normal
# for c in range(60):
# shape_likelihood[:, c] =
# multivariate_normal.pdf(x, mean=mat['class_mu'][c, :2], cov=mat['class_cov'][c, :2, :2])
# Filter out confidence scores below threshold
#函数softmax输出的是所给矩阵的概率分布,获取每个box预测出的最大的概率及对应的列号(实际上是类别序号)
#class_prob 最大值的列号,class_pred最大值
class_prob, class_pred = torch.max(F.softmax(pred[:, 5:], 1), 1)
v = pred[:, 4] > conf_thres#筛选大于置信度阈值的box,并每个box是True或False组成的列表
v = v.nonzero().squeeze()#取出v中True对应的行
if len(v.shape) == 0:
v = v.unsqueeze(0)
pred = pred[v]
class_prob = class_prob[v]
class_pred = class_pred[v]
# If none are remaining => process next image
nP = pred.shape[0]
if not nP:
continue
# From (center x, center y, width, height) to (x1, y1, x2, y2)
pred[:, :4] = xywh2xyxy(pred[:, :4])
# Detections ordered as (x1, y1, x2, y2, obj_conf, class_prob, class_pred)
detections = torch.cat((pred[:, :5], class_prob.float().unsqueeze(1), class_pred.float().unsqueeze(1)), 1)
# Iterate through all predicted classes
unique_labels = detections[:, -1].cpu().unique().to(prediction.device)
nms_style = 'OR' # 'OR' (default), 'AND', 'MERGE' (experimental)
for c in unique_labels:
# Get the detections with class c
dc = detections[detections[:, -1] == c]
# Sort the detections by maximum object confidence
_, conf_sort_index = torch.sort(dc[:, 4] * dc[:, 5], descending=True)
dc = dc[conf_sort_index]#(x1,y1,x2,y2,score)
# Non-maximum suppression
det_max = []
ind = list(range(len(dc)))#
if nms_style == 'OR': # default
while len(ind):
j = ind[0]
det_max.append(dc[j:j + 1]) # save highest conf detection
reject = bbox_iou(dc[j], dc[ind]) > nms_thres #(T or F)
[ind.pop(i) for i in reversed(reject.nonzero())]#剔除相近的box序号包括(与自己的iou)
# while dc.shape[0]: # SLOWER METHOD
# det_max.append(dc[:1]) # save highest conf detection
# if len(dc) == 1: # Stop if we're at the last detection
# break
# iou = bbox_iou(dc[0], dc[1:]) # iou with other boxes
# dc = dc[1:][iou < nms_thres] # remove ious > threshold
# Image Total P R mAP
# 4964 5000 0.629 0.594 0.586
elif nms_style == 'AND': # requires overlap, single boxes erased
while len(dc) > 1:
iou = bbox_iou(dc[0], dc[1:]) # iou with other boxes
if iou.max() > 0.5:
det_max.append(dc[:1])
dc = dc[1:][iou < nms_thres] # remove ious > threshold
elif nms_style == 'MERGE': # weighted mixture box
while len(dc) > 0:
iou = bbox_iou(dc[0], dc[0:]) # iou with other boxes
i = iou > nms_thres
weights = dc[i, 4:5] * dc[i, 5:6]
dc[0, :4] = (weights * dc[i, :4]).sum(0) / weights.sum()
det_max.append(dc[:1])
dc = dc[iou < nms_thres]
# Image Total P R mAP
# 4964 5000 0.633 0.598 0.589 # normal
if len(det_max) > 0:
det_max = torch.cat(det_max)
# Add max detections to outputs
output[image_i] = det_max if output[image_i] is None else torch.cat((output[image_i], det_max))
return output
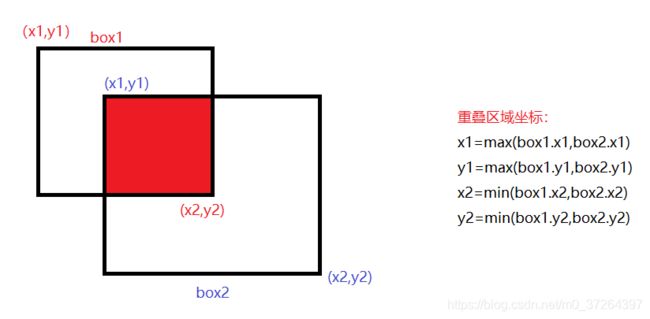
3、iou
iou=(box1与box2的交集)/(box1与box2的并集)
box1与box2的交集:矩形与矩形交集还是矩形只要获得该矩形的左上右下坐标即可,如下图
def bbox_iou(box1, box2, x1y1x2y2=True):
# Returns the IoU of box1 to box2. box1 is 4, box2 is nx4
box2 = box2.t()
# Get the coordinates of bounding boxes
if x1y1x2y2:
# x1, y1, x2, y2 = box1
b1_x1, b1_y1, b1_x2, b1_y2 = box1[0], box1[1], box1[2], box1[3]
b2_x1, b2_y1, b2_x2, b2_y2 = box2[0], box2[1], box2[2], box2[3]
else:
# x, y, w, h = box1
b1_x1, b1_x2 = box1[0] - box1[2] / 2, box1[0] + box1[2] / 2
b1_y1, b1_y2 = box1[1] - box1[3] / 2, box1[1] + box1[3] / 2
b2_x1, b2_x2 = box2[0] - box2[2] / 2, box2[0] + box2[2] / 2
b2_y1, b2_y2 = box2[1] - box2[3] / 2, box2[1] + box2[3] / 2
# Intersection area
inter_area = (torch.min(b1_x2, b2_x2) - torch.max(b1_x1, b2_x1)).clamp(0) * \
(torch.min(b1_y2, b2_y2) - torch.max(b1_y1, b2_y1)).clamp(0)
# Union Area
union_area = ((b1_x2 - b1_x1) * (b1_y2 - b1_y1) + 1e-16) + \
(b2_x2 - b2_x1) * (b2_y2 - b2_y1) - inter_area
return inter_area / union_area # iou4、xyxy2xywh
#bbox(x1,y1,x2,y2)->bbox(x, y, w, h)
def xyxy2xywh(x):
y = torch.zeros_like(x) if x.dtype is torch.float32 else np.zeros_like(x)
y[:, 0] = (x[:, 0] + x[:, 2]) / 2
y[:, 1] = (x[:, 1] + x[:, 3]) / 2
y[:, 2] = x[:, 2] - x[:, 0]
y[:, 3] = x[:, 3] - x[:, 1]
return y5、xywh2xyxy
#bbox(x, y, w, h)->bbox(x1,y1,x2,y2)
def xywh2xyxy(x):
y = torch.zeros_like(x) if x.dtype is torch.float32 else np.zeros_like(x)
y[:, 0] = (x[:, 0] - x[:, 2] / 2)
y[:, 1] = (x[:, 1] - x[:, 3] / 2)
y[:, 2] = (x[:, 0] + x[:, 2] / 2)
y[:, 3] = (x[:, 1] + x[:, 3] / 2)
return y6、padding-resize
def letterbox(img, height=416, color=(127.5, 127.5, 127.5)): # resize a rectangular image to a padded square
shape = img.shape[:2] # shape = [height, width]
ratio = float(height) / max(shape) # ratio = new/ old
new_shape = (round(shape[1] * ratio), round(shape[0] * ratio))#该方法返回 x 的小数点四舍五入到n个数字
#dw,dh二者有一个为0
dw = (height - new_shape[0]) / 2 # width padding
dh = (height - new_shape[1]) / 2 # height padding
#4个方向同时增广
top, bottom = round(dh - 0.1), round(dh + 0.1)
left, right = round(dw - 0.1), round(dw + 0.1)
img = cv2.resize(img, new_shape, interpolation=cv2.INTER_AREA) # resized, no border
img = cv2.copyMakeBorder(img, top, bottom, left, right, cv2.BORDER_CONSTANT, value=color) # padded square
return img, ratio, dw, dh
7、数据预处理加载
class LoadImagesAndLabels: # for training
def __init__(self, path, batch_size=1, img_size=608, augment=False):
with open(path, 'r') as file:
self.img_files = file.readlines()
self.img_files = [x.replace('\n', '') for x in self.img_files]
#图片所有路径
self.img_files = list(filter(lambda x: len(x) > 0, self.img_files))
#存放标签
self.label_files = [x.replace('images', 'labels').replace('.png', '.txt').replace('.jpg', '.txt')
for x in self.img_files]
self.nF = len(self.img_files) # number of image files
self.nB = math.ceil(self.nF / batch_size) # number of batches
self.batch_size = batch_size
self.img_size = img_size
self.augment = augment
assert self.nF > 0, 'No images found in %s' % path
def __iter__(self):
self.count = -1
self.shuffled_vector = np.random.permutation(self.nF) if self.augment else np.arange(self.nF)
return self
def __next__(self):
self.count += 1
if self.count == self.nB:
raise StopIteration
ia = self.count * self.batch_size #以batch_size为步长的训练集位置
ib = min((self.count + 1) * self.batch_size, self.nF)#以batch_size为步长的标签位置
img_all, labels_all, img_paths, img_shapes = [], [], [], []
for index, files_index in enumerate(range(ia, ib)):
img_path = self.img_files[self.shuffled_vector[files_index]]
label_path = self.label_files[self.shuffled_vector[files_index]]
img = cv2.imread(img_path) # BGR
assert img is not None, 'File Not Found ' + img_path
augment_hsv = True
if self.augment and augment_hsv:
# SV augmentation by 50%
fraction = 0.50
#颜色转换hsv处理后再转换
img_hsv = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2HSV)
S = img_hsv[:, :, 1].astype(np.float32)
V = img_hsv[:, :, 2].astype(np.float32)
a = (random.random() * 2 - 1) * fraction + 1
S *= a
if a > 1:
np.clip(S, a_min=0, a_max=255, out=S)
a = (random.random() * 2 - 1) * fraction + 1
V *= a
if a > 1:
np.clip(V, a_min=0, a_max=255, out=V)
img_hsv[:, :, 1] = S.astype(np.uint8)
img_hsv[:, :, 2] = V.astype(np.uint8)
cv2.cvtColor(img_hsv, cv2.COLOR_HSV2BGR, dst=img)
h, w, _ = img.shape
#调整图像尺寸——>416
img, ratio, padw, padh = letterbox(img, height=self.img_size)
# Load labels
if os.path.isfile(label_path):
labels0 = np.loadtxt(label_path, dtype=np.float32).reshape(-1, 5)
# Normalized xywh to pixel xyxy format
#已经归一化坐标的label中whxy转化为在新尺寸下的非归一化的左上右下坐标
labels = labels0.copy()
#新尺寸/原尺寸 *原尺寸*(归一化的中心坐标-宽高/2)+宽高的补偿
labels[:, 1] = ratio * w * (labels0[:, 1] - labels0[:, 3] / 2) + padw #x1-w/2
labels[:, 2] = ratio * h * (labels0[:, 2] - labels0[:, 4] / 2) + padh#y1-h/2
labels[:, 3] = ratio * w * (labels0[:, 1] + labels0[:, 3] / 2) + padw#x2-w/2
labels[:, 4] = ratio * h * (labels0[:, 2] + labels0[:, 4] / 2) + padh#y2-h/2
else:
labels = np.array([])
# Augment image and labels
if self.augment:
img, labels, M = random_affine(img, labels, degrees=(-5, 5), translate=(0.10, 0.10), scale=(0.90, 1.10))
plotFlag = False
if plotFlag:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10)) if index == 0 else None
plt.subplot(4, 4, index + 1).imshow(img[:, :, ::-1])
plt.plot(labels[:, [1, 3, 3, 1, 1]].T, labels[:, [2, 2, 4, 4, 2]].T, '.-')
plt.axis('off')
nL = len(labels)
if nL > 0:
# convert xyxy to xywh
#将新获得的xyxy坐标转化为中心坐标,在除以新图的尺寸 (归一化)
labels[:, 1:5] = xyxy2xywh(labels[:, 1:5].copy()) / self.img_size
if self.augment:
# random left-right flip
#左右旋转
lr_flip = True
if lr_flip & (random.random() > 0.5):
img = np.fliplr(img)
if nL > 0:
labels[:, 1] = 1 - labels[:, 1]
# random up-down flip
#上下旋转
ud_flip = False
if ud_flip & (random.random() > 0.5):
img = np.flipud(img)
if nL > 0:
labels[:, 2] = 1 - labels[:, 2]
if nL > 0:
labels = np.concatenate((np.zeros((nL, 1), dtype='float32') + index, labels), 1)#1维度连接
labels_all.append(labels)
img_all.append(img)
img_paths.append(img_path)
img_shapes.append((h, w))
# Normalize
img_all = np.stack(img_all)[:, :, :, ::-1].transpose(0, 3, 1, 2) # BGR to RGB and cv2 to pytorch
img_all = np.ascontiguousarray(img_all, dtype=np.float32)
img_all /= 255.0
labels_all = torch.from_numpy(np.concatenate(labels_all, 0))
#返回所有图像数据、标签、图像路径、图像尺寸
return torch.from_numpy(img_all), labels_all, img_paths, img_shapes
def __len__(self):
return self.nB # number of batches
8、cfg解析
class Darknet(nn.Module):
"""YOLOv3目标检测模型,实现前向传播"""
def __init__(self, cfg_path, img_size=416): # 模型和参数初始化
super(Darknet, self).__init__()
self.module_defs = parse_model_cfg(cfg_path)
self.module_defs[0]['cfg'] = cfg_path
self.module_defs[0]['height'] = img_size
#获取模型网络结构
self.hyperparams, self.module_list = create_modules(self.module_defs) # 模型构建
self.img_size = img_size
self.loss_names = ['loss', 'xy', 'wh', 'conf', 'cls', 'nT']
self.losses = []
def forward(self, x, var=None): # 前向传播
img_size = x.shape[-1] # 416
layer_outputs = []
output = []
for i, (module_def, module) in enumerate(zip(self.module_defs, self.module_list)):
mtype = module_def['type'] # module_def层信息:Conv、filter、pad... module:层结构
# 'convolutional', 'upsample', 'maxpool'层直接输入层结构
if mtype in ['convolutional', 'upsample', 'maxpool']:
x = module(x)
# 'route' 'shortcut' 'yolo'层单独写的运算
elif mtype == 'route':#路由层主要深度扩充
layer_i = [int(x) for x in module_def['layers'].split(',')]
if len(layer_i) == 1:
x = layer_outputs[layer_i[0]]
else:
x = torch.cat([layer_outputs[i] for i in layer_i], 1)
elif mtype == 'shortcut':#跨层连接:相同纬度相加
layer_i = int(module_def['from'])
x = layer_outputs[-1] + layer_outputs[layer_i]
elif mtype == 'yolo':
x = module[0](x, img_size) # 进入yolo层的前向传播,x:[1,507,85]每行一个bbox信息
output.append(x)
layer_outputs.append(x) # 储存中间层输出
if ONNX_EXPORT:
output = torch.cat(output, 1) # merge the 3 layers 85 x (507, 2028, 8112) to 85 x 10647
return output[5:].t(), output[:4].t() # ONNX scores, boxes
else:
return output if self.training else torch.cat(output, 1) # 整合3个尺度, 85 x (507, 2028, 8112) ——> 85 x 10647
10、损失函数
def compute_loss(p, targets): # predictions, targets
FT = torch.cuda.FloatTensor if p[0].is_cuda else torch.FloatTensor
loss, lxy, lwh, lcls, lconf = FT([0]), FT([0]), FT([0]), FT([0]), FT([0])
txy, twh, tcls, tconf, indices = targets
MSE = nn.MSELoss()#均方误差
CE = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()#二类交叉熵误差
BCE = nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss()#二类交叉熵误差
# Compute losses
# gp = [x.numel() for x in tconf] # grid points
for i, pi0 in enumerate(p): # layer i predictions, i P:两个元组:[4,3,13,13,85]、[4,3,26,26,85]
b, a, gj, gi = indices[i] # 目标第i个尺度的 image, anchor, gridx, gridy
# Compute losses
k = 1 # nT / bs
# 负责预测该物体的anchor的误差:
if len(b) > 0:
pi = pi0[b, a, gj, gi] # 找到perd中负责预测该物体的anchor,[目标数,85],这个anchor和他的4个坐标+C+80类
lxy += k * MSE(torch.sigmoid(pi[..., 0:2]), txy[i]) # xy:方均根误差
lwh += k * MSE(pi[..., 2:4], twh[i]) # wh: 方均根误差
lcls += (k / 4) * CE(pi[..., 5:], tcls[i]) # 80类分类结果: 交叉熵误差 p*log(q) p:期望1, q:实际置信度
# pos_weight = FT([gp[i] / min(gp) * 4.])
# BCE = nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss(pos_weight=pos_weight)
# 所有的预测都要计算的误差C:pi0(看看tconf格式)
lconf += (k * 64) * BCE(pi0[..., 4], tconf[i]) # 二分类交叉熵,如置信度C=0.8,就计算[0.8,0.2]和[1,0]之间的交叉熵误差
loss = lxy + lwh + lconf + lcls
# Add to dictionary
d = defaultdict(float)
losses = [loss.item(), lxy.item(), lwh.item(), lconf.item(), lcls.item()]
for name, x in zip(['total', 'xy', 'wh', 'conf', 'cls'], losses):
d[name] = x
return loss, d11、map
def ap_per_class(tp, conf, pred_cls, target_cls):
""" 计算平均精度,给出召回率和精度曲线。
Source: https://github.com/rafaelpadilla/Object-Detection-Metrics.
# Arguments
tp: True positives (list).分类为的正样本,且分对了的 个数
conf: Objectness value from 0-1 (list).边框置信度
pred_cls: Predicted object classes (list).预测类
target_cls: True object classes (list).实际类
# Returns
平均精度。
"""
# 按置信度降序排列
i = np.argsort(-conf)#返回排序原有的索引列表
tp, conf, pred_cls = tp[i], conf[i], pred_cls[i]
# Find unique classes(np.unique:除去重复元素)
#统计出现所有不同类
unique_classes = np.unique(np.concatenate((pred_cls, target_cls), 0))#按维度进行连接
# Create Precision-Recall curve and compute AP for each class
ap, p, r = [], [], []
for c in unique_classes:#在类别为c的情况下
i = pred_cls == c#列表比较,结果为True/False的列表 [t,f,t,t,f,f,f]为True表示在预测中存在该类别有哪些
n_gt = sum(target_cls == c) # 实际对象数
n_p = sum(i) # 预测对象数
if (n_p == 0) and (n_gt == 0):
continue
elif (n_p == 0) or (n_gt == 0):
ap.append(0)
r.append(0)
p.append(0)
else:
# Accumulate FPs and TPs 假设这一类都是识别为人
# False Positives 窗户认作人
# True Positives 人认作了人
#转化为为一堆0,1来判断tp[i]表示预测为c类的实际也为c类 是哪些列:是为1,不是为0
#1-tp[i]表示预测为c类实际不是c类
fpc = np.cumsum(1 - tp[i])#按照列累加。
tpc = np.cumsum(tp[i])#列表
# Recall:分类器识别为人,且确实是人,占所有‘人’ 的比例
recall_curve = tpc / (n_gt + 1e-16)
r.append(tpc[-1] / (n_gt + 1e-16))
# Precision:分类器认为是人,且确实是人,占分类器认为是人的比例
precision_curve = tpc / (tpc + fpc)
p.append(tpc[-1] / (tpc[-1] + fpc[-1]))
# 从R-P曲线得到曲线下面积AP
ap.append(compute_ap(recall_curve, precision_curve))
return np.array(ap), unique_classes.astype('int32'), np.array(r), np.array(p)