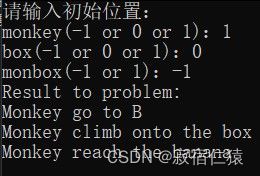
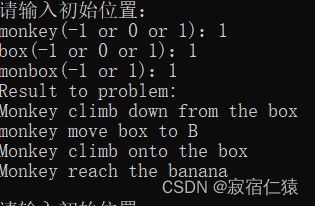
利用一阶谓词逻辑求解猴子摘香蕉问题
利用一阶谓词逻辑求解猴子摘香蕉问题:房内有一个猴子,一个箱子,天花板上挂了一串香蕉,其位置如图1所示,猴子为了拿到香蕉,它必须把箱子搬到香蕉下面,然后再爬到箱子上。请定义必要的谓词,列出问题的初始化状态(可变),目标状态(猴子拿到了香蕉,站在箱子上,箱子位于位置b)。(附加:从初始状态到目标状态的谓词演算过程。)
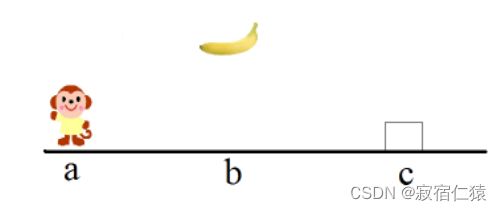
香蕉位置在B即0
思路:
用数字表示猴子和香蕉的位置,-1为A,0为B,1为C;当猴子站在箱子上用1表示,反之则用-1表示。用一个结构体表示整个场景的状态,
其中包括猴子和箱子的位置以及猴子是否在箱子上,猴子每次进行下一次行为记为下一个状态。所有状态用整个结构体数组存储,每一次猴子行为
用另一字符指针数组存储,最后打印输出猴子摘香蕉过程。
代码:
#include
#include
using namespace std;
struct State
{
int monkey;
int box;
int banana;//香蕉在B
int monbox;
};
struct State States[10];
const char* actionsave[10];
void monkeygoto(int b, int i)//猴子走向位置
{
int a;
a = b;
if (a == -1)
{
actionsave[i] = "Monkey go to A";
States[i + 1] = States[i];
States[i + 1].monkey = -1;
}
else if (a == 0)
{
actionsave[i] = "Monkey go to B";
States[i + 1] = States[i];
States[i + 1].monkey = 0;
}
else if (a == 1)
{
actionsave[i] = "Monkey go to C";
States[i + 1] = States[i];
States[i + 1].monkey = 1;
}
}
void movebox(int a, int i)//猴子推箱子移动位置
{
int B;
B = a;
if (B == -1)
{
actionsave[i] = "monkey move box to A";
States[i + 1] = States[i];
States[i + 1].monkey = -1;
States[i + 1].box = -1;
}
else if (B == 0)
{
actionsave[i] = "monkey move box to B";
States[i + 1] = States[i];
States[i + 1].monkey = 0;
States[i + 1].box = 0;
}
else if (B == 1)
{
actionsave[i] = "monkey move box to C";
States[i + 1] = States[i];
States[i + 1].monkey = 1;
States[i + 1].box = 1;
}
}
void climbonto(int i)//猴子爬上箱子
{
actionsave[i] = "Monkey climb onto the box";
States[i + 1] = States[i];
States[i + 1].monbox = 1;
}
void climbdown(int i)//如果初始状态猴子在箱子上,则需要爬下来
{
actionsave[i] = "Monkey climb down from the box";
States[i + 1] = States[i];
States[i + 1].monbox = -1;
}
void reach(int i)//猴子拿到香蕉
{
actionsave[i] = "Monkey reach the banana";
}
void showSolution(int i)//打印猴子过程操作
{
int c;
cout<<"Result to problem:"<= 10)
{
cout << "steplength reached 10,have problem! " << endl;
return;
}
//成功拿到香蕉
if (States[i].monbox == 1 && States[i].monkey == 0 && States[i].banana == 0 && States[i].box == 0)
{
if (i == 0)
{
reach(i);
}
showSolution(i);
return;
}
j = i + 1;//进行数据更新,用来标记当前是第几个状态
if (States[i].monkey == 0)//猴子位置B
{
if (States[i].box == 0)//箱子位置B
{
if (States[i].monbox == -1)//猴子没爬上箱子
{
climbonto(i);
reach(i + 1);
nextStep(j);
}
}
else if(States[i].box == 1)//箱子位置C
{
monkeygoto(States[i].box, i);
nextStep(j);
}
else//箱子位置A
{
monkeygoto(States[i].box, i);
nextStep(j);
}
}
if (States[i].monkey == -1)//猴子位置A
{
if (States[i].box == -1)//同上
{
if (States[i].monbox == -1)
{
movebox(0, i);
nextStep(j);
}
else
{
climbdown(i);
nextStep(j);
}
}
else if (States[i].box == 0)
{
monkeygoto(0, i);
nextStep(j);
}
else
{
monkeygoto(1, i);
nextStep(j);
}
}
if (States[i].monkey == 1)//猴子位置C
{
if (States[i].box == 1)
{
if (States[i].monbox == -1)
{
movebox(0, i);
nextStep(j);
}
else
{
climbdown(i);
nextStep(j);
}
}
else if (States[i].box == -1)
{
monkeygoto(-1, i);
nextStep(j);
}
else
{
monkeygoto(0, i);
nextStep(j);
}
}
}
int main()
{
while (1) //测试
{
States[0].banana = 0;
cout << "请输入初始位置:\n";
cout << "monkey(-1 or 0 or 1):";
cin >> States[0].monkey;
cout << "box(-1 or 0 or 1):";
cin >> States[0].box;
cout << "monbox(-1 or 1):";
cin >> States[0].monbox;
//判断输入是否符合要求,错误则提示并且重新输入
if (States[0].monkey == -1 || States[0].monkey == 0 || States[0].monkey== 1)
{
if (States[0].box == -1 || States[0].box == 0 || States[0].box == 1)
{
if (States[0].monbox == -1 || States[0].monbox == 1)
{
if ((States[0].monkey != States[0].box) && States[0].monbox == 1)
{
cout << "input wrong" << endl< 初始猴子和箱子在C并且在箱子上面,这时猴子需要 箱子上爬下来,然后把箱子推到B,再爬上箱子摘到香蕉。