深度学习(7):基于LSTM算法的股票走势预测
目标:基于LSTM网络实现对股票走势分析,将股票指数输入LSTM模型训练和推理,最后将判断结果进行输出。
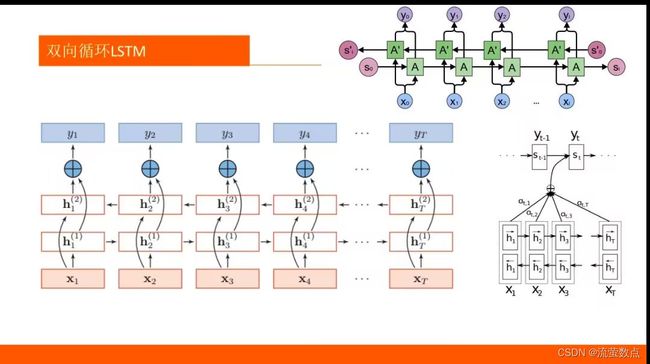
一、原理
先了解RNN,参考博客
好好学习第三天:RNN与股票预测_流萤数点的博客-CSDN博客_rnn 预测
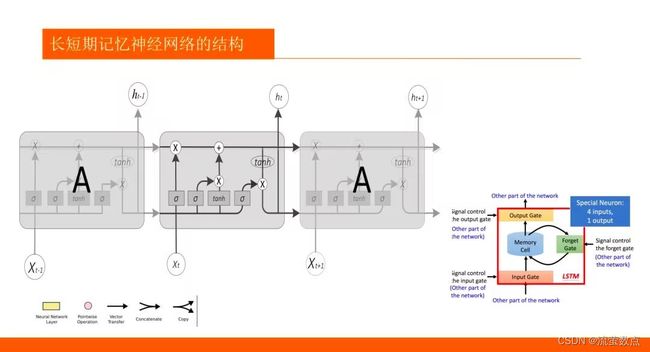
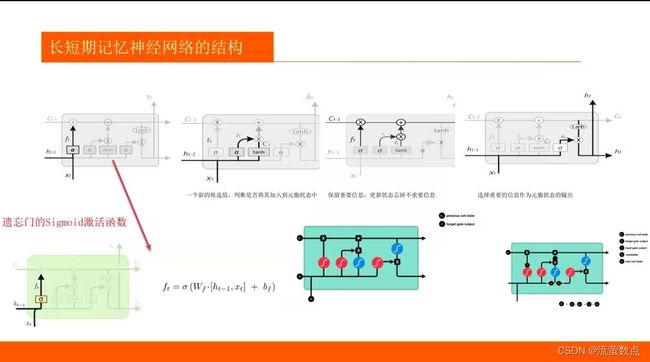
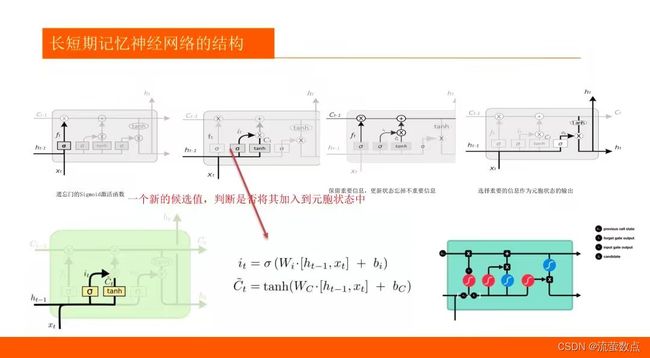
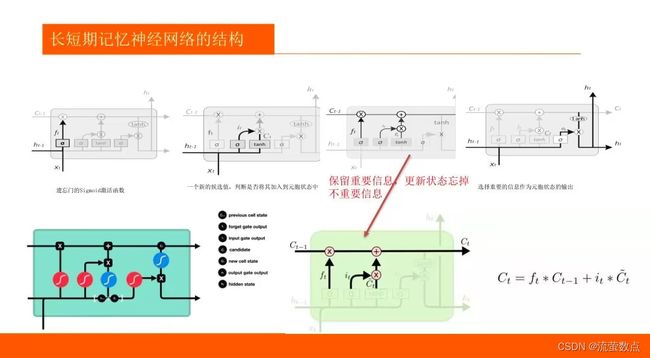
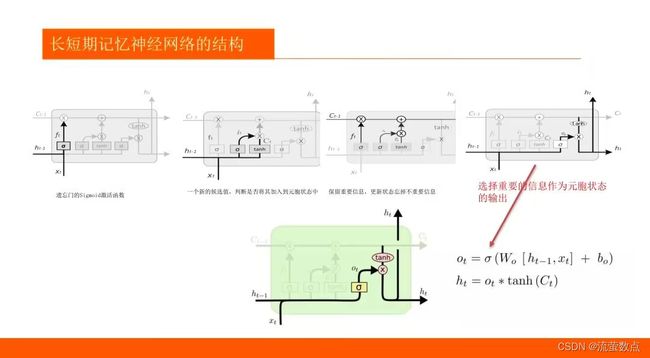
1.了解LSTM算法的基本原理
2.熟悉LSTM趋势预测的常规方法
3.掌握LSTM训练的方法
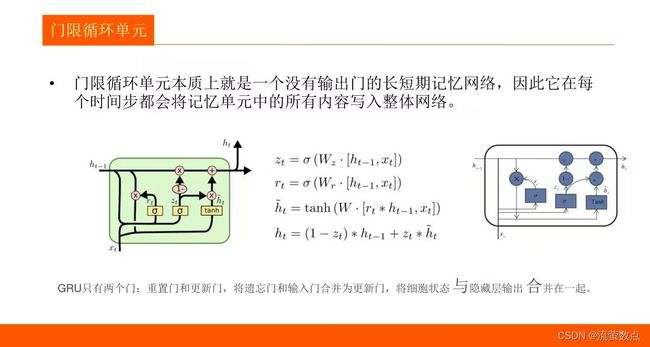
4.LSTM 和 GRU 是解决短时记忆问题的解决方案,它们具有称为“门”的内部机制,可以调节信息流。
二、过程
1.导入库
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import math
import sklearn
import sklearn.preprocessing
import datetime
import os
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import tensorflow as tf2.导入数据
#准备数据,从OSS中获取数据并解压到当前目录:
import oss2
access_key_id = os.getenv('OSS_TEST_ACCESS_KEY_ID', 'LTAI4G1MuHTUeNrKdQEPnbph')
access_key_secret = os.getenv('OSS_TEST_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET', 'm1ILSoVqcPUxFFDqer4tKDxDkoP1ji')
bucket_name = os.getenv('OSS_TEST_BUCKET', 'mldemo')
endpoint = os.getenv('OSS_TEST_ENDPOINT', 'https://oss-cn-shanghai.aliyuncs.com')
# 创建Bucket对象,所有Object相关的接口都可以通过Bucket对象来进行
bucket = oss2.Bucket(oss2.Auth(access_key_id, access_key_secret), endpoint, bucket_name)
# 下载到本地文件
bucket.get_object_to_file('data/c12/stock_data.zip', 'stock_data.zip')![]()
#解压数据
!unzip -o -q stock_data.zip
!rm -rf __MACOSX
!ls stock_data -ilht ![]()
3.可视化
# import all stock prices
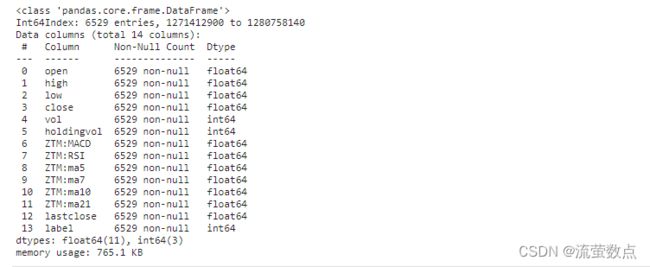
df = pd.read_csv("./stock_data/sh300index.csv", index_col = 0)
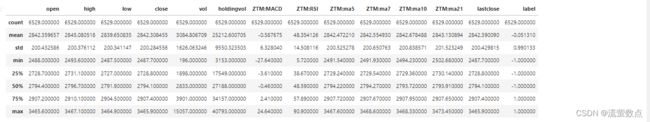
df.info()df.head()df.describe()plt.figure(figsize=(15, 5));
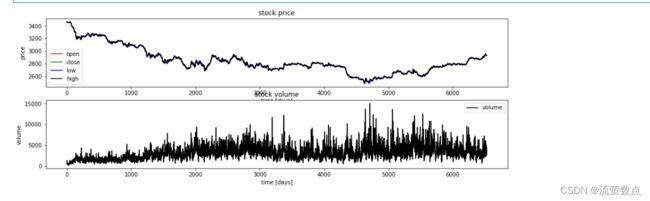
plt.subplot(2,1,1);
plt.plot(df.open.values, color='red', label='open')
plt.plot(df.close.values, color='green', label='close')
plt.plot(df.low.values, color='blue', label='low')
plt.plot(df.high.values, color='black', label='high')
plt.title('stock price')
plt.xlabel('time [days]')
plt.ylabel('price')
plt.legend(loc='best')
plt.subplot(2,1,2);
plt.plot(df.vol.values, color='black', label='volume')
plt.title('stock volume')
plt.xlabel('time [days]')
plt.ylabel('volume')
plt.legend(loc='best');
plt.show()4.数据预处理
# 按照80%/10%/10% 划分训练集、验证集和测试集
valid_set_size_percentage = 10
test_set_size_percentage = 10 # min-max 归一化
def normalize_data(df):
min_max_scaler = sklearn.preprocessing.MinMaxScaler()
df['open'] = min_max_scaler.fit_transform(df.open.values.reshape(-1,1))
df['high'] = min_max_scaler.fit_transform(df.high.values.reshape(-1,1))
df['low'] = min_max_scaler.fit_transform(df.low.values.reshape(-1,1))
df['close'] = min_max_scaler.fit_transform(df['close'].values.reshape(-1,1))
return df# 划分数据集
def load_data(stock, seq_len):
data_raw = stock.to_numpy() # pd to numpy array
data = []
# create all possible sequences of length seq_len
for index in range(len(data_raw) - seq_len):
data.append(data_raw[index: index + seq_len])
data = np.array(data);
valid_set_size = int(np.round(valid_set_size_percentage/100*data.shape[0]));
test_set_size = int(np.round(test_set_size_percentage/100*data.shape[0]));
train_set_size = data.shape[0] - (valid_set_size + test_set_size);
x_train = data[:train_set_size,:-1,:]
y_train = data[:train_set_size,-1,:]
x_valid = data[train_set_size:train_set_size+valid_set_size,:-1,:]
y_valid = data[train_set_size:train_set_size+valid_set_size,-1,:]
x_test = data[train_set_size+valid_set_size:,:-1,:]
y_test = data[train_set_size+valid_set_size:,-1,:]
return [x_train, y_train, x_valid, y_valid, x_test, y_test]# 去除冗余指标
df_stock = df.copy()
df_stock.drop(['vol'],1,inplace=True)
df_stock.drop(['lastclose'],1,inplace=True)
df_stock.drop(['label'],1,inplace=True)
df_stock.drop(['ZTM:ma5'],1,inplace=True)
df_stock.drop(['ZTM:ma7'],1,inplace=True)
df_stock.drop(['ZTM:ma10'],1,inplace=True)
df_stock.drop(['ZTM:ma21'],1,inplace=True)
df_stock.drop(['holdingvol'],1,inplace=True)
df_stock.drop(['ZTM:MACD'],1,inplace=True)
df_stock.drop(['ZTM:RSI'],1,inplace=True)
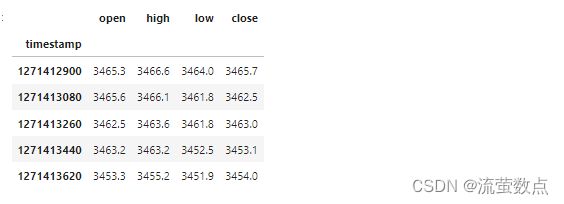
#查看输入数据
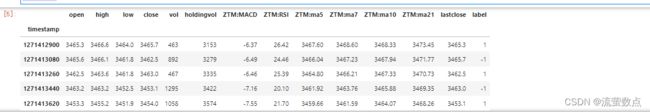
df_stock.head()#输出输入列名
cols = list(df_stock.columns.values)
print('df_stock.columns.values = ', cols)![]()
对指标进行归一化处理:
df_stock_norm = normalize_data(df_stock)
# 查看训练集、验证集和测试集情况
seq_len = 20 # 设置最长序列长度
x_train, y_train, x_valid, y_valid, x_test, y_test = load_data(df_stock_norm, seq_len)
print('x_train.shape = ',x_train.shape)
print('y_train.shape = ', y_train.shape)
print('x_valid.shape = ',x_valid.shape)
print('y_valid.shape = ', y_valid.shape)
print('x_test.shape = ', x_test.shape)
print('y_test.shape = ',y_test.shape)#对指标数据进行可视化
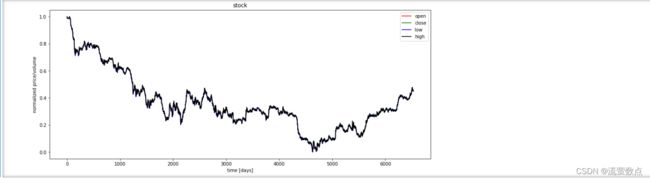
plt.figure(figsize=(15, 6));
plt.plot(df_stock_norm.open.values, color='red', label='open')
plt.plot(df_stock_norm.close.values, color='green', label='close')
plt.plot(df_stock_norm.low.values, color='blue', label='low')
plt.plot(df_stock_norm.high.values, color='black', label='high')
plt.title('stock')
plt.xlabel('time [days]')
plt.ylabel('normalized price/volume')
plt.legend(loc='best')
plt.show()5.RNN建模-LSTM/GRU
#对训练数据随机化处理
index_in_epoch = 0;
perm_array = np.arange(x_train.shape[0])
np.random.shuffle(perm_array)
# 数据读取方法
def get_next_batch(batch_size):
global index_in_epoch, x_train, perm_array
start = index_in_epoch
index_in_epoch += batch_size
if index_in_epoch > x_train.shape[0]:
np.random.shuffle(perm_array) # shuffle permutation array
start = 0 # start next epoch
index_in_epoch = batch_size
end = index_in_epoch
return x_train[perm_array[start:end]], y_train[perm_array[start:end]]#定义超参
n_steps = seq_len-1
#输入大小(与指标数量对应)
n_inputs = 4
n_neurons = 200
#输出大小(与指标数量对应)
n_outputs = 4
#层数
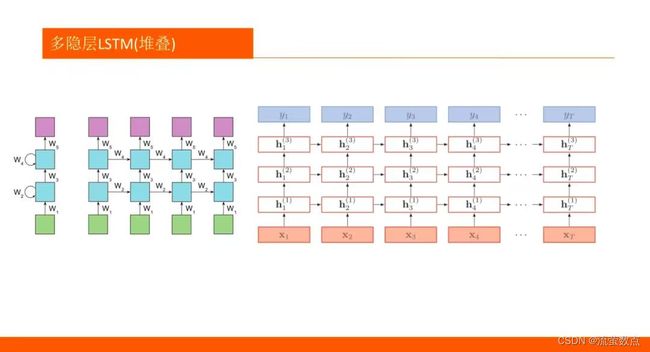
n_layers = 2
#学习率
learning_rate = 0.001
#批大小
batch_size = 50
#迭代训练次数
n_epochs = 20
#训练集大小
train_set_size = x_train.shape[0]
#测试集大小
test_set_size = x_test.shape[0]定义网络结构:
tf.reset_default_graph()
X = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, n_steps, n_inputs])
y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, n_outputs])
# 使用GRU单元结构
layers = [tf.contrib.rnn.GRUCell(num_units=n_neurons, activation=tf.nn.leaky_relu)
for layer in range(n_layers)]
multi_layer_cell = tf.contrib.rnn.MultiRNNCell(layers)
rnn_outputs, states = tf.nn.dynamic_rnn(multi_layer_cell, X, dtype=tf.float32)
stacked_rnn_outputs = tf.reshape(rnn_outputs, [-1, n_neurons])
stacked_outputs = tf.layers.dense(stacked_rnn_outputs, n_outputs)
outputs = tf.reshape(stacked_outputs, [-1, n_steps, n_outputs])
outputs = outputs[:,n_steps-1,:] # 定义输出
loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(outputs - y)) # 使用MSE作为损失
optimizer = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate=learning_rate)
training_op = optimizer.minimize(loss)开始训练:
# 执行训练
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
for iteration in range(int(n_epochs*train_set_size/batch_size)):
x_batch, y_batch = get_next_batch(batch_size) # fetch the next training batch
sess.run(training_op, feed_dict={X: x_batch, y: y_batch})
if iteration % int(5*train_set_size/batch_size) == 0:
mse_train = loss.eval(feed_dict={X: x_train, y: y_train})
mse_valid = loss.eval(feed_dict={X: x_valid, y: y_valid})
print('%.2f epochs: MSE train/valid = %.6f/%.6f'%(
iteration*batch_size/train_set_size, mse_train, mse_valid))
y_train_pred = sess.run(outputs, feed_dict={X: x_train})
y_valid_pred = sess.run(outputs, feed_dict={X: x_valid})
y_test_pred = sess.run(outputs, feed_dict={X: x_test})
6.模型应用-预测
对比查看股票指数的历史值和未来值情况:
ft = 0 # 0 = open, 1 = close, 2 = highest, 3 = lowest
#结果可视化
plt.figure(figsize=(15, 5));
plt.subplot(1,2,1);
plt.plot(np.arange(y_train.shape[0]), y_train[:,ft], color='blue', label='train target')
plt.plot(np.arange(y_train.shape[0], y_train.shape[0]+y_valid.shape[0]), y_valid[:,ft],
color='gray', label='valid target')
plt.plot(np.arange(y_train.shape[0]+y_valid.shape[0],
y_train.shape[0]+y_test.shape[0]+y_test.shape[0]),
y_test[:,ft], color='black', label='test target')
plt.plot(np.arange(y_train_pred.shape[0]),y_train_pred[:,ft], color='red',
label='train prediction')
plt.plot(np.arange(y_train_pred.shape[0], y_train_pred.shape[0]+y_valid_pred.shape[0]),
y_valid_pred[:,ft], color='orange', label='valid prediction')
plt.plot(np.arange(y_train_pred.shape[0]+y_valid_pred.shape[0],
y_train_pred.shape[0]+y_valid_pred.shape[0]+y_test_pred.shape[0]),
y_test_pred[:,ft], color='green', label='test prediction')
plt.title('past and future stock prices')
plt.xlabel('time [days]')
plt.ylabel('normalized price')
plt.legend(loc='best');
plt.subplot(1,2,2);
plt.plot(np.arange(y_train.shape[0], y_train.shape[0]+y_test.shape[0]),
y_test[:,ft], color='black', label='test target')
plt.plot(np.arange(y_train_pred.shape[0], y_train_pred.shape[0]+y_test_pred.shape[0]),
y_test_pred[:,ft], color='green', label='test prediction')
plt.title('future stock prices')
plt.xlabel('time [days]')
plt.ylabel('normalized price')
plt.legend(loc='best');