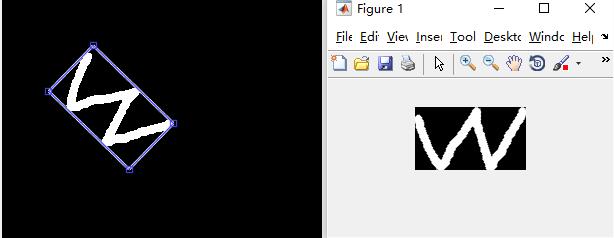
在Matlab中利用OpenCV裁剪出旋转矩形区域
在OpenCV中有minAreaRect()来获取旋转的最小面积矩形,Matlab中暂时没有对应的函数,但我找到一篇同样功能的函数minBoundingBox.m。利用这个函数可以获得旋转矩形的四个顶角,顺序如下图

如果要将目标区域从原图上裁剪下来,需要计算外包络正矩形,然后裁剪下来,然后旋转正,然后再裁剪到旋转矩形的大小。为了解决这种麻烦,并加快执行速度,本文编写了cv_rotateRect.cpp,利用mex和OpenCV的透视变换warpPerspective()来快速裁剪需要的区域。
需要注意的有三个地方:
一是Matlab储存方式是按列储存,左图,OpenCV是按行储存,右图
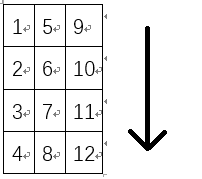
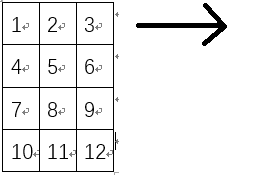
进行参数传递时要转置。
二是OpenCV拷贝有两种,深拷贝和浅拷贝
(1) 浅拷贝:
Mat B;
B = image // 第一种方式
Mat C(image); // 第二种方式
这两种方式称为浅copy,是由于它们有不同的矩阵头,但是它们共享内存空间,即指向一个矩阵。当图像矩阵发生变化时,两者相关联,都会变化。
(2)深拷贝
Mat B,C;
B = image.clone(); // 第一种方式
image.copyTo(C); // 第二种方式
深拷贝是真正的copy了一个新的图像矩阵,此时image,B,C三者相互没有影响。
还要注意的是:方式一是全新的深拷贝,会重新分配内存:
Mat a=b.clone();
如果要拷贝到另一个Mat(避免内存重新分配),必须用copyTo():
Mat a(b.size(),b.type());
b.copyTo(a);
三是minBoundingBox.m对点的表述方式是第一行是x,第二行是y,而不是一般的第一列是x,第二列是y,minBoundingBox的输入是2行n列的点坐标,输出是2行4列的顶角坐标。
minBoundingBox.m
function bb = minBoundingBox(X)
% compute the minimum bounding box of a set of 2D points
% Use: boundingBox = minBoundingBox(point_matrix)
%
% Input: 2xn matrix containing the [x,y] coordinates of n points
% *** there must be at least 3 points which are not collinear
% output: 2x4 matrix containing the coordinates of the bounding box corners
%
% Example : generate a random set of point in a randomly rotated rectangle
% n = 50000;
% t = pi*rand(1);
% X = [cos(t) -sin(t) ; sin(t) cos(t)]*[7 0; 0 2]*rand(2,n);
% X = [X 20*(rand(2,1)-0.5)]; % add an outlier
%
% tic
% c = minBoundingBox(X);
% toc
%
% figure(42);
% hold off, plot(X(1,:),X(2,:),'.')
% hold on, plot(c(1,[1:end 1]),c(2,[1:end 1]),'r')
% axis equal
% compute the convex hull (CH is a 2*k matrix subset of X)
k = convhull(X(1,:),X(2,:));
CH = X(:,k);
% compute the angle to test, which are the angle of the CH edges as:
% "one side of the bounding box contains an edge of the convex hull"
E = diff(CH,1,2); % CH edges
T = atan2(E(2,:),E(1,:)); % angle of CH edges (used for rotation)
T = unique(mod(T,pi/2)); % reduced to the unique set of first quadrant angles
% create rotation matrix which contains
% the 2x2 rotation matrices for *all* angles in T
% R is a 2n*2 matrix
R = cos( reshape(repmat(T,2,2),2*length(T),2) ... % duplicate angles in T
+ repmat([0 -pi ; pi 0]/2,length(T),1)); % shift angle to convert sine in cosine
% rotate CH by all angles
RCH = R*CH;
% compute border size [w1;h1;w2;h2;....;wn;hn]
% and area of bounding box for all possible edges
bsize = max(RCH,[],2) - min(RCH,[],2);
area = prod(reshape(bsize,2,length(bsize)/2));
% find minimal area, thus the index of the angle in T
[a,i] = min(area);
% compute the bound (min and max) on the rotated frame
Rf = R(2*i+[-1 0],:); % rotated frame
bound = Rf * CH; % project CH on the rotated frame
bmin = min(bound,[],2);
bmax = max(bound,[],2);
% compute the corner of the bounding box
Rf = Rf';
bb(:,4) = bmax(1)*Rf(:,1) + bmin(2)*Rf(:,2);
bb(:,1) = bmin(1)*Rf(:,1) + bmin(2)*Rf(:,2);
bb(:,2) = bmin(1)*Rf(:,1) + bmax(2)*Rf(:,2);
bb(:,3) = bmax(1)*Rf(:,1) + bmax(2)*Rf(:,2);
cv_rotateRect.cpp
#include "mex.h"
#include "matrix.h"
#include "math.h"
#include "opencv2/opencv.hpp"
using namespace cv;
void mexFunction(int nlhs, mxArray *plhs[], int nrhs, const mxArray *prhs[])
{
int N = mxGetN(prhs[0]);//number of cols
int M = mxGetM(prhs[0]);//number of rows
char* srcPtr = (char*)mxGetData(prhs[0]);
double* pointPtr = mxGetPr(prhs[1]);
double dstSizeW = 0;
double dstSizeH = 0;
double x1 = *(pointPtr+0);
double x2 = *(pointPtr+1);
double x3 = *(pointPtr+2);
double x4 = *(pointPtr+3);
double y1 = *(pointPtr+4);
double y2 = *(pointPtr+5);
double y3 = *(pointPtr+6);
double y4 = *(pointPtr+7);
Point2f src_vertices[4];//Point2f(x,y)
src_vertices[0] = Point2f(x1,y1);
src_vertices[1] = Point2f(x2,y2);
src_vertices[2] = Point2f(x3,y3);
src_vertices[3] = Point2f(x4,y4);
mexPrintf("src_Vertice: x,y\n");
mexPrintf("%f,%f;\n",src_vertices[0].x,src_vertices[0].y);
mexPrintf("%f,%f;\n",src_vertices[1].x,src_vertices[1].y);
mexPrintf("%f,%f;\n",src_vertices[2].x,src_vertices[2].y);
mexPrintf("%f,%f;\n",src_vertices[3].x,src_vertices[3].y);
Point2f dst_vertices[4];
if(nrhs==3)
{
double* dstPointPtr = mxGetPr(prhs[2]);
dst_vertices[0] = Point2f(*(dstPointPtr+0),*(dstPointPtr+4));
dst_vertices[1] = Point2f(*(dstPointPtr+1),*(dstPointPtr+5));
dst_vertices[2] = Point2f(*(dstPointPtr+2),*(dstPointPtr+6));
dst_vertices[3] = Point2f(*(dstPointPtr+3),*(dstPointPtr+7));
}
else
{
mexPrintf("Auto Dst Point:\n");
double dstSize1 = sqrt(pow((x2-x1),2)+pow((y2-y1),2));
double dstSize2 = sqrt(pow((x3-x2),2)+pow((y3-y2),2));
if(dstSize1 > dstSize2)
{
dstSizeW = dstSize1;
dstSizeH = dstSize2;
dst_vertices[0] = Point2f(dstSizeW,0);
dst_vertices[1] = Point2f(0,0);
dst_vertices[2] = Point2f(0,dstSizeH);
dst_vertices[3] = Point2f(dstSizeW,dstSizeH);
}
else
{
dstSizeW = dstSize2;
dstSizeH = dstSize1;
dst_vertices[0] = Point2f(0,0);
dst_vertices[1] = Point2f(0,dstSizeH);
dst_vertices[2] = Point2f(dstSizeW,dstSizeH);
dst_vertices[3] = Point2f(dstSizeW,0);
}
mexPrintf("dstSizeW,dstSizeH:%f,%f\n",dstSizeW,dstSizeH);
mexPrintf("dst_Vertice: x,y\n");
mexPrintf("%f,%f;\n",dst_vertices[0].x,dst_vertices[0].y);
mexPrintf("%f,%f;\n",dst_vertices[1].x,dst_vertices[1].y);
mexPrintf("%f,%f;\n",dst_vertices[2].x,dst_vertices[2].y);
mexPrintf("%f,%f;\n",dst_vertices[3].x,dst_vertices[3].y);
}
//Acturally it should be Mat(rows,cols,...);
//but Matlab Array is store by cols
Mat src = Mat(N,M,CV_8UC1,srcPtr);
//transposition because Matlab Array store by cols
src = src.t();
//imwrite("cvSrc.bmp",src);
Mat warpMatrix = getPerspectiveTransform(src_vertices, dst_vertices);
plhs[0] = mxCreateNumericMatrix(dstSizeH,dstSizeW,mxUINT8_CLASS,mxREAL);
char* dstPtr = (char*)mxGetData(plhs[0]);
Mat dst = Mat(dstSizeH,dstSizeW,CV_8UC1);
warpPerspective(src, dst, warpMatrix, dst.size(), INTER_LINEAR, BORDER_CONSTANT);
dst = dst.t();
Mat dstMx = Mat(dstSizeW,dstSizeH,CV_8UC1,dstPtr);
dst.copyTo(dstMx);
//imwrite("cvDst.bmp",dst);
}mex -I.\ -I'C:\Program Files\OpenCV249\opencv\build\include' -L'C:\Program Files\OpenCV249\opencv\build\x64\vc10\lib' -lopencv_core249 -lopencv_highgui249 -lopencv_video249 -lopencv_imgproc249 cv_rotateRect.cpp
使用示例:
I = imread('m.bmp');
BW = im2bw(I,0.5);
L = bwlabel(BW);
s = regionprops(L,'Area');
if ~isempty(s)
[maxarea,maxi] = max([s.Area]);
[r, c] = find(L==maxi);
cr = [c';r'];
rRect = minBoundingBox(cr);
figure(1);imshow(L);
imline(gca,[rRect(1,1),rRect(2,1);rRect(1,2),rRect(2,2)]);
imline(gca,[rRect(1,2),rRect(2,2);rRect(1,3),rRect(2,3)]);
imline(gca,[rRect(1,3),rRect(2,3);rRect(1,4),rRect(2,4)]);
imline(gca,[rRect(1,4),rRect(2,4);rRect(1,1),rRect(2,1)]);
rRect = [rRect(1,:)',rRect(2,:)'];
I2 = cv_rotateRect(I,rRect);
figure(2);imshow(I2);
endcv_rotatedRect.mexw64:
http://download.csdn.net/detail/sunflower_boy/9740877
1 http://www.mathworks.com/matlabcentral/fileexchange/31126-2d-minimal-bounding-box
2 http://gis.stackexchange.com/questions/22895/how-to-find-the-minimum-area-rectangle-for-given-points
3 http://www.bubuko.com/infodetail-493981.html
4 http://stackoverflow.com/questions/21659496/deep-copy-of-opencv-cvmat