操作系统实验一·创建进程
创建进程
- 1实验目的
- 2实验内容:
-
- 2.1Windows实现
- 2.2Linux实现
- 3实验环境
-
- 3.1Windows
- 3.2Linux虚拟机
- 4程序设计和实现
-
- 4.1Windows实现
-
- 4.1.1函数解释
- 4.1.2程序代码
- 4.1.3运行结果
- 4.2Linux实现
-
- 4.2.1函数解释
- 4.2.2程序代码
- 4.2.3运行结果
Use system calls to implement a “mytime” command to run an executable program through the command line parameter. Create a new process to run this executable program and record the running time of that program. Implement a Windows version and a Linux version.
1实验目的
使用系统调用实现“mytime”命令,通过命令行参数运行可执行程序。创建一个新进程来运行此可执行程序,并记录该程序的运行时间。实现Windows版本和Linux版本。
2实验内容:
2.1Windows实现
•使用CreateProcess()创建新流程
•在“mytime”命令中使用WaitForSingleObject()与创建的进程同步。
•使用GetSystemTime()获取时间。
2.2Linux实现
•使用fork()/execv()创建新流程
•使用wait()等待创建的进程结束。
•使用gettimeofday()获取当前时间。
3实验环境
3.1Windows
操作系统:Windows 10
处理器:AMD 3800X
3.2Linux虚拟机
操作系统:Ubantu 20.04.3
虚拟机软件:VMware Workstation 15
虚拟处理器:1个6核
4程序设计和实现
4.1Windows实现
4.1.1函数解释
CreateProcess()函数创建进程并为进程指定运行程序。其语句调用如下:
BOOL CreateProcess(LPCTSTR lpApplicationName, LPTSTR lpCommandLine,
LPSECURITY_ATTRIBUTES lpProcessAttributes,
LPSECURITY_ATTRIBUTES lpThreadAttributes,
BOOL bInheritHandles, DWORD dwCreationFlag,
LPVOID lpEnvironment, LPCTSTR lpCurrentDirectory,
LPSTARTUPINFO lpStartupInfo,
LPPROCESS_INFORMTION lpProcessInformation);
几个有用到的参数。
lpApplication:该参数指定新进程将使用的可执行文件
lpCommandLine:该参数指定里传递给新进程的命令行字符串,该函数将按照一定的顺序搜索该可执行文件位置,并执行
lpProcessInformation:该参数是只想包含返回的进程和线程的句柄、进程和线程标识符的指针。在等待同步函数中需要从该结构中调取句柄信息
我使用的是:
CreateProcess
(NULL, //不在此指定可执行文件的文件名
argv[1], //命令行参数
NULL, //默认进程安全性
NULL, //默认线程安全性
FALSE, //当前进程内的句柄不可以被子进程继承
CREATE_NEW_CONSOLE, //为新进程创建一个新的控制台窗口
NULL, //使用本进程的环境变量
NULL, //使用本进程的驱动器和目录
&si, //父进程传给子进程的一些信息
&pi //保存新进程信息的结构
)
WaitForSingleObject()进程等待同步函数使父进程等待子进程,函数描述如下:
DWORD WaitForSingleObject(HANDLE hHandle,DWORD dwMilliseconds);
其中,参数hHandle为等待对象的句柄,实验中通过lpProcessInformation.hProcess给出,dwMillisenconds是以毫秒为单位的等待时间,由于本实验等待子进程完全结束,于是给定值为无限,即INFINITE。
typedef struct_PROCESS_INFORMATION
{ HANDLE hProcess;
HANDLE hThread;
DWORD dwProcessId;
DWORD dwThreadId;
}PROCESS_INFORMATION;
其中成员含义如下。
① hProcess:返回新进程的句柄。
② hThread:返回主线程的句柄。
③ dwProcessId:返回一个全局进程标识符。该标识符用于标识一个进程。从进程被 创建到终止,该值始终有效。
④ dwThreadId:返回一个全局线程标识符。该标识符用于标识一个线程。从线程被创 建到终止,该值始终有效。
4.1.2程序代码
#include 4.1.3运行结果
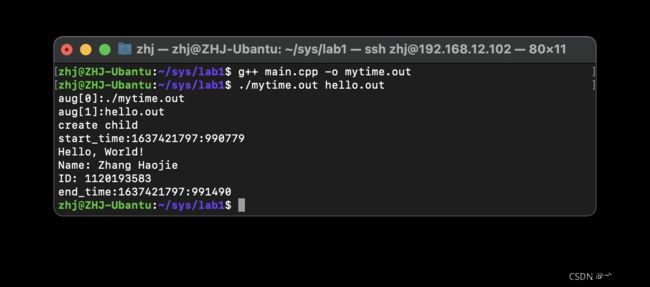
通过运行自己写的另外一个简单程序来实现
#include 4.2Linux实现
4.2.1函数解释
使用fork()创建函数,正确完成时,函数返回给父进程的是被创建子进程的标识,返回给子进程的为0;若创建失败,则返回父进程的为-1;通过返回值,可以判断子进程是否创建成功,以及进程是子进程还是父进程。
pid_t fork(void);
使用execv()为子进程指定运行程序,其函数调用如下:
int execv(const char pathname,char const arg[]);
使用gettimeofday()进行计时,该函数获得从1970年1月1日到现在的时间
int gettimeofday(struct timeval *tv, struct timezone *tz);
struct timeval{
long int tv_sec; //记录秒数
long int tv_usec; //记录微秒数
}
4.2.2程序代码
#include