Linux操作文档——磁盘和文件系统管理(LVM管理)
文章目录
-
- 一、管理磁盘及分区
-
- 1、检测并确认新硬盘
- 2、规划硬盘中的分区
- 3、gdisk命令的使用
- 二、管理文件系统
-
- 1、创建文件系统
- 2、挂载、卸载文件系统
- 三、LVM逻辑卷管理
-
- 1、LVM概述
- 2、LVM的管理命令
- 3、LVM扩展
- 4、使用SSM工具
- 四、设置磁盘配额
-
- 磁盘配额管理
一、管理磁盘及分区
1、检测并确认新硬盘
[root@localhost ~]# fdisk -l
Disk /dev/sda: 21.5 GB, 21474836480 bytes, 41943040 sectors
Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk label type: dos
Disk identifier: 0x000a12dd
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sda1 * 2048 2099199 1048576 83 Linux
/dev/sda2 2099200 41943039 19921920 8e Linux LVM
Disk /dev/sdb: 21.5 GB, 21474836480 bytes, 41943040 sectors
Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk /dev/mapper/centos-root: 18.2 GB, 18249416704 bytes, 35643392 sectors
Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk /dev/mapper/centos-swap: 2147 MB, 2147483648 bytes, 4194304 sectors
Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
如果是在虚拟机中添加磁盘,在不关机的情况下可以这样识别
[root@localhost ~]# echo "- - -" >>/sys/class/scsi_host/host0/scan
[root@localhost ~]# echo "- - -" >>/sys/class/scsi_host/host1/scan
[root@localhost ~]# echo "- - -" >>/sys/class/scsi_host/host2/scan
2、规划硬盘中的分区
进入交互式的分区管理界面
[root@localhost ~]# fdisk /dev/sdb
Welcome to fdisk (util-linux 2.23.2).
Changes will remain in memory only, until you decide to write them.
Be careful before using the write command.
Device does not contain a recognized partition table
Building a new DOS disklabel with disk identifier 0xe1070311.
Command (m for help): n
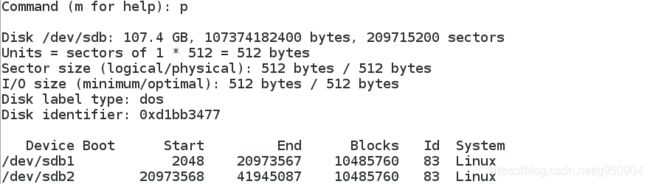
1、 “p”指令:列出硬盘中的分区情况
Command (m for help): p
Disk /dev/sdb: 21.5 GB, 21474836480 bytes, 41943040 sectors
Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk label type: dos
Disk identifier: 0x158df64a
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
2、“n”指令:新建分区
Command (m for help): n
Partition type:
p primary (0 primary, 0 extended, 4 free)
e extended
Select (default p): p
Partition number (1-4, default 1): 1
First sector (2048-41943039, default 2048):
Using default value 2048
Last sector, +sectors or +size{K,M,G} (2048-41943039, default 41943039): +2G
Partition 1 of type Linux and of size 2 GiB is set
Command (m for help): n
Partition type:
p primary (1 primary, 0 extended, 3 free)
e extended
Select (default p): p
Partition number (2-4, default 2): 2
First sector (4196352-41943039, default 4196352):
Using default value 4196352
Last sector, +sectors or +size{K,M,G} (4196352-41943039, default 41943039): +2G
Partition 2 of type Linux and of size 2 GiB is set
Command (m for help): n
Partition type:
p primary (2 primary, 0 extended, 2 free)
e extended
Select (default p): e
Partition number (3,4, default 3):
First sector (8390656-41943039, default 8390656):
Using default value 8390656
Last sector, +sectors or +size{K,M,G} (8390656-41943039, default 41943039):
Using default value 41943039
Partition 3 of type Extended and of size 16 GiB is set
Command (m for help): n
Partition type:
p primary (2 primary, 1 extended, 1 free)
l logical (numbered from 5)
Select (default p): l
Adding logical partition 5
First sector (8392704-41943039, default 8392704):
Using default value 8392704
Last sector, +sectors or +size{K,M,G} (8392704-41943039, default 41943039): +2G
Partition 5 of type Linux and of size 2 GiB is set
Command (m for help): n
Partition type:
p primary (2 primary, 1 extended, 1 free)
l logical (numbered from 5)
Select (default p): l
Adding logical partition 6
First sector (12589056-41943039, default 12589056):
Using default value 12589056
Last sector, +sectors or +size{K,M,G} (12589056-41943039, default 41943039): +2G
Partition 6 of type Linux and of size 2 GiB is set
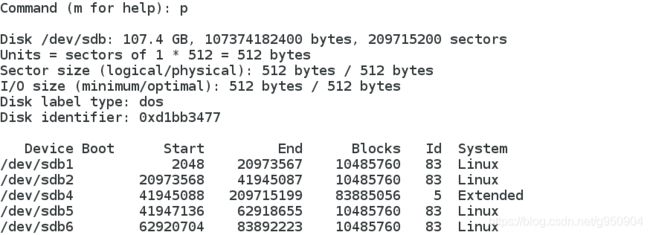
3、 “d”指令:删除分区
![]()
4、“t”指令:变更分区的类型
XFS、Swap文件系统对应的ID号分别为83、82,而用于Windows中的NTFS文件系统对应的ID号一般为86
将逻辑分区"dev/sdb5"的类型更改为Swap

5、“w”和“q”指令:退出fdisk分区工具
"w"指令将保存分区操作,而"q"指令不会保存对硬盘所做的分区操作
Command (m for help): w
The partition table has been altered!
Calling ioctl() to re-read partition table.
Syncing disks.
重新探测/dev/sdb磁盘中的分区变化
[root@localhost ~]# partprobe /dev/sdb
3、gdisk命令的使用
gdisk命令的使用方法和fdisk相似,区别为gdisk命令可以对GPT格式磁盘进行操作,fdisk不可以。
[root@localhost ~]# gdisk /dev/sdb
GPT fdisk (gdisk) version 0.8.10
Partition table scan:
MBR: not present
BSD: not present
APM: not present
GPT: not present
Creating new GPT entries.
Command (? for help): ?
b back up GPT data to a file
c change a partition's name
d delete a partition
i show detailed information on a partition
l list known partition types
n add a new partition
o create a new empty GUID partition table (GPT)
p print the partition table
q quit without saving changes
r recovery and transformation options (experts only)
s sort partitions
t change a partition's type code
v verify disk
w write table to disk and exit
x extra functionality (experts only)
? print this menu
Command (? for help): n
Partition number (1-128, default 1):
First sector (34-41943006, default = 2048) or {+-}size{KMGTP}:
Last sector (2048-41943006, default = 41943006) or {+-}size{KMGTP}: +2G
Current type is 'Linux filesystem'
Hex code or GUID (L to show codes, Enter = 8300):
Changed type of partition to 'Linux filesystem'
Command (? for help): p
Disk /dev/sdb: 41943040 sectors, 20.0 GiB
Logical sector size: 512 bytes
Disk identifier (GUID): C4061B44-7C79-4569-BEB7-216C9F1C2C36
Partition table holds up to 128 entries
First usable sector is 34, last usable sector is 41943006
Partitions will be aligned on 2048-sector boundaries
Total free space is 37748669 sectors (18.0 GiB)
Number Start (sector) End (sector) Size Code Name
1 2048 4196351 2.0 GiB 8300 Linux filesystem
Command (? for help): t //改变磁盘格式为LVM
Using 1
Current type is 'Linux filesystem'
Hex code or GUID (L to show codes, Enter = 8300): 8e00
Changed type of partition to 'Linux LVM'
Command (? for help): p
Disk /dev/sdb: 41943040 sectors, 20.0 GiB
Logical sector size: 512 bytes
Disk identifier (GUID): C4061B44-7C79-4569-BEB7-216C9F1C2C36
Partition table holds up to 128 entries
First usable sector is 34, last usable sector is 41943006
Partitions will be aligned on 2048-sector boundaries
Total free space is 37748669 sectors (18.0 GiB)
Number Start (sector) End (sector) Size Code Name
1 2048 4196351 2.0 GiB 8E00 Linux LVM
Command (? for help): w
Final checks complete. About to write GPT data. THIS WILL OVERWRITE EXISTING
PARTITIONS!!
Do you want to proceed? (Y/N): y
OK; writing new GUID partition table (GPT) to /dev/sdb.
The operation has completed successfully.
二、管理文件系统
1、创建文件系统
1、mkfs命令的使用
创建XFS文件系统
[root@localhost ~]# mkfs -t xfs /dev/sdb1
meta-data=/dev/sdb1 isize=512 agcount=4, agsize=131072 blks
= sectsz=512 attr=2, projid32bit=1
= crc=1 finobt=0, sparse=0
data = bsize=4096 blocks=524288, imaxpct=25
= sunit=0 swidth=0 blks
naming =version 2 bsize=4096 ascii-ci=0 ftype=1
log =internal log bsize=4096 blocks=2560, version=2
= sectsz=512 sunit=0 blks, lazy-count=1
realtime =none extsz=4096 blocks=0, rtextents=0
或者
[root@localhost ~]# mkfs.xfs /dev/sdb5
meta-data=/dev/sdb5 isize=512 agcount=4, agsize=131072 blks
= sectsz=512 attr=2, projid32bit=1
= crc=1 finobt=0, sparse=0
data = bsize=4096 blocks=524288, imaxpct=25
= sunit=0 swidth=0 blks
naming =version 2 bsize=4096 ascii-ci=0 ftype=1
log =internal log bsize=4096 blocks=2560, version=2
= sectsz=512 sunit=0 blks, lazy-count=1
realtime =none extsz=4096 blocks=0, rtextents=0
2、 mkswap命令的使用
将分区/dev/sdb5创建为交换分区(目标分区应先通过fdisk工具将ID号设为82)
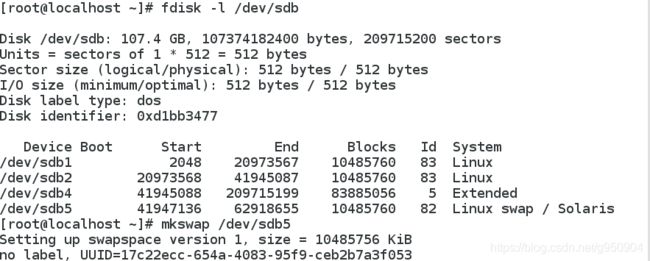
启用、停用交换分区/dev/sdb5

2、挂载、卸载文件系统
1、挂载文件系统
将光盘设备挂载到/media/cdrom目录
ocalhost ~]# mount /dev/cdrom /media/
mount: /dev/sr0 写保护,将以只读方式挂载
将建立的/dev/sdb1分区挂载到新建的/mailbox目录下
[root@localhost ~]# mkdir /mailbox
[root@localhost ~]# mount /dev/sdb1 /mailbox/
将下载的CentoOS 7系统的DVD光盘镜像文件"CentOS-7-x86_64-DVD-1611.iso"挂载到/media/mnt目录下
![]()
2、卸载文件系统
通过挂载点目录卸载对应的分区
[root@localhost ~]# umount /mailbox/
通过设备文件卸载光盘
[root@localhost ~]# umount /dev/cdrom
3、设置文件系统的自动挂载
查看当前系统内自动挂载的设备或分区
[root@localhost ~]# cat /etc/fstab
#
# /etc/fstab
# Created by anaconda on Mon Apr 20 18:04:49 2020
#
# Accessible filesystems, by reference, are maintained under '/dev/disk'
# See man pages fstab(5), findfs(8), mount(8) and/or blkid(8) for more info
#
/dev/mapper/centos-root / xfs defaults 0 0
UUID=8aae3529-8026-496f-8d2c-590d0662b8fc /boot xfs defaults 0 0
/dev/mapper/centos-swap swap swap defaults 0 0
/dev/sdb1 /mailbox xfs defaults 0 0
第1字段:设备名或设备卷标名。 第2字段:文件系统的挂载点目录的位置。 第3字段:文件系统类型,如XFS、Swap等。第4字段:挂载参数,即mount命令"-o"选项后可使用的参数。例如,defaults, rw、ro、noexec 分别表示默认参数、可写、只读、禁用执行程序。
第5字段:表示文件系统是否需要dump备份。一般设为1时表示 需要,设为0时将被dump忽略。
第6字段:该数字决定在系统启动时进行磁盘检查的顺序。0表示不进行检查,1表示优先检查,2表示其次检查。根分区应设为1 ,其他分区设为2。
添加自动挂载分区/dev/sdb1
[root@localhost ~]# cat /etc/fstab
(略)
/dev/sdb1 /mailbox xfs defaults 0 0
4、查看磁盘使用情况
查看当前系统中挂载的各文件系统的磁盘使用情况
[root@localhost ~]# df -Th
文件系统 类型 容量 已用 可用 已用% 挂载点
devtmpfs devtmpfs 894M 0 894M 0% /dev
tmpfs tmpfs 910M 0 910M 0% /dev/shm
tmpfs tmpfs 910M 11M 900M 2% /run
tmpfs tmpfs 910M 0 910M 0% /sys/fs/cgroup
/dev/mapper/centos-root xfs 17G 5.1G 12G 30% /
/dev/sda1 xfs 1014M 232M 783M 23% /boot
tmpfs tmpfs 182M 4.0K 182M 1% /run/user/42
tmpfs tmpfs 182M 40K 182M 1% /run/user/0
/dev/sr0 iso9660 11G 11G 0 100% /media
/dev/sdb1 xfs 2.0G 33M 2.0G 2% /mailbox
三、LVM逻辑卷管理
1、LVM概述
1、PV (Physical Volume,物理卷)
物理卷是LVM机制的基本存储设备,通常对应为一个普通分区或整个硬盘。物理卷一般直接使用设备文件 名称,如/dev/sdb1、/dev/sdb2、/dev/sdd 等。对用于转换成物理卷的普通分区,建议先使用fdisk工具将分区类型的D标记号改为"8e"。
2、VG (Volume Group,卷组)
由一个或多个物理卷组成一个整体,即称为卷组,在卷组中可以动态地添加或移除物理卷。
3、LV ( Logical Volume,逻辑卷)
逻辑卷建立在卷组之上,与物理卷没有直接关系。
2、LVM的管理命令
常用的LVM管理命令
| 功能 | PV管理命令 | VG管理命令 | LV管理命令 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scan(扫描) | pvscan | vgscan | Ivscan |
| Create (建立) | pvcreate | vgcreate | Ivcreate |
| Display (显示) | pvdisplay | vgdisplay | Ivdisplay |
| Remove (移除) | pvremove | vgremove | Ivremove |
| Extend (扩展) | vgextend | Ivextend | |
| Reduce (减少) | vgreduce | Ivreduce |
1、创建PV
配置物理磁盘
[root@localhost ~]# fdisk -l
磁盘 /dev/sda:21.5 GB, 21474836480 字节,41943040 个扇区
Units = 扇区 of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
扇区大小(逻辑/物理):512 字节 / 512 字节
I/O 大小(最小/最佳):512 字节 / 512 字节
磁盘标签类型:dos
磁盘标识符:0x000aa505
设备 Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sda1 * 2048 2099199 1048576 83 Linux
/dev/sda2 2099200 41943039 19921920 8e Linux LVM
WARNING: fdisk GPT support is currently new, and therefore in an experimental phase. Use at your own discretion.
磁盘 /dev/sdb:21.5 GB, 21474836480 字节,41943040 个扇区
Units = 扇区 of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
扇区大小(逻辑/物理):512 字节 / 512 字节
I/O 大小(最小/最佳):512 字节 / 512 字节
磁盘标签类型:gpt
Disk identifier: A1B0B991-CDA2-4617-B654-75084369C446
# Start End Size Type Name
1 2048 2099199 1G Linux LVM Linux LVM
2 2099200 4196351 1G Linux LVM Linux LVM
3 4196352 6293503 1G Linux LVM Linux LVM
4 6293504 8390655 1G Linux LVM Linux LVM
5 8390656 10487807 1G Linux LVM Linux LVM
磁盘 /dev/mapper/centos-root:18.2 GB, 18249416704 字节,35643392 个扇区
Units = 扇区 of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
扇区大小(逻辑/物理):512 字节 / 512 字节
I/O 大小(最小/最佳):512 字节 / 512 字节
磁盘 /dev/mapper/centos-swap:2147 MB, 2147483648 字节,4194304 个扇区
Units = 扇区 of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
扇区大小(逻辑/物理):512 字节 / 512 字节
I/O 大小(最小/最佳):512 字节 / 512 字节
(1)pvcreate命令:用于将分区或整个硬盘转换成物理卷,主要是添加LVM属性信息并划分PE存储单位
pvcreate 设备名1 设备名2 (创建)
[root@localhost ~]# pvcreate /dev/sdb{1..4} //{ .. }意思为1-4
Physical volume "/dev/sdb1" successfully created.
Physical volume "/dev/sdb2" successfully created.
Physical volume "/dev/sdb3" successfully created.
Physical volume "/dev/sdb4" successfully created.
(2)pvscan命令:用于扫描系统中所有的物理卷,并输出相关信息
[root@localhost ~]# pvscan
PV /dev/sda2 VG centos lvm2 [<19.00 GiB / 0 free]
PV /dev/sdb3 lvm2 [1.00 GiB]
PV /dev/sdb1 lvm2 [1.00 GiB]
PV /dev/sdb2 lvm2 [1.00 GiB]
PV /dev/sdb4 lvm2 [1.00 GiB]
Total: 5 [<23.00 GiB] / in use: 1 [<19.00 GiB] / in no VG: 4 [4.00 GiB]
最后一行显示为整体 PV 的量 / 已经被使用到 VG 的 PV 量 / 剩余的 PV 量
(3)pvdisplay命令:显示物理卷的详细信息,需要使用指定的物理卷作为命令参数,默认时将显示所有物理卷的信息
[root@localhost ~]# pvdisplay /dev/sdb1
"/dev/sdb1" is a new physical volume of "1.00 GiB"
--- NEW Physical volume ---
PV Name /dev/sdb1 //实际的partition
VG Name //所在VG组,这还没有分配
PV Size 1.00 GiB //容量大小
Allocatable NO //是否被分配
PE Size 0 //PE大小
Total PE 0 //PE数量
Free PE 0 //没被LV用到的PE
Allocated PE 0 //尚可分配出去的PE
PV UUID ERlA6S-vGlc-bamM-sQPN-DdOp-jKmt-ogoRAn
(4)pvremove命令:用于将物理卷还原成普通分区或磁盘,不再用于LVM体系,被移除的物理卷将无法被pvscan识别
2、创建VG
(1)vgcreate命令:用于将一个或多个物理卷创建为一个卷组,第一个命令参数用于设置新卷组的名称,其后依次指定需要加入该卷组的物理卷作为参数
vgcreate 卷组名 物理卷名1 物理卷名2 (创建)
将刚创建的4个PV中创建成一个VG
[root@localhost ~]# vgcreate vgadmin /dev/sdb{1..4}
Volume group "vgadmin" successfully created
[root@localhost ~]# vgdisplay vgadmin
--- Volume group ---
VG Name vgadmin
System ID
Format lvm2
Metadata Areas 4
Metadata Sequence No 1
VG Access read/write
VG Status resizable
MAX LV 0
Cur LV 0
Open LV 0
Max PV 0
Cur PV 4
Act PV 4
VG Size 3.98 GiB //整个VG容量
PE Size 4.00 MiB //内部每个PE大小
Total PE 1020 //总共PE数量
Alloc PE / Size 0 / 0
Free PE / Size 1020 / 3.98 GiB //可配置给LV的PE数量/总容量
VG UUID LOlWfH-CpR2-6IRd-njMQ-I2HU-V0l3-51CtYr
(2)vgscan命令:用于扫描系统中已建立的LVM卷组及相关信息
[root@localhost ~]# vgscan
Reading volume groups from cache.
Found volume group "centos" using metadata type lvm2
Found volume group "vgadmin" using metadata type lvm2
(3)vgdisplay命令:用于显示系统中各卷组的详细信息,需要使用指定卷组名作为命令参数(未指定卷组时将显示所有卷组的信息)
(4)vgremove命令:用于删除指定的卷组,将指定卷组名称作为参数即可
(5)vgextend命令:用于扩展卷组的磁盘空间
vgextend 卷组名 物理卷名 (扩展vg)
3、创建LV
(1) Ivscan命令:用于扫描系统中已建立的逻辑卷及相关信息
(2)Ivcreate命令:用于从指定的卷组中分割空间,以创建新的逻辑卷
lvcreate -L 容量大小 -n 逻辑卷名 卷组名 (创建)
[root@localhost ~]# lvcreate -L 2G -n lvadmin vgadmin
Logical volume "lvadmin" created.
(3)Ivdispla命令:用于显示逻辑卷的详细信息,可以指定逻辑卷的设备文件作为参数,也可以使用卷组名作为参数,以显示该卷组中所有逻辑卷的信息
(4)Ivextend命令:用于动态扩展逻辑卷的空间
lvextend -L +大小 /dev/卷组名/逻辑卷名 (扩展lv)
(5)Ivremove命令:用于删除指定的逻辑卷,直接使用逻辑卷的设备文件作为参数即可
4、格式化
[root@localhost ~]# mkfs.xfs /dev/vgadmin/lvadmin //LV的名称必须使用全名
meta-data=/dev/vgadmin/lvadmin isize=512 agcount=4, agsize=131072 blks
= sectsz=512 attr=2, projid32bit=1
= crc=1 finobt=0, sparse=0
data = bsize=4096 blocks=524288, imaxpct=25
= sunit=0 swidth=0 blks
naming =version 2 bsize=4096 ascii-ci=0 ftype=1
log =internal log bsize=4096 blocks=2560, version=2
= sectsz=512 sunit=0 blks, lazy-count=1
realtime =none extsz=4096 blocks=0, rtextents=0
5、挂载
[root@localhost ~]# mkdir /mnt/admin
[root@localhost ~]# mount /dev/vgadmin/lvadmin /mnt/admin/ //临时挂载
[root@localhost ~]# df -hT /mnt/admin/
文件系统 类型 容量 已用 可用 已用% 挂载点
/dev/mapper/vgadmin-lvadmin xfs 2.0G 33M 2.0G 2% /mnt/admin
[root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/fstab //开机自动挂载
/dev/vgadmin/lvadmin /mnt/admin/ xfs defaults 0 0
[root@localhost ~]# mount -a //将/etc/fstab的所有内容重新加载
3、LVM扩展
[root@localhost ~]# pvcreate /dev/sdb5 //将/dev/sdb5转换成PV卷
Physical volume "/dev/sdb5" successfully created.
[root@localhost ~]# vgextend vgadmin /dev/sdb5 //添加到vgadmin中
Volume group "vgadmin" successfully extended
[root@localhost ~]# lvextend -L +1G /dev/vgadmin/lvadmin //在LV里面增加容量
Size of logical volume vgadmin/lvadmin changed from 2.00 GiB (512 extents) to 3.00 GiB (768 extents).
Logical volume vgadmin/lvadmin successfully resized.
[root@localhost ~]# xfs_growfs /dev/vgadmin/lvadmin //更新文件系统大小
meta-data=/dev/mapper/vgadmin-lvadmin isize=512 agcount=4, agsize=131072 blks
= sectsz=512 attr=2, projid32bit=1
= crc=1 finobt=0 spinodes=0
data = bsize=4096 blocks=524288, imaxpct=25
= sunit=0 swidth=0 blks
naming =version 2 bsize=4096 ascii-ci=0 ftype=1
log =internal bsize=4096 blocks=2560, version=2
= sectsz=512 sunit=0 blks, lazy-count=1
realtime =none extsz=4096 blocks=0, rtextents=0
data blocks changed from 524288 to 786432
[root@localhost ~]# df -hT /mnt/admin/
文件系统 类型 容量 已用 可用 已用% 挂载点
/dev/mapper/vgadmin-lvadmin xfs 3.0G 33M 3.0G 2% /mnt/admin
4、使用SSM工具
1、查看磁盘信息
[root@localhost ~]# yum -y install system-storage-manager
[root@localhost ~]# ssm list dev //列出设备信息
-----------------------------------------------------------------
Device Free Used Total Pool Mount point
-----------------------------------------------------------------
/dev/sda 20.00 GB
/dev/sda1 1.00 GB /boot
/dev/sda2 0.00 KB 19.00 GB 19.00 GB centos
/dev/sdb 20.00 GB
/dev/sdb1 0.00 KB 1020.00 MB 1.00 GB vgadmin
/dev/sdb2 0.00 KB 1020.00 MB 1.00 GB vgadmin
/dev/sdb3 1012.00 MB 8.00 MB 1.00 GB vgadmin
/dev/sdb4 1020.00 MB 0.00 KB 1.00 GB vgadmin
-----------------------------------------------------------------
[root@localhost ~]# ssm list pool //存储池信息
---------------------------------------------------
Pool Type Devices Free Used Total
---------------------------------------------------
centos lvm 1 0.00 KB 19.00 GB 19.00 GB
vgadmin lvm 4 1.98 GB 2.00 GB 3.98 GB
---------------------------------------------------
2、快速创建存储
格式:ssm create -s lv大小 -n lv名称 --fstype lv文件系统类型 -p 卷组名 设备 挂载点
[root@localhost ~]# mkdir /backup
[root@localhost ~]# ssm create -s 1G -n lvadmin --fstype xfs -p vgadmin /dev/sdb[1-4] /backup
Physical volume "/dev/sdb1" successfully created.
Physical volume "/dev/sdb2" successfully created.
Physical volume "/dev/sdb3" successfully created.
Physical volume "/dev/sdb4" successfully created.
Volume group "vgadmin" successfully created
Logical volume "lvadmin" created.
meta-data=/dev/vgadmin/lvadmin isize=512 agcount=4, agsize=65536 blks
= sectsz=512 attr=2, projid32bit=1
= crc=1 finobt=0, sparse=0
data = bsize=4096 blocks=262144, imaxpct=25
= sunit=0 swidth=0 blks
naming =version 2 bsize=4096 ascii-ci=0 ftype=1
log =internal log bsize=4096 blocks=2560, version=2
= sectsz=512 sunit=0 blks, lazy-count=1
realtime =none extsz=4096 blocks=0, rtextents=0
[root@localhost ~]# df -hT /backup
文件系统 类型 容量 已用 可用 已用% 挂载点
/dev/mapper/vgadmin-lvadmin xfs 1014M 33M 982M 4% /backup
四、设置磁盘配额
查看系统是否支持磁盘配额功能
[root@localhost ~]# grep -i quota /boot/config-3.10.0-1062.18.1.el7.x86_64
CONFIG_NETFILTER_XT_MATCH_QUOTA=m
CONFIG_XFS_QUOTA=y
CONFIG_QUOTA=y //这里是内核支持quota功能
CONFIG_QUOTA_NETLINK_INTERFACE=y
CONFIG_PRINT_QUOTA_WARNING=y
# CONFIG_QUOTA_DEBUG is not set
CONFIG_QUOTA_TREE=y
CONFIG_QUOTACTL=y
CONFIG_QUOTACTL_COMPAT=y
磁盘配额管理
1、以支持配额功能的方式挂载文件系统
创建一个分区并将其格式化
[root@localhost ~]# fdisk /dev/sdb
欢迎使用 fdisk (util-linux 2.23.2)。
更改将停留在内存中,直到您决定将更改写入磁盘。
使用写入命令前请三思。
Device does not contain a recognized partition table
使用磁盘标识符 0x7008d481 创建新的 DOS 磁盘标签。
命令(输入 m 获取帮助):n
Partition type:
p primary (0 primary, 0 extended, 4 free)
e extended
Select (default p): p
分区号 (1-4,默认 1):
起始 扇区 (2048-41943039,默认为 2048):
将使用默认值 2048
Last 扇区, +扇区 or +size{K,M,G} (2048-41943039,默认为 41943039):+5G
分区 1 已设置为 Linux 类型,大小设为 5 GiB
命令(输入 m 获取帮助):w
The partition table has been altered!
Calling ioctl() to re-read partition table.
正在同步磁盘。
[root@localhost ~]# mkfs.ext4 /dev/sdb1
mke2fs 1.42.9 (28-Dec-2013)
文件系统标签=
OS type: Linux
块大小=4096 (log=2)
分块大小=4096 (log=2)
Stride=0 blocks, Stripe width=0 blocks
327680 inodes, 1310720 blocks
65536 blocks (5.00%) reserved for the super user
第一个数据块=0
Maximum filesystem blocks=1342177280
40 block groups
32768 blocks per group, 32768 fragments per group
8192 inodes per group
Superblock backups stored on blocks:
32768, 98304, 163840, 229376, 294912, 819200, 884736
Allocating group tables: 完成
正在写入inode表: 完成
Creating journal (32768 blocks): 完成
Writing superblocks and filesystem accounting information: 完成
[root@localhost ~]# mkdir /quota
[root@localhost ~]# mount -o usrquota,grpquota /dev/sdb1 /quota/ //临时挂载
[root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/fstab //开机自动挂载
/dev/sdb1 /quota ext4 defaults,usrquota,grpquota 0 0
[root@localhost ~]# df -hT /dev/sdb1
文件系统 类型 容量 已用 可用 已用% 挂载点
/dev/sdb1 ext4 4.8G 20M 4.6G 1% /quota
2、创建配额记录文件
[root@localhost ~]# quotacheck -cugv /quota/
quotacheck: Your kernel probably supports journaled quota but you are not using it. Consider switching to journaled quota to avoid running quotacheck after an unclean shutdown.
quotacheck: Scanning /dev/sdb1 [/quota] done
..........
-c:–create 创建磁盘配额的配置文件
-u:–user 针对用户配额的配置文件
-g:–group 针对组配额的配置文件
-v:–verbose 详细显示扫描过程中的信息
-a:–all 检测系统中所有已经挂载的支持quota功能的分区
2、编辑用户和组账号的配额设置
bsoft::设置磁盘容量的软限制数值。
bhard:设置磁盘容量的硬限制数值。
isoft:设置磁盘文件数的硬限制数值。
ihard:设置磁盘文件数的软限制数值。
"-x”表示启动专家模式,在当前模式下允许对配额系统进行修改的所有管理命令可用;
"-c"表示直接调用管理命令
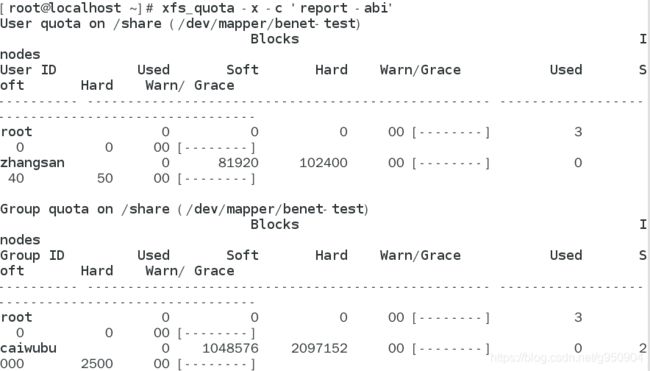
设置用户zhangsan的磁盘配额:磁盘容量软限制80MB、磁盘容量硬限制100MB.文件数软限制40、文件数硬限制50
![]()
查看用户zhangsan的磁盘容量限制

查看zhangsan用户的磁盘文件数限制

设置组账号caiwubu的磁盘配额:磁盘容量软限制1GB、磁盘容量硬限制2GB、文件数软限制2000、文件数硬限制2500

3、查看配额使用情况
查看所有可用分区的磁盘容量配额使用情况
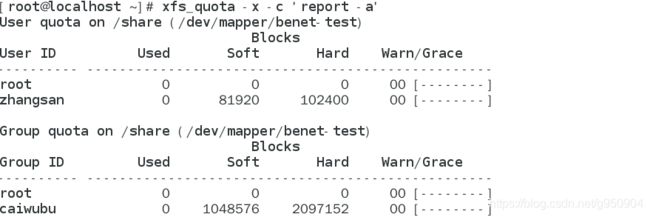
查看磁盘容量和文件输入的报告