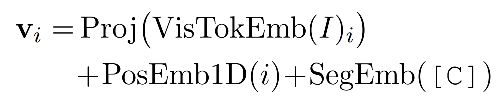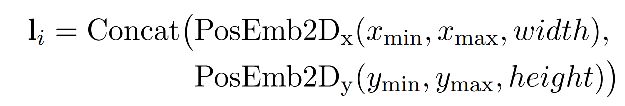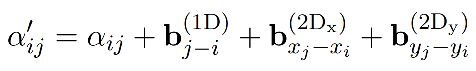【论文笔记】LayoutLMv2: Multi-modal Pre-training for Visually-rich Document Understanding(LayoutLMv2)
文章目录
- LayoutLMv2: Multi-modal Pre-training for Visually-rich Document Understanding
- 基本信息
- 摘要
- 模型结构
-
- Text Embedding
- Visual Embedding
- Layout Embedding
- Spatial-Aware Self-Attention Mechanism
- Pre-training Tasks
-
- Masked visual-Language Modeling(MVLM)
- Text-Image Alignment(TIA)
- Text-Image Matching
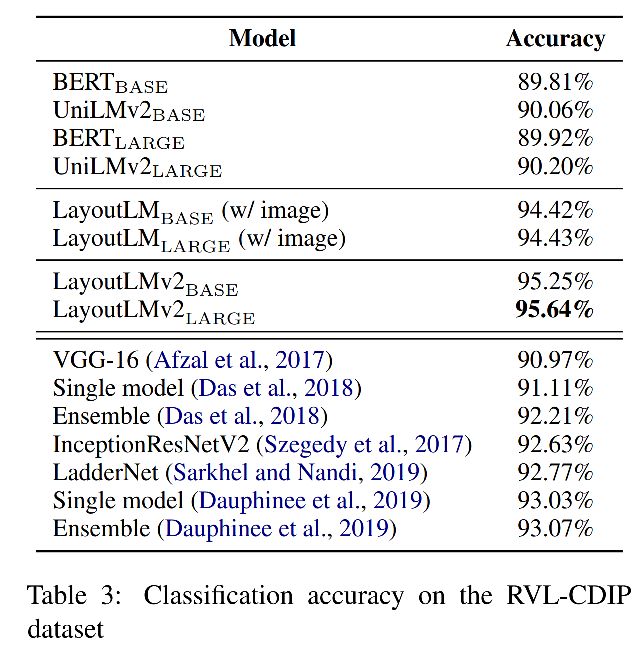
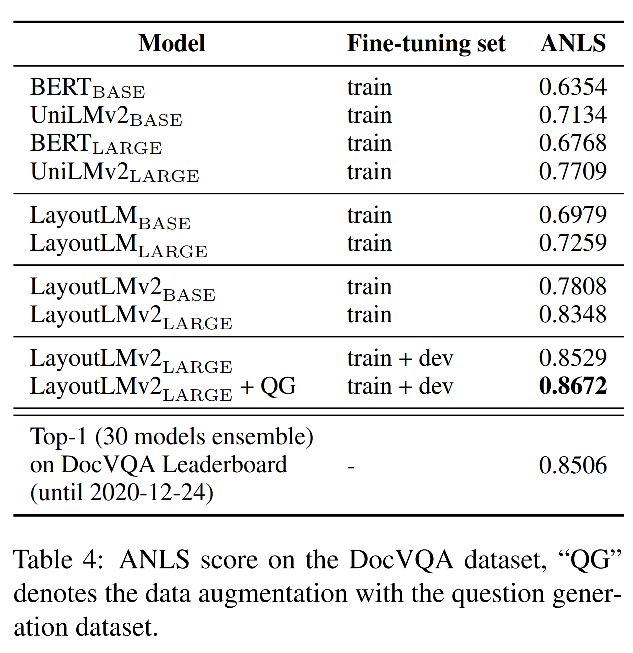
- 实验
- 总结
LayoutLMv2: Multi-modal Pre-training for Visually-rich Document Understanding
基本信息
- 论文链接:arxiv
- 发表时间:2021 - ACL
- 应用场景:文档理解
摘要
| 存在什么问题 | 解决了什么问题 |
|---|---|
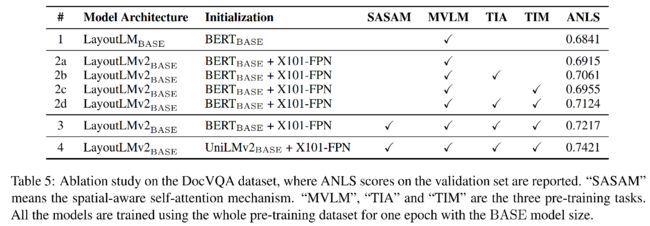
| 1. LayoutLM在预训练任务上不够完善,还是差点意思。 | 1. 在LayoutLM的基础上,提出了新的预训练任务,除了MVLM以外,加入了视觉模态的预训练任务,通过文本-图像对齐以及文本-图像匹配总共三项预训练任务更好的捕捉text、visual、layout之前的跨模态信息,从而提升模型精度。并在VrDU各项任务以及VQA上任务上同时达到SOTA。 2.2. transformer encoder结构中将self-attention修改为spatial-aware self-attention,使模型能够更加充分理解不同文本框间的相对位置关系。 |
模型结构
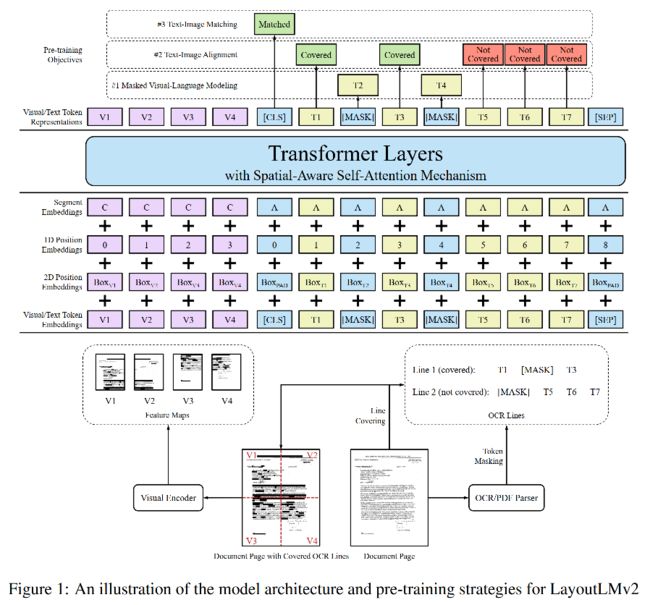
网络整体可以看做成是由双流encoder所组成的。
Text Embedding
对于OCR文本行结果,先用WordPiece进行切词,切词后的单词作为网络的token。前面添加
< c l s > , w 1 , w 2 , . . . , < s e p > , < p a d > , < p a d > . . . < p a d > , 其 中 l e n g t h = L {
对于行内每个token,由以下三种Embedding进行相加得到:
TokEmb就是NLP上常说的TextEmbedding。
PosEmb1D代表该token在输入中的位置Embedding。
SegEmb: 取[A]或者[B](**什么时候取A,什么时候取B?**没搞明白啊。。。)
Visual Embedding
和LayoutLMv1不同之处,v2预训练任务融合了视觉信息,从而让模型能够进一步抓取图片细节信息。
将图像resize到224x224,通过ResNeXt-FPN抽取特征,取出降采样32倍的feature map,接一个FC层(维度和Text Embedding能够匹配,从而进行模态交互),再拉伸成序列即可。
对于该长度为7x7=49的序列上的每个点,还要加上其PosEmbedding以及SegEmbedding。假设文本序列的最大长度为512,那么此时输入给transformer的序列长度为512+49=561,前47个为visual token,剩下512个为text token。
其中PosEmb和文本中的PosEmb1D共用一个embedding matrix,SegEmb则用[C]来表示。所以公式为:
Layout Embedding
对于常规的text token,layout embedding和LayoutLMv1中的方法保持一致。
由于feature map相当去是把原图划成了7*7=49个不同的块,所以49个visual token代表了原图上49个patch的bbox,那么layout embedding就解决了。
对于 < c l s > , < s e p > , < p a d >
Spatial-Aware Self-Attention Mechanism
为了提高模型对版式的局部不变性,相对位置信息是非常重要的。对于所有token,在加完所有的embedding后,送入transformer encoder。一般地,attention matrix logits可用如下公式表示:
对于语义相对位置以及空间相对位置的学习,赋予 α i j \alpha_{ij} αij上每个位置可学习的三个bias并求和相加:
这些bias在每个头是不同的,但是在所有层中共享一份。
那么self-attention的结果可表示为:
Pre-training Tasks
Masked visual-Language Modeling(MVLM)
和LayoutLMv1保持一致,注意要同时mask掉相应token的视觉区域,防止视觉信息泄露。
Text-Image Alignment(TIA)
该任务的目的是为了让模型更好的学习图像与每个bbox坐标之间的关系。
以文本行为粒度,随机mask掉一行,最后通过fc层预测该token是否被覆盖,即为一个二分类,[coverd]或者[not coverd]。
为了防止和MVLM任务产生冲突以及防止模型学到[mask]和[covered]之间没什么用的信息,在某个token同时mask且被[covered]的时候,MVLM任务失效。
预训练的时候15%变成covered。用bce loss对该任务进行优化。
Text-Image Matching
该任务的目的是学习文档图像和文本上下文间的关系。
通过[cls] token学习图片和text是否来自同一个文档。
通常情况下,正样本中图片和text一定是来自同一个文档的,对于负样本,会将图片随机替换成伟其他的图片或者dropped(什么意思?是空白图嘛?)
为了不让模型被前两个预训练任务欺骗,对于负样本也正常采用MVLM以及TIA,只不过对于TIA来说,token的所有标签都是[covered]了。
预训练的时候15%的图片会被随机替换,5%会被dropped。用bce loss对该任务进行优化。
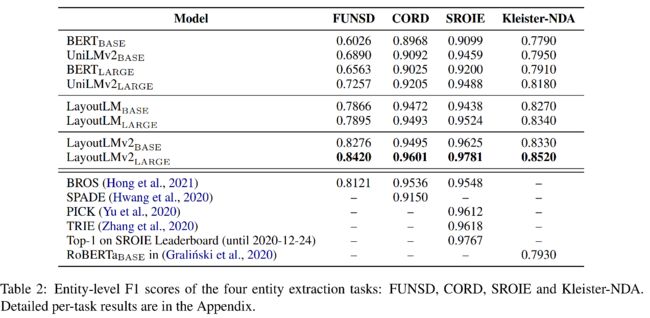
实验
总结
- 在LayoutLM基础上优化并提出了LayoutLMv2模型,通过单一模型融合了三种模态信息,并且进一步丰富了预训练方法手段,并且有了视觉模态的融合,提出了spatial-aware self-attention机制来挖缺每个token间的相对位置关系,在6项不同的富文档理解任务中均达到了SOTA。
- SegEmbedding还是没太搞懂,A和B是怎么确定的?另外TIA任务中droped是什么策略呢?