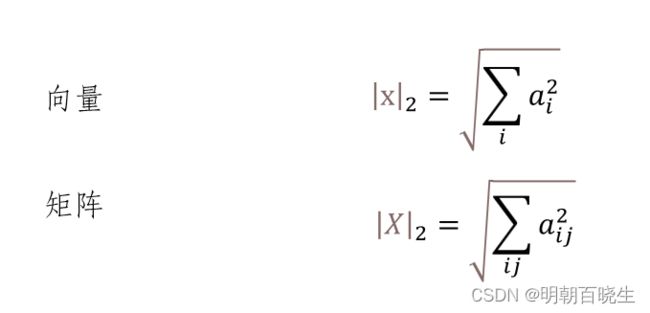P7 PyTorch 属性统计
目录
- Norm
- min max argmax argmin prod sum
- dim keepdim
- topk & kthvalue
- eq&equal
一 Norm
作用: 求范数
1.1 1阶范数
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Thu Dec 22 21:48:02 2022
@author: cxf
"""
import torch
def statistics():
a = torch.full([8],1.0) #向量vector
b = a.view(2,4) #矩阵
c = a.view(2,2,2) #张量
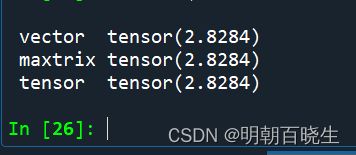
print("\n vector ",a.norm(1), "\n maxtrix",b.norm(1), "\n tensor ",c.norm(1))
statistics()
输出:
绝对值求和
1.2 2阶范数
print("\n vector ",a.norm(2), "\n maxtrix",b.norm(2), "\n tensor ",c.norm(2))1.3 指定维度取范数
计算该维度上的范数
a = torch.full([8],1.0)
b = a.view(2,4) #矩阵
c = a.view(2,2,2)
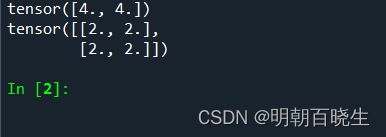
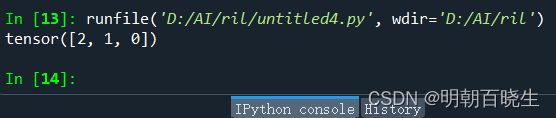
print(b.norm(1,dim=1))
print(c.norm(1,dim=0))这里面要重点说明一下C,
C 是一个[2,2,2]的张量 dim=0
可以看成
C=[A,B]
A=B=[[1,1],
[1,]]
计算其一阶范数
C=[A+B]
=[[2,2]
[2,2]]
二 其它常用统计操作
def statics():
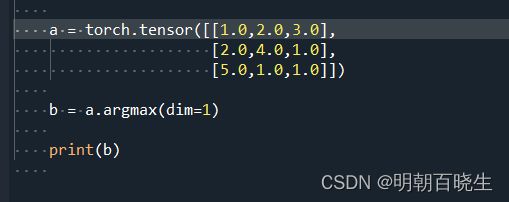
a = torch.arange(0, 8, 1).view(2,4).float()
print("\n a: ",a)
print("\n 最小值:%3.2f 最大值: %3.2f, 均值 %3.2f, 连乘 %3.2f 和:%3.2f"%(a.min(), a.max(),a.mean(),a.prod(),a.sum()))
print("\n 最大值索引: %d 最小值索引: %d "%(a.argmax(), a.argmin()))
statics()
输出
需要注意的是 argmax 可以指定dimension
在dimension=1 维度统计最大值索引:输出为
三 dim keepdim
假设4张图片,识别分成五类
dim
max 后得到的shape
b[0] 为概率最大值,shape 为[4]
b[1] 为最大概率对应的索引位置
keepdim 操作:
c[0] 为概率最大值,shape[4,1]
c[1] 为概率最大值对应索引,shape[4,1]
def img():
a = torch.rand(4,5)
b = a.max(dim=1)
c = a.max(dim=1,keepdim=True)
print("\n a: ",a)
print("\n b ",b[0],b[1])
print("\n c ",c[0],c[1])
img()
四 topk & kthvalue
假设
import torch
def statistics():
a = torch.rand(4,5)
b = a.topk(2, dim=1, largest =True)
c = a.kthvalue(2,dim=1)
print("\n a ",a, "\n b",b, "\n c ",c)
4.1 topk
每行 取最大的两个变量,当largest = False 取最小的
4.2 kthvalue
排序后,取对应索引位置的元素
五 eq&equal
a = torch.tensor([[1.0,2.0],
[1.0,2.0]])
b = torch.full([2,2],1.0)
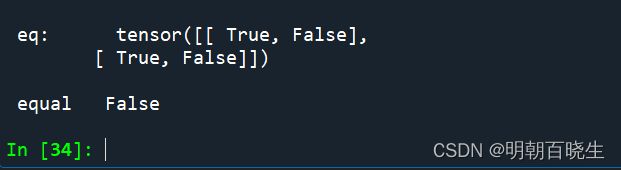
c = torch.eq(a,b)
d = torch.equal(a,b)
print("\n eq: \t ",c)
print("\n equal \t",d)eq 是每个元素比较,输出的是和原来shape 一致的张量
equal 是所有元素比较,输出的是ByteTensor