(pytorch-深度学习系列)深度卷积神经网络AlexNet
深度卷积神经网络AlexNet
文字过多,但是重点已经标出来了
背景
在LeNet提出后的将近20年里,神经网络一度被其他机器学习方法超越,如支持向量机。虽然LeNet可以在早期的小数据集上取得好的成绩,但是在更大的真实数据集上的表现并不尽如人意。一方面,神经网络计算复杂。虽然20世纪90年代也有过一些针对神经网络的加速硬件,但并没有像之后GPU那样大量普及。因此,训练一个多通道、多层和有大量参数的卷积神经网络在当年很难完成。另一方面,当年研究者还没有大量深入研究参数初始化和非凸优化算法等诸多领域,导致复杂的神经网络的训练通常较困难。
神经网络可以直接基于图像的原始像素进行分类。这种称为端到端(end-to-end)的方法节省了很多中间步骤。然而,在很长一段时间里更流行的是研究者通过勤劳与智慧所设计并生成的手工特征。这类图像分类研究的主要流程是:
- 获取图像数据集;
- 使用已有的特征提取函数生成图像的特征;
- 使用机器学习模型对图像的特征分类。
当时认为的机器学习部分仅限最后这一步。如果那时候跟机器学习研究者交谈,他们会认为机器学习既重要又优美。优雅的定理证明了许多分类器的性质。机器学习领域生机勃勃、严谨而且极其有用。然而,如果跟计算机视觉研究者交谈,则是另外一幅景象。他们会告诉你图像识别里“不可告人”的现实是:计算机视觉流程中真正重要的是数据和特征。也就是说,使用较干净的数据集和较有效的特征甚至比机器学习模型的选择对图像分类结果的影响更大。
特征的表示
-
在相当长的时间里,特征都是基于各式各样手工设计的函数从数据中提取的。事实上,不少研究者通过提出新的特征提取函数不断改进图像分类结果。
-
然而,另一些研究者认为特征本身也应该由学习得来。他们还相信,为了表征足够复杂的输入,特征本身应该分级表示。多层神经网络可能可以学得数据的多级表征,并逐级表示越来越抽象的概念或模式。
-
以图像分类为例,(二维卷积层)中物体边缘检测的例子。在多层神经网络中,图像的第一级的表示可以是在特定的位置和⻆度是否出现边缘;
-
而第二级的表示说不定能够将这些边缘组合出有趣的模式,如花纹;
-
在第三级的表示中,也许上一级的花纹能进一步汇合成对应物体特定部位的模式。这样逐级表示下去,最终,模型能够较容易根据最后一级的表示完成分类任务。需要强调的是,输入的逐级表示由多层模型中的参数决定,而这些参数都是学出来的。
AlexNet
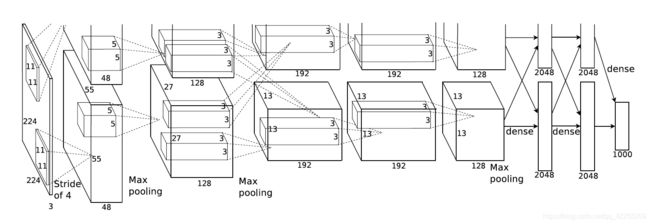
AlexNet网络结构
AlexNet包含8层变换,其中有5层卷积和2层全连接隐藏层,以及1个全连接输出层。
- 第一层中的卷积窗口形状是 11 × 11 11\times11 11×11
- 第二层中的卷积窗口形状减小到 5 × 5 5\times5 5×5
- 之后全采用 3 × 3 3\times3 3×3
- 第一、第二和第五个卷积层之后都使用了窗口形状为 3 × 3 3\times3 3×3、步幅为2的最大池化层
- AlexNet使用的卷积通道数大于LeNet中的卷积通道数几十倍
- 紧接着最后一个卷积层的是两个输出个数为4096的全连接层
简单说网络结构就是:
卷 积 ( 96 个 11 ∗ 11 的 核 ) ( 步 长 为 4 ) → 降 采 样 ( 最 大 池 化 ) ( 3 ∗ 3 的 核 , 步 长 2 ) → . 卷 积 ( 256 个 5 ∗ 5 的 核 ) ( p a d d i n g 为 2 ) → 降 采 样 ( 最 大 池 化 ) ( 3 ∗ 3 的 核 , 步 长 2 ) → . 卷 积 ( 384 个 3 ∗ 3 的 核 ) ( p a d d i n g 为 1 ) → . 卷 积 ( 384 个 3 ∗ 3 的 核 ) ( p a d d i n g 为 1 ) → . 卷 积 ( 256 个 3 ∗ 3 的 核 ) ( p a d d i n g 为 1 ) → 降 采 样 ( 最 大 池 化 ) ( 3 ∗ 3 的 核 , 步 长 2 ) → . 全 连 接 6 ∗ 6 ∗ 256 → 4096 → 全 连 接 4096 → 4096 → 全 连 接 4096 → 10 \begin{matrix}卷积 \\ (96个11*11的核) \\(步长为4)\end{matrix} \rightarrow \begin{matrix}降采样(最大池化) \\ (3*3的核,步长2) \end{matrix}\rightarrow \\.\\ \begin{matrix}卷积 \\ (256个5*5的核)\\(padding为2) \end{matrix} \rightarrow \begin{matrix}降采样(最大池化) \\ (3*3的核,步长2) \end{matrix}\rightarrow \\.\\ \begin{matrix}卷积 \\ (384个3*3的核)\\(padding为1)\end{matrix} \rightarrow \\.\\ \begin{matrix}卷积 \\ (384个3*3的核)\\(padding为1)\end{matrix} \rightarrow \\.\\ \begin{matrix}卷积 \\ (256个3*3的核)\\(padding为1)\end{matrix} \rightarrow \begin{matrix}降采样(最大池化) \\ (3*3的核,步长2) \end{matrix}\rightarrow \\.\\ \begin{matrix}全连接 \\ 6*6*256\rightarrow4096\end{matrix}\rightarrow \begin{matrix}全连接 \\ 4096\rightarrow4096\end{matrix}\rightarrow \begin{matrix}全连接 \\ 4096\rightarrow10\end{matrix} 卷积(96个11∗11的核)(步长为4)→降采样(最大池化)(3∗3的核,步长2)→.卷积(256个5∗5的核)(padding为2)→降采样(最大池化)(3∗3的核,步长2)→.卷积(384个3∗3的核)(padding为1)→.卷积(384个3∗3的核)(padding为1)→.卷积(256个3∗3的核)(padding为1)→降采样(最大池化)(3∗3的核,步长2)→.全连接6∗6∗256→4096→全连接4096→4096→全连接4096→10
每层尺寸解析:
(1)
原始图像的227*227*3的图像(最开始是224*224*3,为后续处理,t需要调整为227)
卷 积 ( 96 个 11 ∗ 11 的 核 ) ( 步 长 为 4 ) ⌊ ( n h − k h + p h + s h ) / s h ⌋ × ⌊ ( n w − k w + p w + s w ) / s w ⌋ = ⌊ ( 227 − 11 + 0 × 2 + 4 ) / 4 ⌋ × ⌊ ( 227 − 11 + 0 × 2 + 4 ) / 4 ⌋ = 55 × 55 . 降 采 样 ( 最 大 池 化 ) ( 3 ∗ 3 的 核 , 步 长 2 ) ⌊ ( n h − k h + p h + s h ) / s h ⌋ × ⌊ ( n w − k w + p w + s w ) / s w ⌋ = ⌊ ( 55 − 3 + 0 × 2 + 2 ) / 2 ⌋ × ⌊ ( 55 − 3 + 0 × 2 + 2 ) / 2 ⌋ = 27 × 27 \begin{matrix}卷积 \\ (96个11*11的核) \\(步长为4)\end{matrix}\\ \lfloor(n_h-k_h+p_h+s_h)/s_h\rfloor \times \lfloor(n_w-k_w+p_w+s_w)/s_w\rfloor = \\ \lfloor(227-11+0\times2+4)/4\rfloor \times \lfloor(227-11+0\times2+4)/4\rfloor = 55 \times 55 \\.\\ \begin{matrix}降采样(最大池化) \\ (3*3的核,步长2) \end{matrix} \\ \lfloor(n_h-k_h+p_h+s_h)/s_h\rfloor \times \lfloor(n_w-k_w+p_w+s_w)/s_w\rfloor = \\ \lfloor(55-3+0\times2+2)/2\rfloor \times \lfloor(55-3+0\times2+2)/2\rfloor = 27 \times 27 卷积(96个11∗11的核)(步长为4)⌊(nh−kh+ph+sh)/sh⌋×⌊(nw−kw+pw+sw)/sw⌋=⌊(227−11+0×2+4)/4⌋×⌊(227−11+0×2+4)/4⌋=55×55.降采样(最大池化)(3∗3的核,步长2)⌊(nh−kh+ph+sh)/sh⌋×⌊(nw−kw+pw+sw)/sw⌋=⌊(55−3+0×2+2)/2⌋×⌊(55−3+0×2+2)/2⌋=27×27
第一层卷积层结束后形成的图像层的规模为 27 ∗ 27 ∗ 96 27*27*96 27∗27∗96.分别由96个卷积核对应生成,这96层数据分为2组,每组48个像素层
(2)
卷 积 ( 256 个 5 ∗ 5 的 核 ) ( p a d d i n g 为 2 ) ⌊ ( n h − k h + p h + s h ) / s h ⌋ × ⌊ ( n w − k w + p w + s w ) / s w ⌋ = ⌊ ( 27 − 5 + 2 × 2 + 1 ) / 1 ⌋ × ⌊ ( 27 − 5 + 2 × 2 + 1 ) / 1 ⌋ = 27 × 27 . 降 采 样 ( 最 大 池 化 ) ( 3 ∗ 3 的 核 , 步 长 2 ) ⌊ ( n h − k h + p h + s h ) / s h ⌋ × ⌊ ( n w − k w + p w + s w ) / s w ⌋ = ⌊ ( 27 − 3 + 0 × 2 + 2 ) / 2 ⌋ × ⌊ ( 27 − 3 + 0 × 2 + 2 ) / 2 ⌋ = 13 × 13 \begin{matrix}卷积 \\ (256个5*5的核)\\(padding为2) \end{matrix}\\ \lfloor(n_h-k_h+p_h+s_h)/s_h\rfloor \times \lfloor(n_w-k_w+p_w+s_w)/s_w\rfloor = \\ \lfloor(27-5+2\times2+1)/1\rfloor \times \lfloor(27-5+2\times2+1)/1\rfloor = 27 \times 27 \\.\\ \begin{matrix}降采样(最大池化) \\ (3*3的核,步长2) \end{matrix} \\ \lfloor(n_h-k_h+p_h+s_h)/s_h\rfloor \times \lfloor(n_w-k_w+p_w+s_w)/s_w\rfloor = \\ \lfloor(27-3+0\times2+2)/2\rfloor \times \lfloor(27-3+0\times2+2)/2\rfloor = 13 \times 13 卷积(256个5∗5的核)(padding为2)⌊(nh−kh+ph+sh)/sh⌋×⌊(nw−kw+pw+sw)/sw⌋=⌊(27−5+2×2+1)/1⌋×⌊(27−5+2×2+1)/1⌋=27×27.降采样(最大池化)(3∗3的核,步长2)⌊(nh−kh+ph+sh)/sh⌋×⌊(nw−kw+pw+sw)/sw⌋=⌊(27−3+0×2+2)/2⌋×⌊(27−3+0×2+2)/2⌋=13×13
第二层输入数据为第一层输出的27*27*96的像素层,分为2组像素数据,两组像素数据分别在两个不同的GPU中进行运算,一共有256个卷积核,即池化后像素的规模为2组13*13*128的像素层。
(3)
卷 积 ( 384 个 3 ∗ 3 的 核 ) ( p a d d i n g 为 1 ) ⌊ ( n h − k h + p h + s h ) / s h ⌋ × ⌊ ( n w − k w + p w + s w ) / s w ⌋ = ⌊ ( 13 − 3 + 1 × 2 + 1 ) / 1 ⌋ × ⌊ ( 13 − 3 + 1 × 2 + 1 ) / 1 ⌋ = 13 × 13 \begin{matrix}卷积 \\ (384个3*3的核)\\(padding为1)\end{matrix} \\ \lfloor(n_h-k_h+p_h+s_h)/s_h\rfloor \times \lfloor(n_w-k_w+p_w+s_w)/s_w\rfloor = \\ \lfloor(13-3+1\times2+1)/1\rfloor \times \lfloor(13-3+1\times2+1)/1\rfloor = 13 \times 13 卷积(384个3∗3的核)(padding为1)⌊(nh−kh+ph+sh)/sh⌋×⌊(nw−kw+pw+sw)/sw⌋=⌊(13−3+1×2+1)/1⌋×⌊(13−3+1×2+1)/1⌋=13×13
一共有384个卷积核,同理,也就是13*13*192两组像素层。
(4)
卷 积 ( 384 个 3 ∗ 3 的 核 ) ( p a d d i n g 为 1 ) ⌊ ( n h − k h + p h + s h ) / s h ⌋ × ⌊ ( n w − k w + p w + s w ) / s w ⌋ = ⌊ ( 13 − 3 + 1 × 2 + 1 ) / 1 ⌋ × ⌊ ( 13 − 3 + 1 × 2 + 1 ) / 1 ⌋ = 13 × 13 \begin{matrix}卷积 \\ (384个3*3的核)\\(padding为1)\end{matrix} \\ \lfloor(n_h-k_h+p_h+s_h)/s_h\rfloor \times \lfloor(n_w-k_w+p_w+s_w)/s_w\rfloor = \\ \lfloor(13-3+1\times2+1)/1\rfloor \times \lfloor(13-3+1\times2+1)/1\rfloor = 13 \times 13 卷积(384个3∗3的核)(padding为1)⌊(nh−kh+ph+sh)/sh⌋×⌊(nw−kw+pw+sw)/sw⌋=⌊(13−3+1×2+1)/1⌋×⌊(13−3+1×2+1)/1⌋=13×13
一共有384个卷积核,同理,也就是13*13*192两组像素层。
(5)
卷 积 ( 256 个 3 ∗ 3 的 核 ) ( p a d d i n g 为 1 ) ⌊ ( n h − k h + p h + s h ) / s h ⌋ × ⌊ ( n w − k w + p w + s w ) / s w ⌋ = ⌊ ( 13 − 3 + 2 × 1 + 1 ) / 1 ⌋ × ⌊ ( 13 − 3 + 2 × 1 + 1 ) / 1 ⌋ = 13 × 13 . 降 采 样 ( 最 大 池 化 ) ( 3 ∗ 3 的 核 , 步 长 2 ) ⌊ ( n h − k h + p h + s h ) / s h ⌋ × ⌊ ( n w − k w + p w + s w ) / s w ⌋ = ⌊ ( 13 − 3 + 0 × 2 + 2 ) / 2 ⌋ × ⌊ ( 13 − 3 + 0 × 2 + 2 ) / 2 ⌋ = 6 × 6 \begin{matrix}卷积 \\ (256个3*3的核)\\(padding为1) \end{matrix}\\ \lfloor(n_h-k_h+p_h+s_h)/s_h\rfloor \times \lfloor(n_w-k_w+p_w+s_w)/s_w\rfloor = \\ \lfloor(13-3+2\times1+1)/1\rfloor \times \lfloor(13-3+2\times1+1)/1\rfloor = 13 \times 13 \\.\\ \begin{matrix}降采样(最大池化) \\ (3*3的核,步长2) \end{matrix} \\ \lfloor(n_h-k_h+p_h+s_h)/s_h\rfloor \times \lfloor(n_w-k_w+p_w+s_w)/s_w\rfloor = \\ \lfloor(13-3+0\times2+2)/2\rfloor \times \lfloor(13-3+0\times2+2)/2\rfloor = 6 \times 6 卷积(256个3∗3的核)(padding为1)⌊(nh−kh+ph+sh)/sh⌋×⌊(nw−kw+pw+sw)/sw⌋=⌊(13−3+2×1+1)/1⌋×⌊(13−3+2×1+1)/1⌋=13×13.降采样(最大池化)(3∗3的核,步长2)⌊(nh−kh+ph+sh)/sh⌋×⌊(nw−kw+pw+sw)/sw⌋=⌊(13−3+0×2+2)/2⌋×⌊(13−3+0×2+2)/2⌋=6×6
一共有256个卷积核,同理,也就是6*6*128两组像素层。
(6)
第6层输入数据的尺寸是6*6*256,采用6*6*256尺寸的滤波器对第六层的输入数据进行卷积运算;每个6*6*256尺寸的滤波器对第六层的输入数据进行卷积运算生成一个运算结果,通过一个神经元输出这个运算结果;共有4096个6*6*256尺寸的滤波器对输入数据进行卷积,通过4096个神经元的输出运算结果;然后通过ReLU激活函数以及dropout运算输出4096个本层的输出结果值。所以结果是2个2048输出结果组
(7)
第6层输出的4096个数据与第7层的4096个神经元进行全连接,然后由ReLU和Dropout进行处理后生成4096个数据。所以结果是2个2048输出结果组
(8)
第7层输入的4096个数据与第8层的1000个神经元进行全连接。
与LeNet的显著区别
- AlexNet将sigmoid激活函数改成了更加简单的ReLU激活函数
(ReLU激活函数的计算更简单,例如它并没有sigmoid激活函数中的求幂运算。另一方面,ReLU激活函数在不同的参数初始化方法下使模型更容易训练。这是由于当sigmoid激活函数输出极接近0或1时,这些区域的梯度几乎为0,从而造成反向传播无法继续更新部分模型参数;而ReLU激活函数在正区间的梯度恒为1。因此,若模型参数初始化不当,sigmoid函数可能在正区间得到几乎为0的梯度,从而令模型无法得到有效训练。) - AlexNet通过丢弃法来控制全连接层的模型复杂度。而LeNet并没有使用丢弃法。
- AlexNet引入了大量的图像增广,如翻转、裁剪和颜色变化,从而进一步扩大数据集来缓解过拟合。
实现简化过的AlexNet
import time
import torch
from torch import nn, optim
import torchvision
device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
class AlexNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(AlexNet, self).__init__()
self.conv = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(1, 96, 11, 4), # in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride, padding
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(3, 2), # kernel_size, stride
# 减小卷积窗口,使用填充为2来使得输入与输出的高和宽一致,且增大输出通道数
nn.Conv2d(96, 256, 5, 1, 2),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(3, 2),
# 连续3个卷积层,且使用更小的卷积窗口。除了最后的卷积层外,进一步增大了输出通道数。
# 前两个卷积层后不使用池化层来减小输入的高和宽
nn.Conv2d(256, 384, 3, 1, 1),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(384, 384, 3, 1, 1),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(384, 256, 3, 1, 1),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(3, 2)
)
# 这里全连接层的输出个数比LeNet中的大数倍。使用丢弃层来缓解过拟合
self.fc = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(256*5*5, 4096),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Dropout(0.5),
nn.Linear(4096, 4096),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Dropout(0.5),
# 输出层。由于这里使用Fashion-MNIST,所以用类别数为10,而非论文中的1000
nn.Linear(4096, 10),
)
def forward(self, img):
feature = self.conv(img)
output = self.fc(feature.view(img.shape[0], -1))
return output
net = AlexNet()
print(net)
AlexNet(
(conv): Sequential(
(0): Conv2d(1, 96, kernel_size=(11, 11), stride=(4, 4))
(1): ReLU()
(2): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
(3): Conv2d(96, 256, kernel_size=(5, 5), stride=(1, 1), padding=(2, 2))
(4): ReLU()
(5): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
(6): Conv2d(256, 384, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(7): ReLU()
(8): Conv2d(384, 384, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(9): ReLU()
(10): Conv2d(384, 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(11): ReLU()
(12): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
)
(fc): Sequential(
(0): Linear(in_features=6400, out_features=4096, bias=True)
(1): ReLU()
(2): Dropout(p=0.5)
(3): Linear(in_features=4096, out_features=4096, bias=True)
(4): ReLU()
(5): Dropout(p=0.5)
(6): Linear(in_features=4096, out_features=10, bias=True)
)
)
读取数据:
def load_data_fashion_mnist(batch_size, resize=None, root='~/Datasets/FashionMNIST'):
"""Download the fashion mnist dataset and then load into memory."""
trans = []
if resize:
trans.append(torchvision.transforms.Resize(size=resize))
trans.append(torchvision.transforms.ToTensor())
transform = torchvision.transforms.Compose(trans)
mnist_train = torchvision.datasets.FashionMNIST(root=root, train=True, download=True, transform=transform)
mnist_test = torchvision.datasets.FashionMNIST(root=root, train=False, download=True, transform=transform)
train_iter = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(mnist_train, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True, num_workers=4)
test_iter = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(mnist_test, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=False, num_workers=4)
return train_iter, test_iter
batch_size = 128
# 如出现“out of memory”的报错信息,可减小batch_size或resize
train_iter, test_iter = load_data_fashion_mnist(batch_size, resize=224)
训练吧:
lr, num_epochs = 0.001, 5
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(net.parameters(), lr=lr)
def train(net, train_iter, test_iter, batch_size, optimizer, device, num_epochs):
net = net.to(device)
print("training on ", device)
loss = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
train_l_sum, train_acc_sum, n, batch_count, start = 0.0, 0.0, 0, 0, time.time()
for X, y in train_iter:
X = X.to(device)
y = y.to(device)
y_hat = net(X)
l = loss(y_hat, y)
optimizer.zero_grad()
l.backward()
optimizer.step()
train_l_sum += l.cpu().item()
train_acc_sum += (y_hat.argmax(dim=1) == y).sum().cpu().item()
n += y.shape[0]
batch_count += 1
test_acc = evaluate_accuracy(test_iter, net)
print('epoch %d, loss %.4f, train acc %.3f, test acc %.3f, time %.1f sec'
% (epoch + 1, train_l_sum / batch_count, train_acc_sum / n, test_acc, time.time() - start))
train(net, train_iter, test_iter, batch_size, optimizer, device, num_epochs)
《动手学深度学习》