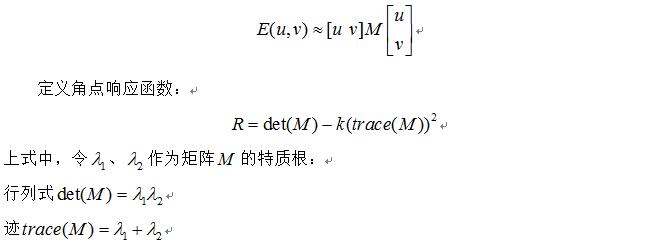Harris原理及opencv源码分析
一、前言
Harri角点检测的原理分析网上已经一大堆,这里则简单介绍Harris角点检测,并结合原理分析opencv实现的源码。
参考资料:
http://blog.csdn.net/ZengDong_1991/article/details/45563301
http://docs.opencv.org/2.4/doc/tutorials/features2d/trackingmotion/harris_detector/harris_detector.html
二、Harris角点原理
感觉Harris角点在Opencv Turorials上已经讲解的很清楚了,原理简介如下:

论文中k=0.04~0.06,opencv指出是0.05-0.5;故通过设定阈值与R进行可以比较,则可获得角点位置。opencv中的cornerHarris实现了计算图像中每个像素的角点响应值。
三、cornerHarris函数分析
a) opencv中的角点响应函数值实现函数为:
void cornerHarris(InputArray src, OutputArray dst, int blockSize, int ksize, double k, int borderType=BORDER_DEFAULT )
各形参的意义为:
src- 输入单通道8bit或浮点图像
dst- 存储所计算得的角点响应值,为CV_32FC1类型且与src具有相同大小
blockSize- 领域大小,也即窗口函数大小W(x, y)
ksize- 用sobel函数计算![]() 的模板大小
的模板大小
k- 计算角点响应值的K值
borderType - 支持BORDER_REFLECT101和borderType两种边界处理
b)opencv 源代码分析
/*Harris角点实现函数,截取cornerHarris中的关键代码并做了简化....
/*出自博客 http://blog.csdn.net/ZengDong_1991/article/details/45563301
*/
void myHarris(const Mat& src, Mat& eigenv, int block_size, int aperture_size, double k )
{
eigenv.create(src.size(), CV_32F);
Mat Dx, Dy;
//sobel operation get Ix, Iy
Sobel(src, Dx, CV_32F, 1, 0, aperture_size);
Sobel(src, Dy, CV_32F, 0, 1, aperture_size);
//get covariance matrix
Size size = src.size();
Mat cov(size, CV_32FC3); //创建一个三通道cov矩阵分别存储[Ix*Ix, Ix*Iy; Iy*Ix, Iy*Iy];
for (int i = 0; i < size.height; i++)
{
float* cov_data = cov.ptr(i);
const float* dxdata = Dx.ptr(i);
const float* dydata = Dy.ptr(i);
for (int j = 0; j < size.width; j++)
{
float dx = dxdata[j];
float dy = dydata[j];
cov_data[j * 3] = dx * dx; //即 Ix*Ix
cov_data[j * 3 + 1] = dx * dy; //即 Ix*Iy
cov_data[j * 3 + 2] = dy * dy; //即 Iy*Iy
}
}
//方框滤波 W(x,y)卷积 , 也可用高斯核加权...
//W(X,Y)与矩阵cov卷积运算得到 H 矩阵,后面通过H矩阵的特征值决定是否是角点
boxFilter(cov, cov, cov.depth(), Size(block_size, block_size), Point(-1, -1), false);
//cale Harris
size = cov.size();
if (cov.isContinuous() && eigenv.isContinuous())
{
size.width *= size.height;
size.height = 1;
//cout << "yes" << endl;
}
//此处计算响应R= det(H) - k*trace(H)*trace(H);
for (int i = 0; i < size.height; i++)
{
const float* covPtr = cov.ptr(i);
float* dstPtr = eigenv.ptr(i);
for (int j = 0; j < size.width; j++)
{
float a = covPtr[j * 3];
float b = covPtr[j * 3 + 1];
float c = covPtr[j * 3 + 2];
//根据公式 R = det(H) - k* trace(H)*trace(H);
dstPtr[j] = (float)(a*c - b*b - k*(a + c)*(a + c));
}
}
} #include "opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp"
#include "opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp"
#include
#include
#include
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
/// Global variables
Mat src, src_gray;
int thresh = 200;
int max_thresh = 255;
char* source_window = "Source image";
char* corners_window = "Corners detected";
/// Function header
void cornerHarris_demo(int, void*);
void myHarris(const Mat& src, Mat& eigenv, int block_size, int aperture_size, double k = 0.);
/** @function main */
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
/// Load source image and convert it to gray
//src = imread(argv[1], 1);
src = imread( "lena.bmp" , 1);
cvtColor(src, src_gray, CV_BGR2GRAY);
/// Create a window and a trackbar
namedWindow(source_window, CV_WINDOW_AUTOSIZE);
createTrackbar("Threshold: ", source_window, &thresh, max_thresh, cornerHarris_demo);
imshow(source_window, src);
cornerHarris_demo(0, 0);
waitKey(0);
return(0);
}
/** @function cornerHarris_demo */
void cornerHarris_demo(int, void*)
{
Mat dst, dst_norm, dst_norm_scaled;
dst = Mat::zeros(src.size(), CV_32FC1);
/// Detector parameters
int blockSize = 2;
int apertureSize = 3;
double k = 0.04;
/// Detecting corners
//cornerHarris(src_gray, dst, blockSize, apertureSize, k, BORDER_DEFAULT);
myHarris(src_gray, dst, blockSize, apertureSize, k);
/// Normalizing
normalize(dst, dst_norm, 0, 255, NORM_MINMAX, CV_32FC1, Mat());
convertScaleAbs(dst_norm, dst_norm_scaled);
/// Drawing a circle around corners
for (int j = 0; j < dst_norm.rows; j++)
{
for (int i = 0; i < dst_norm.cols; i++)
{
if ((int)dst_norm.at(j, i) > thresh)
{
circle(dst_norm_scaled, Point(i, j), 5, Scalar(0), 2, 8, 0);
}
}
}
/// Showing the result
namedWindow(corners_window, CV_WINDOW_AUTOSIZE);
imshow(corners_window, dst_norm_scaled);
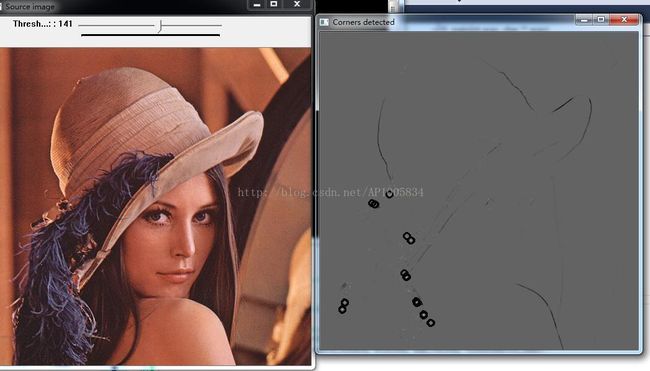
} d)测试结果
四、opencv goodFeaturesToTrack
以上cornerHarris函数需通过设置阈值对角点响应值进行判断,而opencv中的goodFeaturesToTrack已定义了一些角点选择方法。a) goodFeaturesToTrack函数
goodFeaturesToTrack(InputArray image, OutputArray corners, int maxCorners, double qualityLevel, double minDistance, InputArray mask=noArray(), int blockSize=3, bool useHarrisDetector=false, double k=0.04 )
各形参的意义为:
image- 单通道8bit或32bit浮点型图像
corners- 检测得的角点存放的容器
maxCorners- 返回的角点个数,如果检测的角点超过这个数目,从大到小依次返回
qualityLevel- 其与最大角点响应值的乘积作为角点响应阈值,小于该阈值则不考虑作为角点
minDistance- 两角点之间的最小欧式距离
mask- 掩模,必须与image具有同样大小,数据类型为CV_8UC1,非0值表示需要检测区域
blockSize- 内部调用cornerHarris函数用到的w(x, y)大小
useHarrisDetector- 是否使用HarrisDetector
k- cornerHarris中的计算角点响应函数值的 K
b)关键代码
//GoodFeaturesToTrack关键代码截取
void myGoodFeaturesToTrack( Mat& image, double qualityLevel, double minDistance, int maxCorners )
{
Mat eig;
Mat tmp;
cornerHarris(image, eig, 5, 3, 0.06); //Harris corners;
double maxVal = 0;
minMaxLoc(eig, 0, &maxVal, 0, 0, Mat());
//cout << maxVal << endl << maxVal*255. << endl;
//除去角点响应小于 角点最大响应qualityLevel倍的点
threshold(eig, eig, qualityLevel*maxVal, 0, THRESH_TOZERO); //eig is CV_32F
//normalize(eig, result, 0, 255, NORM_MINMAX, CV_8U); //normalize to show image.
//get corners max in 3*3 if Mat();
//为什么膨胀操作:膨胀的本质是用当前像素周围的最大值替代当前像素值,
//因此,通过膨胀前后比较能取得局部角点响应最大的点。
//第一次是在《OpenCV Programming Cookbook》中看到这种做法,觉得这想法太给力了...
//最后结果存储在tmpCorners中
dilate(eig, tmp, Mat()); //for later operation
vector tmpCorners;
Size imageSize = image.size();
{
// HANDLE hSemaphore = CreateSemaphore(NULL, 0, 1, NULL);
// CRITICAL_SECTION g_cs;
//#pragma omp parallel for //【此处并行为什么出错呢???????????????】
for ( int y = 1; y < imageSize.height -1; y++ )
{
float* eig_data = (float*)eig.ptr(y); //角点响应
float* tmp_data = (float*)tmp.ptr(y); // 膨胀之后
//#pragma omp parallel for
for ( int x =1; x < imageSize.width -1; x++ )
{
float val = eig_data[x];
if ( val != 0 && val == tmp_data[x] ) //如果膨胀前后的值不变,说明这个像素点是[3*3]邻域的最大值
{
// #pragma omp atomic //原子操作
// WaitForSingleObject(hSemaphore, NULL);
//EnterCriticalSection(&g_cs);
tmpCorners.push_back(eig_data + x);
//LeaveCriticalSection(&g_cs);
// ReleaseSemaphore(hSemaphore, NULL, NULL);
}
}
}
}
//ShellExecuteEx
//tmpCorners存储角点的地址, 排序操作
sort(tmpCorners, greaterThanPtr());
vector corners;
size_t i, j, total = tmpCorners.size(), ncorners = 0;
if ( minDistance >= 1 ) //如果有角点之间最小距离限制
{
//将图片分为各个grid...每个grid的边长为minDistance
int w = image.cols;
int h = image.rows;
//cvRound :Rounds floating-point number to the nearest integer
const int cell_size = cvRound(minDistance);
const int grid_width = (w + cell_size -1) / cell_size;
const int grid_height = (h + cell_size -1) /cell_size;
//每个grid用一个vector 存储角点
vector > grid(grid_width*grid_height);
minDistance *= minDistance;
for ( i =0; i < total; i++ )
{
//先得到当前点的坐标
int ofs = (int)((const uchar*)tmpCorners[i] - eig.data);
int y = (int)(ofs / eig.step);
int x = (int)((ofs - y*eig.step) / sizeof(float));
bool good = true;
//确定当前点对应哪个grid
int x_cell = x / cell_size;
int y_cell = y / cell_size;
//得到上下,左右[-1,1]范围内grid
int x1 = x_cell - 1;
int y1 = y_cell - 1;
int x2 = x_cell + 1;
int y2 = y_cell + 1;
x1 = max(0, x1);
y1 = max(0, y1);
x2 = min(grid_width-1, x2);
y2 = min(grid_height-1, y2);
//上面说过每个grid用一个vector 存储位于这个区域内的角点
//对当前角点,先得到坐标,然后找到属于哪个grid,并和周围的8(最大是8)个grid中
//的 Point2f 比较距离,如果两点之间的距离小于minDistance则放弃这个角点
//因为我们是按角点响应的降序依次访问的...
for ( int yy = y1; yy <= y2; yy++ )
{
for ( int xx = x1; xx <= x2; xx++ )
{
//m存储对应grid中角点。一个grid中可能有多个角点
vector& m = grid[yy*grid_width + xx];
if ( m.size() )
{
//求当前角点到这个grid内所有角点的距离,若小于当前grid中的某个点,直接跳到break_out,其他
//grid不用再比较,直到周围grid都没有距离小于minstance的值,则将角点push进当前grid中
for ( j =0; j < m.size(); j++ )
{
float dx = x - m[j].x;
float dy = y - m[j].y;
if ( dx*dx + dy*dy < minDistance )
{
good = false;
goto break_out;
}
}
}
}
}
break_out:
if ( good )
{
//将当前角点存入grid中
grid[y_cell*grid_width + x_cell].push_back(Point2f((float)x, (float)y));
circle(image, Point(x, y), 5, Scalar(255), 2);
corners.push_back(Point2f((float)x, (float)y));
++ncorners;
if ( maxCorners > 0 && (int)ncorners == maxCorners )
{
break;
}
}
}
}
else //如果不考虑角点间最小距离限制
{
for ( i = 0; i < total; i++ )
{
//因为eig.step 是Number of bytes each matrix row occupies.
int ofs = (int)((const uchar*)tmpCorners[i] - eig.data);
//通过tmpCorner存储的角点在内存中的地址还原得到图像中的坐标..
int y = (int)(ofs / eig.step);
int x = (int)((ofs - y*eig.step) / sizeof(float));
circle(image, Point(x, y), 5, Scalar(255), 2);
corners.push_back(Point2f((float)x, (float)y));
++ncorners;
if ( maxCorners > 0 && (int)ncorners == maxCorners )
{
break;
}
}
}
imshow("eig", image);
}