opencv源码解析--calcSharrDeriv/copyMakeBorder
calcSharrDeriv(求微分)、copyMakeBorder(边缘扩展)--opencv源码解析
1. 函数体解析
a. static void calcSharrDeriv(const cv::Mat& src, cv::Mat& dst)
| 函数作用 | 对输入图像求微分,并将微分结果存储到dst中,微分模板可见原理 |
| src | 待处理图像,src的depth必须为CV_8U,通道不做要求 |
| dst |
存放微分结果,类型同src,通道数为src的2倍 |
b.void cv::copyMakeBorder( InputArray _src, OutputArray _dst, int top, int bottom,
int left, int right, int borderType, const Scalar& value )
| 函数作用 | 为图像_src扩充边界 |
| _src | 输入图像 |
| _dst | 扩充边缘后的输出图像 |
| top | 图像上部扩充宽度 |
| bottom | 图像下部扩充宽度 |
| left | 图像左边扩充宽度 |
| right | 图像右侧扩充宽度 |
| borderType | 边缘扩充类型: enum BorderTypes { //固定值填充,默认为0 //以边缘值进行填充 //以镜像的方式进行填充 //一种首位翻转的镜像方式填充 BORDER_REFLECT101 = BORDER_REFLECT_101, //!< same as BORDER_REFLECT_101 //如果src为ROI区域,只关注src |
| value | borderType==BORDER_CONSTANT时的输入值,默认为0 |
2. 源码分析
- 1.ca'lSharrDeriv
a.源码分析
static void calcSharrDeriv(const cv::Mat& src, cv::Mat& dst)
{
using namespace cv;
using cv::detail::deriv_type;
int rows = src.rows, cols = src.cols, cn = src.channels(), colsn = cols*cn, depth = src.depth();
CV_Assert(depth == CV_8U);
//CV_MAKETYPE结合了depth,cn*2,例如depth=CV_16S,cn*2=6,则dst的type=CV_16SC6
dst.create(rows, cols, CV_MAKETYPE(DataType::depth, cn*2));
#ifdef HAVE_TEGRA_OPTIMIZATION
if (tegra::useTegra() && tegra::calcSharrDeriv(src, dst))
return;
#endif
//alignsize:返回一个最小值,该值大于(cols+2)*cn,又可被16整除
//实际上,delta为cols+2,并做了16字节对齐
int x, y, delta = (int)alignSize((cols + 2)*cn, 16);
//分配delta*2+64的内存大小给_tempBuf
AutoBuffer _tempBuf(delta*2 + 64);
//trow0指向_tempBuf的第一个元素,throw1在throw0的基础上向后移动delta个单位
deriv_type *trow0 = alignPtr(_tempBuf.data() + cn, 16), *trow1 = alignPtr(trow0 + delta, 16);
#if CV_SIMD128
v_int16x8 c3 = v_setall_s16(3), c10 = v_setall_s16(10);
#endif
for( y = 0; y < rows; y++ )
{
//srow0指向y-1行,越界则令y-1=0行,srow1指向y行,srow2指向y+1行,越界令y+1=rows-2
const uchar* srow0 = src.ptr(y > 0 ? y-1 : rows > 1 ? 1 : 0);
const uchar* srow1 = src.ptr(y);
const uchar* srow2 = src.ptr(y < rows-1 ? y+1 : rows > 1 ? rows-2 : 0);
deriv_type* drow = dst.ptr(y);
// do vertical convolution
x = 0;
#if CV_SIMD128
{
for( ; x <= colsn - 8; x += 8 )
{
v_int16x8 s0 = v_reinterpret_as_s16(v_load_expand(srow0 + x));
v_int16x8 s1 = v_reinterpret_as_s16(v_load_expand(srow1 + x));
v_int16x8 s2 = v_reinterpret_as_s16(v_load_expand(srow2 + x));
v_int16x8 t1 = s2 - s0;
v_int16x8 t0 = v_mul_wrap(s0 + s2, c3) + v_mul_wrap(s1, c10);
v_store(trow0 + x, t0);
v_store(trow1 + x, t1);
}
}
#endif
for( ; x < colsn; x++ )
{
//t0:3 t1:-1
// 10 0
// 3 1
int t0 = (srow0[x] + srow2[x])*3 + srow1[x]*10;
int t1 = srow2[x] - srow0[x];
trow0[x] = (deriv_type)t0;
trow1[x] = (deriv_type)t1;
}
// make border,为throw0/1的列,左右各自扩展一个元素
int x0 = (cols > 1 ? 1 : 0)*cn, x1 = (cols > 1 ? cols-2 : 0)*cn;
for( int k = 0; k < cn; k++ )
{
trow0[-cn + k] = trow0[x0 + k]; trow0[colsn + k] = trow0[x1 + k];
trow1[-cn + k] = trow1[x0 + k]; trow1[colsn + k] = trow1[x1 + k];
}
// do horizontal convolution, interleave the results and store them to dst
x = 0;
#if CV_SIMD128
{
for( ; x <= colsn - 8; x += 8 )
{
v_int16x8 s0 = v_load(trow0 + x - cn);
v_int16x8 s1 = v_load(trow0 + x + cn);
v_int16x8 s2 = v_load(trow1 + x - cn);
v_int16x8 s3 = v_load(trow1 + x);
v_int16x8 s4 = v_load(trow1 + x + cn);
v_int16x8 t0 = s1 - s0;
v_int16x8 t1 = v_mul_wrap(s2 + s4, c3) + v_mul_wrap(s3, c10);
v_store_interleave((drow + x*2), t0, t1);
}
}
#endif
for( ; x < colsn; x++ )
{
//求微分操作
//t0:-3 0 3 t1:-3 -10 -3
// -10 0 -3 0 0 0
// -3 0 -3 3 10 3
deriv_type t0 = (deriv_type)(trow0[x+cn] - trow0[x-cn]);
deriv_type t1 = (deriv_type)((trow1[x+cn] + trow1[x-cn])*3 + trow1[x]*10);
//将结果存放在drow中
drow[x*2] = t0; drow[x*2+1] = t1;
}
}
}
}//namespace b.原理
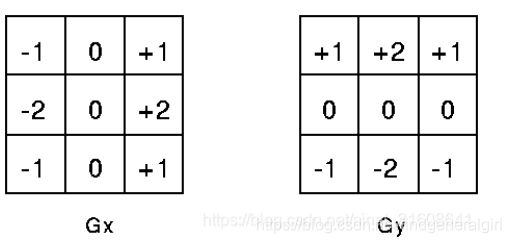
ca'lSharrDeriv函数是opencv中一阶微分算子之一,其算子模板如下:
另外,我们常见的一阶微分算子模板包括:
prewitt算子
sobel算子
对比可知,ca'lSharrDeriv是在prewitt算子的基础上修改了滤波系数。
- 2.copyMakeBorder
a.源码分析
void cv::copyMakeBorder( InputArray _src, OutputArray _dst, int top, int bottom,
int left, int right, int borderType, const Scalar& value )
{
//预处理
CV_INSTRUMENT_REGION();
CV_Assert( top >= 0 && bottom >= 0 && left >= 0 && right >= 0 && _src.dims() <= 2);
CV_OCL_RUN(_dst.isUMat(),
ocl_copyMakeBorder(_src, _dst, top, bottom, left, right, borderType, value))
Mat src = _src.getMat();
int type = src.type();
//如果输入src是一个ROI对象,并且要被看成独立区域
if( src.isSubmatrix() && (borderType & BORDER_ISOLATED) == 0 )
{
Size wholeSize;
Point ofs;
//定位src在整个区域中的偏移坐标ofs,以及整体区域的宽和高
src.locateROI(wholeSize, ofs);
//在top与src与整体图像在y上的偏移量之间找最小,其他亦然
int dtop = std::min(ofs.y, top);
int dbottom = std::min(wholeSize.height - src.rows - ofs.y, bottom);
int dleft = std::min(ofs.x, left);
int dright = std::min(wholeSize.width - src.cols - ofs.x, right);
//src强制向左上移动了dleft,dtop,右下移动了dright,dbottom个单位
src.adjustROI(dtop, dbottom, dleft, dright);
//去掉移动过后的dtop等,重新计算还需移动的上下左右的宽度
top -= dtop;
left -= dleft;
bottom -= dbottom;
right -= dright;
}
//定义一个用来存放边界扩充后的图像的位置_dst
_dst.create( src.rows + top + bottom, src.cols + left + right, type );
Mat dst = _dst.getMat();
//如果边界不需要扩充,则直接进行拷贝
if(top == 0 && left == 0 && bottom == 0 && right == 0)
{
if(src.data != dst.data || src.step != dst.step)
src.copyTo(dst);
return;
}
borderType &= ~BORDER_ISOLATED;
CV_IPP_RUN_FAST(ipp_copyMakeBorder(src, dst, top, bottom, left, right, borderType, value))
//根据boderType是否为BORDER_CONSTANT,分开进行边界扩展
if( borderType != BORDER_CONSTANT )'
//按照边界处理类型进行边界处理
copyMakeBorder_8u( src.ptr(), src.step, src.size(),
dst.ptr(), dst.step, dst.size(),
top, left, (int)src.elemSize(), borderType );
else
{
int cn = src.channels(), cn1 = cn;
AutoBuffer buf(cn);
if( cn > 4 )
{
CV_Assert( value[0] == value[1] && value[0] == value[2] && value[0] == value[3] );
cn1 = 1;
}
//将RGB的颜色值赋值给buf
scalarToRawData(value, buf.data(), CV_MAKETYPE(src.depth(), cn1), cn);
//以固定的RGB值进行边界填充
copyMakeConstBorder_8u( src.ptr(), src.step, src.size(),
dst.ptr(), dst.step, dst.size(),
top, left, (int)src.elemSize(), (uchar*)buf.data() );
}
} 从上面的源码中可知,边界填充是按照两种方式进行的copyMakeBorder_8u、copyMakeConstBorder_8u。
b.copyMakeConstBorder_8u
void copyMakeConstBorder_8u( const uchar* src, size_t srcstep, cv::Size srcroi,
uchar* dst, size_t dststep, cv::Size dstroi,
int top, int left, int cn, const uchar* value )
{
int i, j;
//定义【1,dstroi.widht】的对象constBuf,以及上下左右的宽度
cv::AutoBuffer _constBuf(dstroi.width*cn);
uchar* constBuf = _constBuf.data();
int right = dstroi.width - srcroi.width - left;
int bottom = dstroi.height - srcroi.height - top;
//将目标像素值填充至constBuf中
for( i = 0; i < dstroi.width; i++ )
{
for( j = 0; j < cn; j++ )
constBuf[i*cn + j] = value[j];
}
//
srcroi.width *= cn;
dstroi.width *= cn;
left *= cn;
right *= cn;
//dstInner指向src起始位置
uchar* dstInner = dst + dststep*top + left;
//将src以及left,top的数据拷贝给dst
for( i = 0; i < srcroi.height; i++, dstInner += dststep, src += srcstep )
{
if( dstInner != src )
memcpy( dstInner, src, srcroi.width );
memcpy( dstInner - left, constBuf, left );
memcpy( dstInner + srcroi.width, constBuf, right );
}
dst += dststep*top;
//将constBuf中的数据按top和bottom的宽度填充到dst中去
for( i = 0; i < top; i++ )
memcpy(dst + (i - top)*dststep, constBuf, dstroi.width);
for( i = 0; i < bottom; i++ )
memcpy(dst + (i + srcroi.height)*dststep, constBuf, dstroi.width);
}
} c.copyMakeBorder_8u
void copyMakeBorder_8u( const uchar* src, size_t srcstep, cv::Size srcroi,
uchar* dst, size_t dststep, cv::Size dstroi,
int top, int left, int cn, int borderType )
{
const int isz = (int)sizeof(int);
int i, j, k, elemSize = 1;
bool intMode = false;
if( (cn | srcstep | dststep | (size_t)src | (size_t)dst) % isz == 0 )
{
cn /= isz;
elemSize = isz;
intMode = true;
}
//_tab是一个1维宽度为left+right的对象
cv::AutoBuffer _tab((dstroi.width - srcroi.width)*cn);
int* tab = _tab.data();
int right = dstroi.width - srcroi.width - left;
int bottom = dstroi.height - srcroi.height - top;
//根据left的坐标和src的宽度以及边界填充的方式计算坐标J
for( i = 0; i < left; i++ )
{
j = cv::borderInterpolate(i - left, srcroi.width, borderType)*cn;
for( k = 0; k < cn; k++ )
tab[i*cn + k] = j + k;
}
//同样,根据right坐标以及src的宽度和边界填充的方式计算坐标J,并将其填入相应位置
for( i = 0; i < right; i++ )
{
j = cv::borderInterpolate(srcroi.width + i, srcroi.width, borderType)*cn;
for( k = 0; k < cn; k++ )
tab[(i+left)*cn + k] = j + k;
}
srcroi.width *= cn;
dstroi.width *= cn;
left *= cn;
right *= cn;
//将dst指针,移动到src起始位置对应到dst的起始位置上
uchar* dstInner = dst + dststep*top + left*elemSize;
//进行数据拷贝
for( i = 0; i < srcroi.height; i++, dstInner += dststep, src += srcstep )
{
//先将当前行src的数据拷贝至dst中
if( dstInner != src )
memcpy(dstInner, src, srcroi.width*elemSize);
//依次将当前行,left列的值拷贝至dst,right列的值拷贝至dst
if( intMode )
{
const int* isrc = (int*)src;
int* idstInner = (int*)dstInner;
for( j = 0; j < left; j++ )
idstInner[j - left] = isrc[tab[j]];
for( j = 0; j < right; j++ )
idstInner[j + srcroi.width] = isrc[tab[j + left]];
}
else
{
for( j = 0; j < left; j++ )
dstInner[j - left] = src[tab[j]];
for( j = 0; j < right; j++ )
dstInner[j + srcroi.width] = src[tab[j + left]];
}
}
dstroi.width *= elemSize;
dst += dststep*top;
//再将top行的数据拷贝进来
for( i = 0; i < top; i++ )
{
//每一行top的数据是根据borderInterpolate计算得出
j = cv::borderInterpolate(i - top, srcroi.height, borderType);
memcpy(dst + (i - top)*dststep, dst + j*dststep, dstroi.width);
}
//再将bottom行的数据拷贝进来
for( i = 0; i < bottom; i++ )
{
//每一行bottom的数据也是根据borderInterpolate计算得出
j = cv::borderInterpolate(i + srcroi.height, srcroi.height, borderType);
memcpy(dst + (i + srcroi.height)*dststep, dst + j*dststep, dstroi.width);
}
} 这两个边缘填充函数,填充的过程相同:先填充src,再填充left,再填充right,接着填充top,最后填充bottom。惟一的不同是填充的数据不同。copyMakeBorder_8u的填充数据由borderInterpolate函数决定,而borderInterpolate的计算思路可参考第一小节。