基于Bert-Lstm-Crf的命名实体识别(PyTorch 实现)
1 前言
1-1 简介
命名实体识别(NER)是自然语言处理的基础任务,处于工程性任务的上游,很多的下游任务依赖于命名实体识别的效果,所以命名实体识别也是自然语言处理中非常重要的一环。命名实体识别的任务非常简单,给出一段文本,识别出文本中的人名、机构名称、歌曲名称、专辑名称、地点名称等名词(或者称之为实体)。以下给出百度百科界定的命名实体识别的概念。
1-2 任务背景
由于下游任务是接入“KBQA[基于知识图谱的问答]”、“实体链指”所以对于输入文本要识别出其中存在的实体。任务中的实体类型只有一种,不对实体类别做区分,只需要识别出实体即可。
1-3 数据来源
数据来源于百度百科的词条数据,对百科词条进行处理,由于百科词条中会对可以链指的实体进行“飘蓝”处理,经过解析可以得到一段文本中包含的实体。处理后的训练数据如下所示。
{"text": "三十不惑,来源于中国春秋时期一部语录体散文集《论语》,原出处的语句是:“三十而立,四十而不惑”。其意就是三十岁进入了而立之年的意思。", "label": {"entity": {"春秋时期": [[10, 13]], "论语": [[23, 24]]}}}
{"text": "博科FWS648G-EPREM是博科品牌下的一款交换机。", "label": {"entity": {"交换机": [[24, 26]]}}}2 任务实现
#导入必要的库
import os
import json
import numpy as np
import torch
from transformers.models.bert.modeling_bert import *
from tqdm import tqdm
import NER_config
import jsonlines
import transformers
import torch.nn as nn
from loguru import logger
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score,recall_score,f1_score
from transformers.optimization import get_cosine_schedule_with_warmup, AdamW
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
from transformers import BertTokenizer
from torch.utils.data import Dataset
from torch.nn.utils.rnn import pad_sequence
from torchcrf import CRF
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')
#生成日志
log_path = "/home/zhenhengdong/WORk/NER/Baidu_NER/Log/"
logger.add(log_path + 'Train.log', format="{time} {level} {message}", level="INFO")NER_config.py
import os
import torch
robert_model = '/ssd/Spider/Baidu_NER/Pre_Model/chinese_roberta_wwm_large_ext/'
model_dir = '/home/zhenhengdong/WORk/NER/Baidu_NER/Model/Baidu_ner_model2.pkl'
# 训练集、验证集划分比例
dev_split_size = 0.1
# 是否加载训练好的NER模型
load_before = False
#指定device
device = torch.device('cuda:1' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
# 是否对整个BERT进行fine tuning
full_fine_tuning = True
# hyper-parameter
learning_rate = 3e-5
weight_decay = 0.01
clip_grad = 5
batch_size = 10
epoch_num = 150
min_epoch_num = 5
patience = 0.0002
patience_num = 10
labels = ['entity']
label2id = {
"O": 0,
"B-entity": 1,
"I-entity": 2,
"E-entity": 3,
"S-entity": 4,
}
id2label = {_id: _label for _label, _id in list(label2id.items())}
#BertNER的超参数,也可以设置在预训练模型的config中
#num_labels = len(label2id)
#hidden_dropout_prob = 0.3
#lstm_embedding_size = 768
#hidden_size = 1024
#lstm_dropout_prob = 0.5
2-1.数据处理
在数据处理阶段,将数据格式处理为B-entity、I-entity、E-entity、S-entity、O。其中B-entity表示实体的开头、I-entity表示实体的中间、E-entity表示实体的结束、S-entity表示单个实体、O表示文本中的其他成分。具体代码如下。
#数据处理
def Data_preprocess(input_filename,output_filename):
count = 0
word_list = []
label_list = []
with open(input_filename,'r') as reader:
lines = reader.readlines()
random_list = []
#选取12000条数据
for _ in tqdm(range(12000)):#12000
#设定随机值,进行随机选取
random_index = random.randint(1,4495464) #测试499497 #训练集4495465
if random_index not in random_list:
random_list.append(random_index)
json_line = json.loads(lines[random_index].strip())
text = json_line['text']
#设定了选取长度
if len(text) <= 510:
words = list(text)
label_entity = json_line.get('label',None)
#label先全部设为"O"
label = ['O'] * len(words)
#判断如果不等于None
if label_entity is not None:
count += 1
for key,value in label_entity.items():
for sub_name,sub_index in value.items():
for start_index,end_index in sub_index:
#判断是否超出边界,做一个判断
if ''.join(words[start_index:end_index + 1]) == sub_name:
#单实体标注S-entity
if start_index == end_index:
label[start_index] = 'S-' + key
else:
#多字实体采用B-entity I-entity E-entity 的标注方式
label[start_index] = "B-" + key
label[start_index + 1:end_index + 1] = ['I-' + key] * (len(sub_name) -1 )
label[end_index] = 'E-' + key
word_list.append(words)
label_list.append(label)
else:
continue
print(len(word_list),len(label_list))
#保存成二进制文件
np.savez_compressed(output_filename,words = word_list, lables = label_list)
#统计处理数量
print(count)2-1-1 生成二进制文件
将原始数据DataSet按照9:1的比例进行划分,划分为train.jsonl和test.jsonl。然后对训练数据和测试数据进行数据处理。
train_input = '/ssd/Spider/Baidu_NER/DataSets/Ori_data/train.jsonl'
train_output = '/ssd/Spider/Baidu_NER/DataSets/Binary_file/train.npz'
word_list,label_list = Data_preprocess(train_input,train_output)test_input = '/ssd/Spider/Baidu_NER/DataSets/Ori_data/test.jsonl'
test_output = '/ssd/Spider/Baidu_NER/DataSets/Binary_file/test.npz'
Data_preprocess(test_input,test_output)2-1-2 标注结果实例
words示例:['聚','叶','黔','川','乌','头','(','变','种',')','是','四','川','北','部','青','川','的','植','物','。']
labels示例:['O','O','O','O','O','O','O','O','O','O','O','O','O','O','O','B-entity','E-entity','O','O','O','O']
2-2 数据转化形式
上一步将原始数据中的实体对应位置贴入标签并转换为二进制存储,现在需要对数据进行编码,处理成id的形式。具体代码实现如下。
class NERDataset(Dataset):
def __init__(self, words, labels, config, word_pad_idx=0, label_pad_idx=-1):
self.tokenizer = BertTokenizer.from_pretrained(config.robert_model, do_lower_case=True)
self.label2id = config.label2id
self.id2label = {_id: _label for _label, _id in list(config.label2id.items())}
self.dataset = self.preprocess(words, labels)
self.word_pad_idx = word_pad_idx
self.label_pad_idx = label_pad_idx
self.device = config.device
def preprocess(self, origin_sentences, origin_labels):
data = []
sentences = []
labels = []
for line in tqdm(origin_sentences):
# replace each token by its index
# we can not use encode_plus because our sentences are aligned to labels in list type
words = []
word_lens = []
for token in line:
#bert对字进行编码转化为id表示
words.append(self.tokenizer.tokenize(token))
word_lens.append(len(token))
# 变成单个字的列表,开头加上[CLS]
words = ['[CLS]'] + [item for token in words for item in token]
token_start_idxs = 1 + np.cumsum([0] + word_lens[:-1])
sentences.append((self.tokenizer.convert_tokens_to_ids(words), token_start_idxs))
for tag in origin_labels:
label_id = [self.label2id.get(t) for t in tag]
labels.append(label_id)
for sentence, label in zip(sentences, labels):
if len(sentence[0]) - len(label) == 1:
data.append((sentence, label))
return data
def __getitem__(self, idx):
"""sample data to get batch"""
word = self.dataset[idx][0]
label = self.dataset[idx][1]
return [word, label]
def __len__(self):
return len(self.dataset)
def collate_fn(self, batch):
sentences = [x[0] for x in batch]
labels = [x[1] for x in batch]
# batch length
batch_len = len(sentences)
# compute length of longest sentence in batch
max_len = max([len(s[0]) for s in sentences])
max_label_len = 0 # 改动前max_label_len = 0
# padding data 初始化
batch_data = self.word_pad_idx * np.ones((batch_len, max_len))
batch_label_starts = []
# padding and aligning
for j in range(batch_len):
cur_len = len(sentences[j][0])
batch_data[j][:cur_len] = sentences[j][0]
# 找到有标签的数据的index([CLS]不算)
label_start_idx = sentences[j][-1]
label_starts = np.zeros(max_len)
label_starts[[idx for idx in label_start_idx if idx < max_len]] = 1
batch_label_starts.append(label_starts)
max_label_len = max(int(sum(label_starts)), max_label_len)
# padding label
batch_labels = self.label_pad_idx * np.ones((batch_len, max_label_len))
for j in range(batch_len):
cur_tags_len = len(labels[j])
batch_labels[j][:cur_tags_len] = labels[j]
# convert data to torch LongTensors
batch_data = torch.tensor(batch_data, dtype=torch.long)
batch_label_starts = torch.tensor(batch_label_starts, dtype=torch.long)
batch_labels = torch.tensor(batch_labels, dtype=torch.long)
# shift tensors to GPU if available
batch_data, batch_label_starts = batch_data.to(self.device), batch_label_starts.to(self.device)
batch_labels = batch_labels.to(self.device)
return [batch_data, batch_label_starts, batch_labels]
2-3 定义模型结构
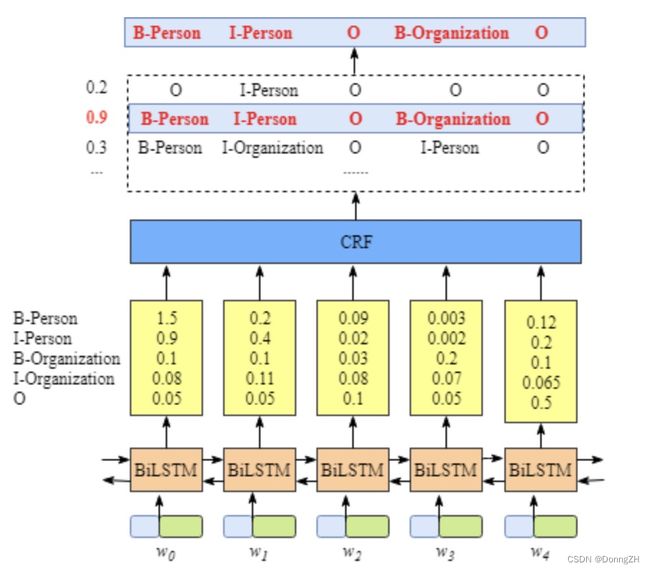
模型设计环节,使用Bert作为底层的特征提取器,并加入双向lstm与线性层进行分类获得每个标签的预测类别,最后将其送入到crf中,根据发射分数和状态转移矩阵获得最佳的标签类别。模型结构设计如下所示。
代码如下所示:
class BertNER(BertPreTrainedModel):
def __init__(self, config):
super(BertNER, self).__init__(config)
#定义分类类别,也可以写在加载预训练模型的config文件中
self.num_labels = 5
self.bert = BertModel(config)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(config.hidden_dropout_prob)
self.bilstm = nn.LSTM(
input_size=config.lstm_embedding_size, # 1024
hidden_size=config.hidden_size // 2, # 1024
batch_first=True,
num_layers=2,
dropout=config.lstm_dropout_prob, # 0.5
bidirectional=True
)
self.classifier = nn.Linear(config.hidden_size, self.num_labels)
self.crf = CRF(self.num_labels, batch_first=True)
self.init_weights()
def forward(self, input_data, token_type_ids=None, attention_mask=None, labels=None,
position_ids=None, inputs_embeds=None, head_mask=None):
input_ids, input_token_starts = input_data
outputs = self.bert(input_ids,
attention_mask=attention_mask,
token_type_ids=token_type_ids,
position_ids=position_ids,
head_mask=head_mask,
inputs_embeds=inputs_embeds)
sequence_output = outputs[0]
# 去除[CLS]标签等位置,获得与label对齐的pre_label表示
origin_sequence_output = [layer[starts.nonzero().squeeze(1)]
for layer, starts in zip(sequence_output, input_token_starts)]
# 将sequence_output的pred_label维度padding到最大长度
padded_sequence_output = pad_sequence(origin_sequence_output, batch_first=True)
# dropout pred_label的一部分feature
padded_sequence_output = self.dropout(padded_sequence_output)
#将结果送入bilstm,再次提取特性
lstm_output, _ = self.bilstm(padded_sequence_output)
# 将lstm的结果送入线性层,进行五分类
logits = self.classifier(lstm_output)
outputs = (logits,)
if labels is not None:
loss_mask = labels.gt(-1)
#将每个标签的概率送入到crf中进行解码,并获得loss
loss = self.crf(logits, labels, loss_mask) * (-1)
outputs = (loss,) + outputs
# contain: (loss), scores
return outputs2-4 定义训练函数
#定义训练函数
def train_epoch(train_loader, model, optimizer, scheduler, epoch):
# 设定训练模式
model.train()
train_losses = 0
for idx, batch_samples in enumerate(tqdm(train_loader)):
batch_data, batch_token_starts, batch_labels = batch_samples
batch_masks = batch_data.gt(0) # get padding mask
# 计算损失值
loss = model((batch_data, batch_token_starts),
token_type_ids=None, attention_mask=batch_masks, labels=batch_labels)[0]
train_losses += loss.item()
#梯度更新
model.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
# 梯度裁剪
nn.utils.clip_grad_norm_(parameters=model.parameters(), max_norm=NER_config.clip_grad)
# 计算梯度
optimizer.step()
scheduler.step()
train_loss = float(train_losses) / len(train_loader)
logger.info("Epoch: {}, train loss: {}",epoch, train_loss)
2-5 定义验证函数
#根据预测值和真实值计算评价指标
def compute_acc_recall(batch_output,batch_tags):
acc = 0
recall = 0
f1 = 0
for index in range(len(batch_output)):
acc += accuracy_score(batch_output[index],batch_tags[index])
recall += recall_score(batch_output[index],batch_tags[index],average='macro')
f1 += f1_score(batch_output[index],batch_tags[index],average='macro')
return (acc/len(batch_output),recall/len(batch_output),f1/len(batch_output))
#定义验证函数
def evaluate(dev_loader, model, mode='dev'):
# 设置为模型为验证模式
model.eval()
if mode == 'test':
tokenizer = BertTokenizer.from_pretrained(NER_config.robert_model, do_lower_case=True, skip_special_tokens=True)
id2label = NER_config.id2label
true_tags = []
pred_tags = []
sent_data = []
dev_losses = 0
with torch.no_grad():
for idx, batch_samples in tqdm(enumerate(dev_loader)):
batch_data, batch_token_starts, batch_tags = batch_samples
if mode == 'test':
sent_data.extend([[tokenizer.convert_ids_to_tokens(idx.item()) for idx in indices
if (idx.item() > 0 and idx.item() != 101)] for indices in batch_data])
batch_masks = batch_data.gt(0) # get padding mask, gt(x): get index greater than x
label_masks = batch_tags.gt(-1) # get padding mask, gt(x): get index greater than x
# compute model output and loss
loss = model((batch_data, batch_token_starts),
token_type_ids=None, attention_mask=batch_masks, labels=batch_tags)[0]
dev_losses += loss.item()
# (batch_size, max_len, num_labels)
batch_output = model((batch_data, batch_token_starts),
token_type_ids=None, attention_mask=batch_masks)[0]
# (batch_size, max_len - padding_label_len)
batch_output = model.crf.decode(batch_output, mask=label_masks)
# (batch_size, max_len)
batch_tags = batch_tags.to('cpu').numpy()
pred_tags.extend([[idx for idx in indices] for indices in batch_output])
# (batch_size, max_len - padding_label_len)
true_tags.extend([[idx for idx in indices if idx > -1] for indices in batch_tags])
#pred_tags.extend([[id2label.get(idx) for idx in indices] for indices in batch_output])
# (batch_size, max_len - padding_label_len)
#true_tags.extend([[id2label.get(idx) for idx in indices if idx > -1] for indices in batch_tags])
assert len(pred_tags) == len(true_tags)
# logging loss, f1 and report
metrics = {}
acc , recall, F1= compute_acc_recall(true_tags,pred_tags)
metrics['acc'] = acc
metrics['recal'] = recal
metrics['f1'] = F1
metrics['loss'] = float(dev_losses) / len(dev_loader)
return metrics2-6 定义测试函数
def test(NER_config):
data = np.load(NER_config.test_dir, allow_pickle=True)
word_test = data["words"]
label_test = data["labels"]
test_dataset = NERDataset(word_test, label_test, NER_config)
# build data_loader
test_loader = DataLoader(test_dataset, batch_size=NER_config.batch_size,
shuffle=False, collate_fn=test_dataset.collate_fn)
# Prepare model
if config.model_dir is not None:
model = BertNER.from_pretrained(NER_config.model_dir)
model.to(NER_config.device)
val_metrics = evaluate(test_loader, model, mode='test')
logging.info("test loss: {}, f1 score: {}".format(val_metrics['loss'], val_metrics['F1']))2-7 训练与验证
def train(train_loader, dev_loader, model, optimizer, scheduler, model_dir):
"""train the model and test model performance"""
# reload weights from restore_dir if specified
best_val_f1 = 0.0
patience_counter = 0
# start training
for epoch in range(1, NER_config.epoch_num + 1):
train_epoch(train_loader, model, optimizer, scheduler, epoch)
#开始验证
val_metrics = evaluate(dev_loader, model, mode='dev')
val_f1 = val_metrics['f1']
logger.info("Epoch: {}, dev loss: {}, f1 score: {}",epoch, val_metrics['loss'], val_f1)
improve_f1 = val_f1 - best_val_f1
if improve_f1 > 1e-5:
best_val_f1 = val_f1
#模型保存需要更改
torch.save(model,model_dir)
logger.info("--------Save best model!--------")
if improve_f1 < NER_config.patience:
patience_counter += 1
else:
patience_counter = 0
else:
patience_counter += 1
# Early stopping and logging best f1
if (patience_counter >= NER_config.patience_num and epoch > NER_config.min_epoch_num) or epoch == NER_config.epoch_num:
logger.info("Best val f1: {}",best_val_f1)
break
logger.info("Training Finished!")2-8 划分训练集、验证集
def dev_split(dataset_dir):
"""从训练集合中划分验证集和训练集"""
data = np.load(dataset_dir, allow_pickle=True)
words = data["words"]
labels = data["lables"]
x_train, x_dev, y_train, y_dev = train_test_split(words, labels, test_size=0.01, random_state=0)
return x_train, x_dev, y_train, y_dev2-9 模型训练函数
def run(config):
"""train the model"""
# 处理数据,
# 分离训练集、验证集
word_train, word_dev, label_train, label_dev = load_dev('train')
# 创建dataset
train_dataset = NERDataset(word_train, label_train, config)
dev_dataset = NERDataset(word_dev, label_dev, config)
# get dataset size
train_size = len(train_dataset)
# 创建dataloader
train_loader = DataLoader(train_dataset, batch_size=config.batch_size,
shuffle=True, collate_fn=train_dataset.collate_fn)
dev_loader = DataLoader(dev_dataset, batch_size=config.batch_size,
shuffle=True, collate_fn=dev_dataset.collate_fn)
# 实例化模型
device = config.device
model = BertNER.from_pretrained(config.roberta_model, num_labels=len(config.label2id))
model.to(device)
# Prepare optimizer
if config.full_fine_tuning:
# model.named_parameters(): [bert, bilstm, classifier, crf]
bert_optimizer = list(model.bert.named_parameters())
lstm_optimizer = list(model.bilstm.named_parameters())
classifier_optimizer = list(model.classifier.named_parameters())
no_decay = ['bias', 'LayerNorm.bias', 'LayerNorm.weight']
optimizer_grouped_parameters = [
{'params': [p for n, p in bert_optimizer if not any(nd in n for nd in no_decay)],
'weight_decay': config.weight_decay},
{'params': [p for n, p in bert_optimizer if any(nd in n for nd in no_decay)],
'weight_decay': 0.0},
{'params': [p for n, p in lstm_optimizer if not any(nd in n for nd in no_decay)],
'lr': config.learning_rate * 5, 'weight_decay': config.weight_decay},
{'params': [p for n, p in lstm_optimizer if any(nd in n for nd in no_decay)],
'lr': config.learning_rate * 5, 'weight_decay': 0.0},
{'params': [p for n, p in classifier_optimizer if not any(nd in n for nd in no_decay)],
'lr': config.learning_rate * 5, 'weight_decay': config.weight_decay},
{'params': [p for n, p in classifier_optimizer if any(nd in n for nd in no_decay)],
'lr': config.learning_rate * 5, 'weight_decay': 0.0},
{'params': model.crf.parameters(), 'lr': config.learning_rate * 5}
]
# only fine-tune the head classifier
else:
param_optimizer = list(model.classifier.named_parameters())
optimizer_grouped_parameters = [{'params': [p for n, p in param_optimizer]}]
optimizer = AdamW(optimizer_grouped_parameters, lr=config.learning_rate, correct_bias=False)
train_steps_per_epoch = train_size // config.batch_size
scheduler = get_cosine_schedule_with_warmup(optimizer,
num_warmup_steps=(config.epoch_num // 10) * train_steps_per_epoch,
num_training_steps=config.epoch_num * train_steps_per_epoch)
# Train the model
logging.info("--------Start Training!--------")
train(train_loader, dev_loader, model, optimizer, scheduler, config.model_dir)
查看dataset
2-10 训练与测试
if __name__ == '__main__':
run(NER_config)
test(NER_config)2-11 定义推断函数
#定义推断函数
def infer_function(dev_loader, model, mode='dev'):
# set model to evaluation mode
model.eval()
if mode == 'test':
tokenizer = BertTokenizer.from_pretrained(NER_config.robert_model, do_lower_case=True, skip_special_tokens=True)
id2label = NER_config.id2label
true_tags = []
pred_tags = []
sent_data = []
dev_losses = 0
with torch.no_grad():
for idx, batch_samples in enumerate(dev_loader):
batch_data, batch_token_starts, batch_tags = batch_samples
if mode == 'test':
sent_data.extend([[tokenizer.convert_ids_to_tokens(idx.item()) for idx in indices
if (idx.item() > 0 and idx.item() != 101)] for indices in batch_data])
batch_masks = batch_data.gt(0) # get padding mask, gt(x): get index greater than x
label_masks = batch_tags.gt(-1) # get padding mask, gt(x): get index greater than x
# compute model output and loss
#loss = model((batch_data, batch_token_starts),
#token_type_ids=None, attention_mask=batch_masks, labels=batch_tags)[0]
#dev_losses += loss.item()
# (batch_size, max_len, num_labels)
batch_output = model((batch_data, batch_token_starts),
token_type_ids=None, attention_mask=batch_masks)[0]
# (batch_size, max_len - padding_label_len)
batch_output = model.crf.decode(batch_output, mask=label_masks)
# (batch_size, max_len)
#batch_tags = batch_tags.to('cpu').numpy()
pred_tags.extend([[id2label.get(idx) for idx in indices] for indices in batch_output])
return pred_tagsdef new_infer(text):
words = list(text)
label = ['O'] * len(words)
word_list = []
label_list = []
word_list.append(words)
label_list.append(label)
output_filename = '/home/zhenhengdong/WORk/NER/Try_ner/Datasets/Binary_file/infer.npz'
np.savez_compressed(output_filename,words = word_list, lables = label_list)
#重新加载
data = np.load(output_filename, allow_pickle=True)
word_test = data["words"]
label_test = data["lables"]
test_dataset = NERDataset(word_test, label_test, NER_config)
# build data_loader
test_loader = DataLoader(test_dataset, batch_size=NER_config.batch_size,
shuffle=False, collate_fn=test_dataset.collate_fn)
# Prepare model
if NER_config.model_dir is not None:
#model = torch.load(NER_config.model_dir)
model = BertNER.from_pretrained(NER_config.model_dir)
model.to(NER_config.device)
logger.info("--------Load model from {}--------".format(NER_config.model_dir))
else:
logger.info("--------No model to test !--------")
return
pre_tegs = infer_function(test_loader, model, mode='test')
return pre_tegs2-12 展示预测结果
text = '2022年11月,马拉西亚随荷兰国家队征战2022年卡塔尔世界杯'
pre_tegs = new_infer(text)
#取出位置
start_index_list = []
end_index_list = []
for index in range(len(pre_tegs[0])):
if index != 0 and pre_tegs[0][index] !='O' and pre_tegs[0][index-1] == 'O':
start_index = index
start_index_list.append(start_index)
if index != len(pre_tegs[0]) - 1 and pre_tegs[0][index] !='O' and pre_tegs[0][index+1] == 'O':
end_index = index
end_index_list.append(end_index)
if index == 0 and pre_tegs[0][index] !='O' :
start_index = index
start_index_list.append(start_index)
if index == len(pre_tegs[0]) - 1 and pre_tegs[0][index] !='O' :
end_index = index
end_index_list.append(end_index)
#展示
for index in range(len(start_index_list)):
print(text[start_index_list[index]:end_index_list[index]+1])写在最后
作为一名初入职的算法工程师,越发觉得数据的重要性。数据样本的均衡、数据的多样性远比更换模型、调整参数来的实在。普通的数据使用LSTM与Attention的组合基本上就能达到性能要求,复杂的数据使用预训练模型也可以搞定。工业中,一个好的算法工程师肯定是以一名好的数据分析师为前提的,训练模型前要对自己的数据做到充分的分析。就比如在这次任务中,初次使用B、I、O、S进行标注后,发现效果并没有预期的好,预测之后发现会有边界溢出问题。其中有两套解决方案,一个方案是更换模型,尝试使用span指针网络进行标注,另一个方案是对标注数据标签进行更改,添加E表示实体的结束。显然使用第二种方案可以更快的达到目的,在添加标签后,边界溢出问题解决。
Reference:
(1)GitHub - hemingkx/CLUENER2020: A PyTorch implementation of a BiLSTM\BERT\Roberta(+CRF) model for Named Entity Recognition.
(2)BiLSTM模型中CRF层的运行原理(2) | 闲记算法