基于Python实现的遗传算法求最值问题
遗传算法求最值问题
目录
人工智能第三次实验报告 1
遗传算法求最值问题 1
一 、遗传算法 1
1.1 遗传算法简介 1
1.2 遗传算法基本要素 2
4. 设定遗传操作: 2
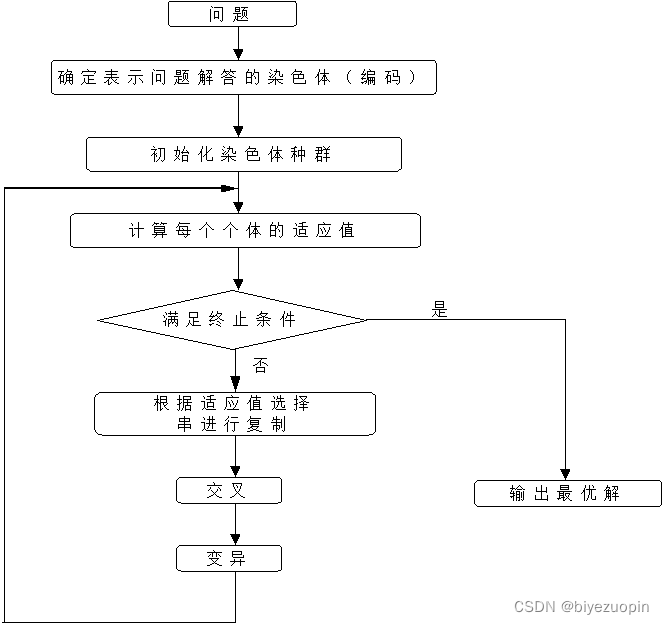
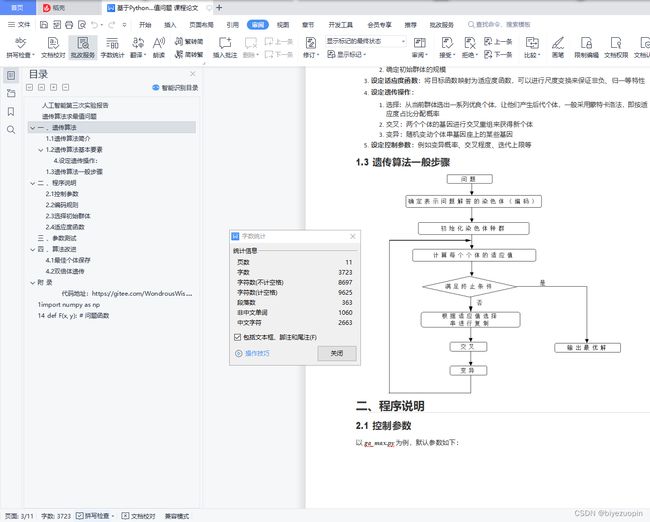
1.3 遗传算法一般步骤 2
二 、程序说明 2
2.1 控制参数 2
2.2 编码规则 3
2.3 选择初始群体 3
2.4 适应度函数 4
三 、参数测试 5
四 、算法改进 6
4.1 最佳个体保存 6
4.2 双倍体遗传 7
附 录 7
1 import numpy as np 8
14 def F(x, y): # 问题函数 8
一 、遗传算法
1.1遗传算法简介
遗传算法是一种进化算法,基于自然选择和生物遗传等生物进化机制的一种搜索算法,其通过选 择、重组和变异三种操作实现优化问题的求解。它的本质是从原问题的一组解出发改进到另一组较好的 解,再从这组改进的解出发进一步改进。在搜索过程中,它利用结构和随机的信息,是满足目标的决策 获得最大的生存可能,是一种概率型算法。
遗传算法主要借用生物中“适者生存”的原则,在遗传算法中,染色体对应的是数据或数组,通常由 一维的串结构数据来表示。串上的各个位置对应一个基因座,而各个位置上所取的值对等位基因。遗传 算法处理的是基因型个体,一定数量的个体组成了群体。群体的规模就是个体的数目。不同个体对环境 的适应度不同,适应度打的个体被选择进行遗传操作产生新个体。每次选择两个染色体进行产生一组新 染色体,染色体也可能发生变异,得到下一代群体。
1.2遗传算法基本要素
1.参数编码:可以采用位串编码、实数编码、多参数级联编码等
2.设定初始群体:
1.启发 / 非启发给定一组解作为初始群体
2.确定初始群体的规模
3.设定适应度函数:本文转载自http://www.biyezuopin.vip/onews.asp?id=16718将目标函数映射为适应度函数,可以进行尺度变换来保证非负、归一等特性
4.设定遗传操作:
1.选择:从当前群体选出一系列优良个体,让他们产生后代个体,一般采用蒙特卡洛法,即按适 应度占比分配概率
2.交叉:两个个体的基因进行交叉重组来获得新个体
3.变异:随机变动个体串基因座上的某些基因
5.设定控制参数:例如变异概率、交叉程度、迭代上限等。
import numpy as np
from matplotlib.ticker import MultipleLocator
from numpy.ma import cos
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib import cm
import time
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
import datetime
from scipy.interpolate import make_interp_spline
DNA_SIZE = 12 # 编码长度
POP_SIZE = 100 # 种群大小
CROSS_RATE = 0.8 # 交叉率
MUTA_RATE = 0.15 # 变异率
Iterations = 100 # 代次数
X_BOUND = [0,10] # X区间
Y_BOUND = [0,10] # Y区间
def F(x, y): # 问题函数
return (6.452*(x+0.125*y)*(cos(x)-cos(2*y))**2)/(0.8+(x-4.2)**2+2*(y-7)**2)+3.226*y
def decodeDNA(pop): # 基因解码
x_pop = pop[:,1::2] # 奇数列表示 X:取 pop 的奇数位
y_pop = pop[:,::2] # 偶数列表示 Y:取 pop 的偶数位
x = x_pop.dot(2**np.arange(DNA_SIZE)[::-1])/float(2**DNA_SIZE-1)*(X_BOUND[1]-X_BOUND[0])+X_BOUND[0] # 二进制转十进制,在归一化塞入区间[0,10]中
y = y_pop.dot(2**np.arange(DNA_SIZE)[::-1])/float(2**DNA_SIZE-1)*(Y_BOUND[1]-Y_BOUND[0])+Y_BOUND[0] # 二进制转十进制,在归一化塞入区间[0,10]中
return x,y
def getfitness(pop): # 计算适应度函数
x,y = decodeDNA(pop)
temp = F(x, y)
return (temp - np.min(temp)) + 0.0001 # 减去最小的适应度是为了防止适应度出现负数
def select(pop, fitness): # 根据适应度选择(蒙特卡罗)
temp = np.random.choice(np.arange(POP_SIZE), size=POP_SIZE, replace=True, p=(fitness)/(fitness.sum()))
return pop[temp]
def crossmuta(pop, CROSS_RATE): # 种群的交叉变异操作
new_pop = []
for i in pop: # 遍历种群中的每一个个体,将该个体作为父代
temp = i # 子代先得到父亲的全部基因
if np.random.rand() < CROSS_RATE: # 以交叉概率发生交叉
j = pop[np.random.randint(POP_SIZE)] # 从种群中随机选择另一个个体,并将该个体作为母代
cpoints1 = np.random.randint(0, DNA_SIZE*2-1) # 随机产生交叉的两个点(区间:[cpoints1, cpoints2])
cpoints2 = np.random.randint(cpoints1,DNA_SIZE*2)
temp[cpoints1:cpoints2] = j[cpoints1:cpoints2] # 子代得到位于交叉点后的母代的基因
mutation(temp,MUTA_RATE) # 每一个后代以变异率发生变异
new_pop.append(temp)
return new_pop
def mutation(temp, MUTA_RATE):
if np.random.rand() < MUTA_RATE: # 以MUTA_RATE的概率进行变异
mutate_point = np.random.randint(0, DNA_SIZE) # 随机产生一个实数,代表要变异基因的位置
temp[mutate_point] = temp[mutate_point] ^ 1 # 将变异点的二进制为反转
def print_info(pop): # 用于输出结果
fitness = getfitness(pop)
maxfitness = np.argmax(fitness) # 返回最大值的索引值
print("迭代次数: ", Iterations)
print("最大适应度: ", fitness[maxfitness])
x,y = decodeDNA(pop)
print("最优基因型: ", pop[maxfitness])
print("最优解 (x,y) = ", (x[maxfitness], y[maxfitness]))
print("最优值 F(x,y) = ", F(x[maxfitness],y[maxfitness]))
# 画图
def plot_3d(ax):
X = np.linspace(*X_BOUND, 100)
Y = np.linspace(*Y_BOUND, 100)
X, Y = np.meshgrid(X, Y)
Z = F(X, Y)
ax.plot_surface(X, Y, Z, rstride=1, cstride=1, cmap=cm.coolwarm)
ax.set_zlim(-20, 100)
ax.set_xlabel('x')
ax.set_ylabel('y')
ax.set_zlabel('z')
plt.pause(3)
plt.show()
# 画图
def draw(l1, l2, l3, l4, testStr):
ax1 = plt.subplot(131)
ax1.plot(l1, l2, 'b')
ax1.set_xlabel(testStr)
ax1.set_ylabel("COST_TIME")
ax1.set_ylim(bottom=0)
ax2 = plt.subplot(132)
ax2.plot(l1, l4, 'r')
ax2.set_xlabel(testStr)
ax2.set_ylabel("BEST_F(X,Y)")
ax2.set_ylim(bottom=0)
ax3 = plt.subplot(133)
ax3.plot(l1, l3, 'g')
ax3.set_xlabel(testStr)
ax3.set_ylabel("BEST_FITNESS")
ax3.set_ylim(bottom=0)
plt.show()
# 研究单一参数的变化对求解结果和求解耗时的影响
# 编码长度测试范围:[6,30],每一个长度重复测试 10 次来减小随机误差
def DNA_SIZE_TEST():
dna_size_list = range(6,30,2)
cost_time = []
best_fitness = []
best_f = []
k = 10 # 重复次数,减小随机误差
for i in dna_size_list:
total_time = 0
total_fitness = 0
total_f = 0
for j in range(k):
global DNA_SIZE
DNA_SIZE= i
start_t = time.time()
pop = np.random.randint(2, size=(POP_SIZE, DNA_SIZE * 2)) # pop(二维矩阵) = 种群数 * (DNA长度 * 2) 个 0,1 随机数
for _ in range(Iterations): # 迭代 N 代
x, y = decodeDNA(pop)
pop = np.array(crossmuta(pop, CROSS_RATE)) # 对种群进行交叉(cross)和变异(muta)
fitness = getfitness(pop) # 计算种群每一个基因的适应度函数
pop = select(pop, fitness) # 选择生成新的种群
end_t = time.time()
fitness = getfitness(pop)
maxfitness = np.argmax(fitness)
x, y = decodeDNA(pop)
total_time += (end_t - start_t)
total_fitness += fitness[maxfitness]
total_f += F(x[maxfitness], y[maxfitness])
cost_time.append(total_time / k)
best_fitness.append(total_fitness / k)
best_f.append(total_f / k)
draw(dna_size_list, cost_time, best_fitness, best_f, "DNA_SIZE")
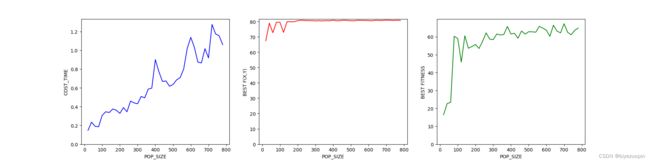
# 种群大小测试范围:[20,800],每一个长度重复测试 3 次来减小随机误差
def POP_SIZE_TEST():
pop_size_list = range(20,800,20)
cost_time = []
best_fitness = []
best_f = []
k = 3
for i in pop_size_list:
total_time = 0
total_fitness = 0
total_f = 0
for j in range(k):
global POP_SIZE
POP_SIZE= i
start_t = time.time() # 开始计时
pop = np.random.randint(2, size=(POP_SIZE, DNA_SIZE * 2)) # pop(二维矩阵) = 种群数 * (DNA长度 * 2) 个 0,1 随机数
for _ in range(Iterations): # 迭代 N 代
x, y = decodeDNA(pop)
pop = np.array(crossmuta(pop, CROSS_RATE)) # 对种群进行交叉(cross)和变异(muta)
fitness = getfitness(pop) # 计算种群每一个基因的适应度函数
pop = select(pop, fitness) # 选择生成新的种群
end_t = time.time()
fitness = getfitness(pop)
maxfitness = np.argmax(fitness)
x, y = decodeDNA(pop)
total_time += (end_t - start_t)
total_fitness += fitness[maxfitness]
total_f += F(x[maxfitness], y[maxfitness])
cost_time.append(total_time / k)
best_fitness.append(total_fitness / k)
best_f.append(total_f / k)
draw(pop_size_list, cost_time, best_fitness, best_f, "POP_SIZE")
# 交叉率测试范围:[0,1],每一个长度重复测试 10 次来减小随机误差
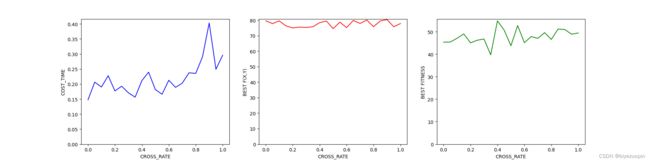
def CROSS_RATE_TEST():
r_list = range(0,21)
cr_list = []
for i in r_list:
cr_list.append(i * 0.05)
cost_time = []
best_fitness = []
best_f = []
k = 10
for i in r_list:
total_time = 0
total_fitness = 0
total_f = 0
for j in range(k):
global CROSS_RATE
CROSS_RATE = cr_list[i]
start_t = time.time() # 开始计时
pop = np.random.randint(2, size=(POP_SIZE, DNA_SIZE * 2)) # pop(二维矩阵) = 种群数 * (DNA长度 * 2) 个 0,1 随机数
for _ in range(Iterations): # 迭代 N 代
x, y = decodeDNA(pop)
pop = np.array(crossmuta(pop, CROSS_RATE)) # 对种群进行交叉(cross)和变异(muta)
fitness = getfitness(pop) # 计算种群每一个基因的适应度函数
pop = select(pop, fitness) # 选择生成新的种群
end_t = time.time()
fitness = getfitness(pop)
maxfitness = np.argmax(fitness)
x, y = decodeDNA(pop)
total_time += (end_t - start_t)
total_fitness += fitness[maxfitness]
total_f += F(x[maxfitness], y[maxfitness])
cost_time.append(total_time / k)
best_fitness.append(total_fitness / k)
best_f.append(total_f / k)
draw(cr_list, cost_time, best_fitness, best_f, "CROSS_RATE")
# 变异率测试范围:[0,1],每一个长度重复测试 10 次来减小随机误差
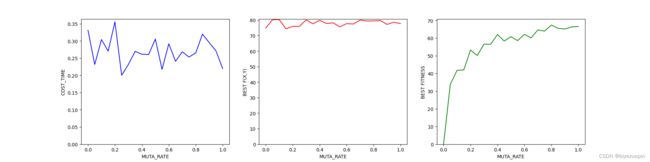
def MUTA_RATE_TEST():
r_list = range(0, 21)
mr_list = []
for i in r_list:
mr_list.append(i * 0.05)
cost_time = []
best_fitness = []
best_f = []
k = 10
for i in r_list:
total_time = 0
total_fitness = 0
total_f = 0
for j in range(k):
global MUTA_RATE
MUTA_RATE = mr_list[i]
start_t = time.time() # 开始计时
pop = np.random.randint(2, size=(POP_SIZE, DNA_SIZE * 2)) # pop(二维矩阵) = 种群数 * (DNA长度 * 2) 个 0,1 随机数
for _ in range(Iterations): # 迭代 N 代
x, y = decodeDNA(pop)
pop = np.array(crossmuta(pop, CROSS_RATE)) # 对种群进行交叉(cross)和变异(muta)
fitness = getfitness(pop) # 计算种群每一个基因的适应度函数
pop = select(pop, fitness) # 选择生成新的种群
end_t = time.time()
fitness = getfitness(pop)
maxfitness = np.argmax(fitness)
x, y = decodeDNA(pop)
total_time += (end_t - start_t)
total_fitness += fitness[maxfitness]
total_f += F(x[maxfitness], y[maxfitness])
cost_time.append(total_time / k)
best_fitness.append(total_fitness / k)
best_f.append(total_f / k)
draw(mr_list, cost_time, best_fitness, best_f, "MUTA_RATE")
# 迭代次数测试范围:[1,1000],每一个长度重复测试 5 次来减小随机误差
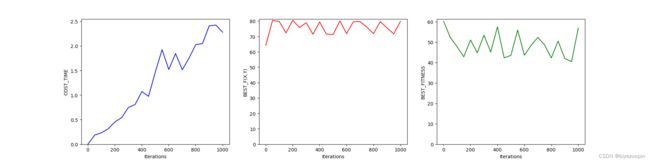
def ITERATION_TEST():
i_list = range(1, 1010, 50)
cost_time = []
best_fitness = []
best_f = []
k = 10 # 重复次数,减小随机误差
for i in i_list:
total_time = 0
total_fitness = 0
total_f = 0
for j in range(k):
global Iterations
Iterations = i
start_t = time.time()
pop = np.random.randint(2, size=(POP_SIZE, DNA_SIZE * 2)) # pop(二维矩阵) = 种群数 * (DNA长度 * 2) 个 0,1 随机数
for _ in range(Iterations): # 迭代 N 代
x, y = decodeDNA(pop)
pop = np.array(crossmuta(pop, CROSS_RATE)) # 对种群进行交叉(cross)和变异(muta)
fitness = getfitness(pop) # 计算种群每一个基因的适应度函数
pop = select(pop, fitness) # 选择生成新的种群
end_t = time.time()
fitness = getfitness(pop)
maxfitness = np.argmax(fitness)
x, y = decodeDNA(pop)
total_time += (end_t - start_t)
total_fitness += fitness[maxfitness]
total_f += F(x[maxfitness], y[maxfitness])
cost_time.append(total_time / k)
best_fitness.append(total_fitness / k)
best_f.append(total_f / k)
draw(i_list, cost_time, best_fitness, best_f, "ITERATIONS")
# 非优化迭代遗传代码
def NonOpt():
start_t = datetime.datetime.now()
pop = np.random.randint(2, size=(POP_SIZE, DNA_SIZE * 2)) # pop(二维矩阵) = 种群数 * (DNA长度 * 2) 个 0,1 随机数
for _ in range(Iterations): # 迭代 N 代
pop = np.array(crossmuta(pop, CROSS_RATE)) # 对种群进行交叉(cross)和变异(muta)
fitness = getfitness(pop) # 计算种群每一个基因的适应度函数
pop = select(pop, fitness) # 选择生成新的种群
end_t = datetime.datetime.now()
print("非优化\n耗时: ",(end_t - start_t))
print_info(pop)
fitness = getfitness(pop)
maxfitness = np.argmax(fitness)
x, y = decodeDNA(pop)
return F(x[maxfitness],y[maxfitness])
# 最佳个体保存优化遗传代码
def Opt_1():
start_t = datetime.datetime.now()
pop = np.random.randint(2, size=(POP_SIZE, DNA_SIZE * 2)) # pop(二维矩阵) = 种群数 * (DNA长度 * 2) 个 0,1 随机数
for _ in range(Iterations): # 迭代 N 代
pop = np.array(crossmuta(pop, CROSS_RATE)) # 对种群进行交叉(cross)和变异(muta)
fitness = getfitness(pop) # 计算种群每一个基因的适应度函数
best = pop[np.argmax(fitness)]
pop = select(pop, fitness) # 选择生成新的种群
pop[0] = best
end_t = datetime.datetime.now()
print("\n最佳个体保存\n耗时: ",(end_t - start_t))
print_info(pop)
fitness = getfitness(pop)
maxfitness = np.argmax(fitness)
x, y = decodeDNA(pop)
return F(x[maxfitness],y[maxfitness])
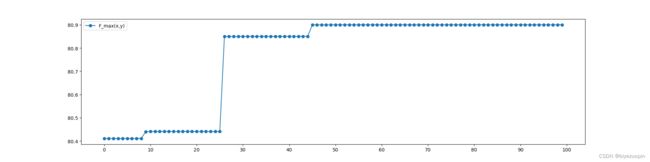
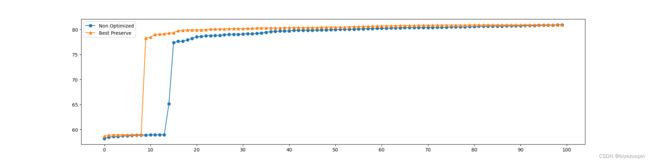
# 对比测试最佳个体保存与非优化代码的性能
def OPT1_TEST():
i_list = range(100)
f = []
f_opt = []
for i in i_list:
print(i)
f.append(NonOpt())
f_opt.append(Opt_1())
f.sort()
f_opt.sort()
plt.plot(i_list, f, marker='o', label="Non Optimized")
plt.plot(i_list, f_opt, marker='^', label="Best Preserve")
plt.gca().xaxis.set_major_locator(MultipleLocator(10))
plt.legend()
plt.show()
if __name__ == "__main__":
OPT1_TEST()
# DNA_SIZE_TEST()
# POP_SIZE_TEST()
# CROSS_RATE_TEST()
# MUTA_RATE_TEST()
# ITERATION_TEST()
# fig = plt.figure()
# ax = Axes3D(fig)
# plt.ion()
# plot_3d(ax)
#
# start_t = datetime.datetime.now()
# pop = np.random.randint(2, size=(POP_SIZE, DNA_SIZE * 2)) # pop(二维矩阵) = 种群数 * (DNA长度 * 2) 个 0,1 随机数
# for _ in range(Iterations): # 迭代 N 代
# x, y = decodeDNA(pop)
#
# # 更新画图
# if 'sca' in locals():
# sca.remove()
# sca = ax.scatter(x, y, F(x, y), c='black', marker='o')
# plt.show()
# plt.pause(0.1)
#
# pop = np.array(crossmuta(pop, CROSS_RATE)) # 对种群进行交叉(cross)和变异(muta)
# fitness = getfitness(pop) # 计算种群每一个基因的适应度函数
# pop = select(pop, fitness) # 选择生成新的种群
#
# end_t = datetime.datetime.now()
# print("耗时: ",(end_t - start_t))
# print_info(pop)
# plt.ioff()
# plot_3d(ax)