Pytorch学习笔记---自动求导机制,线性回归模型搭建
一、自动求导机制
torch框架可以自动进行求导,这在搭建网络过程中提供了很大的便利。需要求导的话就在创建tensor时,将求导参数设置为True
import torch
import numpy as np
x = torch.randn(5, 5, requires_grad=True)
这个参数默认为False,因此需要求导时,就将其设置为True。
利用这个机制进行求导:
import torch
import numpy as np
x = torch.randn(5, 5, requires_grad=True)
w = torch.randn(5, 5, requires_grad=True)
c = x*w
a = c.sum()
a.backward()
print(x.grad, w.grad)
上面的流程其实就是神经网络常见的 表达式:
F = w ∗ x + b F = w*x + b F=w∗x+b
在这里b = 0。根据链式求导法则容易得到,对于上述式子,x的梯度就是w, 同样的w的梯度就是x。
在反向梯度传播时,torch会保留上一次运算得到的梯度,并且将梯度进行一次累加操作:
import torch
import numpy as np
x = torch.randn(5, 5, requires_grad=True)
y = torch.randn(5, 5, requires_grad=True)
c = x*y
b = torch.randn(1, requires_grad=True)
a = c.sum() + b
# 求十次梯度, b的梯度累加为10
for i in range(10):
a.backward(retain_graph=True)
print(b.grad)
二、搭建线性回归模型
线性回归就是一个不加激活函数的全连接层
代码:
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def test():
x = torch.randn(5, 5, requires_grad=True)
y = torch.randn(5, 5, requires_grad=True)
c = x*y
b = torch.randn(1, requires_grad=True)
a = c.sum() + b
for i in range(10):
a.backward(retain_graph=True)
print(b.grad)
def linear_regress_data():
"""
torch搭建线性回归模型
:return:
"""
x_train = np.linspace(0, 11, 11, dtype=np.float32).reshape(-1, 1)
y_values = [2*i + 1 for i in range(11)]
y_train = np.array(y_values, dtype=np.float32).reshape(-1, 1)
# print(x_train, '\n', y_train)
# 将numpy数据类型转换为tensor类型,方便后续训练
# print(type(x_train))
x_train = torch.from_numpy(x_train)
y_train = torch.from_numpy(y_train)
# print(type(x_train))
return x_train, y_train
class LinearRegressionModel(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_dim, output_dim):
super(LinearRegressionModel, self).__init__()
# 从框架调用网络框架函数
self.linear = nn.Linear(input_dim, output_dim)
def forward(self, x):
out = self.linear(x)
return out
if __name__ == '__main__':
model = LinearRegressionModel(input_dim=1, output_dim=1)
loss_list = []
# 准备线性拟合数据
x_train, y_train = linear_regress_data()
# 设置参数、损失函数
epochs = 1000
# 学习率
learning_rate = 0.01
# 优化器
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=learning_rate)
# 损失函数(判别器)
criterion = nn.MSELoss()
# 开始训练
for epoch in range(epochs):
epoch += 1
# 每一次迭代都要梯度清零
optimizer.zero_grad()
# 前向传播
outputs = model(x_train)
# 计算损失函数
loss = criterion(outputs, y_train)
# 根据损失进行反向梯度传播
loss.backward()
# 更新权重参数
optimizer.step()
# 显示迭代的损失
if epoch % 50 == 0:
print('epoch :{}, loss :{}'.format(epoch, loss.item()))
loss_list.append(loss.item())
# 转换为numpy类型方便绘图
predict = torch.detach(outputs).numpy()
# 绘制损失函数曲线
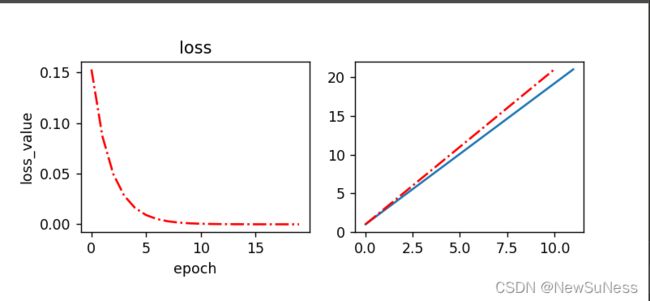
plt.subplot(221)
plt.plot(loss_list, 'r-.')
plt.title('loss')
plt.xlabel('epoch')
plt.ylabel('loss_value')
plt.subplot(222)
plt.plot(x_train, y_train)
plt.plot(predict,'r-.')
plt.show()
# 保存模型,包括权重,偏置参数
torch.save(model.state_dict(), 'model.pkl')
# 读取模型
model.load_state_dict(torch.load('model.pkl'))