Pytorch的 Dataset 的使用
此案例教我们加载并处理TorchVision的FashionMNIST Dataset。
-
root目录是 train/test data 存储的地方 -
download=True如果root目录没有,则从网上下载 -
transformandtarget_transformspecify the feature and label transformations
import torch
from torch.utils.data import Dataset
from torchvision import datasets
from torchvision.transforms import ToTensor
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
training_data = datasets.FashionMNIST(
root="data",
train=True,
download=True,
transform=ToTensor()
)
test_data = datasets.FashionMNIST(
root="data",
train=False,
download=True,
transform=ToTensor()
)运行得到的结果是这样的:
遍历并可视化数据集
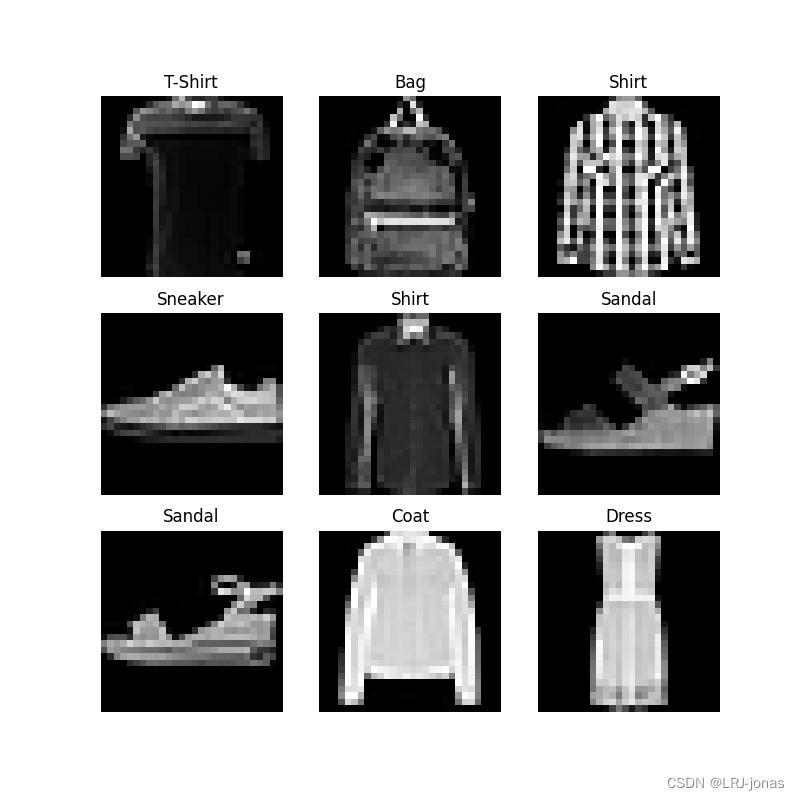
给数据集手动加上序号sample_idx,并用matplotlib进行绘制:
labels_map = {
0: "T-Shirt",
1: "Trouser",
2: "Pullover",
3: "Dress",
4: "Coat",
5: "Sandal",
6: "Shirt",
7: "Sneaker",
8: "Bag",
9: "Ankle Boot",
}
figure = plt.figure(figsize=(8, 8))
cols, rows = 3, 3
for i in range(1, cols * rows + 1):
sample_idx = torch.randint(len(training_data), size=(1,)).item()
img, label = training_data[sample_idx]
figure.add_subplot(rows, cols, i)
plt.title(labels_map[label])
plt.axis("off")
plt.imshow(img.squeeze(), cmap="gray")
plt.show()traning_data
torch.randint(len(training_data), size=(1,)).item()
为我的文件自定义一个Dataset
一个自定义的Dataset必须有三个函数:__init__, __len__, and __getitem__
图片存储在img_dir
import os
import pandas as pd
from torchvision.io import read_image
class CustomImageDataset(Dataset):
def __init__(self, annotations_file, img_dir, transform=None, target_transform=None):
self.img_labels = pd.read_csv(annotations_file)
self.img_dir = img_dir
self.transform = transform
self.target_transform = target_transform
def __len__(self):
return len(self.img_labels)
def __getitem__(self, idx):
img_path = os.path.join(self.img_dir, self.img_labels.iloc[idx, 0])
image = read_image(img_path)
label = self.img_labels.iloc[idx, 1]
if self.transform:
image = self.transform(image)
if self.target_transform:
label = self.target_transform(label)
return image, label__init__函数 初始化包含图像、注释文件和两个转换的目录。
labels.csv 文件长这个样子:
tshirt1.jpg, 0
tshirt2.jpg, 0
......
ankleboot999.jpg, 9
__len__函数
返回样例sample的个数
__getitem__函数
从数据集中加载并返回一个给定index的样本。 Based on the index, it identifies the image’s location on disk, converts that to a tensor using read_image, retrieves the corresponding label from the csv data in self.img_labels, calls the transform functions on them (if applicable), and returns the tensor image and corresponding label in a tuple.
实际情况更常使用 DataLoader
The Dataset retrieves our dataset’s features and labels one sample at a time. While training a model, we typically want to pass samples in “minibatches”, reshuffle the data at every epoch to reduce model overfitting, and use Python’s multiprocessing to speed up data retrieval.
DataLoader 是一个能做到上述功能的迭代器API。
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
train_dataloader = DataLoader(training_data, batch_size=64, shuffle=True)
test_dataloader = DataLoader(test_data, batch_size=64, shuffle=True)We have loaded that dataset into the DataLoader and can iterate through the dataset as needed. Each iteration below returns a batch of train_features and train_labels (containing batch_size=64 features and labels respectively). Because we specified shuffle=True, after we iterate over all batches the data is shuffled (for finer-grained control over the data loading order, take a look at Samplers)
# Display image and label.
train_features, train_labels = next(iter(train_dataloader))
print(f"Feature batch shape: {train_features.size()}")
print(f"Labels batch shape: {train_labels.size()}")
img = train_features[0].squeeze()
label = train_labels[0]
plt.imshow(img, cmap="gray")
plt.show()
print(f"Label: {label}")