VGAE(Variational graph auto-encoders)论文及代码解读
一,论文来源
论文pdf
Variational graph auto-encoders
论文代码
github代码
二,论文解读
理论部分参考:
Variational Graph Auto-Encoders(VGAE)理论参考和源码解析
VGAE(Variational graph auto-encoders)论文详解
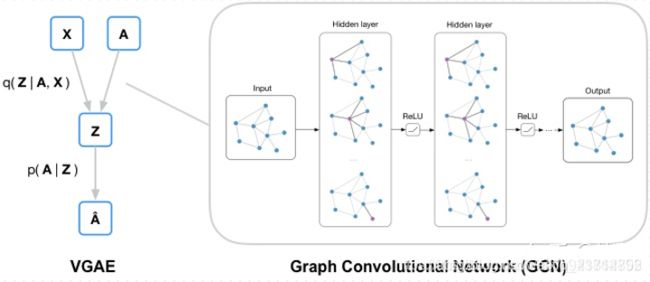
简要介绍: 本文是将变分自编码器(Variational Auto-Encoders, VAE
)迁移到了图领域,基本思路是:用已知的图经过编码(图卷积)学到节点向量表示的分布,在分布中采样得到节点的向量表示,然后进行解码(链路预测)重新构建图。
简要介绍引用来自: 7. Variational Graph Auto-Encoders论文阅读笔记
细节方面感觉这个小姐姐讲的非常好:
【GNN五大类 VGAE】(变分图自编码器):Variational Graph Auto-Encoders
理论方面其实前面几位大佬说的很好了,这里我只是来阐述两点:
1.测试方法:
模型在数据集的不完整版本上训练,其中部分引用链接(边)已被移除,而所有节点特征被保留。 我们从先前移除的边和相同数量的随机采样的未连接节点对(非边)形成验证和测试集。我们根据模型正确分类边缘和非边缘的能力来比较模型。 验证和测试集分别包含5%和10%的引用链接。 验证集用于优化超参数。 我们对比了两个流行的基线:谱聚类(SC) [5]和深度行走(DW) [6]。 SC和DW都提供节点嵌入z。 我们用Eq.4(左侧)计算重构邻接矩阵元素的得分。
2.熵
参考
交叉熵、相对熵(KL散度)、JS散度和Wasserstein距离(推土机距离)
正态分布N(mu,sigma)和N(0,1)之间的KL散度推导
三,代码解读
preprocessing.py
import numpy as np
import scipy.sparse as sp
def sparse_to_tuple(sparse_mx):
if not sp.isspmatrix_coo(sparse_mx): #是否为csr_matrix类型
sparse_mx = sparse_mx.tocoo() #实现csc矩阵转换为coo矩阵
coords = np.vstack((sparse_mx.row, sparse_mx.col)).transpose()
# np.vstack按垂直方向(行顺序)堆叠数组构成一个新的数组,堆叠的数组需要具有相同的维度,transpose()作用是转置
values = sparse_mx.data
shape = sparse_mx.shape
return coords, values, shape
def preprocess_graph(adj):
adj = sp.coo_matrix(adj) #csr_matrix转成coo_matrix
adj_ = adj + sp.eye(adj.shape[0]) #S=A+I #注意adj_的类型为csr_matrix
rowsum = np.array(adj_.sum(1)) #rowsum的shape=(节点数,1),对于cora数据集来说就是(2078,1),sum(1)求每一行的和
degree_mat_inv_sqrt = sp.diags(np.power(rowsum, -0.5).flatten()) #计算D^{-0.5}
#p.diags:提取输入矩阵(大小为m×n)的所有非零对角列。输出的大小为 min(m,n)×p,其中p表示输入矩阵的p个非零对角列
#numpy.power():用于数组元素求n次方
#flatten():返回一个折叠成一维的数组。
adj_normalized = adj_.dot(degree_mat_inv_sqrt).transpose().dot(degree_mat_inv_sqrt).tocoo()
# adj_.dot(degree_mat_inv_sqrt)得到 SD^{-0.5}
# adj_.dot(degree_mat_inv_sqrt).transpose()得到(D^{-0.5})^{T}S^{T}=D^{-0.5}S,因为D和S都是对称矩阵
# adj_normalized即为D^{-0.5}SD^{-0.5}
return sparse_to_tuple(adj_normalized)
def mask_test_edges(adj):
# Function to build test set with 10% positive links
# NOTE: Splits are randomized and results might slightly deviate from reported numbers in the paper.
# TODO: Clean up.
# Remove diagonal elements
adj = adj - sp.dia_matrix((adj.diagonal()[np.newaxis, :], [0]), shape=adj.shape)
adj.eliminate_zeros()
# Check that diag is zero:
assert np.diag(adj.todense()).sum() == 0
#assert断言是声明其布尔值必须为真的判定,如果发生异常就说明表达示为假。
#todense()方法将稀疏矩阵b转换成稠密矩阵c
adj_triu = sp.triu(adj) #取出稀疏矩阵的上三角部分的非零元素,返回的是coo_matrix类型
adj_tuple = sparse_to_tuple(adj_triu)
edges = adj_tuple[0]
# 取除去节点自环的所有边(注意,由于adj_tuple仅包含原始邻接矩阵上三角的边,所以edges中的边虽然只记录了边,而不冗余记录边),shape=(边数,2)每一行记录一条边的起始节点和终点节点的编号
edges_all = sparse_to_tuple(adj)[0]
# 取原始graph中的所有边,shape=(边数,2)每一行记录一条边的起始节点和终点节点的编号
num_test = int(np.floor(edges.shape[0] / 10.)) #划分测试集
# np.floor返回数字的下舍整数
num_val = int(np.floor(edges.shape[0] / 20.)) #划分验证集
all_edge_idx = list(range(edges.shape[0]))
np.random.shuffle(all_edge_idx) #打乱all_edge_idx的顺序
val_edge_idx = all_edge_idx[:num_val] #划分验证集
test_edge_idx = all_edge_idx[num_val:(num_val + num_test)] #划分测试集
test_edges = edges[test_edge_idx] #edges是除去节点自环的所有边(因为数据集中的边都是无向的,edges只是存储了,没有存储,因为没必要浪费内存),shape=(边数,2)每一行记录一条边的起始节点和终点节点的编号
val_edges = edges[val_edge_idx]
train_edges = np.delete(edges, np.hstack([test_edge_idx, val_edge_idx]), axis=0)
# np.vstack():在竖直方向上堆叠,np.hstack():在水平方向上平铺。
# np.hstack([test_edge_idx, val_edge_idx])将两个list水平方向拼接成一维数组
# np.delete的参数axis=0,表示删除多行,删除的行号由第一个参数确定
def ismember(a, b, tol=5):
rows_close = np.all(np.round(a - b[:, None], tol) == 0, axis=-1)
# np.round返回浮点数x的四舍五入值,第二参数是保留的小数的位数
# b[:, None]使b从shape=(边数,2)变为shape=(边数,1,2),而a是长度为2的list,a - b[:, None]触发numpy的广播机制
# np.all()判断给定轴向上的所有元素是否都为True,axis=-1(此时等同于axis=2)表示3维数组最里层的2维数组的每一行的元素是否都为True
return np.any(rows_close)
# np.any()判断给定轴向上是否有一个元素为True,现在不设置axis参数则是判断所有元素中是否有一个True,有一个就返回True。
# rows_close的shape=(边数,1)
# 至此,可以知道,ismember( )方法用于判断随机生成的这条边是否是已经真实存在的边,如果是,则返回True,否则返回False
test_edges_false = []
while len(test_edges_false) < len(test_edges):
idx_i = np.random.randint(0, adj.shape[0]) #生成负样本
idx_j = np.random.randint(0, adj.shape[0])
if idx_i == idx_j:
continue
if ismember([idx_i, idx_j], edges_all):
continue
if test_edges_false:
if ismember([idx_j, idx_i], np.array(test_edges_false)):
continue
if ismember([idx_i, idx_j], np.array(test_edges_false)):
continue
test_edges_false.append([idx_i, idx_j])
val_edges_false = []
while len(val_edges_false) < len(val_edges):
idx_i = np.random.randint(0, adj.shape[0])
idx_j = np.random.randint(0, adj.shape[0])
if idx_i == idx_j:
continue
if ismember([idx_i, idx_j], train_edges):
continue
if ismember([idx_j, idx_i], train_edges):
continue
if ismember([idx_i, idx_j], val_edges):
continue
if ismember([idx_j, idx_i], val_edges):
continue
if val_edges_false:
if ismember([idx_j, idx_i], np.array(val_edges_false)):
continue
if ismember([idx_i, idx_j], np.array(val_edges_false)):
continue
val_edges_false.append([idx_i, idx_j])
assert ~ismember(test_edges_false, edges_all) #assert(断言)用于判断一个表达式,在表达式条件为 false 的时候触发异常。所以,这里是想要edges_all不含有test_edges_false,否则抛异常
assert ~ismember(val_edges_false, edges_all)
assert ~ismember(val_edges, train_edges)
assert ~ismember(test_edges, train_edges)
assert ~ismember(val_edges, test_edges)
data = np.ones(train_edges.shape[0])
# 重建出用于训练阶段的邻接矩阵
adj_train = sp.csr_matrix((data, (train_edges[:, 0], train_edges[:, 1])), shape=adj.shape)
adj_train = adj_train + adj_train.T
# #注意:这些边列表只包含一个方向的边(adj_train是矩阵,不是edge lists)
return adj_train, train_edges, val_edges, val_edges_false, test_edges, test_edges_false
1.hstack()/vstack()分析
参考:Numpy中stack(),hstack(),vstack()函数详解
np.vstack():在竖直方向上堆叠,np.hstack():在水平方向上平铺。
np.hstack([test_edge_idx, val_edge_idx])将两个list水平方向拼接成一维数组
2.preprocess_graph函数中格式转换:
参考:scipy中稀疏矩阵coo_matrix, csr_matrix 的使用
3.b[:, None]维度扩充
这个我做了测试:
import numpy as np
a = np.array([[1,2,3,4],
[5,6,7,8],
[9,10,11,12],
[13,14,15,16]])
b = a[:,None]
c = a[None,:]
d = a[:,:,None]
print(a.shape)
print(b.shape)
print(c.shape)
print(d.shape)
结果:
(4, 4)
(4, 1, 4)
(1, 4, 4)
(4, 4, 1)
可以发现None在哪,哪扩充了一维
model.py
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import os
import numpy as np
import args
class VGAE(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, adj):
super(VGAE,self).__init__()
self.base_gcn = GraphConvSparse(args.input_dim, args.hidden1_dim, adj)
self.gcn_mean = GraphConvSparse(args.hidden1_dim, args.hidden2_dim, adj, activation=lambda x:x)
#lambda是匿名函数,冒号左边是参数,多个参数用逗号隔开,右边是表达式
self.gcn_logstddev = GraphConvSparse(args.hidden1_dim, args.hidden2_dim, adj, activation=lambda x:x)
def encode(self, X):
hidden = self.base_gcn(X)
self.mean = self.gcn_mean(hidden)
self.logstd = self.gcn_logstddev(hidden)
gaussian_noise = torch.randn(X.size(0), args.hidden2_dim)
sampled_z = gaussian_noise*torch.exp(self.logstd) + self.mean
# 这里使用torch.exp是因为论文中log(sigma)=GCN_{sigma}(X,A),torch.exp(self.logstd)即torch.exp(log(sigma))得到的是sigma;另外还有mu=GCN_{mu}(X,A).
# 由于每个节点向量经过GCN后都有且仅有一个节点向量表示,所以呢,方差的对数log(sigma)和节点向量表示的均值mu分别是节点经过GCN_{sigma}(X,A)和GCN_{mu}(X,A)后得到的向量表示本身。
# 从N(mu,sigma^2)中采样一个样本Z相当于在N(0,1)中采样一个xi,然后Z = mu + xi×sigma
return sampled_z
def forward(self, X):
Z = self.encode(X)
A_pred = dot_product_decode(Z)
return A_pred
class GraphConvSparse(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_dim, output_dim, adj, activation = F.relu, **kwargs):
super(GraphConvSparse, self).__init__(**kwargs)
self.weight = glorot_init(input_dim, output_dim)
self.adj = adj
self.activation = activation
def forward(self, inputs):
x = inputs
x = torch.mm(x,self.weight)
#torch.mm(a, b)是矩阵a和b矩阵相乘
x = torch.mm(self.adj, x)
outputs = self.activation(x)
return outputs
def dot_product_decode(Z):
A_pred = torch.sigmoid(torch.matmul(Z,Z.t()))
return A_pred
def glorot_init(input_dim, output_dim):
init_range = np.sqrt(6.0/(input_dim + output_dim))
initial = torch.rand(input_dim, output_dim)*2*init_range - init_range
return nn.Parameter(initial)
class GAE(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,adj):
super(GAE,self).__init__()
self.base_gcn = GraphConvSparse(args.input_dim, args.hidden1_dim, adj)
self.gcn_mean = GraphConvSparse(args.hidden1_dim, args.hidden2_dim, adj, activation=lambda x:x)
def encode(self, X):
hidden = self.base_gcn(X)
z = self.mean = self.gcn_mean(hidden)
return z
def forward(self, X):
Z = self.encode(X)
A_pred = dot_product_decode(Z)
return A_pred
# class GraphConv(nn.Module):
# def __init__(self, input_dim, hidden_dim, output_dim):
# super(VGAE,self).__init__()
# self.base_gcn = GraphConvSparse(args.input_dim, args.hidden1_dim, adj)
# self.gcn_mean = GraphConvSparse(args.hidden1_dim, args.hidden2_dim, adj, activation=lambda x:x)
# self.gcn_logstddev = GraphConvSparse(args.hidden1_dim, args.hidden2_dim, adj, activation=lambda x:x)
# def forward(self, X, A):
# out = A*X*self.w0
# out = F.relu(out)
# out = A*X*self.w0
# return out
1.lambda匿名函数
参考:python的匿名函数lambda解释及用法
这里注意:匿名函数不需要return来返回值,表达式本身结果就是返回值。
train.py
import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F
from torch.optim import Adam
from sklearn.metrics import roc_auc_score, average_precision_score
import scipy.sparse as sp
import numpy as np
import os
import time
from input_data import load_data
from preprocessing import *
import args
import model
# Train on CPU (hide GPU) due to memory constraints
os.environ['CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES'] = ""
adj, features = load_data(args.dataset)
# 存储原始邻接矩阵(无对角线条目)以备后用
adj_orig = adj
adj_orig = adj_orig - sp.dia_matrix((adj_orig.diagonal()[np.newaxis, :], [0]), shape=adj_orig.shape)
# Scipy的dia_matrix函数见1.其中offsets数组中0表示对角线,-1表示对角线下面,正数表示对角线上面
# np.newaxis的作用是增加一个维度。[np.newaxis,:]是在np.newaxis这里增加1维。这样改变维度的作用往往是将一维的数据转变成一个矩阵
#diagonal()是获得矩阵对角线
#adj_orig.diagonal()[np.newaxis, :], [0]代码意思是先将对角线提取出来然后增加一维变为矩阵,方便后续计算
adj_orig.eliminate_zeros()
#eliminite_zeros() 存储去掉0元素,返回的是稀疏存储
adj_train, train_edges, val_edges, val_edges_false, test_edges, test_edges_false = mask_test_edges(adj)
adj = adj_train #用于训练的邻接矩阵,类型为csr_matrix
# Some preprocessing
adj_norm = preprocess_graph(adj)
#返回D^{-0.5}SD^{-0.5}的coords(坐标), data, shape,其中S=A+I
num_nodes = adj.shape[0]
features = sparse_to_tuple(features.tocoo())
#features的类型原为lil_matrix,sparse_to_tuple返回features的coords, data, shape
num_features = features[2][1]
features_nonzero = features[1].shape[0]
# Create Model
pos_weight = float(adj.shape[0] * adj.shape[0] - adj.sum()) / adj.sum()
#注意,adj的每个元素非1即0。pos_weight是用于训练的邻接矩阵中负样本边(既不存在的边)和正样本边的倍数(即比值),这个数值在二分类交叉熵损失函数中用到,
#如果正样本边所占的比例和负样本边所占比例失衡,比如正样本边很多,负样本边很少,那么在求loss的时候可以提供weight参数,将正样本边的weight设置小一点,负样本边的weight设置大一点,
#此时能够很好的平衡两类在loss中的占比,任务效果可以得到进一步提升。参考:https://www.zhihu.com/question/383567632
norm = adj.shape[0] * adj.shape[0] / float((adj.shape[0] * adj.shape[0] - adj.sum()) * 2)
adj_label = adj_train + sp.eye(adj_train.shape[0]) #adj_train是用于训练的邻接矩阵,类型为csr_matrix
adj_label = sparse_to_tuple(adj_label)
adj_norm = torch.sparse.FloatTensor(torch.LongTensor(adj_norm[0].T), #其中adj_norm是D^{-0.5}SD^{-0.5}的coords, data, shape
torch.FloatTensor(adj_norm[1]),
torch.Size(adj_norm[2]))
adj_label = torch.sparse.FloatTensor(torch.LongTensor(adj_label[0].T),
torch.FloatTensor(adj_label[1]),
torch.Size(adj_label[2]))
features = torch.sparse.FloatTensor(torch.LongTensor(features[0].T),
torch.FloatTensor(features[1]),
torch.Size(features[2]))
#torch.sparse.FloatTensor见详解
weight_mask = adj_label.to_dense().view(-1) == 1
# view的参数-1 表示做自适应性调整,如果参数只有一个参数-1,则表示将Tensor变成一维张量。
weight_tensor = torch.ones(weight_mask.size(0))
weight_tensor[weight_mask] = pos_weight
#用于在binary_cross_entropy中设置正样本边的weight。负样本边的weight都为1,正样本边的weight都为pos_weight
# init model and optimizer
model = getattr(model,args.model)(adj_norm)
#getattr() 函数用于返回一个对象属性值。
optimizer = Adam(model.parameters(), lr=args.learning_rate)
def get_scores(edges_pos, edges_neg, adj_rec):
def sigmoid(x):
return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-x))
# Predict on test set of edges
preds = []
pos = []
for e in edges_pos:
# print(e)
# print(adj_rec[e[0], e[1]])
preds.append(sigmoid(adj_rec[e[0], e[1]].item()))
#item()取出单元素张量的元素值并返回该值,保持原元素类型不变,从而能够保留原来的精度。所以在求loss,以及accuracy rate的时候一般用item()
pos.append(adj_orig[e[0], e[1]])
preds_neg = []
neg = []
for e in edges_neg:
preds_neg.append(sigmoid(adj_rec[e[0], e[1]].data))
neg.append(adj_orig[e[0], e[1]])
preds_all = np.hstack([preds, preds_neg])
labels_all = np.hstack([np.ones(len(preds)), np.zeros(len(preds_neg))])
roc_score = roc_auc_score(labels_all, preds_all)
ap_score = average_precision_score(labels_all, preds_all)
return roc_score, ap_score
def get_acc(adj_rec, adj_label):
labels_all = adj_label.to_dense().view(-1).long() #long()将数字或字符串转换为一个长整型
preds_all = (adj_rec > 0.5).view(-1).long()
accuracy = (preds_all == labels_all).sum().float() / labels_all.size(0)
return accuracy
# train model
for epoch in range(args.num_epoch):
t = time.time()
A_pred = model(features) #得到的A_pred每个元素不再是非1即0
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss = log_lik = norm*F.binary_cross_entropy(A_pred.view(-1), adj_label.to_dense().view(-1), weight = weight_tensor)
# binary_cross_entropy参考:https://www.zhihu.com/question/383567632
if args.model == 'VGAE':
kl_divergence = 0.5/ A_pred.size(0) * (1 + 2*model.logstd - model.mean**2 - torch.exp(model.logstd)**2).sum(1).mean()
# kl_divergence就是正态分布的KL散度,即n个(0.5*(1+log(sigma^2)-mu^2-sigma^2))的和,n为图中节点的数量,也就是这里的A_pred.size(0)
# 2*model.logstd即为2*log(sigma),根据运算法则,log(sigma^2)=2*log(sigma);model.mean**2即为mu^2;torch.exp(model.logstd)**2即为sigma^2
# 1+log(sigma^2)-mu^2-sigma^2
# sum(1)表示矩阵每一行内元素求和
loss -= kl_divergence
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
train_acc = get_acc(A_pred,adj_label)
val_roc, val_ap = get_scores(val_edges, val_edges_false, A_pred)
print("Epoch:", '%04d' % (epoch + 1), "train_loss=", "{:.5f}".format(loss.item()),
"train_acc=", "{:.5f}".format(train_acc), "val_roc=", "{:.5f}".format(val_roc),
"val_ap=", "{:.5f}".format(val_ap),
"time=", "{:.5f}".format(time.time() - t))
test_roc, test_ap = get_scores(test_edges, test_edges_false, A_pred)
print("End of training!", "test_roc=", "{:.5f}".format(test_roc),
"test_ap=", "{:.5f}".format(test_ap))
1.pos_weight = float(adj.shape[0] * adj.shape[0] - adj.sum()) / adj.sum()分析
参考:pytorch中binary_cross_entropy损失函数中weight参数是如何设置的?
2.torch.sparse.FloatTensor详解
参考:tensor torch 构造_TORCH.SPARSE
3.np.newaxis函数
参考:np.newaxis作用
4.Scipy的dia_matrix函数
参考:Python scipy中的dia_matrix详解
这里进行进一步的讲解:
例如代码:
from scipy.sparse import dia_matrix
import numpy as np
if __name__ == '__main__':
data = np.array([[1,2,3,4],
[4,2,3,8],
[7,2,4,5]])
offsets = np.array([0,-1,2])
a = dia_matrix((data,offsets),shape=(4,4)).toarray()
print(a)

这样排列是按照:offsets中第一个元素与data第一行元素对应,并且按照data中第一行第一个元素为起始点,对角线排列。同理:

然后以0为对角线开始节点,向下记录,按照shape的格式,得到最后结果:
[[1 0 4 0]
[4 2 0 5]
[0 2 3 0]
[0 0 3 4]]