torch学习笔记之——tensor维度变换
1, (函数API)View , reshape
本上没有区别,0.3版本之前默认view之后默认使用reshape,现在版本建议使用view。
a = torch.rand(4, 1, 28, 28)
print(a.shape)
a=a.view(4, 28, 28)
# print(a.shape)
# print(a)
a=a.view(4*28, 28)
print(a.shape)
print(a)介绍:torch.Tensor.view会返回具有相同数据但大小不同的新张量。 返回的张量必须有与原张量相同的数据和相同数量的元素,但可以有不同的大小。一个张量必须是连续contiguous()的才能被查看。类似于Numpy的np.reshape()。
2,squeeze 和 unsqueeze
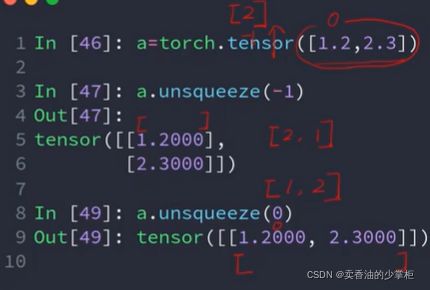
维度的插入unsqueeze:
不改变数据的本身,只是增加一个维度。
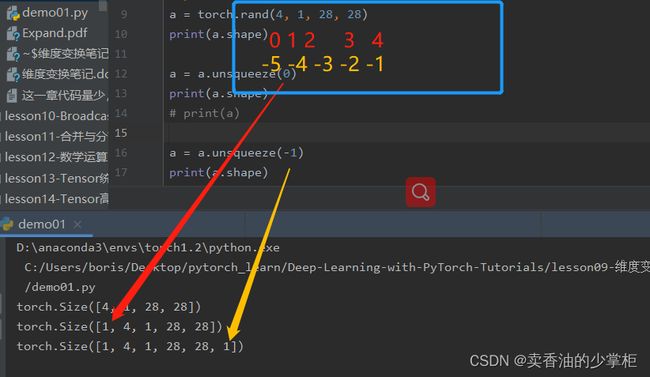
a = torch.rand(4, 1, 28, 28)
print(a.shape)
a = a.unsqueeze(0)
print(a.shape)
# print(a)
a = a.unsqueeze(-1)
print(a.shape)
# print(a)维度的挤压/删减unsqueeze:
squeeze操作 注意写indx参数,如果没有写的话,会将能挤压的参数都挤压出来,挤压包含有数据元素的维度,返回原数据,没有发生改变。
# squeeze操作 注意写indx参数,如果没有写的话,会将能挤压的参数都挤压出来
b = torch.rand(1, 32, 1, 1)
print(b.shape)
b = b.squeeze(0)
print(b.shape)
b = b.squeeze(-1)
print(b.shape)
# 挤压包含有数据元素的维度,返回原数据,没有发生改变
b = b.squeeze(1)
print(b.shape)
b = b.squeeze(-4)
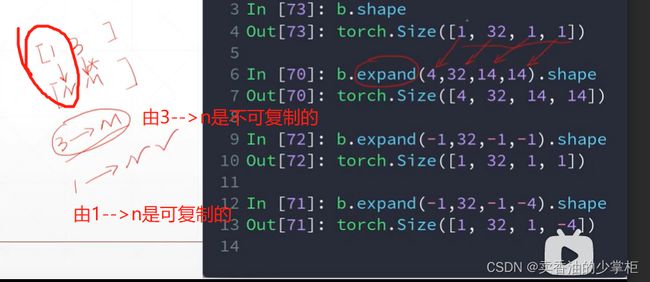
print(b.shape)3, expand 和repeat唯独扩展:
Expand 的维度扩展类似于广播性质的,节省内存,灵活。
Repeat 的唯独扩展是复制内存的形式改变tensor形式的。
a = torch.rand(4, 32, 14, 14)
# 扩展的前提是 dim 需要一致
b = torch.rand(1,32,1,1)
print(b)
print(b.expand(4, 32, 14, 14).shape)
print(b.expand(4, 32, 14, 14))
# -1表示不改变这个维度的状态
print(b.expand(-1, 32, -1, -1).shape)Repeat:例子
a = torch.rand(4, 32, 14, 14)
b = torch.rand(1,32,1,1)
# repeat方式复制内存
# ()参数中的数字表示相应位置上的数据重复复制多少次。
print(b.repeat(4, 32, 1, 1).shape)注意:()参数中的数字表示相应位置上的数据重复复制多少次。
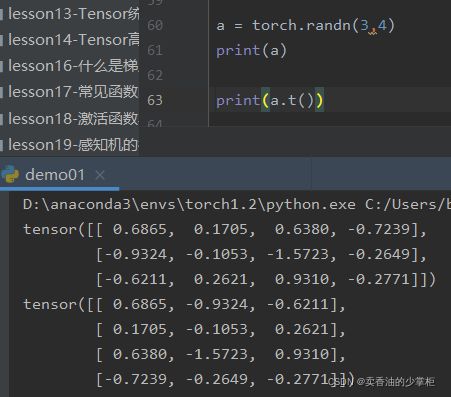
4, 二维度的数据装置操作
要注意.t() 转置操作只能用于2D 的tensor,其他维度报错。
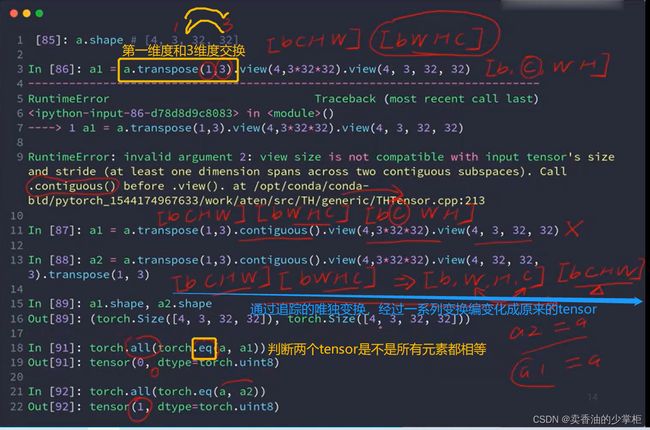
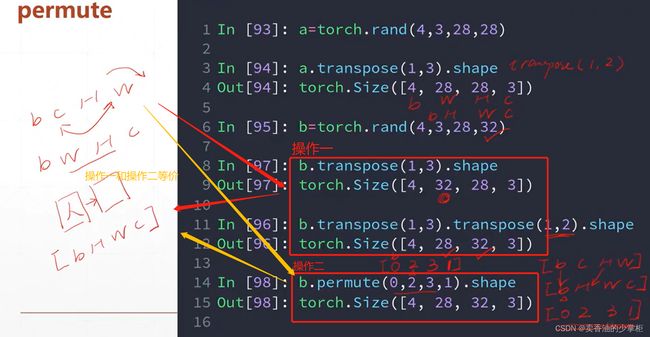
5,补充 transpose/ permute交换维度,.eq判断相等:
transpose交换维度:
注意的点:[b,h,w,c]是numpy储存图片的格式
Permute:改变维度的次序,重新排序。