Python 手写实现梯度下降法,并进行迭代轨迹可视化详细教程(以单元线性回归为例)
本文主要介绍梯度下降法可视化教程
1、读取数据
#read data
from IPython.core.interactiveshell import InteractiveShell
InteractiveShell.ast_node_interactivity = "all"
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
def computeCost2(X, y, theta0, theta1):
m = X.shape[0]
diff = theta0 + theta1 * (X) - y;
cost = np.power(diff, 2).sum() / 2 / m
return cost
data = pd.read_csv('/home/ciro/AL_ML/ex1data1.txt', header=None, names=['Pop', 'Price'])
print('shape of data:', data.shape)
cols = data.shape[1]
X = data.iloc[:, 0:cols - 1] # X是data所有行,去掉最后一列
y = data.iloc[:, cols - 1:cols]
X = np.array(X)
y = np.array(y)2、构造损失函数、梯度函数、梯度下降函数
#deine functions
def computeCost(X, y, theta): # define cost function
m = X.shape[0]
theta0 = theta[0,0]
theta1 = theta[1,0]
diff = theta0 + theta1*(X) - y;
cost = np.power(diff, 2).sum()/2/m
return cost
### END CODE HERE ###
def gradient(X, y, theta): #caluculate gradient
### START CODE HERE ###
m = X.shape[0]
theta0 = theta[0,0]
theta1 = theta[1,0]
diff1 = theta0 + theta1*(X) - y;
diff2 = diff1*X;
j1 = diff1.sum()/m;
j2 = diff2.sum()/m
res = np.array([j1, j2])
return j1, j2
### END CODE HERE ###
def batch_gradient_descent(X, y, theta, epoch, lr=0.01):# gradient desend by iterating
### START CODE HERE ###
for k in range(epoch):
#cost = computeCost(X, y, theta)
j1, j2 = gradient(X, y, theta)
theta[0, 0] = theta[0, 0] - lr*j1
theta[1, 0] = theta[1, 0] - lr*j2
cost = computeCost(X, y, theta)
return np.array(theta),cost
3、存储每次迭代的线性回归系数与代价
lr = 0.01 #set learing rate
theta = np.zeros((2,1))#set initial theta
theta_pred_series = np.zeros((10,2))# store theta of each epoch
costs_series =np.zeros((10,1))#store the cost of each epoch
for epochs in range(1,11):
theta_pred,costs = batch_gradient_descent(X, y, theta, epoch=epochs, lr=lr)
theta_pred_series[epochs-1,:] = np.array(theta_pred)[:,-1]
costs_series[epochs-1] = (costs)
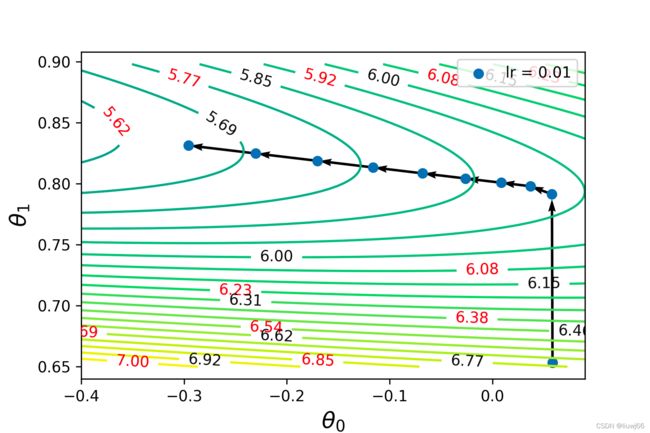
4、构建损失函数的等高线图
#set the theta range
theta0 = np.linspace(theta_pred_series[:,0].min(),theta_pred_series[:,0].max() , 100)
theta1 = np.linspace(theta_pred_series[:,1].min(),theta_pred_series[:,1].max() , 200)
#build meshgrid
theta00, theta11 = np.meshgrid(theta0, theta1)
#define cost funtion
def computeCost2(X, y, theta0, theta1):
m = X.shape[0]
diff = theta0 + theta1*(X) - y;
cost = np.power(diff, 2).sum()/2/m
return cost
costs = np.zeros((theta1.size, theta0.size));#store the cost of each theta0 and theta1
#calculate cost of each theta
for kk in range(theta0.size):
for ii in range(theta1.size):
costs[ii, kk] = computeCost2(X, y, theta0[kk], theta1[ii])
fig = plt.figure() #定义新的三维坐标轴
cs = plt.contour(theta00, theta11, costs, np.linspace(4,10,40))#np.linspace(4,10,40) indicates the z value range in contour
plt.xlim([theta0.min(),theta0.max()])
plt.ylim([theta1.min()-0.01,theta1.max()+0.01])
plt.xlabel(r'$\theta_0$',fontsize = 15)
plt.ylabel(r'$\theta_1$',fontsize = 15)
plt.clabel(cs,fontsize=10,colors=('k','r'),fmt='%.2f')5、绘制梯度下降的轨迹图
for i in range(9):
dx = theta_pred_series[i+1,0] - theta_pred_series[i,0]
dy = theta_pred_series[i+1,1] - theta_pred_series[i,1]
plt.quiver(theta_pred_series[i,0], theta_pred_series[i,1], dx, dy, angles='xy', scale=1.03, scale_units='xy', width=0.005)
plt.scatter(theta_pred_series[:,0],theta_pred_series[:,1],label = 'lr = 0.01')
#ax3.contour(X,Y,Z, zdim='z',offset=-2,cmap='rainbow) #等高线图,要设置offset,为Z的最小值
plt.legend()6、结果如下
7、要想可视化更好看,最重要的是调整图中theta0,theta1的范围,以及等高线z值的范围。
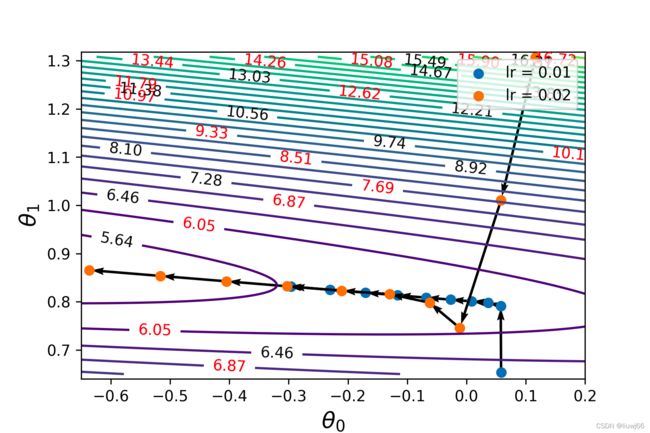
8、若要比较不同学习率下的迭代轨迹,可使用一下代码
lr2 = 0.02; epochs = 100
lr = 0.01
theta = np.zeros((2,1))
theta_pred_series = np.zeros((10,2))
costs_series =np.zeros((10,1))
theta_pred_series2 = np.zeros((10,2))
costs_series2 =np.zeros((10,1))
for epochs in range(1,11):
theta_pred,costs = batch_gradient_descent(X, y, theta, epoch=epochs, lr=lr2)
theta_pred_series2[epochs-1,:] = np.array(theta_pred)[:,-1]
costs_series2[epochs-1] = (costs)
theta = np.zeros((2,1))
for epochs in range(1,11):
theta_pred,costs = batch_gradient_descent(X, y, theta, epoch=epochs, lr=lr)
theta_pred_series[epochs-1,:] = np.array(theta_pred)[:,-1]
costs_series[epochs-1] = (costs)
theta0 = np.arange(-0.65, 0.2, 0.01)
theta1 = np.arange(0.65, 1.31, 0.002)
theta00, theta11 = np.meshgrid(theta0, theta1)
def computeCost2(X, y, theta0, theta1):
m = X.shape[0]
diff = theta0 + theta1*(X) - y;
cost = np.power(diff, 2).sum()/2/m
return cost
costs = np.zeros((theta1.size, theta0.size));
for kk in range(theta0.size):
for ii in range(theta1.size):
costs[ii, kk] = computeCost2(X, y, theta0[kk], theta1[ii])
fig = plt.figure() #定义新的三维坐标轴
cs = plt.contour(theta00, theta11, costs, np.linspace(4,20,40))
plt.xlim([theta0.min(),theta0.max()])
plt.ylim([theta1.min()-0.01,theta1.max()+0.01])
plt.xlabel(r'$\theta_0$',fontsize = 15)
plt.ylabel(r'$\theta_1$',fontsize = 15)
plt.clabel(cs,fontsize=10,colors=('k','r'),fmt='%.2f')
for i in range(9):
dx = theta_pred_series[i+1,0] - theta_pred_series[i,0]
dy = theta_pred_series[i+1,1] - theta_pred_series[i,1]
plt.quiver(theta_pred_series[i,0], theta_pred_series[i,1], dx, dy, angles='xy', scale=1.03, scale_units='xy', width=0.005)
plt.scatter(theta_pred_series[:,0],theta_pred_series[:,1],label = 'lr = 0.01')
#ax3.contour(X,Y,Z, zdim='z',offset=-2,cmap='rainbow) #等高线图,要设置offset,为Z的最小值
for i in range(9):
dx = theta_pred_series2[i+1,0] - theta_pred_series2[i,0]
dy = theta_pred_series2[i+1,1] - theta_pred_series2[i,1]
plt.quiver(theta_pred_series2[i,0], theta_pred_series2[i,1], dx, dy, angles='xy', scale=1.03, scale_units='xy', width=0.005)
plt.scatter(theta_pred_series2[:,0],theta_pred_series2[:,1],label = 'lr = 0.02')
plt.legend()
plt.savefig('batch_GD_iter_compare',dpi = 300)迭代结果如下: