DeepSort之源码解读
文章有点长…
代码地址:https://github.com/ZQPei/deep_sort_pytorch
traker是一个类,负责对多个track的进行操作,包括预测和更新。
self.tracker.predict()
self.tracker.update(detections)
tracker预测阶段是对每个track进行预测,包括
- 卡尔曼预测
- track年龄 age+1
- time_since_update+1,此变量用于记录track上次更新的时间
代码如下:
def predict(self, kf):
"""Propagate the state distribution to the current time step using a
Kalman filter prediction step.
Parameters
----------
kf : kalman_filter.KalmanFilter
The Kalman filter.
"""
self.mean, self.covariance = kf.predict(self.mean, self.covariance)
self.age += 1
self.time_since_update += 1
tracker更新是对多个track更新:
- track和det的匹配
- track更新
- 距离指标更新
代码如下:
def update(self, detections):
"""Perform measurement update and track management.
Parameters
----------
detections : List[deep_sort.detection.Detection]
A list of detections at the current time step.
"""
# Run matching cascade.
matches, unmatched_tracks, unmatched_detections = \
self._match(detections)
print("matches:",matches, "unmatched_tracks:",unmatched_tracks, "unmatched_detections:", unmatched_detections)
# Update track set.
for track_idx, detection_idx in matches:
self.tracks[track_idx].update(
self.kf, detections[detection_idx])
for track_idx in unmatched_tracks:
self.tracks[track_idx].mark_missed()
for detection_idx in unmatched_detections:
self._initiate_track(detections[detection_idx])
self.tracks = [t for t in self.tracks if not t.is_deleted()]
# Update distance metric.
active_targets = [t.track_id for t in self.tracks if t.is_confirmed()]
features, targets = [], []
for track in self.tracks:
if not track.is_confirmed():
continue
features += track.features
print("1 features",track.track_id,np.array(features).shape)
targets += [track.track_id for _ in track.features]
print("1 targets_id",track.track_id,targets)
track.features = []
self.metric.partial_fit(
np.asarray(features), np.asarray(targets), active_targets)
第一帧
检测结果如下:
det [array([307, 97, 105, 345]), array([546, 151, 72, 207]), array([215, 154, 59, 184]), array([400, 181, 45, 126])]
得到检测结果后进入track predict阶段,但是第一帧还没有track,所以没有predict结果。
#code1
for track in self.tracks:
track.predict(self.kf)
接着进入track update阶段,首先对检测结果进行匹配
matches, unmatched_tracks, unmatched_detections = \
self._match(detections)
在匹配中,首先要将track分成confirmed_track和unconfirmed_track,
confirmed_tracks = [
i for i, t in enumerate(self.tracks) if t.is_confirmed()]
unconfirmed_tracks = [
i for i, t in enumerate(self.tracks) if not t.is_confirmed()]
显然
confirmed_track: [] unconfirmed_track: []
对confirmed_track进行级连匹配
matches_a, unmatched_tracks_a, unmatched_detections = \
linear_assignment.matching_cascade(
gated_metric, self.metric.matching_threshold, self.max_age,
self.tracks, detections, confirmed_tracks)
显然,没有匹配的track,也没有没匹配的track,只有没匹配的检测。
matches_a [] unmatched_track_a [] unmatched_detections [0, 1, 2, 3]
对所有检测创建新的track:
for detection_idx in unmatched_detections:
self._initiate_track(detections[detection_idx])
初始化代码如下:
def _initiate_track(self, detection):
mean, covariance = self.kf.initiate(detection.to_xyah())
self.tracks.append(Track(
mean, covariance, self._next_id, self.n_init, self.max_age,
detection.feature))
self._next_id += 1
通过Track类初始化一个track, self._next_id += 1,因为创建一个track后,id也多一个了。
每个track初始化的属性如下:
self.mean = mean
self.covariance = covariance
self.track_id = track_id
self.hits = 1
self.age = 1
self.time_since_update = 0
self.state = TrackState.Tentative
self.features = []
if feature is not None:
self.features.append(feature)
self._n_init = n_init
self._max_age = max_age
初始化的track,状态为Tentative,age=1,time_since_update = 0,features=[]。
默然3帧以内track的状态都是tentative。3帧以后便是conformed。30帧不更新则是deleted
第二帧
检测结果:
det [array([227, 152, 52, 189]), array([546, 153, 66, 203]), array([ 35, 52, 114, 466]), array([339, 130, 92, 278]), array([273, 134, 90, 268])]
因为第一帧得到了4个track,每个track进入predict阶段,进行卡尔曼预测,age和time_since_update都分别+1
def predict(self, kf):
"""Propagate the state distribution to the current time step using a
Kalman filter prediction step.
Parameters
----------
kf : kalman_filter.KalmanFilter
The Kalman filter.
"""
self.mean, self.covariance = kf.predict(self.mean, self.covariance)
self.age += 1
self.time_since_update += 1
此时,每个track的age和time_since_update分别为:
track update age 2 time_since_update 1
track update age 2 time_since_update 1
track update age 2 time_since_update 1
track update age 2 time_since_update 1
预测后进入track更新阶段
对预测的检测结果与之前得到的track进行匹配,首先将之前的track划分tracks为 confirmed_tracks 和unconfirmed_tracks,结果为:
confirmed_track [] unconfirmed_track [0, 1, 2, 3]
因confirmed_track为空,所以级联匹配结果为:
matches_a [] unmatched_track_a [] unmatched_detections [0, 1, 2, 3,4]
接着,unconfirmed_track跟级联匹配结果的unmatched_track_a中time_since_update=1(上一帧得到更新)的track组成候选track。
iou_track_candidates = unconfirmed_tracks + [
k for k in unmatched_tracks_a if
self.tracks[k].time_since_update == 1]
unmatched_tracks_a = [
k for k in unmatched_tracks_a if
self.tracks[k].time_since_update != 1]
候选track跟unmatched_track_a结果为:
iou_track_candidates [0, 1, 2, 3],unmatched_track_a []
对候选track和没匹配的检测进行iou匹配
matches_b, unmatched_tracks_b, unmatched_detections = \
linear_assignment.min_cost_matching(
iou_matching.iou_cost, self.max_iou_distance, self.tracks,
detections, iou_track_candidates, unmatched_detections)
IOU匹配的结果为:
matches_b [(0, 0), (1, 1), (2, 2), (3, 3)] unmatches_track_b [] unmatched_detections [4]
最后将结果合并,级联匹配到的track跟iou匹配到track合并成最终的匹配结果,级联匹配中time_since_update!=1的track和iou没匹配到的track合并成最终的没匹配的track。可以看出,上一帧有更新的confirmed track会进行级联匹配和iou匹配,上一帧没更新的confirmed track会直接成为没匹配的track,从概率上说,上一帧有更新的track,当前帧会继续更新的概率会更大。
matches = matches_a + matches_b
unmatched_tracks = list(set(unmatched_tracks_a + unmatched_tracks_b))
最后结果为:
matches: [(0, 0), (1, 1), (2, 2), (3, 3)] unmatched_tracks: [] unmatched_detections: [4]
匹配完后,会有三种结果,分别是匹配到检测,未匹配到的track和未匹配的检测框。
接下来进入track数据更新阶段
对于匹配的结果,执行
for track_idx, detection_idx in matches:
self.tracks[track_idx].update(
self.kf, detections[detection_idx])
每个track进行update
- 卡尔曼
- 检测边框特征,每个track都会存储一系列的特征,用作特征匹配
- hits
- time_since_update置0
- track状态,判断能够将状态设置为confirmed
def update(self, kf, detection):
"""Perform Kalman filter measurement update step and update the feature
cache.
Parameters
----------
kf : kalman_filter.KalmanFilter
The Kalman filter.
detection : Detection
The associated detection.
"""
self.mean, self.covariance = kf.update(
self.mean, self.covariance, detection.to_xyah())
self.features.append(detection.feature)
self.hits += 1
self.time_since_update = 0
if self.state == TrackState.Tentative and self.hits >= self._n_init:
self.state = TrackState.Confirmed
此时,所有track都能匹配到,他们的time_since_update都是0,。
对于未匹配到的track,对其状态进行标记,如果当前track状态为tentative,则该状态更新为deleted。如果太久没更新,time_since_update>max_age,该状态也将更新为deleted。
for track_idx in unmatched_tracks:
self.tracks[track_idx].mark_missed()
def mark_missed(self):
"""Mark this track as missed (no association at the current time step).
"""
if self.state == TrackState.Tentative:
self.state = TrackState.Deleted
elif self.time_since_update > self._max_age:
self.state = TrackState.Deleted
对于没有匹配到检测,创建新的track
for detection_idx in unmatched_detections:
self._initiate_track(detections[detection_idx])
然后检查所有track,将deleted状态的track删除。
self.tracks = [t for t in self.tracks if not t.is_deleted()]
第三帧
检测结果为:
[array([307, 105, 108, 325]), array([547, 148, 70, 211]), array([216, 151, 59, 190]), array([402, 183, 43, 124]), array([ 35, 87, 70, 376])]
跟踪过程跟上一帧差不多,这里检测结果跟之前的track都能匹配上,track年龄和time_since_update为
track update age 3 time_since_update 1
track update age 3 time_since_update 1
track update age 3 time_since_update 1
track update age 3 time_since_update 1
track update age 2 time_since_update 1
匹配完之后,track set的更新会将部分track的状态更新为confirmed。
我们直接看第四帧。
第四帧
检测结果:
[array([318, 119, 105, 301]), array([545, 146, 71, 215]), array([216, 151, 59, 192]), array([ 30, 75, 82, 398]), array([403, 185, 41, 121])]
得到检测结果后进入预测阶段,track更新卡尔曼预测,age和time_since_update。
track update age 4 time_since_update 1
track update age 4 time_since_update 1
track update age 4 time_since_update 1
track update age 4 time_since_update 1
track update age 3 time_since_update 1
预测完成后进入track更新阶段
首先是检测的结果跟track匹配,在匹配中,要将track分成confirmed_track和unconfirmed_track,结果如下:
confirmed_t [0, 1, 2, 3] unconfirmed [4]
因为第4个det是第2帧才检出,所以状态还是unconfirmed。
接着对confirmed的track进行级联匹配
首先是对dets和confirmed_tracks创建索引
if track_indices is None:
track_indices = list(range(len(tracks)))
if detection_indices is None:
detection_indices = list(range(len(detections)))
结果为:
track_indices [0, 1, 2, 3] detection_indices [0, 1, 2, 3, 4]
当level=0时候,track_indices_l 索引中对应的time_since_update都是1,然后得到matches_l的匹配结果 ,当然level=1时候,track_indices_l 索引中对应的time_since_update都是2,然后再次得到匹配结果与之间结果进行合并,如此循环…,也就是先匹配最近有更新的track,由近到远…,保证了最近更新track的优先级。
unmatched_detections = detection_indices
matches = []
for level in range(cascade_depth):
if len(unmatched_detections) == 0: # No detections left
break
track_indices_l = [
k for k in track_indices
if tracks[k].time_since_update == 1 + level
]
if len(track_indices_l) == 0: # Nothing to match at this level
continue
matches_l, _, unmatched_detections = \
min_cost_matching(
distance_metric, max_distance, tracks, detections,
track_indices_l, unmatched_detections)
matches += matches_l
unmatched_tracks = list(set(track_indices) - set(k for k, _ in matches))
经过级联匹配后,得到的结果为:
matches_a [(0, 0), (1, 1), (2, 2), (3, 4)] unmatched_track_a [] unmatched_detections [3]
剩下了一个没匹配的det。
unconfirmed_tracks和级联匹配中未匹配并且time_since_update =1的track组成了候选tracks。
iou_track_candidates [4]
候选tracks跟未匹配的det进行IOU匹配,结果如下:
matches_b [(4, 3)] unmatches_track_b [] unmatched_detections []
最终结果如下:
matches: [(0, 0), (1, 1), (2, 2), (3, 4), (4, 3)] unmatched_tracks: [] unmatched_detections: []
匹配结束后,将当前帧dets的feature更新到map(trackid->feature)中。
active_targets = [t.track_id for t in self.tracks if t.is_confirmed()]
features, targets = [], []
for track in self.tracks:
if not track.is_confirmed():
continue
features += track.features
targets += [track.track_id for _ in track.features]
track.features = []
self.metric.partial_fit(
np.asarray(features), np.asarray(targets), active_targets)
def partial_fit(self, features, targets, active_targets):
for feature, target in zip(features, targets):
self.samples.setdefault(target, []).append(feature)
if self.budget is not None:
self.samples[target] = self.samples[target][-self.budget:]
self.samples = {k: self.samples[k] for k in active_targets}
整个deepsort过程就这样子了,我们来看看更加细节的问题。
IOU匹配
如何得到代价矩阵?
初始化代价矩阵,矩阵(i,j)代表track i和det j的代价。然后计算卡尔曼滤波预测的bbx和det的IOU,代价=1-IOU。但是如果track已经有一帧以上(包含)没有更新,那么cost将会设置得很大,即为INFTY( 1e+5)。
def iou_cost(tracks, detections, track_indices=None,
detection_indices=None):
if track_indices is None:
track_indices = np.arange(len(tracks))
if detection_indices is None:
detection_indices = np.arange(len(detections))
cost_matrix = np.zeros((len(track_indices), len(detection_indices)))
for row, track_idx in enumerate(track_indices):
if tracks[track_idx].time_since_update > 1:
cost_matrix[row, :] = linear_assignment.INFTY_COST
continue
bbox = tracks[track_idx].to_tlwh()
candidates = np.asarray([detections[i].tlwh for i in detection_indices])
cost_matrix[row, :] = 1. - iou(bbox, candidates)
return cost_matrix
得到代价矩阵后,如果元素大于max_distance,该元素会设置为max_distance + 1e-5
cost_matrix[cost_matrix > max_distance] = max_distance + 1e-5
第二帧代价矩阵为:
[[0.04281178 1. 1. 0.96899767 1. ]
[1. 0.03566279 1. 1. 1. ]
[1. 1. 0.04389799 1. 1. ]
[0.95802783 1. 1. 0.08525083 1. ]]
#处理后
[[0.04281178 0.70001 0.70001 0.70001 0.70001 ]
[0.70001 0.03566279 0.70001 0.70001 0.70001 ]
[0.70001 0.70001 0.04389799 0.70001 0.70001 ]
[0.70001 0.70001 0.70001 0.08525083 0.70001 ]]
得到代价矩阵后,将其输入到匈牙利算法中
row_indices, col_indices = linear_assignment(cost_matrix)
当然也不是所有track和det都能得到匹配,iou匹配中把大于max_distacne的被认为是不匹配的。
matches, unmatched_tracks, unmatched_detections = [], [], []
for col, detection_idx in enumerate(detection_indices):
if col not in col_indices:
unmatched_detections.append(detection_idx)
for row, track_idx in enumerate(track_indices):
if row not in row_indices:
unmatched_tracks.append(track_idx)
for row, col in zip(row_indices, col_indices):
track_idx = track_indices[row]
detection_idx = detection_indices[col]
if cost_matrix[row, col] > max_distance:
unmatched_tracks.append(track_idx)
unmatched_detections.append(detection_idx)
else:
matches.append((track_idx, detection_idx))
级联匹配
看看如何得到代价矩阵。一个track中保存了多个det的特征,所以该track跟当前帧某个det的特征会有多个余弦距离,取最小值作为该track与该det的最终余弦距离,然后再结合马氏矩阵进行处理。
def gated_metric(tracks, dets, track_indices, detection_indices):
features = np.array([dets[i].feature for i in detection_indices])
targets = np.array([tracks[i].track_id for i in track_indices])
cost_matrix = self.metric.distance(features, targets) #计算代价矩阵
cost_matrix = linear_assignment.gate_cost_matrix( #结合马氏矩阵进行处理
self.kf, cost_matrix, tracks, dets, track_indices, #
detection_indices)
return cost_matrix
def distance(self, features, targets):
cost_matrix = np.zeros((len(targets), len(features)))
for i, target in enumerate(targets):
cost_matrix[i, :] = self._metric(self.samples[target], features)
return cost_matrix
def _nn_cosine_distance(x, y):
distances = _cosine_distance(x, y)
return distances.min(axis=0) #取最小值
首先将det转换成xyah格式,
measurements = np.asarray(
[detections[i].to_xyah() for i in detection_indices])
接着计算track预测结果和检测结果的马氏距离,将马氏距离中大于gating_threshold( 9.4877 )的代价设置为gated_cost(100000.0)
for row, track_idx in enumerate(track_indices):
track = tracks[track_idx]
gating_distance = kf.gating_distance(
track.mean, track.covariance, measurements, only_position)
cost_matrix[row, gating_distance > gating_threshold] = gated_cost
最后将代价矩阵中大于max_distance的设置为max_distance(级接匹配中设为0.2) + 1e-5。
在第四帧中,余弦距离得到的代价矩阵为
[[0.02467382 0.29672492 0.14992237 0.20593166 0.25746107]
[0.27289903 0.01389802 0.2490201 0.26275396 0.18523771]
[0.1549592 0.25630915 0.00923228 0.10906434 0.27596951]
[0.26783013 0.19509423 0.26934785 0.24842238 0.01052856]]
计算马氏距离,将马氏距离作用于余弦距离,将马氏大于gating_threshold的余弦代价设置为gated_cost(100000.0)。
然后得到的结果为
[[2.46738195e-02 1.00000000e+05 1.00000000e+05 1.00000000e+05
1.00000000e+05]
[1.00000000e+05 1.38980150e-02 1.00000000e+05 1.00000000e+05
1.00000000e+05]
[1.00000000e+05 1.00000000e+05 9.23228264e-03 1.00000000e+05
1.00000000e+05]
[1.00000000e+05 1.00000000e+05 1.00000000e+05 1.00000000e+05
1.05285645e-02]]
代价矩阵中大于max_distance的设置为max_distance(级接匹配中设为0.2) + 1e-5,最终得到的代价矩阵为:
[[0.02467382 0.20001 0.20001 0.20001 0.20001 ]
[0.20001 0.01389802 0.20001 0.20001 0.20001 ]
[0.20001 0.20001 0.00923228 0.20001 0.20001 ]
[0.20001 0.20001 0.20001 0.20001 0.01052856]]
然后将代价矩阵输入到匈牙利算法中求解。
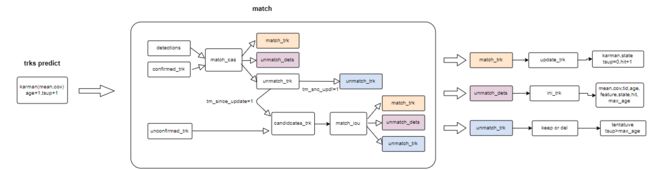
deepsrot步骤如下
- track划分为uncomfirmed_track和comfirmed_track
- confirmed_track和det进行级联匹配
- 1.计算track和检测结果的特征余弦距离cost matrix
- 2.计算马氏距离,将马氏距离作用与cost matrix,若马氏距离中大于gating_threshold,cost matrix中相应的代价设置为gated_cost。
- 3.将const matrix中大于max_distance的设置为max_distance
- 4.匈牙利求解,删除匹配值较大的结果。
- 根据track的time_since_update,循环1-4,并合并结果。
- unconfirmed_track和级联匹配中未能匹配并且time_since_update=1的track组成候选track,候选track和没匹配的det进行iou匹配
- 对预测结果和检测结果计算iou代价矩阵
- 匈牙利求解
- 合并级联匹配和iou匹配结果。
- 对于最终匹配到track进行以下操作
- 卡尔曼更新
- 存储边框特征
- hits+1
- time_since_update置0
- track状态更新,判断能够将状态设置为confirmed
- 对于最终未能匹配到的track进行以下操作
- 判断保留还是删除track,如果30帧没能更新,就删除。
- 对于最终未能匹配到的det创建新的track
整个流程如下图
欢迎指正!
ref:
Deep Sort 算法代码解读
[SIMPLE ONLINE AND REALTIME TRACKING WITH A DEEP ASSOCIATION METRIC](https:/