Xgboost模型调参
第一步:导包
import math
import datetime
import time
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.metrics import roc_curve,auc,accuracy_score,classification_report,confusion_matrix
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler,MaxAbsScaler
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression,LogisticRegressionCV
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier,GradientBoostingClassifier
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split,GridSearchCV,StratifiedKFold,cross_val_score
from sklearn.feature_selection import RFECV
from scorecardbundle.feature_discretization import ChiMerge as cm
from scorecardbundle.feature_discretization import FeatureIntervalAdjustment as fia
from scorecardbundle.feature_encoding import WOE as woe
from scorecardbundle.feature_selection import FeatureSelection as fs
from scorecardbundle.model_training import LogisticRegressionScoreCard as lrsc
from scorecardbundle.model_evaluation import ModelEvaluation as me
from scorecardbundle.model_interpretation import ScorecardExplainer as mise
import xgboost as xgb
from xgboost import plot_importance
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import warnings
from xgboost.sklearn import XGBClassifier
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
from sklearn import metrics
# 解决中文乱码问题
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif']=['SimHei']
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus']=False
pd.set_option('max_columns',1000)
pd.set_option('max_row',300)
de_date = time.strftime('%Y%m%d',time.localtime(time.time()))
de_date = '202205'
第二步:读取相关文件
df = pd.read_csv(f'../data/{de_date}/xxx.csv')
df.columns = []
df.head()
第三步:缺失值填充
df = df.dropna(axis=0,how='all',subset=df.columns[2:])
df.fillna(0, inplace=True)
第四步:转成列表,查看数据,分训练集和测试集
df.columns.tolist()
df.describe()
df_x = df.iloc[:,2:-1]
df_y = df.iloc[:,-1]
df_x.shape
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X_train, X_test, Y_train, Y_test = train_test_split(df_x, df_y, test_size=0.3, random_state=42)
第五步:采用交叉验证方法对数据进行训练和验证
xgbc_model=XGBClassifier()
print("\n使用5折交叉验证方法得随机森林模型的准确率(每次迭代的准确率的均值):")
print("\tXGBoost模型:",cross_val_score(xgbc_model,X_train,Y_train,cv=5).mean())
# 性能评估以XGboost为例
xgb = XGBClassifier()
# 对训练集训练模型
xgb.fit(X_train,Y_train)
# 对测试集进行预测
y_pred = xgb.predict(X_test)
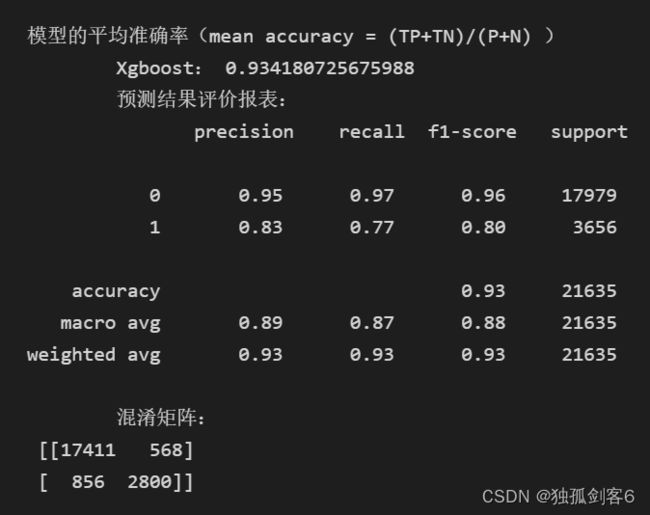
print("\n模型的平均准确率(mean accuracy = (TP+TN)/(P+N) )")
print("\tXgboost:",xgb.score(X_test,Y_test))
# print('(y_test,y_pred)', y_test,y_pred) print("\n性能评价:")
print("\t预测结果评价报表:\n", metrics.classification_report(Y_test,y_pred))
print("\t混淆矩阵:\n", metrics.confusion_matrix(Y_test,y_pred))
第六步:Xgboost参数调优的一般步骤:
1、学习速率(learning rate)。在0.05~0.3之间波动,通常首先设置为0.1。
2、进行决策树特定参数调优(max_depth , min_child_weight , gamma , subsample,colsample_bytree)在确定一棵树的过程中,我们可以选择不同的参数。
3、正则化参数的调优。(lambda , alpha)。这些参数可以降低模型的复杂度,从而提高模型的表现。
4、降低学习速率,确定理想参数。
#max_depth和min_child_weight参数调优
# max_depth和min_child_weight参数对最终结果有很大的影响。max_depth通常在3-10之间,min_child_weight。采用栅格搜索(grid search),我们先大范围地粗略参数,然后再小范围的微调。
# 网格搜索scoring = 'roc_auc' 只支持二分类,多分类需要修改scoring(默认支持多分类)
param_test1 = {
'max_depth':[i for i in range(3,10,2)],
'min_child_weight':[i for i in range(1,6,2)]
}
from sklearn import svm, datasets
gsearch = GridSearchCV(
estimator = XGBClassifier(
learning_rate =0.1,
n_estimators=140, max_depth=5,
min_child_weight=1,
gamma=0,
subsample=0.8,
colsample_bytree=0.8,
objective= 'binary:logistic',
nthread=4,
scale_pos_weight=1,
seed=27),
param_grid = param_test1,
scoring='roc_auc',
n_jobs=4,
iid=False,
cv=5)
gsearch.fit(X_train,Y_train)
print('max_depth_min_child_weight')
print('gsearch1.grid_scores_', gsearch.cv_results_)#grid_scores_被cv_results_替换了
print('gsearch1.best_params_', gsearch.best_params_)
print('gsearch1.best_score_', gsearch.best_score_)
# gamma参数调优
# 在已经调整好其他参数的基础上,我们可以进行gamma参数的调优了。Gamma参数取值范围很大,这里我们设置为5,其实你也可以取更精确的gamma值。
param_test3 = {
'gamma':[i/10.0 for i in range(0,5)]
}
gsearch = GridSearchCV(
estimator = XGBClassifier(
learning_rate =0.1,
n_estimators=140,
max_depth=9,
min_child_weight=3,
gamma=0,
subsample=0.8,
colsample_bytree=0.8,
objective= 'binary:logistic',
nthread=4,
scale_pos_weight=1,
seed=27),
param_grid = param_test3,
scoring='roc_auc',
n_jobs=4,
iid=False,
cv=5)
gsearch.fit(X_train,Y_train)
print('gamma')
print('gsearch1.grid_scores_', gsearch.cv_results_)
print('gsearch1.best_params_', gsearch.best_params_)
print('gsearch1.best_score_', gsearch.best_score_)
#调整subsample 和 colsample_bytree参数
# 尝试不同的subsample 和 colsample_bytree 参数。我们分两个阶段来进行这个步骤。这两个步骤都取0.6,0.7,0.8,0.9作为起始值。
#取0.6,0.7,0.8,0.9作为起始值
param_test4 = {
'subsample':[i/10.0 for i in range(6,10)],
'colsample_bytree':[i/10.0 for i in range(6,10)]
}
gsearch = GridSearchCV(
estimator = XGBClassifier(
learning_rate =0.1,
n_estimators=140,
max_depth=9,
min_child_weight=3,
gamma=0.1,
subsample=0.8,
colsample_bytree=0.8,
objective= 'binary:logistic',
nthread=4,
scale_pos_weight=1,
seed=27),
param_grid = param_test4,
scoring='roc_auc',
n_jobs=4,
iid=False,
cv=5)
gsearch.fit(X_train,Y_train)
print('subsample_colsample_bytree------------------')
print('gsearch1.grid_scores_', gsearch.cv_results_)
print('gsearch1.best_params_', gsearch.best_params_)
print('gsearch1.best_score_', gsearch.best_score_)
#正则化参数调优reg_alpha
# 由于gamma函数提供了一种更加有效的降低过拟合的方法,大部分人很少会用到这个参数,但是我们可以尝试用一下这个参数。
from sklearn import svm, datasets
param_test6 = {
'reg_alpha':[1e-5, 1e-2, 0.1, 1, 100]
}
gsearch = GridSearchCV(
estimator = XGBClassifier(
learning_rate =0.1,
n_estimators=140,
max_depth=9,
min_child_weight=3,
gamma=0.1,
subsample=0.8,
colsample_bytree=0.7,
objective= 'binary:logistic',
nthread=4,
scale_pos_weight=1,
seed=27),
param_grid = param_test6,
scoring='roc_auc',
n_jobs=4,
iid=False,
cv=5)
gsearch.fit(X_train,Y_train)
print('reg_alpha------------------')
print('gsearch1.grid_scores_', gsearch.cv_results_)
print('gsearch1.best_params_', gsearch.best_params_)
print('gsearch1.best_score_', gsearch.best_score_)
#正则化参数调优reg_lambda
# 由于gamma函数提供了一种更加有效的降低过拟合的方法,大部分人很少会用到这个参数,但是我们可以尝试用一下这个参数。
param_test7 = {
'reg_lambda':[1e-5, 1e-2, 0.1, 1, 100]
}
gsearch = GridSearchCV(
estimator = XGBClassifier(
learning_rate =0.1,
n_estimators=140,
max_depth=9,
min_child_weight=3,
gamma=0.1,
subsample=0.8,
colsample_bytree=0.7,
objective= 'binary:logistic',
nthread=4,
scale_pos_weight=1,
seed=27),
param_grid = param_test7,
scoring='roc_auc',
n_jobs=4,
iid=False,
cv=5)
gsearch.fit(X_train,Y_train)
print('reg_lambda------------------')
print('gsearch1.grid_scores_', gsearch.cv_results_)
print('gsearch1.best_params_', gsearch.best_params_)
print('gsearch1.best_score_', gsearch.best_score_)
参考文档