激光雷达与相机融合(一)
一.激光雷达点云俯视图提取
文末有相应的代码数据包免费下载链接。
将激光雷达点云投影到俯视图平面上,同时将距离的远近利用颜色表示出来。
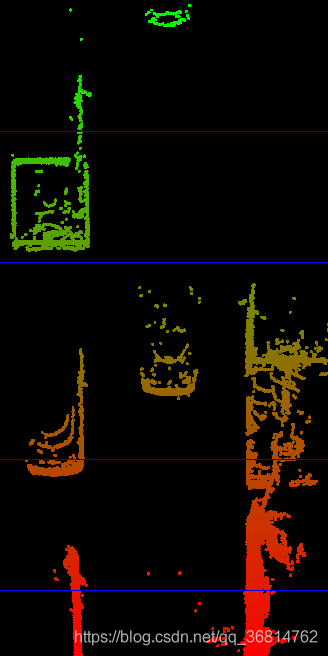
这里的滤除地面只是简单的利用高度值将地面去除。会存在效果不好的情况。代码即相应注释。
#include 二.将激光雷达点云投影到图像上
要将点云投影到图片上,需要知道激光雷达与相机之间的位置转换矩阵以及相机内参。
这里涉及的坐标转换流程是:激光雷达坐标系—》摄像头坐标系—》图像平面坐标系。中间过程相应的就涉及到两个转换矩阵。
![]()
这里采用的KITTI的数据图片,其中(R|T)就是激光雷达到相机的转换矩阵(4X4),P_rect_xx是相机的内参矩阵(3x4),而中间多一个R_rect_00是两个相机之间的转换矩阵(4X4),因为KITTI设备采集车上安装有两个摄像头,为了让多个摄像头的检测画面能够对应,所以需要转换矩阵来将各个摄像头的数据画面转换到相同的平面下,这里所用的R_rect_00就是将左侧灰度摄像头转换到共同平面的转换矩阵。X则代表激光雷达点(4X1)。
激光雷达与相机外参
calib_time: 15-Mar-2012 11:37:16
R: 7.533745e-03 -9.999714e-01 -6.166020e-04 1.480249e-02 7.280733e-04 -9.998902e-01 9.998621e-01 7.523790e-03 1.480755e-02
T: -4.069766e-03 -7.631618e-02 -2.717806e-01
…
相机与相机外参以及相机内参
calib_time: 09-Jan-2012 13:57:47
…
//使相机图像平面共面,所以只需要旋转矩阵。
R_rect_00: 9.999239e-01 9.837760e-03 -7.445048e-03 -9.869795e-03 9.999421e-01 -4.278459e-03 7.402527e-03 4.351614e-03 9.999631e-01
P_rect_00: 7.215377e+02 0.000000e+00 6.095593e+02 0.000000e+00 0.000000e+00 7.215377e+02 1.728540e+02 0.000000e+00 0.000000e+00 0.000000e+00 1.000000e+00 0.000000e+00
…
#include 下载代码后:
进入与src同级的目录
mkdir build
cd build
cmake ..
make
./project_lidar_to_camera
./show_lidar_top_view
即可运行,注意修改Cmakelist文件中opencv版本,修改为与本身安装的匹配。
另外编译时候如果找不到opencv头文件,参考:博客
注意,添加的路径要与cmakelist里的版本对应。
代码及数据下载路径:https://github.com/jhzhang19/sensor_fusion/tree/master

