2020 cs231n 作业1笔记 knn
作业链接:cs231n官网Assignment 1
刚开始遇到一个坑,就是py文件老是没保存,后来才知道需要运行.ipynb文件后面的代码来保存py文件
打开knn.ipynb,首先要实现的是cs231n/classifiers/k_nearest_neighbor.py文件里的compute_distances_two_loops(self, X)这个函数。函数计算的是L2 distance。
公式:
for i in range(num_test):
for j in range(num_train):
#####################################################################
# TODO: #
# Compute the l2 distance between the ith test point and the jth #
# training point, and store the result in dists[i, j]. You should #
# not use a loop over dimension, nor use np.linalg.norm(). #
#####################################################################
# *****START OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)*****
dists[i,j] = np.sqrt(np.sum(np.square(X[i] - self.X_train[j])))
# *****END OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)*****
return dists然后需要实现cs231n/classifiers/k_nearest_neighbor.py文件里的predict_labels(self, dists, k=1)函数,
for i in range(num_test):
# A list of length k storing the labels of the k nearest neighbors to
# the ith test point.
closest_y = []
#########################################################################
# TODO: #
# Use the distance matrix to find the k nearest neighbors of the ith #
# testing point, and use self.y_train to find the labels of these #
# neighbors. Store these labels in closest_y. #
# Hint: Look up the function numpy.argsort. #
#########################################################################
# *****START OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)*****
#从dists每行中选出前k个距离最短的k列的索引
#就是找与第i的test样本距离最短的前k个测试样本的标签
min_idx = np.argsort(dists[i,:])[0:k]
#从k个标签中找出出现次数最多的那个标签
closest_y = Counter(self.y_train[min_idx]).most_common(1)[0][0]
# *****END OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)*****
#########################################################################
# TODO: #
# Now that you have found the labels of the k nearest neighbors, you #
# need to find the most common label in the list closest_y of labels. #
# Store this label in y_pred[i]. Break ties by choosing the smaller #
# label. #
#########################################################################
# *****START OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)*****
y_pred[i] = closest_y
# *****END OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)*****接下来实现计算dists的one loop版本compute_distances_one_loop(self, X)
for i in range(num_test):
#######################################################################
# TODO: #
# Compute the l2 distance between the ith test point and all training #
# points, and store the result in dists[i, :]. #
# Do not use np.linalg.norm(). #
#######################################################################
# *****START OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)*****
dists[i] = np.sqrt(np.sum(np.square(X[i] - self.X_train),axis = 1))
# *****END OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)*****接着是计算dists的no loop版本compute_distances_no_loops(self, X):
这里不好直接计算![]() 和
和 ![]() 的距离,所以用
的距离,所以用![]() 拆开来算的,
拆开来算的,
#########################################################################
# TODO: #
# Compute the l2 distance between all test points and all training #
# points without using any explicit loops, and store the result in #
# dists. #
# #
# You should implement this function using only basic array operations; #
# in particular you should not use functions from scipy, #
# nor use np.linalg.norm(). #
# #
# HINT: Try to formulate the l2 distance using matrix multiplication #
# and two broadcast sums. #
#########################################################################
# *****START OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)*****
#(a+b)^2 = a^2 + b^2 + 2ab
ab = np.dot(X, self.X_train.T)
a2 = np.sum(np.square(X), axis=1).reshape(-1, 1)
b2 = np.sum(np.square(self.X_train.T), axis=0).reshape(1, -1)
dists = -2 * ab + a2 + b2
dists = np.sqrt(dists)
# *****END OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)*****现在dists计算的三种版本都实现了,跑来看看效率:
Two loop version took 36.053391 seconds
One loop version took 30.978007 seconds
No loop version took 0.544291 seconds
可以看到使用矩阵方式的效率会高很多
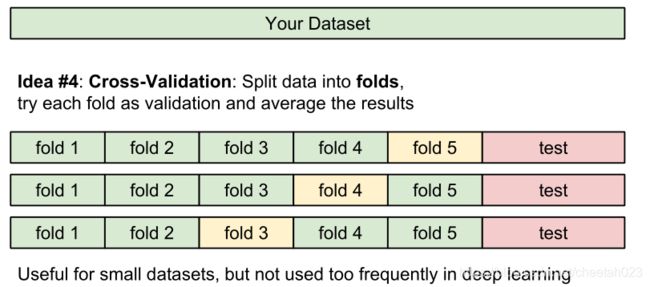
最后就是使用Cross-validation来寻找最好的超参数k
################################################################################
# TODO: #
# Split up the training data into folds. After splitting, X_train_folds and #
# y_train_folds should each be lists of length num_folds, where #
# y_train_folds[i] is the label vector for the points in X_train_folds[i]. #
# Hint: Look up the numpy array_split function. #
################################################################################
# *****START OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)*****
print(X_train.shape)
print(y_train.shape)
X_train_folds = np.split(X_train,5,axis=0)
y_train_folds = np.split(y_train,5,axis=0)
# *****END OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)*****
# A dictionary holding the accuracies for different values of k that we find
# when running cross-validation. After running cross-validation,
# k_to_accuracies[k] should be a list of length num_folds giving the different
# accuracy values that we found when using that value of k.
k_to_accuracies = {}
################################################################################
# TODO: #
# Perform k-fold cross validation to find the best value of k. For each #
# possible value of k, run the k-nearest-neighbor algorithm num_folds times, #
# where in each case you use all but one of the folds as training data and the #
# last fold as a validation set. Store the accuracies for all fold and all #
# values of k in the k_to_accuracies dictionary. #
################################################################################
# *****START OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)*****
for k in k_choices:
accuracies = []
for i in range(num_folds):
#每次选第i个集合为验证集,剩下的集合拼接为测试集
X_train_cv = np.vstack(X_train_folds[0:i] + X_train_folds[i+1:])
y_train_cv = np.hstack(y_train_folds[0:i] + y_train_folds[i+1:])
X_cv_cv = X_train_folds[i]
y_cv_cv = y_train_folds[i]
classifier.train(X_train_cv, y_train_cv)
dists = classifier.compute_distances_no_loops(X_cv_cv)
y_cv_pred = classifier.predict_labels(dists, k=k)
num_correct = np.sum(y_cv_pred == y_cv_cv)
accuracy = float(num_correct) / y_cv_cv.shape[0]
accuracies.append(accuracy)
k_to_accuracies[k] = accuracies
# *****END OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)*****我这边跑出来的最好的k=8
对应的test data上的正确率:
Got 147 / 500 correct => accuracy: 0.294000
最后记得运行保存文件:
import os
FOLDER_TO_SAVE = os.path.join('drive/My Drive/', FOLDERNAME)
FILES_TO_SAVE = ['cs231n/classifiers/k_nearest_neighbor.py']
for files in FILES_TO_SAVE:
with open(os.path.join(FOLDER_TO_SAVE, '/'.join(files.split('/')[1:])), 'w') as f:
f.write(''.join(open(files).readlines()))