Java中常见的文件操作
作者:~小明学编程
文章专栏:JavaEE
格言:热爱编程的,终将被编程所厚爱。
目录
操作文件
File类
属性
构造方法
常见方法
重要方法的操作演示
文件内容的读写
FileInputStream
OutputStream
按照字符读入
按照字符写入
实战用法
操作文件
Java 中通过 java.io.File 类来对一个文件(包括目录)进行抽象的描述。注意,有 File 对象,并不
代表真实存在该文件。
File类
属性
| 修饰符及类型 | 属性 | 说明 |
| static String | pathSeparator | 依赖于系统的路径分隔符,String 类型的表示 |
| static char | pathSeparator | 依赖于系统的路径分隔符,char 类型的表示 |
构造方法
| 签名 | 说明 |
| File(File parent, String child) |
根据父目录 + 孩子文件路径,创建一个新的 File 实例 |
| File(String pathname) | 根据文件路径创建一个新的 File 实例,路径可以是绝对路径或者 相对路径 |
| File(String parent, String child) |
根据父目录 + 孩子文件路径,创建一个新的 File 实例,父目录用 路径表示 |
常见方法
| 修饰符及返回 值类型 |
方法签名 | 说明 |
| String | getParent() | 返回 File 对象的父目录文件路径 |
| String | getName() | 返回 FIle 对象的纯文件名称 |
| String | getPath() | 返回 File 对象的文件路径 |
| String | getAbsolutePath() | 返回 File 对象的绝对路径 |
| String | getCanonicalPath() | 返回 File 对象的修饰过的绝对路径 |
| boolean | exists() | 判断 File 对象描述的文件是否真实存在 |
| boolean | isDirectory() | 判断 File 对象代表的文件是否是一个目录 |
| boolean | isFile() | 判断 File 对象代表的文件是否是一个普通文件 |
| boolean | createNewFile() | 根据 File 对象,自动创建一个空文件。成功创建后返 回 true |
| boolean | delete() | 根据 File 对象,删除该文件。成功删除后返回 true |
| void | deleteOnExit() | 根据 File 对象,标注文件将被删除,删除动作会到 JVM 运行结束时才会进行 |
| String[] | list() | 返回 File 对象代表的目录下的所有文件名 |
| File[] | listFiles() | 返回 File 对象代表的目录下的所有文件,以 File 对象 表示 |
| boolean | mkdir() | 创建 File 对象代表的目录 |
| boolean | mkdirs() | 创建 File 对象代表的目录,如果必要,会创建中间目 录 |
| boolean | renameTo(File dest) |
进行文件改名,也可以视为我们平时的剪切、粘贴操 作 |
| boolean | canRead() | 判断用户是否对文件有可读权限 |
| boolean | canWrite() | 判断用户是否对文件有可写权限 |
重要方法的操作演示
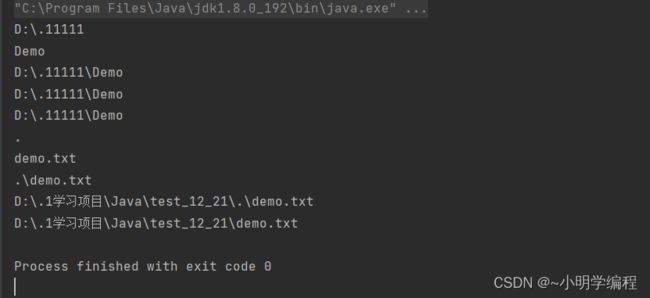
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File file = new File("D:\\.11111\\Demo");
System.out.println(file.getParent());//获取父目录的文件名称
System.out.println(file.getName());//获取文件名
System.out.println(file.getPath());//获取到文件的路径
System.out.println(file.getAbsoluteFile());//返回 File 对象的绝对路径
System.out.println(file.getCanonicalPath());//返回 File 对象的修饰过的绝对路径
File file1 = new File("./demo.txt");//输入一个基准路径
System.out.println(file1.getParent());//获取父目录的文件名称
System.out.println(file1.getName());//获取文件名
System.out.println(file1.getPath());//获取到文件的路径(构造方法中的路径)
System.out.println(file1.getAbsoluteFile());//在基准路径的基础上把相对路径给拼接上去
System.out.println(file1.getCanonicalPath());//返回 File 对象的修饰过的绝对路径
}
首先给大家介绍的就是绝对路径和相对路径,绝对路径就是我们常见的D:\.1学习资料\JavaEE初阶
这种写法,而相对路径就是./test.txt 的这种写法其中的点就是我们当前所在的路径。
这是上述代码的打印结果,值得注意的是 getAbsoluteFile()是对我们相对路径和基准路径的一个拼接,而getCanonicalPath()是直接打印这个完整的路径。
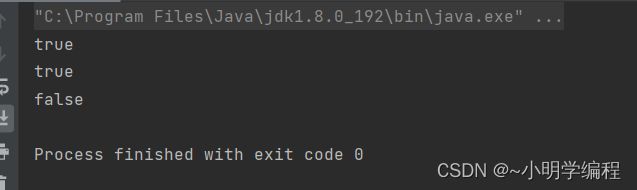
public static void main(String[] args) {
File file = new File("D:\\.11111\\Demo");
System.out.println(file.exists());//判断对象描述的文件是否存在
System.out.println(file.isDirectory());//判断对象描述的是否是一个目录
System.out.println(file.isFile());//判断当前是否是一个普通的文件
} public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File file = new File("./test.txt");
System.out.println(file.exists());
System.out.println("创建文件");
file.createNewFile();//创建文件
System.out.println(file.exists());
} public static void main(String[] args) {
File file = new File("./test.txt");
System.out.println(file.exists());//true
file.delete();//删除文件
System.out.println(file.exists());//false
} public static void main(String[] args) {
File file = new File("./aaa/bbb/ccc/ddd");
file.mkdirs();//创建多级目录
}
public static void main1(String[] args) {
File file = new File("./aaa");
file.mkdir();//创建该目录
System.out.println(file.isDirectory());
} public static void main(String[] args) {
File file = new File("./");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(file.list()));//返回当前目录下的所有文件
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(file.listFiles()));//返回当前目录下的所有文件,以file对象表示
} public static void main(String[] args) {
File file = new File("./aaa");
File file1 = new File("./www");
file.renameTo(file1);//更改当前目录的名字
}文件内容的读写
FileInputStream
常用方法
| 修饰符及 返回值类 型 |
方法签名 | 说明 |
| int | read() | 读取一个字节的数据,返回 -1 代表已经完全读完了 |
| int | read(byte[] b) | 最多读取 b.length 字节的数据到 b 中,返回实际读到的数 量;-1 代表以及读完了 |
| int | read(byte[] b, int off, int len) |
最多读取 len - off 字节的数据到 b 中,放在从 off 开始,返 回实际读到的数量;-1 代表以及读完了 |
| void | close() | 关闭字节流 |
public static void main(String[] args){
//构造方法里面的路径可以是绝对路径也可以是相对路径
InputStream input = null;
try {
input = new FileInputStream("D:\\.11111\\Demo\\as.txt");
int b = 0;
while (b!=-1) {
b = input.read();
System.out.println(b);
}
input.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
input.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}这里要注意我们的回收资源,但是这种写法有些的繁琐,所以我们就有了下面的这种写法。
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (InputStream input = new FileInputStream("D:\\.11111\\Demo\\as.txt")){//自动回收
int b = 0;
while (b!=-1) {
b = input.read();
System.out.println(b);
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}我们在try里面把对象就给构造出来,这样就不用我们再去回收资源了,但是这种写法要保证我们当前的类是实现了Closeable接口的。
public static void main3(String[] args) {
try(InputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream("D:\\.11111\\Demo\\as.txt")) {
while (true) {
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
int len = inputStream.read(bytes);//返回的是读到的长度
if (len==-1) {
break;
}
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
System.out.println(bytes[i]);
}
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}我们也可以一次性读多个字节然后把读到的字节放到数组里面去。
OutputStream
| 修饰 符及 返回 值类 型 |
方法签名 | 说明 |
| void | write(int b) | 写入要给字节的数据 |
| void | write(byte[] b) |
将 b 这个字符数组中的数据全部写入 os 中 |
| int | write(byte[] b, int off, int len) |
将 b 这个字符数组中从 off 开始的数据写入 os 中,一共写 len 个 |
| void | close() | 关闭字节流 |
| void | flush() | 重要:我们知道 I/O 的速度是很慢的,所以,大多的 OutputStream 为 了减少设备操作的次数,在写数据的时候都会将数据先暂时写入内存的 一个指定区域里,直到该区域满了或者其他指定条件时才真正将数据写 入设备中,这个区域一般称为缓冲区。但造成一个结果,就是我们写的 数据,很可能会遗留一部分在缓冲区中。需要在最后或者合适的位置, 调用 flush(刷新)操作,将数据刷到设备中 |
public static void main2(String[] args) {
//按照字节来写文件
try(OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream("D:\\.11111\\Demo\\as.txt")){
out.write(97);
out.write(98);
out.write(99);
out.write(100);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}按照字符读入
public static void main1(String[] args) {
try(Reader reader = new FileReader("D:\\.11111\\Demo\\as.txt")){
//按照字符来读文件
while (true) {
char[] buffer = new char[1024];
int len = reader.read(buffer);
if (len==-1) {
break;
}
// for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
// System.out.println(buffer[i]);
// }
String str = new String(buffer,0,len);
System.out.println(str);
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}按照字符写入
//按照字符来写文件
public static void main(String[] args) {
try(Writer writer = new FileWriter("D:\\.11111\\Demo\\as.txt")){
writer.write("qweq");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}实战用法
扫描指定目录,并找到名称中包含指定字符的所有普通文件(不包含目录),并且后续询问用户是否要删除该文件。
//删除文件的操作
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入你要删除文件所存在的根路径");
String root = scanner.next();
System.out.println("请输入想要删除的文件名");
String name = scanner.next();
File file = new File(root);
//如果当前文件不是目录
if (!file.isDirectory()){
System.out.println("您所输入的文件路径有误");
}
scannerDir(file,name);
}
private static void scannerDir(File root, String name) throws IOException {
File[] files = root.listFiles();
if (files==null) {
return;
}
for (File file:files) {
if (file.isFile()) {
if (file.getName().contains(name)) {
deleteFile(file);
}
} else if (file.isDirectory()) {//如果当前的文件还是目录那就往下递归
scannerDir(file,name);
}
}
}
private static void deleteFile(File file) throws IOException {
System.out.println("是否确定要删除文件(Y/N):"+file.getCanonicalPath());
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
String choice = scanner.next();
if (choice.equals("Y")) {
file.delete();
System.out.println("文件删除成功");
} else {
System.out.println("删除失败");
}
}
进行普通文件的复制。
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入源文件的路径:");
String src = scanner.next();
System.out.println("请输入想要复制的文件所在的路径");
String dest = scanner.next();
File file = new File(src);
if (!file.isFile()) {
System.out.println("文件的路径不存在");
}
try(InputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream(src)) {
try(OutputStream outputStream = new FileOutputStream(dest)){
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
int len = 0;
while(true) {
len = inputStream.read(bytes);
if (len==-1) {
break;
}
outputStream.write(bytes,0,len);
System.out.println("复制完毕");
}
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}扫描指定目录,并找到名称或者内容中包含指定字符的所有普通文件(不包含目录)
//查找指定字符串所在的路径
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入根路径:");
String src = scanner.next();
System.out.println("请输入想要查找的字符串:");
String str = scanner.next();
File file = new File(src);
if (!file.isDirectory()) {
System.out.println("当前所在的路径不存在");
return;
}
scannerDir(file,str);
}
private static void scannerDir(File file, String str) {
File[] files = file.listFiles();//列出当前的目录
if (files==null) {
return;
}
for (File file1:files) {
if (file1.isFile()) {
//查找当前文本
if (containStr(file1,str)) {
System.out.println(file1.getAbsoluteFile());
}
}else if (file.isDirectory()) {
scannerDir(file1,str);
}
}
}
private static boolean containStr(File file1, String str) {
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
try(Reader reader = new FileReader(file1)) {
char[] chars = new char[1024];
while (true) {
int len = reader.read(chars);
if (len==-1) {
break;
}
stringBuilder.append(chars,0,len);
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return stringBuilder.indexOf(str)!=-1;
}