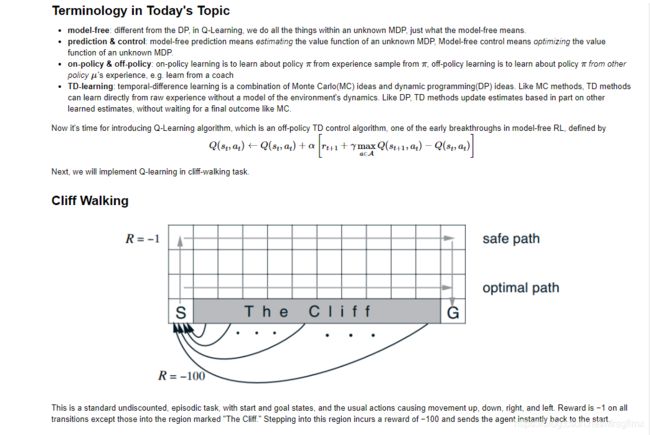
强化学习 之 Q-Learning与SARSA
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import random
import time
#定义一个类,对格子宽高和智能体的初始位置进行定义
class Env():
def __init__(self, length, height):
# define the height and length of the map
self.length = length
self.height = height
# define the agent's start position
self.x = 0
self.y = 0
# 对智能体在格子中的行进每一步的图像进行渲染出来
def render(self, frames=50):
for i in range(self.height):
if i == 0: # cliff is in the line 0
line = ['S'] + ['x']*(self.length - 2) + ['T'] # 'S':start, 'T':terminal, 'x':the cliff
else:
line = ['.'] * self.length
if self.x == i:
line[self.y] = 'o' # mark the agent's position as 'o'
print(''.join(line))
print('\033['+str(self.height+1)+'A') # printer go back to top-left
time.sleep(1.0 / frames)
# 智能体与环境进行交互,进行每一步时智能体告诉环境往上下左右哪个方向走,执行后环境返回 reward、states、terminal
def step(self, action):
"""4 legal actions, 0:up, 1:down, 2:left, 3:right"""
change = [[0, 1], [0, -1], [-1, 0], [1, 0]]
#里面的 max 函数控制智能体别超出方格的下界,外面的 min 函数控制智能体别超出方格的上界
self.x = min(self.height - 1, max(0, self.x + change[action][0]))
# 里面的 max 函数控制智能体别超出方格的左界,外面的 min 函数控制智能体别超出方格的右界
self.y = min(self.length - 1, max(0, self.y + change[action][1]))
states = [self.x, self.y]
reward = -1
terminal = False
if self.x == 0: # if agent is on the cliff line "SxxxxxT"
if self.y > 0: # if agent is not on the start position
terminal = True
if self.y != self.length - 1: # if agent is not on the terminal position
reward = -100 # if agent falls
return reward, states, terminal
#开始新的一轮
def reset(self):
self.x = 0
self.y = 0
class Q_table():
def __init__(self, length, height, actions=4, alpha=0.1, gamma=0.9):
self.table = [0] * actions * length * height # initialize all Q(s,a) to zero,初始化一个Q表
self.actions = actions
self.length = length
self.height = height
self.alpha = alpha
self.gamma = gamma
#由Q_table中 agent 位置和方向确定返回的Q值
def _index(self, a, x, y):
"""Return the index of Q([x,y], a) in Q_table."""
return a * self.height * self.length + x * self.length + y
#设置 epsilon 值
def _epsilon(self):
return 0.1 #将 epsilon 设置为0.1
# version for better convergence:
# """At the beginning epsilon is 0.2, after 300 episodes decades to 0.05, and eventually go to 0."""
# return 20. / (num_episode + 100)
# epsilon-greedy 策略
def take_action(self, x, y, num_episode):
"""epsilon-greedy action selection"""
if random.random() < self._epsilon(): #如果生成随机数小于epsilon,就随机选择一个action
return int(random.random() * 4)
else: #如果生成随机数大于epsilon,就选择最优的那个action
actions_value = [self.table[self._index(a, x, y)] for a in range(self.actions)]
return actions_value.index(max(actions_value))
# Q_Learning Model-Free TD-learning off-policy
# maxaQ(S',a)公式操作
def max_q(self, x, y):
actions_value = [self.table[self._index(a, x, y)] for a in range(self.actions)]
return max(actions_value)
#Q值更新操作,也就是Q-Learning的核心公式 Q(S,A)←Q(S,A)+α[R+γmaxaQ(S',a)−Q(S,A)]
def update(self, a, s0, s1, r, is_terminated):
# both s0, s1 have the form [x,y]
q_predict = self.table[self._index(a, s0[0], s0[1])]
if not is_terminated:
q_target = r + self.gamma * self.max_q(s1[0], s1[1])
else:
q_target = r
self.table[self._index(a, s0[0], s0[1])] += self.alpha * (q_target - q_predict)
"""
# SARSA Model-Free TD-learning on-policy
def epsilon_q(self, x, y):
actions_value = [self.table[self._index(a, x, y)] for a in range(self.actions)]
return max(actions_value) if random.random() > self._epsilon() else actions_value[int(random.random() * 4)]
def update(self, a, s0, s1, r, is_terminated):
# both s0, s1 have the form [x,y]
q_predict = self.table[self._index(a, s0[0], s0[1])]
if not is_terminated:
q_target = r + self.gamma * self.epsilon_q(s1[0], s1[1])
else:
q_target = r
self.table[self._index(a, s0[0], s0[1])] += self.alpha * (q_target - q_predict)
"""
def cliff_walk():
plt.ion() # 开启interactive mode 成功的关键函数
plt.figure(1)
t = [0]
m = [0]
env = Env(length=12, height=4) #初始化环境
table = Q_table(length=12, height=4) #设置 Q_table 大小
for num_episode in range(3000):
# within the whole learning process
episodic_reward = 0
is_terminated = False
s0 = [0, 0]
while not is_terminated:
# within one episode
action = table.take_action(s0[0], s0[1], num_episode) # agent 不断与环境交互
r, s1, is_terminated = env.step(action) #记录下 reward 和 state值
table.update(action, s0, s1, r, is_terminated) #Q_Learning算法更新Q表
episodic_reward += r
# env.render(frames=100) #每一步的方格图展示
s0 = s1
if num_episode % 20 == 0:
print("Episode: {}, Score: {}".format(num_episode, episodic_reward))
plt.clf() # 清空画布上的所有内容
t.append(num_episode) # 模拟数据增量流入,保存历史数据
m.append(episodic_reward) # 模拟数据增量流入,保存历史数据
plt.plot(t, m, '-r')
plt.pause(0.01)
env.reset()
cliff_walk()
Q_Learning 优化曲线

Q_Learning前500个解
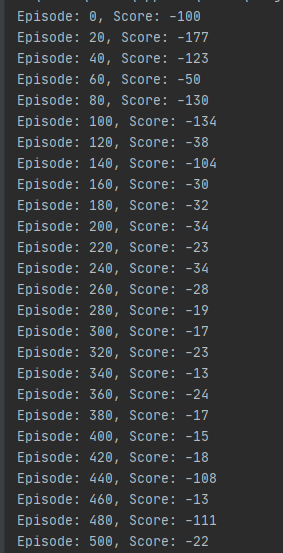
Q_Learning后500个解

SARSA优化曲线
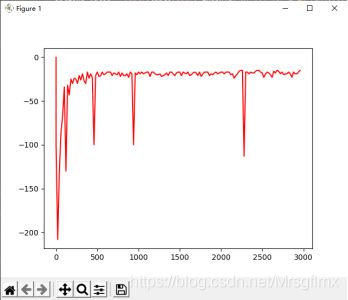
SARSA前500个解

SARSA后500个解

综上可见,Q-Learning算法更激进,SARSA算法更保守,整体效果是Q-Learning更好一些
。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。
如果大家喜欢这篇文章的话,希望大家收藏、转发、关注、评论、点赞,转载请注明出自这里。 PS:本随笔属个人学习小结,文中内容有参考互联网上的相关文章。如果您博文的链接被我引用,我承诺不会参杂经济利益;如果有版权纠纷,请私信留言。其中如果发现文中有不正确的认知或遗漏的地方请评论告知,谢谢! 还是那句话:不是我喜欢copy,是站在巨人的肩膀上~~