【python3】10.python高阶内容:装饰器
10.python高阶内容:装饰器
2022.12.28 装饰器
装饰器(Decorators)是 Python 的一个重要部分。简单地说:他们是修改其他函数的功能的函数。参数可以是函数,返回值也可以是函数。
10.1 形式
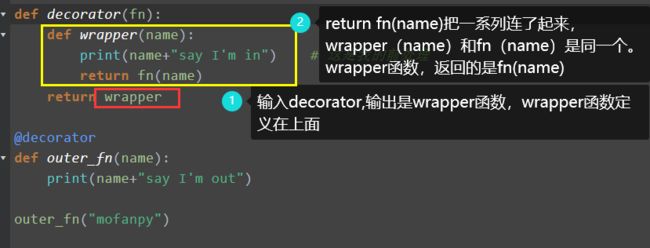
def decorator(fn):
def wrapper(name):
print(name+"say I'm in") # 这是我的前处理
return fn(name)
return wrapper
@decorator
def outer_fn(name):
print(name+"say I'm out")
outer_fn("mofanpy")
@decorator 这就是装饰器
@decorator
def outer_fn(name):
相当于
decorator(outer_fn(name))
- ① 我们输入:
outer_fn("mofanpy") - ② 这个函数在
@decorator下面,所以是个装饰器,相当于decorator(outer_fn(name)) - ③
decorator()返回的是wrapper(),所以实际执行的是wrapper(mofanpy) - ④ 执行print,输出:mofanpysay I’m in
- ⑤执行return,返回
fn("mofanpy")也就是outer_fn("mofanpy"),输出:mofanpysay I’m out
【结果】
mofanpysay I'm in
mofanpysay I'm out
10.2 实例讲解
【实例1】:在写装饰器的时候,装饰器就被调用
def funA(fn):
print("调用funB前")
def new_fun(arg):
print("增加的内容:",arg)
print("调用funB后")
return new_fun # 如果返回fn就是返回funB()的结果
@funA
def funB(arg):
print("funB被调用",arg)
print("============")
funB("funB1")
funB("funB2")
【说明】
@funA
def funB(arg):
- ① 时就被调用,相当于执行了
funA(funB(arg)),此时输出了:
调用funB前
调用funB后
并返回了new_fun()函数。
- ② 然后执行:
print("============")
funB("funB1")
funB("funB2")
相当于执行
print("============")
new_fun("funB1")
new_fun("funB2")
- ③ 输出结果
调用funB前
调用funB后
============
增加的内容: funB1
增加的内容: funB2
【实例2】:输出什么顺序
#funA 作为装饰器函数
def funA(fn):
print("调用funB前")
fn() # 执行传入的fn参数
print("调用funB后")
return fn # 如果返回fn就是返回funB()的结果
@funA
def funB():
print("funB被调用")
【说明】
- 其实上一个例子也是顺着这行,只是
def new_fun(arg):定义了函数,所以先执行了print("调用funB后").当实例调用这个装饰器时候,才输出返回值。 - 这里,顺着执行,执行
fn()的时候,有print,所以在定义装饰器的时候全输出顺序如下,在中间。
调用funB前
funB被调用
调用funB后
10.3 用在哪里
我这个也是直接抄过来,没有实际运用过。基本上是要做同样的前置处理或后置处理的时候
- 授权(Authorization)
装饰器能有助于检查某个人是否被授权去使用一个web应用的端点(endpoint)。它们被大量使用于Flask和Django web框架中。这里是一个例子来使用基于装饰器的授权
- 日志(Logging)
参考
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/593088978
https://www.runoob.com/w3cnote/python-func-decorators.html