动手学深度学习笔记-线性回归的从零开始实现
文章目录
- 引入所需库
- 生成带噪声的人造数据集
- 随机取小批量函数
- 定义线性回归模型
- 定义损失函数
- 定义小批量随机梯度下降优化算法
- 初始化模型参数
- 训练模块
引入所需库
若有ModuleNotFoundError: No Module named 'matplotlib_inline’错误,可参考博客
生成带噪声的人造数据集
# 生成带噪声的人造数据集w=[2, -3.4]T b=4.2
def synthetic_data(w, b, num_examples): # 权重w 偏移量b 数据量大小num_examples
# y = Xw + b + 噪声
# torch.normal返回从单独的正态分布中提取的随机数的张量,均值为0,方差为1(个数为num_examples,列数为w的长度)
X = torch.normal(0, 1, (num_examples, len(w)))
# torch.matmul是tensor的乘法,输入可以是高维的
y = torch.matmul(X, w) + b
# 加入噪声
y += torch.normal(0, 0.01, y.shape)
return X, y.reshape((-1, 1))# 将y重置为列向量并返回
true_w = torch.tensor([2, -3.4])
true_b = 4.2
features, labels = synthetic_data(true_w, true_b, 1000) # 根据真实w和b生成1000数据
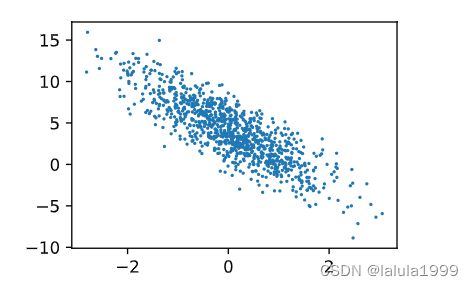
d2l.set_figsize()
# 人造数据散点图
d2l.plt.scatter(features[:, 1].detach().numpy(),
labels.detach().numpy(),
1)
随机取小批量函数
def data_iter(batch_size, features, labels): # batch_size批量大小 features特征 labels标记
#样本数量1000
num_examples = len(features)
# 生成随机顺序下标,以便使用打乱的下标进行随机访问,1000个随机下标
indices = list(range(num_examples))
random.shuffle(indices)
for i in range(0, num_examples, batch_size): # 0到num_examples每次跳batch_size大小
# batch_indices为batch_size长度个随机下标
batch_indices = torch.tensor(indices[i:min(i+batch_size, num_examples)])
# yield就是 return 返回一个值,并且记住这个返回的位置,下次迭代就从这个位置后(下一行)开始
yield features[batch_indices], labels[batch_indices]
batch_size = 10
# 随机生成10批量的小样本
for X, y in data_iter(batch_size, features, labels):
print(X, '\n', y)
break # 只取第一遍循环的10批量
定义线性回归模型
# 定义线性回归模型
def linreg(X, w, b):
return torch.matmul(X, w) + b
定义损失函数
# 定义均方损失函数
def squared_loss(y_hat, y): # y_hat为预测值,y为真实值
return (y_hat - y.reshape(y_hat.shape))**2 / 2
定义小批量随机梯度下降优化算法
# 定义小批量随机梯度下降优化算法
def sgd(params, lr, batch_size): # params所有参数包括w和b,lr为学习率,batch_size批量大小
with torch.no_grad(): # 使用优化算法时不需要进行梯度计算
for param in params: # 对每一个参数进行更新,包括w和b
param -= lr * param.grad / batch_size # 优化算法,y=-学习率*梯度,取平均是因为在损失函数中未计算平均
param.grad.zero_() # 将梯度重设为0
初始化模型参数
# 初始化模型参数
# 定义初始w和b进行训练,以下过程会对w和b逐渐调整至接近真实值w=[2, -3.4]T b=4.2
w = torch.normal(0, 0.01, size=(2, 1), requires_grad=True)
b = torch.zeros(1, requires_grad=True)
训练模块
# 训练模块
# 定义学习率
lr = 0.03
# 定义扫描数据轮次
num_epochs = 3
# 选择训练网络类型
net = linreg
# 选择损失函数
loss = squared_loss
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
for X, y in data_iter(batch_size, features, labels):
l = loss(net(X, w, b), y) # 将预测值的y'也就是net(X, w, b)和真实值y进行损失计算
l.sum().backward() # 对损失求和然后进行梯度计算
sgd([w, b], lr, batch_size) # 用优化算法对w和b进行更新
with torch.no_grad():
train_l = loss(net(features, w, b), labels) # 对参数调整进行评价
print(f'epoch {epoch + 1}, loss {float(train_l.mean()):f}')