POJ 2049 Finding Nemo bfs 建图很难。。
Finding Nemo
| Time Limit: 2000MS | Memory Limit: 30000K | |
| Total Submissions: 6952 | Accepted: 1584 |
Description
Nemo is a naughty boy. One day he went into the deep sea all by himself. Unfortunately, he became lost and couldn't find his way home. Therefore, he sent a signal to his father, Marlin, to ask for help.
After checking the map, Marlin found that the sea is like a labyrinth with walls and doors. All the walls are parallel to the X-axis or to the Y-axis. The thickness of the walls are assumed to be zero.
All the doors are opened on the walls and have a length of 1. Marlin cannot go through a wall unless there is a door on the wall. Because going through a door is dangerous (there may be some virulent medusas near the doors), Marlin wants to go through as few doors as he could to find Nemo.
Figure-1 shows an example of the labyrinth and the path Marlin went through to find Nemo.
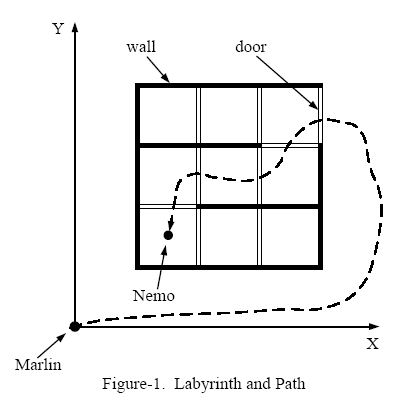
We assume Marlin's initial position is at (0, 0). Given the position of Nemo and the configuration of walls and doors, please write a program to calculate the minimum number of doors Marlin has to go through in order to reach Nemo.
After checking the map, Marlin found that the sea is like a labyrinth with walls and doors. All the walls are parallel to the X-axis or to the Y-axis. The thickness of the walls are assumed to be zero.
All the doors are opened on the walls and have a length of 1. Marlin cannot go through a wall unless there is a door on the wall. Because going through a door is dangerous (there may be some virulent medusas near the doors), Marlin wants to go through as few doors as he could to find Nemo.
Figure-1 shows an example of the labyrinth and the path Marlin went through to find Nemo.

We assume Marlin's initial position is at (0, 0). Given the position of Nemo and the configuration of walls and doors, please write a program to calculate the minimum number of doors Marlin has to go through in order to reach Nemo.
Input
The input consists of several test cases. Each test case is started by two non-negative integers M and N. M represents the number of walls in the labyrinth and N represents the number of doors.
Then follow M lines, each containing four integers that describe a wall in the following format:
x y d t
(x, y) indicates the lower-left point of the wall, d is the direction of the wall -- 0 means it's parallel to the X-axis and 1 means that it's parallel to the Y-axis, and t gives the length of the wall.
The coordinates of two ends of any wall will be in the range of [1,199].
Then there are N lines that give the description of the doors:
x y d
x, y, d have the same meaning as the walls. As the doors have fixed length of 1, t is omitted.
The last line of each case contains two positive float numbers:
f1 f2
(f1, f2) gives the position of Nemo. And it will not lie within any wall or door.
A test case of M = -1 and N = -1 indicates the end of input, and should not be processed.
Then follow M lines, each containing four integers that describe a wall in the following format:
x y d t
(x, y) indicates the lower-left point of the wall, d is the direction of the wall -- 0 means it's parallel to the X-axis and 1 means that it's parallel to the Y-axis, and t gives the length of the wall.
The coordinates of two ends of any wall will be in the range of [1,199].
Then there are N lines that give the description of the doors:
x y d
x, y, d have the same meaning as the walls. As the doors have fixed length of 1, t is omitted.
The last line of each case contains two positive float numbers:
f1 f2
(f1, f2) gives the position of Nemo. And it will not lie within any wall or door.
A test case of M = -1 and N = -1 indicates the end of input, and should not be processed.
Output
For each test case, in a separate line, please output the minimum number of doors Marlin has to go through in order to rescue his son. If he can't reach Nemo, output -1.
Sample Input
8 9 1 1 1 3 2 1 1 3 3 1 1 3 4 1 1 3 1 1 0 3 1 2 0 3 1 3 0 3 1 4 0 3 2 1 1 2 2 1 2 3 1 3 1 1 3 2 1 3 3 1 1 2 0 3 3 0 4 3 1 1.5 1.5 4 0 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 2 1 1 1 1 2 0 1 1.5 1.7 -1 -1
Sample Output
5 -1

1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <string.h> 3 #include <queue> 4 using namespace std; 5 6 struct block 7 { 8 int x, y, door; 9 bool operator<(struct block b)const 10 { 11 return door > b.door; 12 } 13 }; 14 priority_queue<struct block>q; 15 16 int wall[410][410]; 17 bool vis[410][410]; 18 int end_x, end_y; 19 20 int bfs() 21 { 22 while(!q.empty())q.pop(); 23 q.push((struct block){end_x, end_y, 0}); 24 vis[end_x][end_y] = 1; 25 while(!q.empty()) 26 { 27 struct block u = q.top(); 28 q.pop(); 29 if(u.x == 1 && u.y == 1) 30 return u.door; 31 32 if(wall[u.x-1][u.y] != 1 && !vis[u.x-1][u.y]) 33 { 34 vis[u.x-1][u.y] = 1; 35 if(wall[u.x-1][u.y] == 2) 36 q.push((struct block){u.x-1, u.y, u.door+1}); 37 else q.push((struct block){u.x-1, u.y, u.door}); 38 } 39 40 if(wall[u.x+1][u.y] != 1 && !vis[u.x+1][u.y]) 41 { 42 vis[u.x+1][u.y] = 1; 43 if(wall[u.x+1][u.y] == 2) 44 q.push((struct block){u.x+1, u.y, u.door+1}); 45 else q.push((struct block){u.x+1, u.y, u.door}); 46 } 47 48 if(wall[u.x][u.y-1] != 1 && !vis[u.x][u.y-1]) 49 { 50 vis[u.x][u.y-1] = 1; 51 if(wall[u.x][u.y-1] == 2) 52 q.push((struct block){u.x, u.y-1, u.door+1}); 53 else q.push((struct block){u.x, u.y-1, u.door}); 54 } 55 56 if(wall[u.x][u.y+1] != 1 && !vis[u.x][u.y+1]) 57 { 58 vis[u.x][u.y+1] = 1; 59 if(wall[u.x][u.y+1] == 2) 60 q.push((struct block){u.x, u.y+1, u.door+1}); 61 else q.push((struct block){u.x, u.y+1, u.door}); 62 } 63 } 64 return -1; 65 } 66 67 int main() 68 { 69 int n, m, x, y, d, t; 70 while(scanf("%d %d", &n, &m) != EOF) 71 { 72 if(n == -1 && m == -1)break; 73 memset(wall, 0, sizeof(wall)); 74 memset(vis, 0, sizeof(vis)); 75 for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) 76 { 77 scanf("%d %d %d %d", &x, &y, &d, &t); 78 if(d == 1) 79 { 80 for(int i = y*2; i <= (y+t)*2; i++) 81 wall[x*2][i] = 1; 82 } 83 else 84 { 85 for(int i = x*2; i <= (x+t)*2; i++) 86 wall[i][y*2] = 1; 87 } 88 } 89 for(int i = 0; i < m; i++) 90 { 91 scanf("%d %d %d", &x, &y, &d); 92 if(d == 1) 93 wall[x*2][y*2+1] = 2; 94 else wall[x*2+1][y*2] = 2; 95 } 96 double x_tmp, y_tmp; 97 scanf("%lf %lf", &x_tmp, &y_tmp); 98 if(x_tmp < 0 || x_tmp > 199 || y_tmp < 0 || y_tmp > 199) 99 printf("0\n"); 100 else 101 { 102 end_x = (int)x_tmp * 2 + 1; 103 end_y = (int)y_tmp * 2 + 1; 104 for(int i = 0; i <= 400; i++) 105 wall[0][i] = wall[i][0] = wall[400][i] = wall[i][400] = 1; 106 printf("%d\n", bfs()); 107 } 108 } 109 return 0; 110 }
