centos 初学者
If you are walking the path of becoming a data scientist, you might have already come across the term Time Series and you might have also realized the importance of Time Series Analysis and Forecasting. In this post, I will try to give a gentle introduction so that it can kick start your learning.
如果您正在走上成为数据科学家的道路,那么您可能已经遇到过时间序列一词,并且您可能已经意识到时间序列分析和预测的重要性。 在这篇文章中,我将尝试给出一个简短的介绍,以便它可以开始您的学习。
什么是时间序列? (What is Time series?)
As the name suggests, time series is just a series of observations collected over different points in time. There exists a correlation between the observations collected at adjacent time points, therefore the previous observations of a variable can be used in predicting the same variable. This distinguishes time series data from general machine learning data where the observations are collected at a single point in time.
顾名思义,时间序列只是在不同时间点收集的一系列观测值。 在相邻时间点收集的观察值之间存在相关性,因此变量的先前观察值可用于预测同一变量。 这将时间序列数据与常规机器学习数据区分开,在常规机器学习数据中,观测值是在单个时间点收集的。
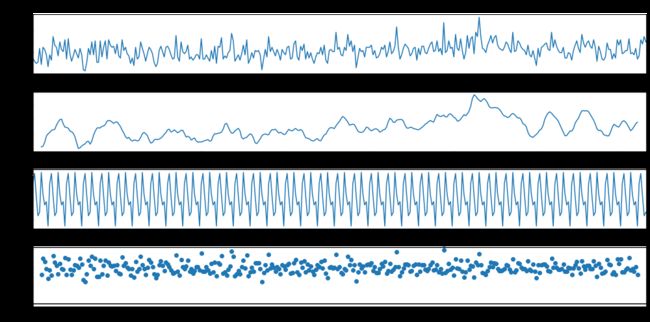
The data collected over time represents a time series only if the observations are dependent on time. If the data collected is purely random in nature, forecasting the future values is not possible and such data is called white noise.
仅当观察结果依赖于时间时,随时间收集的数据才代表时间序列。 如果收集到的数据本质上是纯随机的,则不可能预测未来的值,此类数据称为白噪声。
单变量与多变量时间序列 (Univariate vs Multivariate time series)
If only a single variable is varying over time, it is called Univariate time series. For example, temperature of a room measured every hour. Here there are no other variables recorded, hence predicting temperature only depends on the temperature values recorded at previous time points.
如果只有一个变量随时间变化,则称为单变量时间序列。 例如,每小时测量一个房间的温度。 这里没有其他变量记录,因此预测温度仅取决于先前时间点记录的温度值。
If there are more than one variable varying over time, it is called Multivariate time series. For example, if the humidity is recorded along with the temperature then both temperature and humidity are to be considered in order to predict the temperature.
如果有多个随时间变化的变量,则称为多元时间序列。 例如,如果湿度与温度一起记录,则温度和湿度都将被考虑以便预测温度。
Note: Predicting the future is not the only goal of time series data. We can have different goals while working with time series. These goals can be mainly categorized into analysis and forecasting.
注意:预测未来并不是时间序列数据的唯一目标。 在处理时间序列时,我们可以有不同的目标。 这些目标可以主要分为分析和预测。
时间序列分析 (Time Series Analysis)
The main goal of time series analysis is extracting useful statistics from data in order to understand the nature and underlying causes of the past. It helps to describe available data and provide interpretation to understand the problem domain better. Time series analysis can help to make better predictions.
时间序列分析的主要目标是从数据中提取有用的统计信息,以了解过去的性质和根本原因。 它有助于描述可用数据并提供解释以更好地理解问题域。 时间序列分析可以帮助做出更好的预测。
时间序列预测 (Time Series Forecasting)
The main goal of forecasting is to build models on the past data and use them to predict future observations. For example, predicting number of births in a country based on the data collected in past years. This is challenging as the future observations are unavailable and must be predicted from what has already happened in the past.
预测的主要目标是在过去的数据上建立模型,并使用它们来预测未来的观察结果。 例如,根据过去几年收集的数据预测一个国家的出生人数。 这是具有挑战性的,因为无法获得将来的观察结果,并且必须根据过去已经发生的情况进行预测。
时间序列的平稳性 (Stationarity in Time Series)
If all the statistical characteristics of data like mean, auto correlation, variance do not vary with time then the time series is called stationary. But in general, most of the data recorded in not stationary i.e. the properties vary with time.
如果数据的所有统计特性(例如均值,自相关,方差)均不随时间变化,则时间序列称为平稳。 但是通常,大多数记录的数据不是固定的,即属性随时间变化。
Analyzing such time series helps to understand the patterns such as trend, seasonality,cyclicality and irregularity. Trend is a general direction the data is changing as time passes. Seasonality is when a pattern recurs over fixed regular time intervals. Cyclicality is when there are any fluctuations around the trend. Unlike seasonality, cyclicality may vary in length. Irregularity is when there are random fluctuations which are not systematic and are irregular. These fluctuations cannot be controlled. These are called as time series components.
分析此类时间序列有助于了解趋势,季节性,周期性和不规律性等模式。 趋势是数据随时间变化的总体方向。 季节性是指模式在固定的固定时间间隔内重复出现。 周期性是指趋势周围存在任何波动。 与季节性不同,周期性的长度可能会有所不同。 不规则性是指存在不系统且不规则的随机波动。 这些波动无法控制。 这些被称为时间序列组件。
Most of the forecasting methods assume that the data is stationary because it is easy to predict the stationary data. Therefore, it is important to convert non-stationary data to stationary in order to apply forecasting models.
大多数预测方法都假定数据是固定的,因为它很容易预测固定数据。 因此,重要的是将非平稳数据转换为平稳数据以应用预测模型。
Check out this post by Mehul Gupta which explains Why time series has to be stationary more clearly.
请查看Mehul Gupta的这篇文章,其中解释了为什么必须更清楚地确定时间序列是固定的。
It is important to analyze these components carefully in order to better understand the problem during analysis or forecasting. Since it is difficult to see all the components in a time series, a method called Decomposition can be used to identify them. These components can either combine in an additive way or in a multiplicative way.
仔细分析这些组件很重要,这样才能更好地理解分析或预测过程中的问题。 由于很难看到时间序列中的所有组件,因此可以使用一种称为“分解”的方法来识别它们。 这些组件可以加法或乘法相结合。
An Additive time series is when the fluctuations in the data do not vary over time. Additive model is linear and seasonality has same frequency although the time increases.
加性时间序列是数据的波动不随时间变化的时间。 加性模型是线性的,尽管时间增加,但季节性具有相同的频率。
Time series = trend + seasonality + cyclicality + irregularity
时间序列=趋势+季节性+周期性+不规律性
A Multiplicative time series is when the variations or the fluctuations in the data increases as the time increases. Multiplicative model is non-linear and seasonality has either increasing or decreasing frequency.
乘法时间序列是指数据的变化或波动随着时间的增加而增加的时间。 乘法模型是非线性的,并且季节性具有增加或减少的频率。
Time series = trend * seasonality * cyclicality * irregularity
时间序列=趋势*季节性*周期性*不规则性
时间序列分解(Time Series Decomposition)
The purpose of decomposition is to identify and separate components from a time series in order to perform better analysis and forecasting.
分解的目的是从时间序列中识别和分离各个组成部分,以便执行更好的分析和预测。
In general, the cyclical component is hard to separate and it is left by grouping it with the trend component, to form a trend-cycle component. It is often simply referred to as the trend component, even though it may contain cyclical behavior.
通常,周期性成分很难分离,可以通过将其与趋势成分分组而保留下来,以形成趋势周期成分。 即使它可能包含周期性行为,也通常简称为趋势成分。
Classical decomposition can be either a multiplicative or an additive decomposition. A function called seasonal_decompose() can be used to perform classical decomposition. You need to mention whether the model is additive or multiplicative.
经典分解可以是乘法分解或加法分解。 可以使用称为Season_decompose()的函数执行经典分解。 您需要提及模型是可加还是可乘的。
Below is an example which shows decomposition of a dataset into components including the original data, trend, seasonality and irregularity(residual).
下面的示例显示了将数据集分解为包括原始数据,趋势,季节性和不规则性(残差)的组件。
Let’s first load the dataset and plot a simple graph:
首先加载数据集并绘制一个简单图形:
Since the variations are very complex, we cannot see all the components clearly. Now, Decomposing this will give us clear picture of the components. Let’s look how we can decompose this using seasonal_decompose() function:
由于变化非常复杂,因此我们无法清楚地看到所有组件。 现在,将其分解将使我们对组件有清晰的了解。 让我们看看如何使用Seasonal_decompose()函数将其分解:
Now you can see all the components, you can analyze them and remove any of them them if not needed. For example, if you want to analyze the trend of a stock data, you would need to remove the seasonality found in the data and the noise due to irregularity.
现在,您可以看到所有组件,可以分析它们,并在不需要时删除其中的任何一个。 例如,如果要分析库存数据的趋势,则需要删除数据中发现的季节性和不规则性引起的噪声。
Let’s look into the basic steps to be followed while performing a forecasting task -
让我们研究执行预测任务时应遵循的基本步骤-
预测的基本步骤 (Basic steps for Forecasting)
Defining the problem: Understanding the problem domain and clearly knowing the end goal of the forecast. The most important skill needed for a data scientist is being able to explain why a prediction is made and present results in a proper way. This is possible only with having a clear knowledge of who needs the forecast, why and how it will be used.
定义问题:了解问题领域并清楚地知道预测的最终目标。 数据科学家所需的最重要技能是能够解释为什么进行预测并以适当的方式呈现结果。 只有清楚地知道谁需要预测,为什么以及如何使用预测,才有可能做到这一点。
Data Collection: Collecting the past data related to the problem domain, gathering other important information from domain experts.
数据收集:收集与问题域相关的过去数据,并从域专家那里收集其他重要信息。
Data preparation: This includes exploring the data to know components like trend or seasonality, cleaning the data to fill the missing values and remove outliers if any, basic feature engineering to understand the relation ship between features or to add any new features, resampling and data transforms to remove noise and improve the forecasting.
数据准备:包括探索数据以了解诸如趋势或季节性之类的成分,清理数据以填充缺失值并消除异常值(如有),基本特征工程以了解特征之间的关系或添加任何新特征,重采样和数据进行转换以消除噪音并改善预测。
Modeling: This includes configuring the right forecast model for the data. Widely used time series models are Auto Regressive(AR) models, Moving Average(MA) models, Integrated(I) models and the combination of these models like Auto Regressive Moving Average models(ARMA), Auto Regressive Integrated Moving Average models(ARIMA). It is better to try models of different types, from simple to advanced approaches.
建模:这包括为数据配置正确的预测模型。 广泛使用的时间序列模型是自动回归( AR )模型,移动平均( MA )模型,集成( I )模型以及这些模型的组合,例如自动回归移动平均模型( ARMA ),自动回归集成移动平均模型( ARIMA ) 。 最好尝试使用从简单到高级方法的不同类型的模型。
Evaluation: The time series forecasting model can only be trusted through its performance at predicting the future. This may include testing the model on previous data by creating train-test splits and calculating error or wait for the new observations to occur to compare the predictions.
评估:时间序列预测模型只能通过其预测未来的性能来信任。 这可能包括通过创建训练测试拆分并计算误差来对先前的数据进行测试,或者等待新的观测结果发生以比较预测。
时间序列预测的应用 (Applications of Time Series Forecasting)
- Forecasting of agricultural commodity price农产品价格预测
- Stock market analysis and forecasting股市分析与预测
- Sales forecasting销售预测
- Forecasting supply chain components预测供应链组件
- Weather forecasting天气预报
- Forecasting the birth rate in a country预测一个国家的出生率
any many more …..
还有更多…..
结论 (Conclusion)
This is a basic introduction to time series for beginners. In this post, I’ve explained
这是初学者对时间序列的基本介绍。 在这篇文章中,我已经解释了
- What a time series is and why they are important.时间序列是什么,为什么它们如此重要。
- Components in a time series data. 时间序列数据中的组件。
- Decomposition of time series into it’s components. 将时间序列分解为其组成部分。
- Basic steps to be followed while performing a forecasting task. 执行预测任务时应遵循的基本步骤。
The data for plotting the graphs in this post is taken from here.
这篇文章中用于绘制图形的数据来自此处。
Thanks for reading! Please feel free to reach me via twitter.
谢谢阅读! 请随时通过Twitter与我联系。
Originally published at https://jithendrabsy.me on September 14, 2020.
最初于2020年9月14日发布于https://jithendrabsy.me 。
翻译自: https://medium.com/datadriveninvestor/time-series-for-beginners-2c9bd720ecb5
centos 初学者