【无人机路径规划】基于IRM和RRTstar进行无人机路径规划(Matlab代码实现)
欢迎来到本博客❤️❤️
博主优势:博客内容尽量做到思维缜密,逻辑清晰,为了方便读者。
⛳️座右铭:行百里者,半于九十。
本文目录如下:
目录
1 概述
2 运行结果
3 参考文献
4 Matlab代码、文章详细讲解
1 概述
本文将无人机路径规划这一非线性规划问题(NLP)转化为一般二次约束二次规划问题(QCQP),并使用IRM方法求解该QCQP问题。本文的方法不需要给定初值并且在保证线性收敛速率的情况下收敛到局部最小解,克服了NLP求解器和配点法(Collocation Method)初值难猜测和收敛到局部最小值速度很慢,甚至有时不能收敛到可行解的问题。
- 这里是列表文本引言
- 问题建模
- 数值优化法
3.1 运动规划问题转化为QCQP问题:采用数值微分的方法将问题离散化,消除约束中的三角函数,将NLP问题转化为非凸QCQP问题
3.2 使用IRM法求解一般QCQP问题- 启发式搜索法
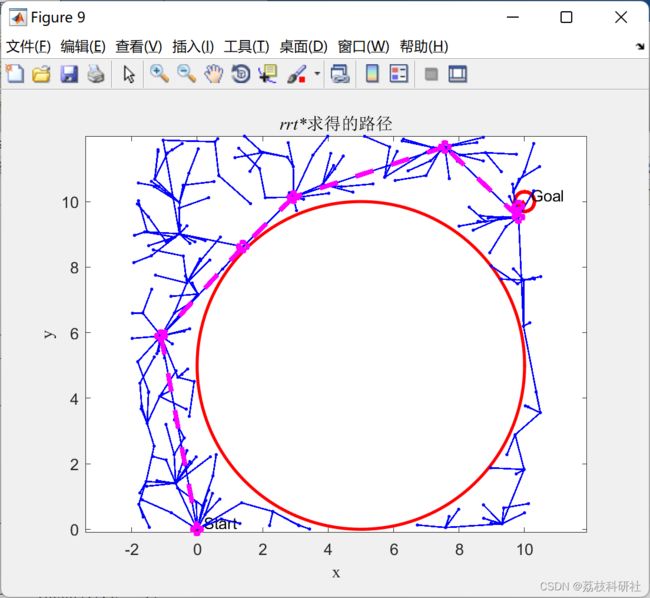
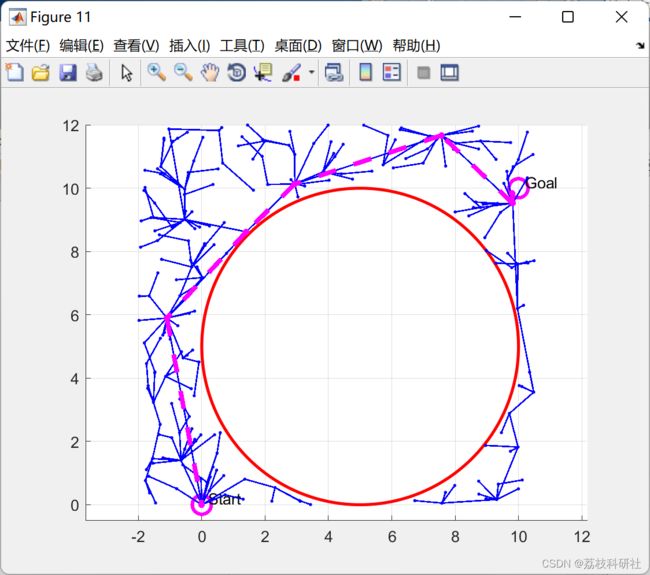
4.1 RRT算法
4.2 改进的RRT算法- 仿真验证
- 结论
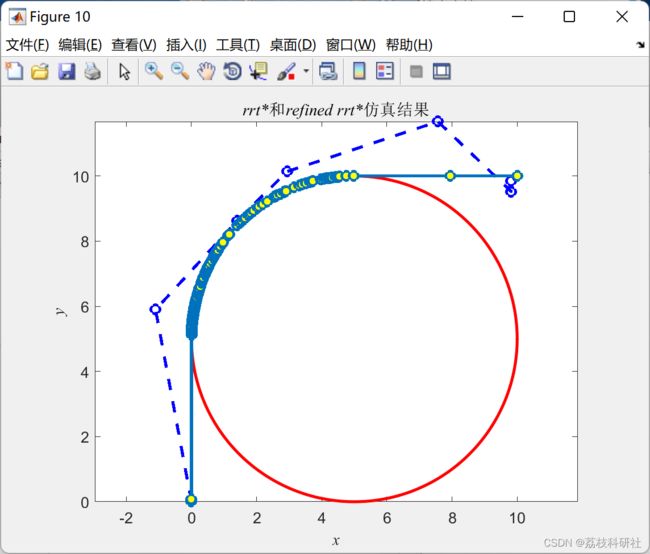
- 先使用传统RRTstar算法求解一条可行路径PP,Path_Opt()函数以PP为输入,从路径PP上随机采样不共线两点p1,p2p1,p2,如果p1,p2p1,p2连线不与障碍物冲突,用p1,p2p1,p2代替p1,p2p1,p2间的原本可行路径PP中的路径点,这样可以求出一条比路径PP短的路径。
- Steering_eval()函数判断路径是否满足方向角速率θ˙θ˙约束。路径上三个相邻点组成一个圆弧s,圆心角θθ除以通过该段圆弧所用时间tt近似等于θ˙
文献来源:
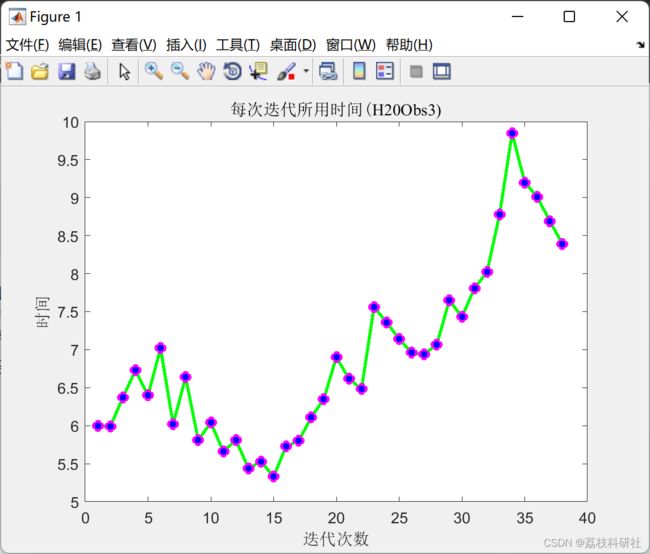
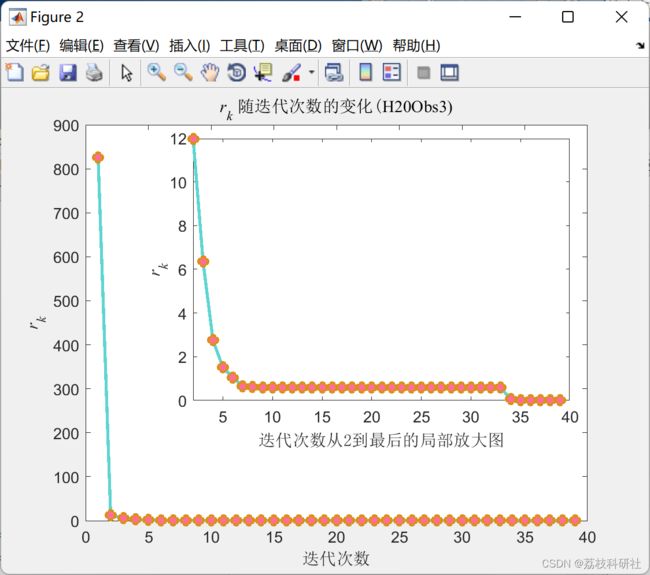
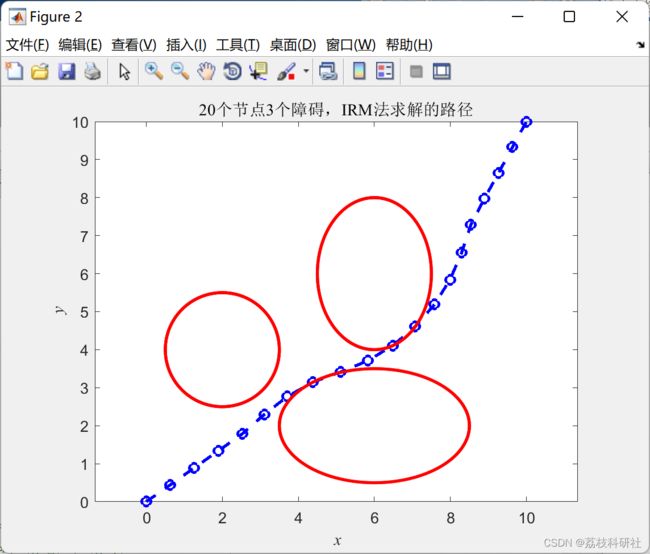
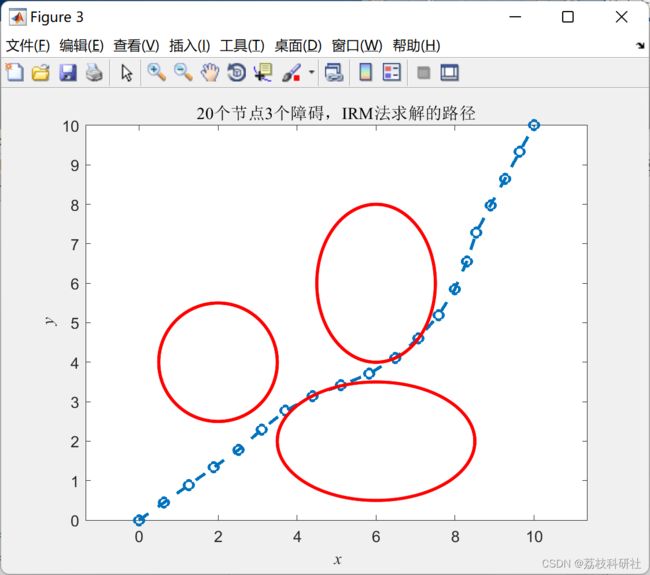
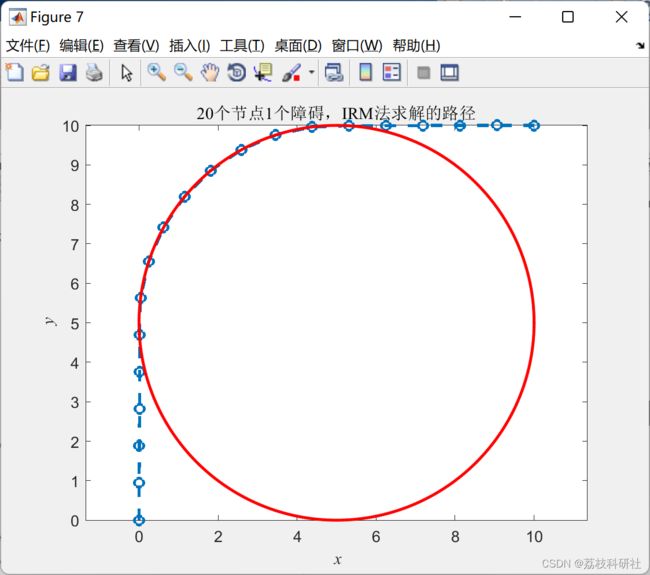
2 运行结果
部分代码:
function result = RRTstar(param, p_start, p_goal)
% RRT*
% credit : Anytime Motion Planning using the RRT*, S. Karaman, et. al.
% calculates the path using RRT* algorithm
% param : parameters for the problem
% 1) threshold : stopping criteria (distance between goal and current
% node)
% 2) maxNodes : maximum nodes for rrt tree
% 3) neighborhood : distance limit used in finding neighbors
% 4) obstacle : must be rectangle-shaped #limitation
% 5) step_size : the maximum distance that a robot can move at a time
% (must be equal to neighborhood size) #limitation
% 6) random_seed : to control the random number generation
% p_start : [x;y] coordinates
% p_goal : [x;y] coordinates
% variable naming : when it comes to describe node, if the name is with
% 'node', it means the coordinates of that node or it is just an index of
% rrt tree
% rrt struct : 1) p : coordinate, 2) iPrev : parent index, 3) cost :
% distance
% obstacle can only be detected at the end points but not along the line
% between the points
% for cost, Euclidean distance is considered.
% output : cost, rrt, time_taken
% whether goal is reached or not, depends on the minimum distance between
% any node and goal
field1 = 'p'; %position
field2 = 'iPrev'; %partent
field3 = 'cost';
field4 = 'goalReached';
rng(param.random_seed);
tic;
start();
function start()
rrt(1) = struct(field1, p_start, field2, 0, field3, 0, field4, 0);
N = param.maxNodes; % iterations
j = 1;
% while endcondition>param.threshold %&& j<=N
while ~rrt(end).goalReached && j<=N
sample_node = getSample(param.searchFeild);
% plot(sample_node(1), sample_node(2), '.g');
% text(sample_node(1), sample_node(2), strcat('random',num2str(j)))
% idx = 1;
% mincost = rrt(1).cost + norm(sample_node-rrt(1).p);
% for k = 2:length(rrt)
% cost = rrt(k).cost + norm(sample_node-rrt(k).p);
% if cost < mincost
% % mincost = cost;
end
function rrt=setReachGoal(rrt)
rrt(end).goalReached = 1;
end
for i = 1: length(rrt)
p1 = rrt(i).p;
% rob.x = p1(1); rob.y=p1(2);
plot(p1(1),p1(2),'.b')
child_ind = find([rrt.iPrev]==i);
for j = 1: length(child_ind)
p2 = rrt(child_ind(j)).p;
plot([p1(1),p2(1)], [p1(2),p2(2)], 'b', 'LineWidth', 1);
end
end
end
end
result.time_taken = toc;
end
function [value,min_node_ind] = getFinalResult(rrt)
goal_ind = find([rrt.goalReached]==1);
if ~(isempty(goal_ind))
disp('Goal has been reached!');
rrt_goal = rrt(goal_ind);
value = min([rrt_goal.cost]);
min_node_ind = find([rrt.cost]==value);
if length(min_node_ind)>1
min_node_ind = min_node_ind(1);
end
else
disp('Goal has not been reached!');
for i =1:length(rrt)
norm_rrt(i) = norm(p_goal-rrt(i).p);
end
[~,min_node_ind]= min(norm_rrt);
value = rrt(min_node_ind).cost;
end
end
end
% if it is obstacle-free, return 1.
% otherwise, return 0
function free=isObstacleFree(node_free) %4
free = 1;
for i = 1: length(param.obstacles(:,1))
obs = param.obstacles(i,:);
% op1 = [obstacle(1), obstacle(2)];
% op2 = [op1(1)+obstacle(3), op1(2)];
% op3 = [op2(1), op1(2) + obstacle(4)];
% op4 = [op1(1), op3(2)];
nx = node_free(1);
ny = node_free(2);
ha = (nx-obs(1))^2 / obs(3)^2 + (ny-obs(2))^2 / obs(4)^2;
if (ha <= 1)
free = 0;
end
end
end
function new_node=steering(nearest_node, random_node) %3
dist = norm(random_node-nearest_node);
ratio_distance = param.step_size/dist;
if ratio_distance < 1
x = (1-ratio_distance).* nearest_node(1)+ratio_distance .* random_node(1);
y = (1-ratio_distance).* nearest_node(2)+ratio_distance .* random_node(2);
new_node = [x;y];
else
new_node = random_node;
end
end
function rrt = reWire(rrt, neighbors, parent, new) %8
for i=1:length(neighbors)
cost = rrt(new).cost + norm(rrt(neighbors(i)).p - rrt(new).p);
if (cost
% rrt(neighbors(i)).p = steering(rrt(new).p, rrt(neighbors(i)).p);
% end
% plot(rrt(neighbors(i)).p(1), rrt(neighbors(i)).p(2), '.m');
rrt(neighbors(i)).iPrev = new;
rrt(neighbors(i)).cost = cost;
end
end
end
function rrt = insertNode(rrt, parent, new_node) %7
rrt(end+1) = struct(field1, new_node, field2, parent, field3,...
rrt(parent).cost + norm(rrt(parent).p-new_node), field4, 0);
end
function parent = chooseParent(rrt, neighbors, nearest, new_node) %6
min_cost = getCostFromRoot(rrt, nearest, new_node);
parent = nearest;
for i=1:length(neighbors)
cost = getCostFromRoot(rrt, neighbors(i), new_node);
if (cost
parent = neighbors(i);
end
end
end
function cost = getCostFromRoot(rrt, parent, child_node) %6.1
cost = rrt(parent).cost + norm(child_node - rrt(parent).p);
end
if isObstacleFree(node)
3 参考文献
部分理论来源于网络,如有侵权请联系删除。
[1] Sun C , Liu Y C , Dai R , et al. Two Approaches for Path Planning of Unmanned Aerial Vehicles with Avoidance Zones[J]. Journal of Guidance Control & Dynamics, 2017, 40(8).
[2] Sun C , Dai R . An iterative approach to Rank Minimization Problems[C]// Decision & Control. IEEE, 2016.