Pytorch CIFAR10图像分类 EfficientNet v1篇
Pytorch CIFAR10图像分类 EfficientNet v1篇
文章目录
- Pytorch CIFAR10图像分类 EfficientNet v1篇
-
- 4. 定义网络(EfficientNet)
-
- EfficientNet介绍
-
- EfficientNet性能比较
- EfficientNet的baseline
- EfficientNet模型混合缩放方法
- 其他版本的EfficientNet(B1-B7)
- 判断是否使用GPU
- SE模块
- MBConv 结构
- 定义EfficientNet的网络
- 定义EfficientNetB0~B7
- summary查看网络
- 测试和定义网络
- 5. 定义损失函数和优化器
- 6. 训练及可视化(增加TensorBoard可视化)
-
- 开始训练
- 训练曲线可视化
- 7. 测试
-
- 查看准确率
- 查看每一类的准确率
- 抽样测试并可视化一部分结果
- 8. 保存模型
- 9. 预测
-
- 读取本地图片进行预测
- 读取图片地址进行预测
- 10.总结
再次介绍一下我的专栏,很适合大家初入深度学习或者是Pytorch和Keras,希望这能够帮助初学深度学习的同学一个入门Pytorch或者Keras的项目和在这之中更加了解Pytorch&Keras和各个图像分类的模型。
他有比较清晰的可视化结构和架构,除此之外,我是用jupyter写的,所以说在文章整体架构可以说是非常清晰,可以帮助你快速学习到各个模块的知识,而不是通过python脚本一行一行的看,这样的方式是符合初学者的。
除此之外,如果你需要变成脚本形式,也是很简单的。
这里贴一下汇总篇:汇总篇
4. 定义网络(EfficientNet)
EfficientNet介绍
EfficientNet源自Google Brain的论文EfficientNet: Rethinking Model Scaling for Convolutional Neural Networks. 从标题也可以看出,这篇论文最主要的创新点是Model Scaling. 论文提出了compound scaling,混合缩放,把网络缩放的三种方式:深度、宽度、分辨率,组合起来按照一定规则缩放,从而提高网络的效果。EfficientNet在网络变大时效果提升明显,把精度上限进一步提升,成为了当前最强网络。EfficientNet-B7在ImageNet上获得了最先进的 84.4%的top-1精度 和 97.1%的top-5精度,比之前最好的卷积网络(GPipe, Top-1: 84.3%, Top-5: 97.0%)大小缩小8.4倍、速度提升6.1倍。
在一般情况下,我们知道,增加网络参数可以获得更好的精度(有足够的数据,不过拟合的条件下),例如ResNet可以加深从ResNet-18到ResNet-200,GPipe将baseline模型放大四倍在ImageNet数据集上获得了84.3%的top-1精度。增加网络参数的方式有三种:深度、宽度和分辨率。
深度是指网络的层数,宽度指网络中卷积的channel数(例如wide resnet中通过增加channel数获得精度收益),分辨率是指通过网络输入大小(例如从112x112到224x224)。在EfficientNet之前,没有研究工作只是针对这三个维度中的某一个维度进行调整,因为没钱啊!!有限的计算能力,很少有研究对这三个维度进行综合调整的。
直观上来讲,这三种缩放方式并不不独立。对于分辨率高的图像,应该用更深的网络,因为需要更大的感受野,同时也应该增加网络宽度来获得更细粒度的特征。
EfficientNet性能比较
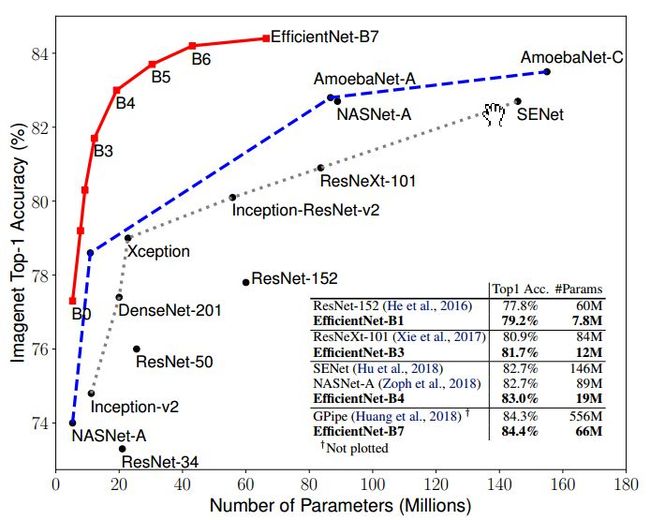
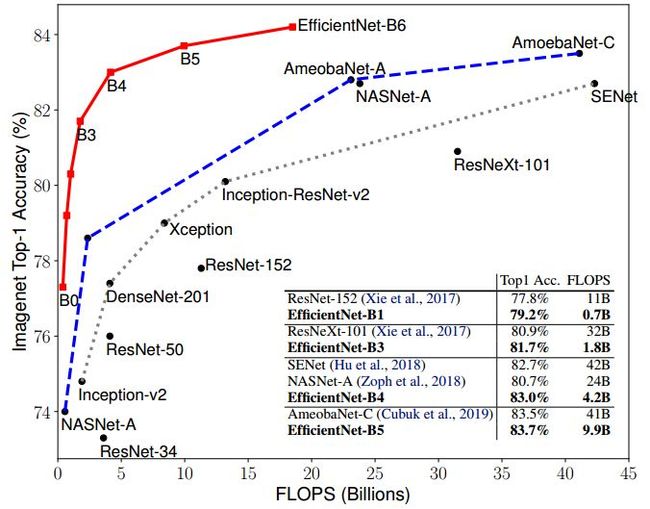
之前增加网络参数都是单独放大这三种方式中的一种,并没有同时调整,也没有调整方式的研究。EfficientNet使用了compound scaling方法,统一缩放网络深度、宽度和分辨率。类似于靠强大的搜索能力和计算能力,EfficientNet的主要创新点并不是结构,不像ResNet、SENet发明了shortcut或attention机制,EfficientNet的base结构是利用结构搜索搜出来的,然后使用compound scaling规则放缩,得到一系列表现优异的网络:B0~B7.下面两幅图分别是ImageNet的Top-1 Accuracy随参数量和flops变化关系图,可以看到EfficientNet饱和值高,并且到达速度快。可以这样说:对于ImageNet历史上的各种网络而言,可以说EfficientNet在效果上实现了碾压
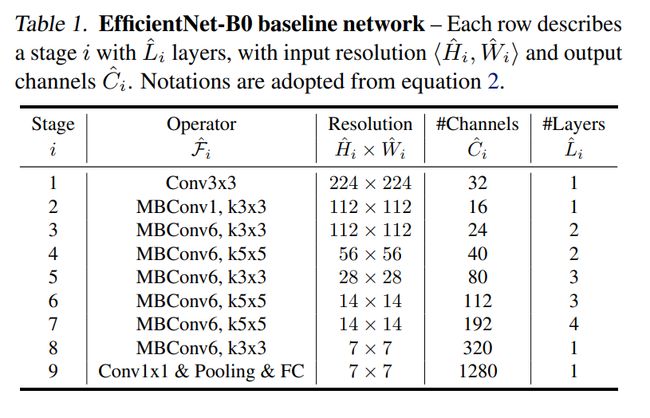
EfficientNet的baseline
EfficientNet使用了MobileNet V2中的MBCConv作为模型的主干网络,同时也是用了SENet中的squeeze and excitation方法对网络结构进行了优化。MBConv在MobileNet V2中已经介绍过了,SENet会单独在之后的博文中进行详细讲解。
总之呢,综合了MBConv和squeeze and excitation方法的EfficientNet-B0的网络结构如下表所示:
这里找了一个更形象的图,方便我们理解和进行构建EfficientNet网络。
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-JmYLDSsa-1673061774717)(https://www.researchgate.net/publication/344410350/figure/fig4/AS:1022373302128641@1620764198841/Architecture-of-EfficientNet-B0-with-MBConv-as-Basic-building-blocks.png)]
EfficientNet模型混合缩放方法
EfficientNet的规范化混合调参方法使用了一个复合系数 ϕ \phi ϕ ,来对三个参数进行符合调整:使用了compound scaling方法,统一缩放网络深度、宽度和分辨率。
其中的 α , β , γ \alpha, \beta, \gamma α,β,γ都是常数,可以通过网格搜索获得。复合系数通过人工调节。考虑到如果网络深度翻番那么对应的计算量翻番,网络宽度和图像分辨率翻番对应的计算量会翻4番,卷积操作的计算量与d , w 2 , r 2 w^2 ,r^2 w2,r2成正比,。在这个约束下,网络的计算量大约是之前的 2 ϕ 2^\phi 2ϕ。
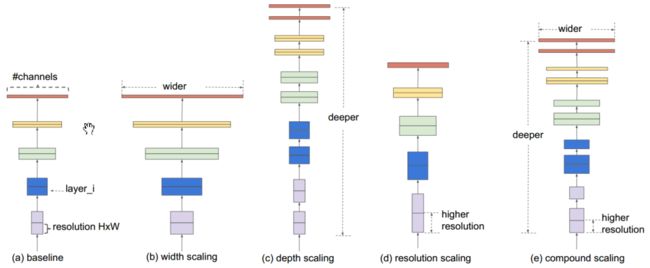
后续就可以利用混合缩放的方法进行对baseline网络进行改进,如下图所示,(a)为baseline网络,(b)、©、(d)为单独通过增加width,depth以及resolution使得网络变大的方式,(e)为compound scaling的方式。
这样就衍生出了EfficientB1-B7,从上面的图我们可以看到使用了compound scaling后,效果非常显著,在不同参数量和计算量都取得了多倍的提升。EfficientNet在ImageNet上的效果碾压,而且模型规模比此前的GPipe小了8.4倍。
其他版本的EfficientNet(B1-B7)
| Model | input_size | width_coefficient | depth_coefficient | drop_connect_rate | dropout_rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EfficientNetB0 | 224x224 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 0.2 | 0.2 |
| EfficientNetB1 | 240x240 | 1.0 | 1.1 | 0.2 | 0.2 |
| EfficientNetB2 | 260x260 | 1.1 | 1.2 | 0.2 | 0.3 |
| EfficientNetB3 | 300x300 | 1.2 | 1.4 | 0.2 | 0.3 |
| EfficientNetB4 | 380x380 | 1.4 | 1.8 | 0.2 | 0.4 |
| EfficientNetB5 | 456x456 | 1.6 | 2.2 | 0.2 | 0.4 |
| EfficientNetB6 | 528x528 | 1.8 | 2.6 | 0.2 | 0.5 |
| EfficientNetB7 | 600x600 | 2.0 | 3.1 | 0.2 | 0.5 |
-
input_size代表训练网络时输入网络的图像大小 -
width_coefficient代表channel维度上的倍率因子,比如在 EfficientNetB0中Stage1的3x3卷积层所使用的卷积核个数是32,那么在B6中就是 32 × 1.8 = 57.6 32 \times 1.8=57.6 32×1.8=57.6接着取整到离它最近的8的整数倍即56,其它Stage同理。 -
depth_coefficient代表depth维度上的倍率因子(仅针对Stage2到Stage8),比如在EfficientNetB0中Stage7的 L ^ i = 4 {\widehat L}_i=4 L i=4,那么在B6中就是 4 × 2.6 = 10.4 4 \times 2.6=10.4 4×2.6=10.4接着向上取整即11。 -
drop_connect_rate是在MBConv结构中dropout层使用的drop_rate,在官方keras模块的实现中MBConv结构的drop_rate是从0递增到drop_connect_rate的(注意,在源码实现中只有使用shortcut的时候才有Dropout层),还需要注意的是,这里的Dropout层是Stochastic Depth,即会随机丢掉整个block的主分支(只剩捷径分支,相当于直接跳过了这个block)也可以理解为减少了网络的深度。 -
dropout_rate是最后一个全连接层前的dropout层(在stage9的Pooling与FC之间)的dropout_rate。最后给出原论文中关于EfficientNet与当时主流网络的性能参数对比:
判断是否使用GPU
首先我们还是得判断是否可以利用GPU,因为GPU的速度可能会比我们用CPU的速度快20-100倍左右,特别是对卷积神经网络来说,更是提升特别明显。
device = 'cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu'
我们首先定义一下激活函数Swish和DropConnect方法,DropConnect是一种正则化方法,它在训练过程中随机将网络中的某些权重设置为0,在有些实现中,大家会使用DropPath进行,也是可以的。
# 激活函数
def swish(x):
return x * x.sigmoid()
# DropConnect是一种正则化方法,它在训练过程中随机将网络中的某些权重设置为0
# DropConnect是对网络中每一个权重进行随机设置的
def drop_connect(x, drop_ratio):
keep_ratio = 1.0 - drop_ratio
mask = torch.empty([x.shape[0], 1, 1, 1], dtype=x.dtype, device=x.device)
mask.bernoulli_(keep_ratio)
x.div_(keep_ratio)
x.mul_(mask)
return x
SE模块
有时候对于SE模块来说,我们会用1x1的卷积层实现,因为在这里,实际上1x1的卷积层是等价于全连接层,也就是Linear层的
SE模块如下所示,由一个全局平均池化,两个全连接层组成。第一个全连接层的节点个数是输入该MBConv特征矩阵channels的$ \frac{1}{4} $,且使用Swish激活函数。第二个全连接层的节点个数等于Depthwise Conv层输出的特征矩阵channels,且使用Sigmoid激活函数。
![]()
# SE模块实现
class SE(nn.Module):
'''Squeeze-and-Excitation MBconv with Swish.'''
def __init__(self, in_channels, se_channels):
super(SE, self).__init__()
# 这里的1x1的卷积核与全连接层是等价的
self.se1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, se_channels,
kernel_size=1, bias=True)
self.se2 = nn.Conv2d(se_channels, in_channels,
kernel_size=1, bias=True)
def forward(self, x):
out = F.adaptive_avg_pool2d(x, (1, 1)) # 平均池化
out = swish(self.se1(out))
out = self.se2(out).sigmoid()
out = x * out # 进行连接相乘
return out
MBConv 结构
![]()
如图所示,MBConv 结构主要由一个 1x1 的普通卷积(升维作用),一个 kxk 的 Depthwise Conv 卷积。k 的具体值主要有 3x3 和 5x5 两种情况,一个 SE 模块,一个 1x1 的普通卷积(降维作用),一个 Droupout 层构成
-
第一个升维的 1x1 卷积层,它的卷积核个数是输入特征矩阵 channel 的 n 倍,n ∈ { 1 , 6 }
-
当 n = 1 时,不要第一个升维的 1x1 卷积层,即 Stage2 中的 MBConv 结构都没有第一个升维的 1x1 卷积层(这和MobileNetV3网络类似)。
-
仅当输入 MBConv 结构的特征矩阵与输出的特征矩阵 shape 相同时才存在 shortcut 连接(代码中可通过
stride==1 and inputc_channels==output_channels条件来判断)。 -
在源码实现中只有使用 shortcut 的时候才有 Dropout 层
# MBconv模块
class MBconv(nn.Module):
'''expansion + depthwise + pointwise + squeeze-excitation'''
def __init__(self,
in_channels,
out_channels,
kernel_size,
stride,
expand_ratio=1,
se_ratio=0.25, # 也就是1/4
drop_rate=0.):
super(MBconv, self).__init__()
self.stride = stride
self.drop_rate = drop_rate
self.expand_ratio = expand_ratio
# Expansion 第一个升维的 1x1 卷积层
channels = expand_ratio * in_channels
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels,
channels,
kernel_size=1,
stride=1,
padding=0,
bias=False)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(channels)
# Depthwise conv
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(channels,
channels,
kernel_size=kernel_size,
stride=stride,
padding=(1 if kernel_size == 3 else 2),
groups=channels,
bias=False)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(channels)
# SE layers SE模块
se_channels = int(in_channels * se_ratio)
self.se = SE(channels, se_channels)
# Output
self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(channels,
out_channels,
kernel_size=1,
stride=1,
padding=0,
bias=False)
self.bn3 = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels)
# Skip connection if in and out shapes are the same (MV-V2 style)
# 仅当输入 MBConv 结构的特征矩阵与输出的特征矩阵 shape 相同时才存在 shortcut 连接
self.has_skip = (stride == 1) and (in_channels == out_channels)
def forward(self, x):
# 当n = 1的时候,是不要第一个升维的1x1的卷积层
out = x if self.expand_ratio == 1 else swish(self.bn1(self.conv1(x)))
out = swish(self.bn2(self.conv2(out)))
out = self.se(out)
out = self.bn3(self.conv3(out))
if self.has_skip:
if self.training and self.drop_rate > 0: # 有shortcut的时候用Dropout
out = drop_connect(out, self.drop_rate)
out = out + x
return out
定义EfficientNet的网络
这样我们就可以根据EFficientNet的论文的架构定义我们的网络,用到上述的SE模块和MBconv模块进行
# 定义EfficientNet方法
class EfficientNet(nn.Module):
# 默认识别的类别为10
def __init__(self,
width_coefficient=1.0,
depth_coefficient=1.0,
dropout_rate = 0.2,
num_classes=10):
super(EfficientNet, self).__init__()
# kernel_size, in_channel, out_channel, exp_ratio, strides, use_SE, drop_connect_rate, repeats
cfg = {
'num_blocks': [1, 2, 2, 3, 3, 4, 1], # repeats
'expansion': [1, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6, 6], # expansion
'out_channels': [16, 24, 40, 80, 112, 192, 320], # out_channels
'kernel_size': [3, 3, 5, 3, 5, 5, 3], # kernel_size
'stride': [1, 2, 2, 2, 1, 2, 1], # stride
'dropout_rate': dropout_rate,
'drop_connect_rate': 0.2,
}
# 配置文件
self.cfg = cfg
self.width_coefficient = width_coefficient
self.depth_coefficient = depth_coefficient
# 第一个3x3的卷积层
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3,
32,
kernel_size=3,
stride=1,
padding=1,
bias=False)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(32)
self.layers = self._make_layers(in_channels=32)
self.linear = nn.Linear(cfg['out_channels'][-1]*int(self.width_coefficient), num_classes)
def _make_layers(self, in_channels):
layers = []
cfg = [self.cfg[k] for k in ['expansion', 'out_channels', 'num_blocks', 'kernel_size', 'stride']]
b = 0
blocks = sum(self.cfg['num_blocks'])
for expansion, out_channels, num_blocks, kernel_size, stride in zip(*cfg):
import math
num_blocks = math.floor(self.depth_coefficient) * num_blocks
strides = [stride] + [1] * (num_blocks - 1)
for stride in strides:
drop_rate = self.cfg['drop_connect_rate'] * b / blocks
layers.append(
MBconv(in_channels,
out_channels*int(self.width_coefficient),
kernel_size,
stride,
expansion,
se_ratio=0.25,
drop_rate=drop_rate))
in_channels = out_channels*int(self.width_coefficient)
return nn.Sequential(*layers)
def forward(self, x):
out = swish(self.bn1(self.conv1(x)))
out = self.layers(out)
out = F.adaptive_avg_pool2d(out, 1)
out = out.view(out.size(0), -1)
dropout_rate = self.cfg['dropout_rate']
if self.training and dropout_rate > 0:
out = F.dropout(out, p=dropout_rate)
out = self.linear(out)
return out
定义EfficientNetB0~B7
在上面我们已经定义了两个参数,我们可以根据参数的配置,进行设置,这样就可以定义出我们的EfficientNetB0~B7的模型
def EfficientNetB0(num_classes = 10):
# input image size 224x224
return EfficientNet(width_coefficient=1.0,
depth_coefficient=1.0,
num_classes=num_classes)
def EfficientNetB1(num_classes = 10):
# input image size 240x240
return EfficientNet(width_coefficient=1.0,
depth_coefficient=1.1,
num_classes=num_classes)
def EfficientNetB2(num_classes = 10):
# input image size 260x260
return EfficientNet(width_coefficient=1.1,
depth_coefficient=1.2,
dropout_rate=0.3,
num_classes=num_classes)
def EfficientNetB3(num_classes = 10):
# input image size 300x300
return EfficientNet(width_coefficient=1.2,
depth_coefficient=1.4,
dropout_rate=0.3,
num_classes=num_classes)
def EfficientNetB4(num_classes = 10):
# input image size 380x380
return EfficientNet(width_coefficient=1.4,
depth_coefficient=1.8,
dropout_rate=0.4,
num_classes=num_classes)
def EfficientNetB5(num_classes = 10):
# input image size 456x456
return EfficientNet(width_coefficient=1.6,
depth_coefficient=2.2,
dropout_rate=0.4,
num_classes=num_classes)
def EfficientNetB6(num_classes = 10):
# input image size 528x528
return EfficientNet(width_coefficient=1.8,
depth_coefficient=2.6,
dropout_rate=0.5,
num_classes=num_classes)
def EfficientNetB7(num_classes = 10):
# input image size 600x600
return EfficientNet(width_coefficient=2.0,
depth_coefficient=3.1,
dropout_rate=0.5,
num_classes=num_classes)
net = EfficientNetB0(num_classes = 10).to(device)
summary查看网络
我们可以通过summary来看到,模型的维度的变化,经过层后shape的变化,是否最后也是输出(batch,shape)
summary(net,(2,3,32,32))
==========================================================================================
Layer (type:depth-idx) Output Shape Param #
==========================================================================================
EfficientNet [2, 10] --
├─Conv2d: 1-1 [2, 32, 32, 32] 864
├─BatchNorm2d: 1-2 [2, 32, 32, 32] 64
├─Sequential: 1-3 [2, 320, 2, 2] --
│ └─MBconv: 2-1 [2, 16, 32, 32] 1,088
│ │ └─Conv2d: 3-1 [2, 32, 32, 32] 288
│ │ └─BatchNorm2d: 3-2 [2, 32, 32, 32] 64
│ │ └─SE: 3-3 [2, 32, 32, 32] 552
│ │ └─Conv2d: 3-4 [2, 16, 32, 32] 512
│ │ └─BatchNorm2d: 3-5 [2, 16, 32, 32] 32
│ └─MBconv: 2-2 [2, 24, 16, 16] --
│ │ └─Conv2d: 3-6 [2, 96, 32, 32] 1,536
│ │ └─BatchNorm2d: 3-7 [2, 96, 32, 32] 192
│ │ └─Conv2d: 3-8 [2, 96, 16, 16] 864
│ │ └─BatchNorm2d: 3-9 [2, 96, 16, 16] 192
│ │ └─SE: 3-10 [2, 96, 16, 16] 868
│ │ └─Conv2d: 3-11 [2, 24, 16, 16] 2,304
│ │ └─BatchNorm2d: 3-12 [2, 24, 16, 16] 48
│ └─MBconv: 2-3 [2, 24, 16, 16] --
│ │ └─Conv2d: 3-13 [2, 144, 16, 16] 3,456
│ │ └─BatchNorm2d: 3-14 [2, 144, 16, 16] 288
│ │ └─Conv2d: 3-15 [2, 144, 16, 16] 1,296
│ │ └─BatchNorm2d: 3-16 [2, 144, 16, 16] 288
│ │ └─SE: 3-17 [2, 144, 16, 16] 1,878
│ │ └─Conv2d: 3-18 [2, 24, 16, 16] 3,456
│ │ └─BatchNorm2d: 3-19 [2, 24, 16, 16] 48
│ └─MBconv: 2-4 [2, 40, 8, 8] --
│ │ └─Conv2d: 3-20 [2, 144, 16, 16] 3,456
│ │ └─BatchNorm2d: 3-21 [2, 144, 16, 16] 288
│ │ └─Conv2d: 3-22 [2, 144, 8, 8] 3,600
│ │ └─BatchNorm2d: 3-23 [2, 144, 8, 8] 288
│ │ └─SE: 3-24 [2, 144, 8, 8] 1,878
│ │ └─Conv2d: 3-25 [2, 40, 8, 8] 5,760
│ │ └─BatchNorm2d: 3-26 [2, 40, 8, 8] 80
│ └─MBconv: 2-5 [2, 40, 8, 8] --
│ │ └─Conv2d: 3-27 [2, 240, 8, 8] 9,600
│ │ └─BatchNorm2d: 3-28 [2, 240, 8, 8] 480
│ │ └─Conv2d: 3-29 [2, 240, 8, 8] 6,000
│ │ └─BatchNorm2d: 3-30 [2, 240, 8, 8] 480
│ │ └─SE: 3-31 [2, 240, 8, 8] 5,050
│ │ └─Conv2d: 3-32 [2, 40, 8, 8] 9,600
│ │ └─BatchNorm2d: 3-33 [2, 40, 8, 8] 80
│ └─MBconv: 2-6 [2, 80, 4, 4] --
│ │ └─Conv2d: 3-34 [2, 240, 8, 8] 9,600
│ │ └─BatchNorm2d: 3-35 [2, 240, 8, 8] 480
│ │ └─Conv2d: 3-36 [2, 240, 4, 4] 2,160
│ │ └─BatchNorm2d: 3-37 [2, 240, 4, 4] 480
│ │ └─SE: 3-38 [2, 240, 4, 4] 5,050
│ │ └─Conv2d: 3-39 [2, 80, 4, 4] 19,200
│ │ └─BatchNorm2d: 3-40 [2, 80, 4, 4] 160
│ └─MBconv: 2-7 [2, 80, 4, 4] --
│ │ └─Conv2d: 3-41 [2, 480, 4, 4] 38,400
│ │ └─BatchNorm2d: 3-42 [2, 480, 4, 4] 960
│ │ └─Conv2d: 3-43 [2, 480, 4, 4] 4,320
│ │ └─BatchNorm2d: 3-44 [2, 480, 4, 4] 960
│ │ └─SE: 3-45 [2, 480, 4, 4] 19,700
│ │ └─Conv2d: 3-46 [2, 80, 4, 4] 38,400
│ │ └─BatchNorm2d: 3-47 [2, 80, 4, 4] 160
│ └─MBconv: 2-8 [2, 80, 4, 4] --
│ │ └─Conv2d: 3-48 [2, 480, 4, 4] 38,400
│ │ └─BatchNorm2d: 3-49 [2, 480, 4, 4] 960
│ │ └─Conv2d: 3-50 [2, 480, 4, 4] 4,320
│ │ └─BatchNorm2d: 3-51 [2, 480, 4, 4] 960
│ │ └─SE: 3-52 [2, 480, 4, 4] 19,700
│ │ └─Conv2d: 3-53 [2, 80, 4, 4] 38,400
│ │ └─BatchNorm2d: 3-54 [2, 80, 4, 4] 160
│ └─MBconv: 2-9 [2, 112, 4, 4] --
│ │ └─Conv2d: 3-55 [2, 480, 4, 4] 38,400
│ │ └─BatchNorm2d: 3-56 [2, 480, 4, 4] 960
│ │ └─Conv2d: 3-57 [2, 480, 4, 4] 12,000
│ │ └─BatchNorm2d: 3-58 [2, 480, 4, 4] 960
│ │ └─SE: 3-59 [2, 480, 4, 4] 19,700
│ │ └─Conv2d: 3-60 [2, 112, 4, 4] 53,760
│ │ └─BatchNorm2d: 3-61 [2, 112, 4, 4] 224
│ └─MBconv: 2-10 [2, 112, 4, 4] --
│ │ └─Conv2d: 3-62 [2, 672, 4, 4] 75,264
│ │ └─BatchNorm2d: 3-63 [2, 672, 4, 4] 1,344
│ │ └─Conv2d: 3-64 [2, 672, 4, 4] 16,800
│ │ └─BatchNorm2d: 3-65 [2, 672, 4, 4] 1,344
│ │ └─SE: 3-66 [2, 672, 4, 4] 38,332
│ │ └─Conv2d: 3-67 [2, 112, 4, 4] 75,264
│ │ └─BatchNorm2d: 3-68 [2, 112, 4, 4] 224
│ └─MBconv: 2-11 [2, 112, 4, 4] --
│ │ └─Conv2d: 3-69 [2, 672, 4, 4] 75,264
│ │ └─BatchNorm2d: 3-70 [2, 672, 4, 4] 1,344
│ │ └─Conv2d: 3-71 [2, 672, 4, 4] 16,800
│ │ └─BatchNorm2d: 3-72 [2, 672, 4, 4] 1,344
│ │ └─SE: 3-73 [2, 672, 4, 4] 38,332
│ │ └─Conv2d: 3-74 [2, 112, 4, 4] 75,264
│ │ └─BatchNorm2d: 3-75 [2, 112, 4, 4] 224
│ └─MBconv: 2-12 [2, 192, 2, 2] --
│ │ └─Conv2d: 3-76 [2, 672, 4, 4] 75,264
│ │ └─BatchNorm2d: 3-77 [2, 672, 4, 4] 1,344
│ │ └─Conv2d: 3-78 [2, 672, 2, 2] 16,800
│ │ └─BatchNorm2d: 3-79 [2, 672, 2, 2] 1,344
│ │ └─SE: 3-80 [2, 672, 2, 2] 38,332
│ │ └─Conv2d: 3-81 [2, 192, 2, 2] 129,024
│ │ └─BatchNorm2d: 3-82 [2, 192, 2, 2] 384
│ └─MBconv: 2-13 [2, 192, 2, 2] --
│ │ └─Conv2d: 3-83 [2, 1152, 2, 2] 221,184
│ │ └─BatchNorm2d: 3-84 [2, 1152, 2, 2] 2,304
│ │ └─Conv2d: 3-85 [2, 1152, 2, 2] 28,800
│ │ └─BatchNorm2d: 3-86 [2, 1152, 2, 2] 2,304
│ │ └─SE: 3-87 [2, 1152, 2, 2] 111,792
│ │ └─Conv2d: 3-88 [2, 192, 2, 2] 221,184
│ │ └─BatchNorm2d: 3-89 [2, 192, 2, 2] 384
│ └─MBconv: 2-14 [2, 192, 2, 2] --
│ │ └─Conv2d: 3-90 [2, 1152, 2, 2] 221,184
│ │ └─BatchNorm2d: 3-91 [2, 1152, 2, 2] 2,304
│ │ └─Conv2d: 3-92 [2, 1152, 2, 2] 28,800
│ │ └─BatchNorm2d: 3-93 [2, 1152, 2, 2] 2,304
│ │ └─SE: 3-94 [2, 1152, 2, 2] 111,792
│ │ └─Conv2d: 3-95 [2, 192, 2, 2] 221,184
│ │ └─BatchNorm2d: 3-96 [2, 192, 2, 2] 384
│ └─MBconv: 2-15 [2, 192, 2, 2] --
│ │ └─Conv2d: 3-97 [2, 1152, 2, 2] 221,184
│ │ └─BatchNorm2d: 3-98 [2, 1152, 2, 2] 2,304
│ │ └─Conv2d: 3-99 [2, 1152, 2, 2] 28,800
│ │ └─BatchNorm2d: 3-100 [2, 1152, 2, 2] 2,304
│ │ └─SE: 3-101 [2, 1152, 2, 2] 111,792
│ │ └─Conv2d: 3-102 [2, 192, 2, 2] 221,184
│ │ └─BatchNorm2d: 3-103 [2, 192, 2, 2] 384
│ └─MBconv: 2-16 [2, 320, 2, 2] --
│ │ └─Conv2d: 3-104 [2, 1152, 2, 2] 221,184
│ │ └─BatchNorm2d: 3-105 [2, 1152, 2, 2] 2,304
│ │ └─Conv2d: 3-106 [2, 1152, 2, 2] 10,368
│ │ └─BatchNorm2d: 3-107 [2, 1152, 2, 2] 2,304
│ │ └─SE: 3-108 [2, 1152, 2, 2] 111,792
│ │ └─Conv2d: 3-109 [2, 320, 2, 2] 368,640
│ │ └─BatchNorm2d: 3-110 [2, 320, 2, 2] 640
├─Linear: 1-4 [2, 10] 3,210
==========================================================================================
Total params: 3,599,686
Trainable params: 3,599,686
Non-trainable params: 0
Total mult-adds (M): 60.76
==========================================================================================
Input size (MB): 0.02
Forward/backward pass size (MB): 17.59
Params size (MB): 14.39
Estimated Total Size (MB): 32.01
==========================================================================================
测试和定义网络
我们也可以打印出我们的模型观察一下
print(net)
EfficientNet(
(conv1): Conv2d(3, 32, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn1): BatchNorm2d(32, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(layers): Sequential(
(0): MBconv(
(conv1): Conv2d(32, 32, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn1): BatchNorm2d(32, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(conv2): Conv2d(32, 32, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), groups=32, bias=False)
(bn2): BatchNorm2d(32, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(se): SE(
(se1): Conv2d(32, 8, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1))
(se2): Conv2d(8, 32, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1))
)
(conv3): Conv2d(32, 16, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn3): BatchNorm2d(16, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
)
(1): MBconv(
(conv1): Conv2d(16, 96, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn1): BatchNorm2d(96, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(conv2): Conv2d(96, 96, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(2, 2), padding=(1, 1), groups=96, bias=False)
(bn2): BatchNorm2d(96, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(se): SE(
(se1): Conv2d(96, 4, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1))
(se2): Conv2d(4, 96, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1))
)
(conv3): Conv2d(96, 24, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn3): BatchNorm2d(24, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
)
(2): MBconv(
(conv1): Conv2d(24, 144, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn1): BatchNorm2d(144, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(conv2): Conv2d(144, 144, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), groups=144, bias=False)
(bn2): BatchNorm2d(144, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(se): SE(
(se1): Conv2d(144, 6, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1))
(se2): Conv2d(6, 144, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1))
)
(conv3): Conv2d(144, 24, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn3): BatchNorm2d(24, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
)
(3): MBconv(
(conv1): Conv2d(24, 144, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn1): BatchNorm2d(144, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(conv2): Conv2d(144, 144, kernel_size=(5, 5), stride=(2, 2), padding=(2, 2), groups=144, bias=False)
(bn2): BatchNorm2d(144, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(se): SE(
(se1): Conv2d(144, 6, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1))
(se2): Conv2d(6, 144, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1))
)
(conv3): Conv2d(144, 40, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn3): BatchNorm2d(40, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
)
(4): MBconv(
(conv1): Conv2d(40, 240, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn1): BatchNorm2d(240, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(conv2): Conv2d(240, 240, kernel_size=(5, 5), stride=(1, 1), padding=(2, 2), groups=240, bias=False)
(bn2): BatchNorm2d(240, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(se): SE(
(se1): Conv2d(240, 10, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1))
(se2): Conv2d(10, 240, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1))
)
(conv3): Conv2d(240, 40, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn3): BatchNorm2d(40, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
)
(5): MBconv(
(conv1): Conv2d(40, 240, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn1): BatchNorm2d(240, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(conv2): Conv2d(240, 240, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(2, 2), padding=(1, 1), groups=240, bias=False)
(bn2): BatchNorm2d(240, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(se): SE(
(se1): Conv2d(240, 10, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1))
(se2): Conv2d(10, 240, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1))
)
(conv3): Conv2d(240, 80, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn3): BatchNorm2d(80, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
)
(6): MBconv(
(conv1): Conv2d(80, 480, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn1): BatchNorm2d(480, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(conv2): Conv2d(480, 480, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), groups=480, bias=False)
(bn2): BatchNorm2d(480, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(se): SE(
(se1): Conv2d(480, 20, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1))
(se2): Conv2d(20, 480, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1))
)
(conv3): Conv2d(480, 80, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn3): BatchNorm2d(80, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
)
(7): MBconv(
(conv1): Conv2d(80, 480, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn1): BatchNorm2d(480, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(conv2): Conv2d(480, 480, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), groups=480, bias=False)
(bn2): BatchNorm2d(480, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(se): SE(
(se1): Conv2d(480, 20, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1))
(se2): Conv2d(20, 480, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1))
)
(conv3): Conv2d(480, 80, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn3): BatchNorm2d(80, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
)
(8): MBconv(
(conv1): Conv2d(80, 480, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn1): BatchNorm2d(480, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(conv2): Conv2d(480, 480, kernel_size=(5, 5), stride=(1, 1), padding=(2, 2), groups=480, bias=False)
(bn2): BatchNorm2d(480, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(se): SE(
(se1): Conv2d(480, 20, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1))
(se2): Conv2d(20, 480, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1))
)
(conv3): Conv2d(480, 112, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn3): BatchNorm2d(112, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
)
(9): MBconv(
(conv1): Conv2d(112, 672, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn1): BatchNorm2d(672, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(conv2): Conv2d(672, 672, kernel_size=(5, 5), stride=(1, 1), padding=(2, 2), groups=672, bias=False)
(bn2): BatchNorm2d(672, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(se): SE(
(se1): Conv2d(672, 28, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1))
(se2): Conv2d(28, 672, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1))
)
(conv3): Conv2d(672, 112, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn3): BatchNorm2d(112, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
)
(10): MBconv(
(conv1): Conv2d(112, 672, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn1): BatchNorm2d(672, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(conv2): Conv2d(672, 672, kernel_size=(5, 5), stride=(1, 1), padding=(2, 2), groups=672, bias=False)
(bn2): BatchNorm2d(672, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(se): SE(
(se1): Conv2d(672, 28, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1))
(se2): Conv2d(28, 672, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1))
)
(conv3): Conv2d(672, 112, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn3): BatchNorm2d(112, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
)
(11): MBconv(
(conv1): Conv2d(112, 672, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn1): BatchNorm2d(672, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(conv2): Conv2d(672, 672, kernel_size=(5, 5), stride=(2, 2), padding=(2, 2), groups=672, bias=False)
(bn2): BatchNorm2d(672, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(se): SE(
(se1): Conv2d(672, 28, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1))
(se2): Conv2d(28, 672, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1))
)
(conv3): Conv2d(672, 192, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn3): BatchNorm2d(192, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
)
(12): MBconv(
(conv1): Conv2d(192, 1152, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn1): BatchNorm2d(1152, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(conv2): Conv2d(1152, 1152, kernel_size=(5, 5), stride=(1, 1), padding=(2, 2), groups=1152, bias=False)
(bn2): BatchNorm2d(1152, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(se): SE(
(se1): Conv2d(1152, 48, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1))
(se2): Conv2d(48, 1152, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1))
)
(conv3): Conv2d(1152, 192, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn3): BatchNorm2d(192, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
)
(13): MBconv(
(conv1): Conv2d(192, 1152, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn1): BatchNorm2d(1152, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(conv2): Conv2d(1152, 1152, kernel_size=(5, 5), stride=(1, 1), padding=(2, 2), groups=1152, bias=False)
(bn2): BatchNorm2d(1152, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(se): SE(
(se1): Conv2d(1152, 48, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1))
(se2): Conv2d(48, 1152, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1))
)
(conv3): Conv2d(1152, 192, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn3): BatchNorm2d(192, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
)
(14): MBconv(
(conv1): Conv2d(192, 1152, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn1): BatchNorm2d(1152, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(conv2): Conv2d(1152, 1152, kernel_size=(5, 5), stride=(1, 1), padding=(2, 2), groups=1152, bias=False)
(bn2): BatchNorm2d(1152, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(se): SE(
(se1): Conv2d(1152, 48, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1))
(se2): Conv2d(48, 1152, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1))
)
(conv3): Conv2d(1152, 192, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn3): BatchNorm2d(192, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
)
(15): MBconv(
(conv1): Conv2d(192, 1152, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn1): BatchNorm2d(1152, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(conv2): Conv2d(1152, 1152, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), groups=1152, bias=False)
(bn2): BatchNorm2d(1152, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(se): SE(
(se1): Conv2d(1152, 48, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1))
(se2): Conv2d(48, 1152, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1))
)
(conv3): Conv2d(1152, 320, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn3): BatchNorm2d(320, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
)
)
(linear): Linear(in_features=320, out_features=10, bias=True)
)
接下来可以简单测试一下,是否输入后能得到我们的正确的维度shape
test_x = torch.randn(2,3,32,32).to(device)
test_y = net(test_x)
print(test_y.shape)
torch.Size([2, 10])
定义网络和设置类别
net = EfficientNetB0(num_classes=10)
5. 定义损失函数和优化器
pytorch将深度学习中常用的优化方法全部封装在torch.optim之中,所有的优化方法都是继承基类optim.Optimizier
损失函数是封装在神经网络工具箱nn中的,包含很多损失函数
这里我使用的是SGD + momentum算法,并且我们损失函数定义为交叉熵函数,除此之外学习策略定义为动态更新学习率,如果5次迭代后,训练的损失并没有下降,那么我们便会更改学习率,会变为原来的0.5倍,最小降低到0.00001
如果想更加了解优化器和学习率策略的话,可以参考以下资料
- Pytorch Note15 优化算法1 梯度下降(Gradient descent varients)
- Pytorch Note16 优化算法2 动量法(Momentum)
- Pytorch Note34 学习率衰减
这里决定迭代10次
import torch.optim as optim
optimizer = optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr=1e-3, momentum=0.9, weight_decay=5e-4)
optimizer = optim.AdamW(net.parameters(), lr=1e-2)
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
scheduler = optim.lr_scheduler.ReduceLROnPlateau(optimizer, 'min', factor=0.94 ,patience = 1,min_lr = 0.000001) # 动态更新学习率
# scheduler = optim.lr_scheduler.MultiStepLR(optimizer, milestones=[75, 150], gamma=0.5)
import time
epoch = 10
6. 训练及可视化(增加TensorBoard可视化)
首先定义模型保存的位置
import os
if not os.path.exists('./model'):
os.makedirs('./model')
else:
print('文件已存在')
save_path = './model/EfficientNet-B0.pth'
文件已存在
这次更新了tensorboard的可视化,可以得到更好看的图片,并且能可视化出不错的结果
# 使用tensorboard
from torch.utils.tensorboard import SummaryWriter
os.makedirs("./logs", exist_ok=True)
tbwriter = SummaryWriter(log_dir='./logs/EfficientNet-B0', comment='EfficientNet-B0') # 使用tensorboard记录中间输出
tbwriter.add_graph(model= net, input_to_model=torch.randn(size=(2, 3, 32, 32)))
如果存在GPU可以选择使用GPU进行运行,并且可以设置并行运算
if device == 'cuda':
net.to(device)
net = nn.DataParallel(net) # 使用并行运算
开始训练
我定义了一个train函数,在train函数中进行一个训练,并保存我们训练后的模型,这一部分一定要注意,这里的utils文件是我个人写的,所以需要下载下来
或者可以参考我们的工具函数篇,我还更新了结果和方法。
from utils import plot_history
from utils import train
Acc, Loss, Lr = train(net, trainloader, testloader, epoch, optimizer, criterion, scheduler, save_path, tbwriter, verbose = True)
Train Epoch 1/10: 100%|██████████| 391/391 [01:14<00:00, 5.28it/s, Train Acc=0.377, Train Loss=1.67]
Test Epoch 1/10: 100%|██████████| 79/79 [00:03<00:00, 25.05it/s, Test Acc=0.458, Test Loss=1.65]
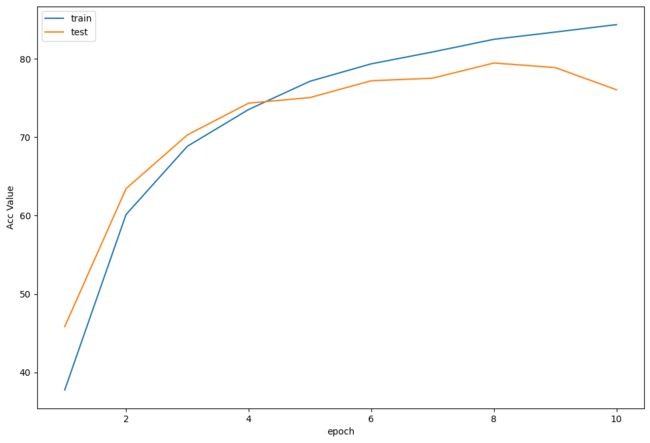
Epoch [ 1/ 10] Train Loss:1.670216 Train Acc:37.75% Test Loss:1.651851 Test Acc:45.83% Learning Rate:0.010000
Train Epoch 2/10: 100%|██████████| 391/391 [01:12<00:00, 5.38it/s, Train Acc=0.601, Train Loss=1.12]
Test Epoch 2/10: 100%|██████████| 79/79 [00:03<00:00, 19.84it/s, Test Acc=0.634, Test Loss=1.05]
Epoch [ 2/ 10] Train Loss:1.115703 Train Acc:60.13% Test Loss:1.049351 Test Acc:63.43% Learning Rate:0.010000
Train Epoch 3/10: 100%|██████████| 391/391 [01:12<00:00, 5.40it/s, Train Acc=0.688, Train Loss=0.888]
Test Epoch 3/10: 100%|██████████| 79/79 [00:03<00:00, 24.33it/s, Test Acc=0.703, Test Loss=0.856]
Epoch [ 3/ 10] Train Loss:0.888298 Train Acc:68.83% Test Loss:0.856442 Test Acc:70.28% Learning Rate:0.010000
Train Epoch 4/10: 100%|██████████| 391/391 [01:11<00:00, 5.45it/s, Train Acc=0.735, Train Loss=0.763]
Test Epoch 4/10: 100%|██████████| 79/79 [00:03<00:00, 25.79it/s, Test Acc=0.743, Test Loss=0.738]
Epoch [ 4/ 10] Train Loss:0.762550 Train Acc:73.53% Test Loss:0.738470 Test Acc:74.34% Learning Rate:0.010000
Train Epoch 5/10: 100%|██████████| 391/391 [01:12<00:00, 5.36it/s, Train Acc=0.771, Train Loss=0.667]
Test Epoch 5/10: 100%|██████████| 79/79 [00:03<00:00, 22.48it/s, Test Acc=0.75, Test Loss=0.713]
Epoch [ 5/ 10] Train Loss:0.666550 Train Acc:77.13% Test Loss:0.712513 Test Acc:75.05% Learning Rate:0.010000
Train Epoch 6/10: 100%|██████████| 391/391 [01:10<00:00, 5.54it/s, Train Acc=0.794, Train Loss=0.602]
Test Epoch 6/10: 100%|██████████| 79/79 [00:03<00:00, 24.28it/s, Test Acc=0.772, Test Loss=0.693]
Epoch [ 6/ 10] Train Loss:0.601911 Train Acc:79.35% Test Loss:0.693019 Test Acc:77.20% Learning Rate:0.010000
Train Epoch 7/10: 100%|██████████| 391/391 [01:12<00:00, 5.42it/s, Train Acc=0.809, Train Loss=0.56]
Test Epoch 7/10: 100%|██████████| 79/79 [00:03<00:00, 25.42it/s, Test Acc=0.775, Test Loss=0.655]
Epoch [ 7/ 10] Train Loss:0.559702 Train Acc:80.86% Test Loss:0.654783 Test Acc:77.52% Learning Rate:0.010000
Train Epoch 8/10: 100%|██████████| 391/391 [01:11<00:00, 5.48it/s, Train Acc=0.825, Train Loss=0.511]
Test Epoch 8/10: 100%|██████████| 79/79 [00:03<00:00, 23.75it/s, Test Acc=0.795, Test Loss=0.614]
Epoch [ 8/ 10] Train Loss:0.510548 Train Acc:82.48% Test Loss:0.614094 Test Acc:79.46% Learning Rate:0.010000
Train Epoch 9/10: 100%|██████████| 391/391 [01:11<00:00, 5.44it/s, Train Acc=0.834, Train Loss=0.482]
Test Epoch 9/10: 100%|██████████| 79/79 [00:03<00:00, 25.49it/s, Test Acc=0.789, Test Loss=0.634]
Epoch [ 9/ 10] Train Loss:0.482006 Train Acc:83.40% Test Loss:0.634270 Test Acc:78.88% Learning Rate:0.010000
Train Epoch 10/10: 100%|██████████| 391/391 [01:11<00:00, 5.46it/s, Train Acc=0.844, Train Loss=0.456]
Test Epoch 10/10: 100%|██████████| 79/79 [00:04<00:00, 19.49it/s, Test Acc=0.76, Test Loss=0.742]
Epoch [ 10/ 10] Train Loss:0.455699 Train Acc:84.36% Test Loss:0.742326 Test Acc:76.05% Learning Rate:0.010000
训练曲线可视化
plot_history(epoch ,Acc, Loss, Lr)
可以运行以下代码进行tensorboard可视化
tensorboard --logdir logs
7. 测试
查看准确率
correct = 0 # 定义预测正确的图片数,初始化为0
total = 0 # 总共参与测试的图片数,也初始化为0
for data in testloader: # 循环每一个batch
images, labels = data
images = images.to(device)
labels = labels.to(device)
net.eval() # 把模型转为test模式
if hasattr(torch.cuda, 'empty_cache'):
torch.cuda.empty_cache()
outputs = net(images) # 输入网络进行测试
# outputs.data是一个4x10张量,将每一行的最大的那一列的值和序号各自组成一个一维张量返回,第一个是值的张量,第二个是序号的张量。
_, predicted = torch.max(outputs.data, 1)
total += labels.size(0) # 更新测试图片的数量
correct += (predicted == labels).sum() # 更新正确分类的图片的数量
print('Accuracy of the network on the 10000 test images: %.2f %%' % (100 * correct / total))
Accuracy of the network on the 10000 test images: 76.13 %
程序中的 torch.max(outputs.data, 1) ,返回一个tuple (元组)
而这里很明显,这个返回的元组的第一个元素是image data,即是最大的 值,第二个元素是label, 即是最大的值 的 索引!我们只需要label(最大值的索引),所以就会有_,predicted这样的赋值语句,表示忽略第一个返回值,把它赋值给 _, 就是舍弃它的意思;
查看每一类的准确率
# 定义2个存储每类中测试正确的个数的 列表,初始化为0
class_correct = list(0. for i in range(10))
class_total = list(0. for i in range(10))
net.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
for data in testloader:
images, labels = data
images = images.to(device)
labels = labels.to(device)
if hasattr(torch.cuda, 'empty_cache'):
torch.cuda.empty_cache()
outputs = net(images)
_, predicted = torch.max(outputs.data, 1)
#(batch_size)数据中,输出于label相同的,标记为1,否则为0
c = (predicted == labels).squeeze()
for i in range(len(images)): # 因为每个batch都有len(iamges)张图片,所以还需要一个len(iamges)的小循环
label = labels[i] # 对各个类的进行各自累加
class_correct[label] += c[i]
class_total[label] += 1
for i in range(10):
print('Accuracy of %5s : %.2f %%' % (classes[i], 100 * class_correct[i] / class_total[i]))
Accuracy of airplane : 80.40 %
Accuracy of automobile : 92.20 %
Accuracy of bird : 75.70 %
Accuracy of cat : 52.30 %
Accuracy of deer : 50.00 %
Accuracy of dog : 75.80 %
Accuracy of frog : 64.40 %
Accuracy of horse : 92.60 %
Accuracy of ship : 89.10 %
Accuracy of truck : 88.80 %
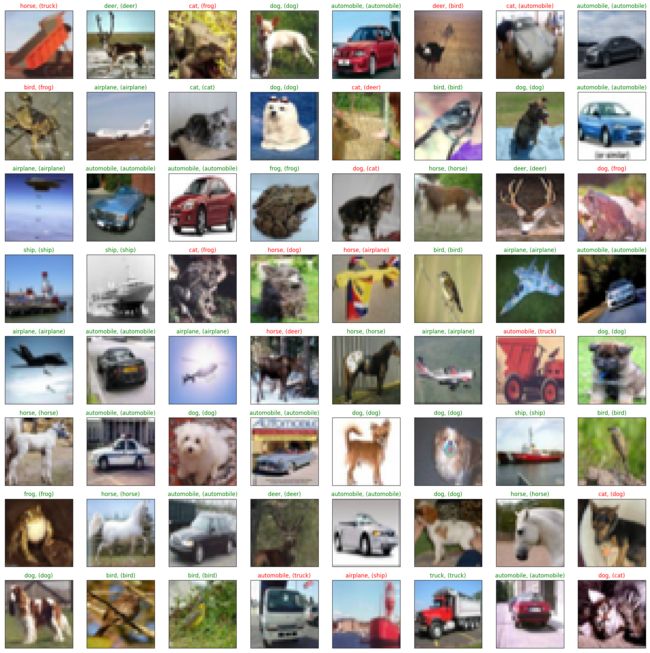
抽样测试并可视化一部分结果
dataiter = iter(testloader)
images, labels = dataiter.next()
images_,labels = images.to(device),labels.to(device)
val_output = net(images_)
_, val_preds = torch.max(val_output, 1)
correct = torch.sum(val_preds == labels.data).item()
val_preds,labels = val_preds.cpu(),labels.cpu()
print("Accuracy Rate = {}%".format(correct/len(images) * 100))
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(25,25))
for idx in np.arange(64):
ax = fig.add_subplot(8, 8, idx+1, xticks=[], yticks=[])
imshow(images[idx])
ax.set_title("{}, ({})".format(classes[val_preds[idx].item()], classes[labels[idx].item()]),
color = ("green" if val_preds[idx].item()==labels[idx].item() else "red"))
Accuracy Rate = 78.125%
8. 保存模型
这里保存成前面设定的模型的名字
torch.save(net,save_path[:-4]+'_'+str(epoch)+'.pth')
9. 预测
import torch
from PIL import Image
from torch.autograd import Variable
import torch.nn.functional as F
from torchvision import datasets, transforms
import numpy as np
device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
model = EfficientNetB0(num_classes=10)
model = torch.load(save_path, map_location="cpu") # 加载模型
model.to(device)
model.eval() # 把模型转为test模式
DataParallel(
(module): EfficientNet(
(conv1): Conv2d(3, 32, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn1): BatchNorm2d(32, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(layers): Sequential(
(0): MBconv(
(conv1): Conv2d(32, 32, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn1): BatchNorm2d(32, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(conv2): Conv2d(32, 32, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), groups=32, bias=False)
(bn2): BatchNorm2d(32, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(se): SE(
(se1): Conv2d(32, 8, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1))
(se2): Conv2d(8, 32, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1))
)
(conv3): Conv2d(32, 16, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn3): BatchNorm2d(16, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
)
(1): MBconv(
(conv1): Conv2d(16, 96, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn1): BatchNorm2d(96, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(conv2): Conv2d(96, 96, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(2, 2), padding=(1, 1), groups=96, bias=False)
(bn2): BatchNorm2d(96, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(se): SE(
(se1): Conv2d(96, 4, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1))
(se2): Conv2d(4, 96, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1))
)
(conv3): Conv2d(96, 24, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn3): BatchNorm2d(24, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
)
(2): MBconv(
(conv1): Conv2d(24, 144, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn1): BatchNorm2d(144, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(conv2): Conv2d(144, 144, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), groups=144, bias=False)
(bn2): BatchNorm2d(144, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(se): SE(
(se1): Conv2d(144, 6, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1))
(se2): Conv2d(6, 144, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1))
)
(conv3): Conv2d(144, 24, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn3): BatchNorm2d(24, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
)
(3): MBconv(
(conv1): Conv2d(24, 144, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn1): BatchNorm2d(144, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(conv2): Conv2d(144, 144, kernel_size=(5, 5), stride=(2, 2), padding=(2, 2), groups=144, bias=False)
(bn2): BatchNorm2d(144, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(se): SE(
(se1): Conv2d(144, 6, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1))
(se2): Conv2d(6, 144, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1))
)
(conv3): Conv2d(144, 40, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn3): BatchNorm2d(40, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
)
(4): MBconv(
(conv1): Conv2d(40, 240, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn1): BatchNorm2d(240, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(conv2): Conv2d(240, 240, kernel_size=(5, 5), stride=(1, 1), padding=(2, 2), groups=240, bias=False)
(bn2): BatchNorm2d(240, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(se): SE(
(se1): Conv2d(240, 10, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1))
(se2): Conv2d(10, 240, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1))
)
(conv3): Conv2d(240, 40, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn3): BatchNorm2d(40, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
)
(5): MBconv(
(conv1): Conv2d(40, 240, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn1): BatchNorm2d(240, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(conv2): Conv2d(240, 240, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(2, 2), padding=(1, 1), groups=240, bias=False)
(bn2): BatchNorm2d(240, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(se): SE(
(se1): Conv2d(240, 10, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1))
(se2): Conv2d(10, 240, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1))
)
(conv3): Conv2d(240, 80, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn3): BatchNorm2d(80, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
)
(6): MBconv(
(conv1): Conv2d(80, 480, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn1): BatchNorm2d(480, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(conv2): Conv2d(480, 480, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), groups=480, bias=False)
(bn2): BatchNorm2d(480, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(se): SE(
(se1): Conv2d(480, 20, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1))
(se2): Conv2d(20, 480, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1))
)
(conv3): Conv2d(480, 80, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn3): BatchNorm2d(80, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
)
(7): MBconv(
(conv1): Conv2d(80, 480, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn1): BatchNorm2d(480, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(conv2): Conv2d(480, 480, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), groups=480, bias=False)
(bn2): BatchNorm2d(480, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(se): SE(
(se1): Conv2d(480, 20, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1))
(se2): Conv2d(20, 480, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1))
)
(conv3): Conv2d(480, 80, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn3): BatchNorm2d(80, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
)
(8): MBconv(
(conv1): Conv2d(80, 480, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn1): BatchNorm2d(480, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(conv2): Conv2d(480, 480, kernel_size=(5, 5), stride=(1, 1), padding=(2, 2), groups=480, bias=False)
(bn2): BatchNorm2d(480, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(se): SE(
(se1): Conv2d(480, 20, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1))
(se2): Conv2d(20, 480, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1))
)
(conv3): Conv2d(480, 112, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn3): BatchNorm2d(112, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
)
(9): MBconv(
(conv1): Conv2d(112, 672, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn1): BatchNorm2d(672, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(conv2): Conv2d(672, 672, kernel_size=(5, 5), stride=(1, 1), padding=(2, 2), groups=672, bias=False)
(bn2): BatchNorm2d(672, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(se): SE(
(se1): Conv2d(672, 28, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1))
(se2): Conv2d(28, 672, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1))
)
(conv3): Conv2d(672, 112, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn3): BatchNorm2d(112, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
)
(10): MBconv(
(conv1): Conv2d(112, 672, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn1): BatchNorm2d(672, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(conv2): Conv2d(672, 672, kernel_size=(5, 5), stride=(1, 1), padding=(2, 2), groups=672, bias=False)
(bn2): BatchNorm2d(672, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(se): SE(
(se1): Conv2d(672, 28, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1))
(se2): Conv2d(28, 672, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1))
)
(conv3): Conv2d(672, 112, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn3): BatchNorm2d(112, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
)
(11): MBconv(
(conv1): Conv2d(112, 672, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn1): BatchNorm2d(672, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(conv2): Conv2d(672, 672, kernel_size=(5, 5), stride=(2, 2), padding=(2, 2), groups=672, bias=False)
(bn2): BatchNorm2d(672, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(se): SE(
(se1): Conv2d(672, 28, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1))
(se2): Conv2d(28, 672, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1))
)
(conv3): Conv2d(672, 192, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn3): BatchNorm2d(192, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
)
(12): MBconv(
(conv1): Conv2d(192, 1152, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn1): BatchNorm2d(1152, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(conv2): Conv2d(1152, 1152, kernel_size=(5, 5), stride=(1, 1), padding=(2, 2), groups=1152, bias=False)
(bn2): BatchNorm2d(1152, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(se): SE(
(se1): Conv2d(1152, 48, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1))
(se2): Conv2d(48, 1152, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1))
)
(conv3): Conv2d(1152, 192, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn3): BatchNorm2d(192, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
)
(13): MBconv(
(conv1): Conv2d(192, 1152, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn1): BatchNorm2d(1152, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(conv2): Conv2d(1152, 1152, kernel_size=(5, 5), stride=(1, 1), padding=(2, 2), groups=1152, bias=False)
(bn2): BatchNorm2d(1152, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(se): SE(
(se1): Conv2d(1152, 48, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1))
(se2): Conv2d(48, 1152, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1))
)
(conv3): Conv2d(1152, 192, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn3): BatchNorm2d(192, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
)
(14): MBconv(
(conv1): Conv2d(192, 1152, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn1): BatchNorm2d(1152, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(conv2): Conv2d(1152, 1152, kernel_size=(5, 5), stride=(1, 1), padding=(2, 2), groups=1152, bias=False)
(bn2): BatchNorm2d(1152, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(se): SE(
(se1): Conv2d(1152, 48, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1))
(se2): Conv2d(48, 1152, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1))
)
(conv3): Conv2d(1152, 192, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn3): BatchNorm2d(192, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
)
(15): MBconv(
(conv1): Conv2d(192, 1152, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn1): BatchNorm2d(1152, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(conv2): Conv2d(1152, 1152, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), groups=1152, bias=False)
(bn2): BatchNorm2d(1152, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(se): SE(
(se1): Conv2d(1152, 48, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1))
(se2): Conv2d(48, 1152, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1))
)
(conv3): Conv2d(1152, 320, kernel_size=(1, 1), stride=(1, 1), bias=False)
(bn3): BatchNorm2d(320, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
)
)
(linear): Linear(in_features=320, out_features=10, bias=True)
)
)
并且为了方便,定义了一个predict函数,简单思想就是,先resize成网络使用的shape,然后进行变化tensor输入即可,不过这里有一个点,我们需要对我们的图片也进行transforms,因为我们的训练的时候,对每个图像也是进行了transforms的,所以我们需要保持一致
def predict(model, img):
trans = transforms.Compose([transforms.Resize((32,32)),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize(mean=(0.5, 0.5, 0.5),
std=(0.5, 0.5, 0.5)),
])
img = trans(img)
img = img.to(device)
# 图片扩展多一维,因为输入到保存的模型中是4维的[batch_size,通道,长,宽],而普通图片只有三维,[通道,长,宽]
img = img.unsqueeze(0) # 扩展后,为[1,3,32,32]
output = model(img)
prob = F.softmax(output,dim=1) #prob是10个分类的概率
print("概率",prob)
value, predicted = torch.max(output.data, 1)
print("类别",predicted.item())
print(value)
pred_class = classes[predicted.item()]
print("分类",pred_class)
读取本地图片进行预测
# 读取要预测的图片
img = Image.open("./airplane.jpg").convert('RGB') # 读取图像
img
predict(model, img)
概率 tensor([[9.9339e-01, 1.9589e-05, 4.6372e-04, 2.1349e-06, 3.1111e-05, 6.9647e-07,
1.7551e-06, 4.4248e-06, 5.8533e-03, 2.3146e-04]], device='cuda:0',
grad_fn=)
类别 0
tensor([9.4914], device='cuda:0')
分类 airplane
读取图片地址进行预测
我们也可以通过读取图片的url地址进行预测,这里我找了多个不同的图片进行预测
import requests
from PIL import Image
url = 'https://dss2.bdstatic.com/70cFvnSh_Q1YnxGkpoWK1HF6hhy/it/u=947072664,3925280208&fm=26&gp=0.jpg'
url = 'https://ss0.bdstatic.com/70cFuHSh_Q1YnxGkpoWK1HF6hhy/it/u=2952045457,215279295&fm=26&gp=0.jpg'
url = 'https://ss0.bdstatic.com/70cFvHSh_Q1YnxGkpoWK1HF6hhy/it/u=2838383012,1815030248&fm=26&gp=0.jpg'
url = 'https://gimg2.baidu.com/image_search/src=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.goupuzi.com%2Fnewatt%2FMon_1809%2F1_179223_7463b117c8a2c76.jpg&refer=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.goupuzi.com&app=2002&size=f9999,10000&q=a80&n=0&g=0n&fmt=jpeg?sec=1624346733&t=36ba18326a1e010737f530976201326d'
url = 'https://img2.baidu.com/it/u=3210145212,1163645841&fm=253&fmt=auto&app=120&f=JPEG?w=875&h=537' # horse
response = requests.get(url, stream=True)
print (response)
img = Image.open(response.raw)
img
predict(model, img)
概率 tensor([[1.5856e-03, 2.1046e-04, 3.9647e-03, 1.0489e-02, 7.3925e-02, 4.8408e-02,
3.3223e-04, 8.6051e-01, 1.6616e-04, 4.1264e-04]], device='cuda:0',
grad_fn=<SoftmaxBackward>)
类别 7
tensor([5.2634], device='cuda:0')
分类 horse
可以看到,分类还是比较正确的,正确分类了,并且他的置信度大概有86%,还是比较不错的。
10.总结
在这个模型中,其实我们只迭代了10次,EfficientNet实际上已经在10个迭代中已经达到了一个相当不错的结果,之前也被誉为是2020年最好的卷积神经网络,大概在训练集达到了84%的准确率,在测试集有76%的准确率,并且我也暂时没有做任何的数据增强。在原本的论文中,EfficientNet-B0进行分类是用224x224的图片,不过我这里用了32x32的原始CIFAR10图片,所以这个也是可以改进的,并且用更大的分辨率,不过这样可能会导致显存占的比较多,所以可以个人权衡一下资源来进行学习。
顺带提一句,我们的数据和代码都在我的汇总篇里有说明,如果需要,可以自取
这里再贴一下汇总篇:汇总篇