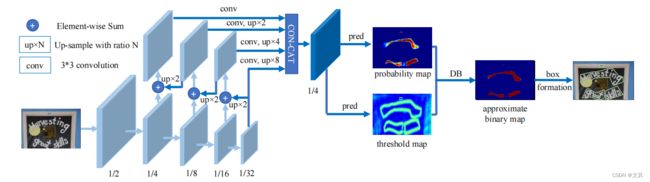
【DBNet模型】
DBNet模型
一、简述
DBNet是基于分割的文本检测算法,算法将可微分二值化模块(Differentiable Binarization)引入了分割模型,使得分割模型能够通过自适应的阈值进行二值化。经过验证,该方案不仅简化了后处理过程而且提升了文本检测的效果。相较于其他文本检测模型,DBNet在效果和性能上都有比较大的优势,是当前常用的文本检测算法。
二、模型结构
- Backbone网络,负责提取图像的特征
- FPN网络,特征金子塔结构增强特征
- Head网络,计算文本区域概率图
1.Backbone网络
DB文本检测网络的Backbone部分采用的是图像分类网络,论文中使用了ResNet50。这里结合具体的输入图像尺寸进行说明如下:
输入图像[1,3,640, 640] ,进入Backbone骨架网络,经过一系列卷积计算和下采样后,输出四个尺度特征图如下,这些特征将输入给特征金字塔FPN网络进一步的增强特征。
原图1/4特征图: [1, 16, 160, 160]
原图1/8特征图: [1, 24, 80, 80]
原图1/16特征图: [1, 56, 40, 40]
原图1/32特征图: [1, 480, 20, 20]
2.FPN网络
特征金字塔结构FPN是一种卷积网络来高效提取图片中各维度特征的常用方法。
FPN网络的输入为Backbone部分的输出,经FPN计算后输出的特征图的高度和宽度为原图的1/4, 即[1, 256, 160, 160] 。
(1)计算新的特征图
新1/32特征图: [1, 64, 20, 20]
新1/16特征图:[1, 64, 40, 40] # 原图1/16特征图与新1/32特征图上采样图相加
新1/8特征图:[1, 64, 80, 80] # 原图1/8特征图与新1/16特征图上采样图相加
新1/4特征图:[1, 64, 160, 160] # 原图1/4特征图与新1/8特征图上采样图相加
(2)特征图融合
新1/32特征图: [1, 64, 20, 20] ===> 卷积 + 8倍上采样 ===> [1, 64, 160, 160]
新1/16特征图:[1, 64, 40, 40] ===> 卷积 + 4倍上采样 ===> [1, 64, 160, 160]
新1/8特征图:[1, 64, 80, 80] ===> 卷积 + 2倍上采样 ===> [1, 64, 160, 160]
新1/4特征图:[1, 64, 160, 160] ===> 卷积 ===> [1, 64, 160, 160]
融合特征图:[1, 256, 160, 160] # 将1/4,1/8, 1/16, 1/32特征图按通道层合并在一起
3.Head网络
计算文本区域概率图,文本区域阈值图以文本区域二值图。
Head网络会在FPN特征的基础上作上采样,将FPN特征由原来的1/4大小映射到原图大小,最终将生成的三个图合并,输出为[1, 3, 640, 640]
三、标签生成
DB算法在进行模型训练的时,需要根据标注框生成两幅图像:概率图和阈值图。生成过程如下图所示:
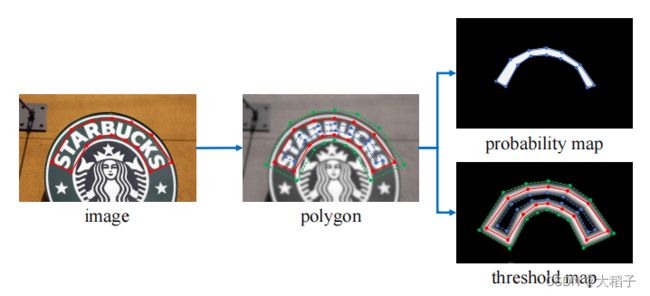
image图像中的红线是文本的标注框,文本标注框的点集合用如下形式表示:
G = { S k } k = 1 n G = \{S_k\}_{k=1}^n G={Sk}k=1n, n表示顶点的数量
在polygon图像中,将红色的标注框外扩distance得到绿色的polygon框,内缩distance得到蓝色的polygon框。
论文中标注框内缩和外扩使用相同的distance,其计算公式为:
D = A ( 1 − r 2 ) L D =\cfrac{A(1 - r^2)}{L} D=LA(1−r2), L代表周长,A代表面积,r代表缩放比例,通常r=0.4
多边形轮廓的周长L和面积A通过Polygon库计算获得。
根据计算出的distance,对标注框进行外扩和内缩操作,用Vatti算法实现,参考链接https://github.com/fonttools/pyclipper和中文文档https://www.cnblogs.com/zhigu/p/11943118.html,在python中调用pyclipper库的接口操作即可,简单示例如下。
import cv2
import pyclipper
import numpy as np
from shapely.geometry import Polygon
def draw_img(subject, canvas, color=(255,0,0)):
"""作图函数"""
for i in range(len(subject)):
j = (i+1)%len(subject)
cv2.line(canvas, subject[i], subject[j], color)
# 论文默认shrink值
r=0.4
# 假定标注框
subject = ((100, 100), (250, 100), (250, 200), (100, 200))
# 创建Polygon对象
polygon = Polygon(subject)
# 计算偏置distance
distance = polygon.area*(1-np.power(r, 2))/polygon.length
print(distance)
# 25.2
# 创建PyclipperOffset对象
padding = pyclipper.PyclipperOffset()
# 向ClipperOffset对象添加一个路径用来准备偏置
# padding.AddPath(subject, pyclipper.JT_ROUND, pyclipper.ET_CLOSEDPOLYGON)
# adding.AddPath(subject, pyclipper.JT_SQUARE, pyclipper.ET_CLOSEDPOLYGON)
padding.AddPath(subject, pyclipper.JT_MITER, pyclipper.ET_CLOSEDPOLYGON)
# polygon外扩
polygon_expand = padding.Execute(distance)[0]
polygon_expand = [tuple(l) for l in polygon_expand]
print(polygon_expand)
# [(75, 75), (275, 75), (275, 225), (75, 225)]
# polygon内缩
polygon_shrink = padding.Execute(-distance)[0]
polygon_shrink = [tuple(l) for l in polygon_shrink]
print(polygon_shrink)
# [(125, 125), (225, 125), (225, 175), (125, 175)]
# 作图
canvas = np.zeros((300,350,3), dtype=np.uint8)
# 原轮廓用红色线条展示
draw_img(subject, canvas, color=(0,0,255))
# 外扩轮廓用绿色线条展示
draw_img(polygon_expand, canvas, color=(0,255,0))
# 内缩轮廓用蓝色线条展示
draw_img(polygon_shrink, canvas, color=(255,0,0))
cv2.imshow("Canvas", canvas)
cv2.waitKey(0)
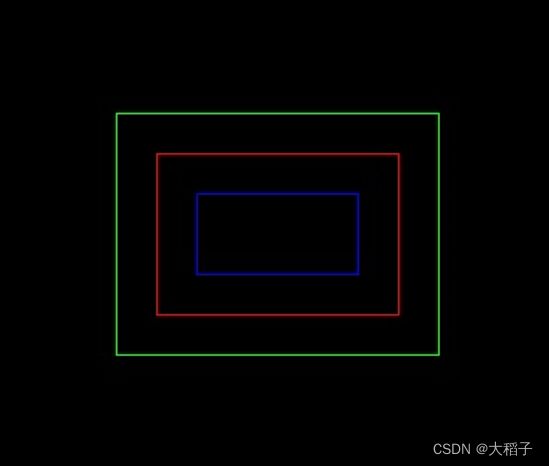
整体效果图如下,红色框为标注框,绿色框外扩后的效果,蓝色框为内缩后的效果。
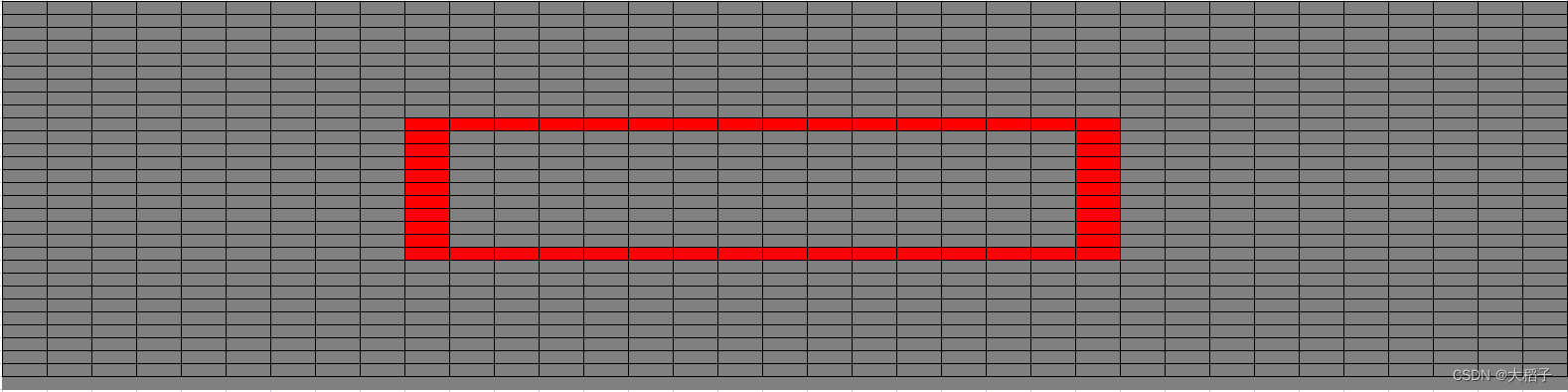
0.示例说明
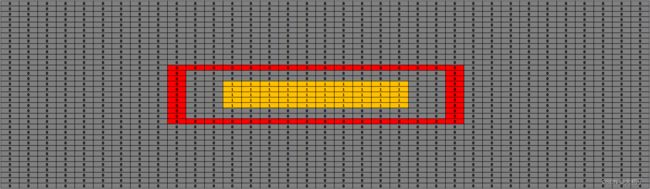
假定图像尺寸为(35,30,3), 图中存在文字标注框 text_box: [[10,10], [25,10], [25,20], [10,20]],如下图所示,红色框即为文本标注框。
以此示例简单说明概率图、阈值图和二值化图的创建。
1.概率图标签
使用收缩的方式获取算法训练需要的概率图标签。
标注框内缩后,覆盖区域的概率值为1,其余区域概率值为0
# 创建概率图
h, w = 30, 35
probability_map = np.zero((h, w), dtype=np.float32)
# 标注区域内缩
# 经过distance的公式计算(D=2.52)和pyclipper库的内缩坐标处理
# text_box: [[10,10], [25,10], [25,20], [10,20]] ===> shrink_box: [[13,13], [22,13], [22,17], [13,17]]
# shrink_box为标注框经过内缩后的区域
shrink_box = [[13,13], [22,13], [22,17], [13,17]]
shrink_box = np.array(shrink_box).reshape(-1,2)
# 将概率图中的shrink区域赋值为1
cv2.fillPoly(probability_map, [shrink_box.astype(np.int32)], 1)
下图所示即为概率图,其中文字区域的概率值为1,背景区域的概率值为0
2.阈值图标签
阈值图中,需计算各位置到标注框的距离,距离越近的位置,阈值越高。
基本步骤如下:
(1) 标注框外扩
import pyclipper
import numpy as np
from shapely.geometry import Polygon
# 论文默认shrink值
r=0.4
# 标注框
subject = [[10,10],[25,10],[25,20],[10,20]]
# 创建Polygon对象
polygon = Polygon(subject)
# 计算偏置distance
distance = polygon.area*(1-np.power(r, 2))/polygon.length
print(distance)
# 2.52
# 创建PyclipperOffset对象
padding = pyclipper.PyclipperOffset()
# 向ClipperOffset对象添加一个路径用来准备偏置
padding.AddPath(subject, pyclipper.JT_MITER, pyclipper.ET_CLOSEDPOLYGON)
# polygon外扩
polygon_expand = padding.Execute(distance)[0]
polygon_expand = [tuple(l) for l in polygon_expand]
print(polygon_expand)
# [(7, 7), (28, 7), (28, 23), (7, 23)]
(2) 计算距离
标注框外扩后,文字区域扩大,需计算区域内每个点到标注框的距离。标注框看作四条线段,计算出每个位置点到这四条线段的距离,取最小值为最终距离。距离的计算借助两个三角形公式: 余弦定理和面积公式。具体的计算过程如下:
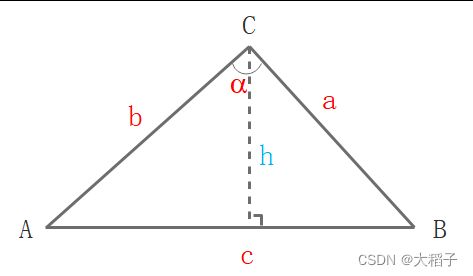
由三角形面积公式,推导出h:
{ S = 1 2 ⋅ c ⋅ h S = 1 2 ⋅ a ⋅ b ⋅ s i n α ⇒ h = a ⋅ b c ⋅ s i n α \begin{cases} S = \cfrac{1}{2}\cdot c \cdot h \\ S = \cfrac{1}{2}\cdot a \cdot b \cdot sin\alpha \end{cases} ⇒ h = \cfrac{a \cdot b}{c} \cdot sin\alpha ⎩⎪⎨⎪⎧S=21⋅c⋅hS=21⋅a⋅b⋅sinα⇒h=ca⋅b⋅sinα
其中,a, b和c的值可以通过位置距离计算, s i n α sin\alpha sinα 通过余弦定理计算得出:
c o s 2 α = a 2 + b 2 − c 2 2 a b ⇒ s i n α = 1 − c o s 2 α cos^2\alpha = \cfrac{a^2 + b^2 - c^2}{2ab} ⇒ sin\alpha = \sqrt{\smash[b]{1 - cos^2\alpha}} cos2α=2aba2+b2−c2⇒sinα=1−cos2α
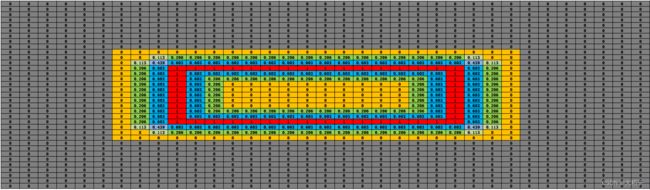
(3) 距离归一化
计算出每个位置点的值后,进行归一化。区域内所有的值除以前面计算出来的distance,限定取值在[0, 1]之间。得到相对距离比例的数值,如下图所示。

(4) 计算阈值图
用1减去距离归一化的值,即获取到阈值图。靠近标注框的位置,阈值接近1,阈值图如下所示。
 参照核心代码如下,详见paddleocr。
参照核心代码如下,详见paddleocr。
import cv2
import numpy as np
import pyclipper
from shapely.geometry import Polygon
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
class MakeBorderMap(object):
def __init__(self,
shrink_ratio=0.4,
thresh_min=0.3,
thresh_max=0.7,
**kwargs):
self.shrink_ratio = shrink_ratio
self.thresh_min = thresh_min
self.thresh_max = thresh_max
def __call__(self, data):
img = data['image']
text_polys = data['polys']
ignore_tags = data['ignore_tags']
canvas = np.zeros(img.shape[:2], dtype=np.float32)
mask = np.zeros(img.shape[:2], dtype=np.float32)
for i in range(len(text_polys)):
if ignore_tags[i]:
continue
self.draw_border_map(text_polys[i], canvas, mask=mask,data=data)
#canvas = canvas * (self.thresh_max - self.thresh_min) + self.thresh_min
data['threshold_map'] = canvas
data['threshold_mask'] = mask
return data
def draw_border_map(self, polygon, canvas, mask, data):
polygon = np.array(polygon)
assert polygon.ndim == 2
assert polygon.shape[1] == 2
polygon_shape = Polygon(polygon)
if polygon_shape.area <= 0:
return
distance = polygon_shape.area * (
1 - np.power(self.shrink_ratio, 2)) / polygon_shape.length
subject = [tuple(l) for l in polygon]
padding = pyclipper.PyclipperOffset()
#padding.AddPath(subject, pyclipper.JT_ROUND, pyclipper.ET_CLOSEDPOLYGON)
padding.AddPath(subject, pyclipper.JT_MITER, pyclipper.ET_CLOSEDPOLYGON)
padded_polygon = np.array(padding.Execute(distance)[0])
cv2.fillPoly(mask, [padded_polygon.astype(np.int32)], 1.0)
xmin = padded_polygon[:, 0].min()
xmax = padded_polygon[:, 0].max()
ymin = padded_polygon[:, 1].min()
ymax = padded_polygon[:, 1].max()
width = xmax - xmin + 1
height = ymax - ymin + 1
polygon[:, 0] = polygon[:, 0] - xmin
polygon[:, 1] = polygon[:, 1] - ymin
xs = np.broadcast_to(
np.linspace(
0, width - 1, num=width).reshape(1, width), (height, width))
ys = np.broadcast_to(
np.linspace(
0, height - 1, num=height).reshape(height, 1), (height, width))
distance_map = np.zeros(
(polygon.shape[0], height, width), dtype=np.float32)
for i in range(polygon.shape[0]):
j = (i + 1) % polygon.shape[0]
absolute_distance = self._distance(xs, ys, polygon[i], polygon[j])
distance_map[i] = np.clip(absolute_distance / distance, 0, 1)
distance_map = distance_map.min(axis=0)
distance_map = np.round(distance_map, 3)
data['distance_map'] = distance_map
xmin_valid = min(max(0, xmin), canvas.shape[1] - 1)
xmax_valid = min(max(0, xmax), canvas.shape[1] - 1)
ymin_valid = min(max(0, ymin), canvas.shape[0] - 1)
ymax_valid = min(max(0, ymax), canvas.shape[0] - 1)
canvas[ymin_valid:ymax_valid + 1, xmin_valid:xmax_valid + 1] = np.fmax(
1 - distance_map[ymin_valid - ymin:ymax_valid - ymax + height,
xmin_valid - xmin:xmax_valid - xmax + width],
canvas[ymin_valid:ymax_valid + 1, xmin_valid:xmax_valid + 1])
def _distance(self, xs, ys, point_1, point_2):
'''
compute the distance from point to a line
ys: coordinates in the first axis
xs: coordinates in the second axis
point_1, point_2: (x, y), the end of the line
'''
height, width = xs.shape[:2]
square_distance_1 = np.square(xs - point_1[0]) + np.square(ys - point_1[1])
square_distance_2 = np.square(xs - point_2[0]) + np.square(ys - point_2[1])
square_distance = np.square(point_1[0] - point_2[0]) + np.square(point_1[1] - point_2[1])
cosin = (square_distance - square_distance_1 - square_distance_2) / (
2 * np.sqrt(square_distance_1 * square_distance_2))
square_sin = 1 - np.square(cosin)
square_sin = np.nan_to_num(square_sin)
result = np.sqrt(square_distance_1 * square_distance_2 * square_sin / square_distance)
result[cosin < 0] = np.sqrt(np.fmin(square_distance_1, square_distance_2))[cosin< 0]
return result
if __name__ == "__main__":
data = dict()
data['image'] = np.zeros((30, 35, 1), dtype=np.uint8)
data['polys'] = [[[10,10],[25,10],[25,20],[10,20]]]
data['ignore_tags'] = [False]
# 1. 声名MakeBorderMap函数
generate_text_border = MakeBorderMap()
# 2. 根据解码后的输入数据计算border
data = generate_text_border(data)
threshold_map = data['threshold_map']
# 3. 阈值图可视化
plt.imshow(threshold_map)
3.二值化图标签
三、损失计算
由于模型的输出为3个预测图,所以在损失函数中,也需要结合这3个预测图与它们对应的真实标签分别构建3部分损失函数。总的损失函数公式定义如下:
L = L s + ɑ × L b + β × L t L=L_s + ɑ×L_b + β×L_t L=Ls+ɑ×Lb+β×Lt
其中,L为总的损失, L s L_s Ls为概率图损失, L b L_b Lb为二值化图损失, L t L_t Lt为阈值图损失。ɑ和β为权重系数,论文中分别设置为1和10。