FATE —— 2.5 Homo-NN自定义模型
前言
FATE版本为1.10.0单机部署版,win10+centos7
构建模型
在FATE 1.10.0中,您可以使用管道提交PyTorch Sequential模型。然而,Sequential模型结合PyTorch的内置层可能不足以表示更复杂的模型。例如,当构建与ResNet中发现的模块类似的剩余模块时,需要重用某些模块的输出,这可能无法使用Sequential模型。
为了解决这个问题,FATE 1.10.0中引入了model_zoo模块,该模块位于federatedml.nn.model_goo下。该模块允许您自定义自己的PyTorch模型,前提是它是基于torch.nn.module开发的并实现了转发接口。有关更多信息,请参阅自定义模块上的PyTorch文档PyTorch模块。要在联合任务中使用自定义模型,只需将其放置在federatedml/nn/model_zoo目录中,并在提交任务时通过接口指定模块和模型类。Homo NN将自动搜索并导入您已实现的模型。
例如,考虑MNIST手写识别的任务。我们可以先在本地编写一个带有残余连接的简单神经网络模块,然后在联合任务中使用它。
定制模型
将模型代码命名为image_net.py,您可以将其直接放在fedratedml/nn/model_zoo下,也可以使用jupyter笔记本的快捷界面将其直接保存到fedratedml/nn/model_zoo
frompipeline.component.nnimportsave_to_fate%%save_to_fate model image_net.py
import torch as t
from torch import nn
from torch.nn import Module
# the residual component
class Residual(Module):
def __init__(self, ch, kernel_size=3, padding=1):
super(Residual, self).__init__()
self.convs = t.nn.ModuleList([nn.Conv2d(ch, ch, kernel_size=kernel_size, padding=padding) for i in range(2)])
self.act = nn.ReLU()
def forward(self, x):
x = self.act(self.convs[0](x))
x_ = self.convs[1](x)
return self.act(x + x_)
# we call it image net
class ImgNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, class_num=10):
super(ImgNet, self).__init__()
self.seq = t.nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=3, out_channels=12, kernel_size=5),
Residual(12),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3),
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=12, out_channels=12, kernel_size=3),
Residual(12),
nn.AvgPool2d(kernel_size=3)
)
self.fc = t.nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(48, 32),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(32, class_num)
)
self.softmax = nn.Softmax(dim=1)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.seq(x)
x = x.flatten(start_dim=1)
x = self.fc(x)
if self.training:
return x
else:
return self.softmax(x)img_model = ImgNet(10)
img_modelImgNet(
(seq): Sequential(
(0): Conv2d(3, 12, kernel_size=(5, 5), stride=(1, 1))
(1): Residual(
(convs): ModuleList(
(0): Conv2d(12, 12, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(1): Conv2d(12, 12, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
)
(act): ReLU()
)
(2): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=3, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
(3): Conv2d(12, 12, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1))
(4): Residual(
(convs): ModuleList(
(0): Conv2d(12, 12, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(1): Conv2d(12, 12, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
)
(act): ReLU()
)
(5): AvgPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=3, padding=0)
)
(fc): Sequential(
(0): Linear(in_features=48, out_features=32, bias=True)
(1): ReLU()
(2): Linear(in_features=32, out_features=10, bias=True)
)
(softmax): Softmax(dim=1)
)from federatedml.nn.dataset.image import ImageDataset
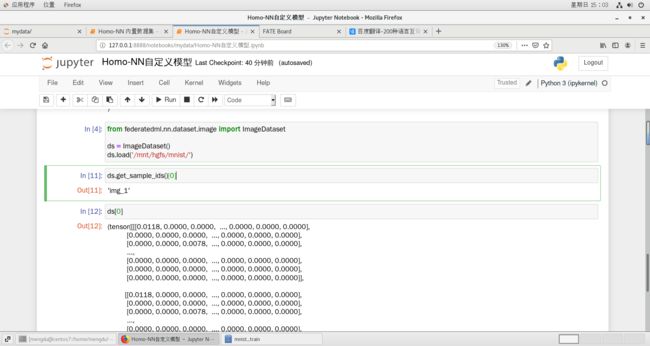
ds = ImageDataset()
ds.load('/mnt/hgfs/mnist/')ds.get_sample_ids()[0] # 数据展示
ds[0]运行本地测试
我们可以使用我们的数据集、自定义模型和Trainer进行本地调试,以测试程序是否可以运行。在本地测试的情况下,将跳过所有联合过程,并且模型将不执行fed平均。
import torch as t
from federatedml.nn.homo.trainer.fedavg_trainer import FedAVGTrainer
trainer = FedAVGTrainer(epochs=3, batch_size=256, shuffle=True, data_loader_worker=8, pin_memory=False)
trainer.set_model(img_model) # set modeltrainer.local_mode() # !! use local mode to skip federation process !!optimizer = t.optim.Adam(img_model.parameters(), lr=0.01)
loss = t.nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
trainer.train(train_set=ds, optimizer=optimizer, loss=loss)它起作用了!现在我们可以提交联合任务了。
提交具有自定义模型的Homo NN任务
import torch as t
from torch import nn
from pipeline import fate_torch_hook
from pipeline.component import HomoNN
from pipeline.backend.pipeline import PipeLine
from pipeline.component import Reader, Evaluation, DataTransform
from pipeline.interface import Data, Model
t = fate_torch_hook(t)import os
# bind data path to name & namespace
# fate_project_path = os.path.abspath('../../../../')
host = 10000
guest = 9999
arbiter = 10000
pipeline = PipeLine().set_initiator(role='guest', party_id=guest).set_roles(guest=guest, host=host,
arbiter=arbiter)
data_0 = {"name": "mnist_guest", "namespace": "experiment"}
data_1 = {"name": "mnist_host", "namespace": "experiment"}
# 路径根据自己得文件位置及名称进行调整,这里以FATE 1.10.0 版本为例
data_path_0 = '/mnt/hgfs/mnist/'
data_path_1 = '/mnt/hgfs/mnist/'
pipeline.bind_table(name=data_0['name'], namespace=data_0['namespace'], path=data_path_0)
pipeline.bind_table(name=data_1['name'], namespace=data_1['namespace'], path=data_path_1){'namespace': 'experiment', 'table_name': 'mnist_host'}
# 定义reader
reader_0 = Reader(name="reader_0")
reader_0.get_party_instance(role='guest', party_id=guest).component_param(table=data_0)
reader_0.get_party_instance(role='host', party_id=host).component_param(table=data_1)nn.CustModel
在fate_arch_hook之后,我们可以使用t.nn.CustModel来指定模型。您应该在此处指定模块名和类名。也可以在此设置模型初始化参数。初始化参数必须是JSON可序列化的,否则无法提交此PipeLine。
from pipeline.component.homo_nn import DatasetParam, TrainerParam
model = t.nn.Sequential(
# the class_num=10 is the initialzation parameter for your model
t.nn.CustModel(module_name='image_net', class_name='ImgNet', class_num=10)
)
nn_component = HomoNN(name='nn_0',
model=model, # your cust model
loss=t.nn.CrossEntropyLoss(),
optimizer=t.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=0.01),
dataset=DatasetParam(dataset_name='image'), # use image dataset
trainer=TrainerParam(trainer_name='fedavg_trainer', epochs=3, batch_size=1024, validation_freqs=1),
torch_seed=100 # global random seed
)pipeline.add_component(reader_0)
pipeline.add_component(nn_component, data=Data(train_data=reader_0.output.data))
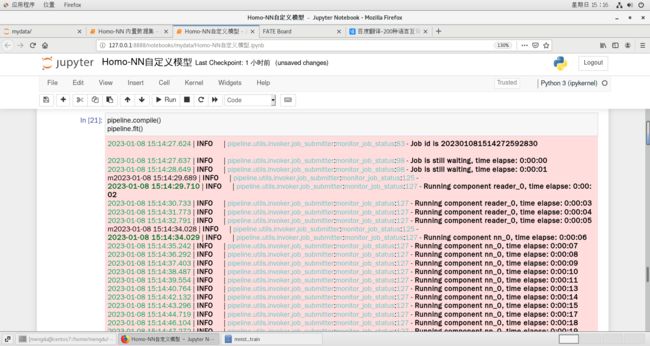
pipeline.add_component(Evaluation(name='eval_0', eval_type='multi'), data=Data(data=nn_component.output.data))pipeline.compile()
pipeline.fit()