文章目录
- PointNet 模型代码详解
- PointNet++ 点云处理任务的代码
-
- PointNet++ 物体形状分类代码
- PointNet++ 部件分割代码
- PointNet++ 语义分割代码
- PointNet++ Util工具函数代码
-
- Farthest Point Sample 最远点采样
- Ball Query 球查询
- Sample and Group
- Set Abstraction
- 分割中的 Feature Prepogation
PointNet 模型代码详解
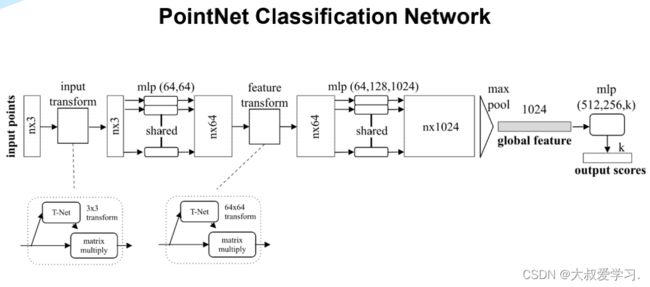
整个模型概览图
下面分部分的代码:
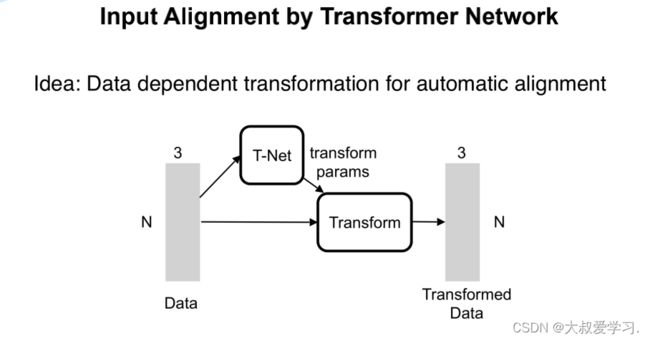
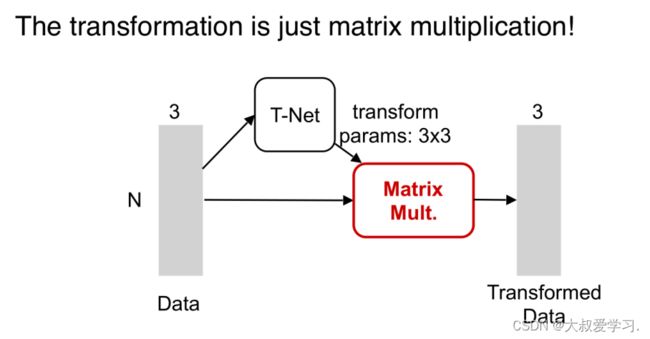
import torch.utils.data
from torch.autograd import Variable
import numpy as np
import torch.nn.functional as F
class STN3d(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, channel):
super(STN3d, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = torch.nn.Conv1d(channel, 64, 1)
self.conv2 = torch.nn.Conv1d(64, 128, 1)
self.conv3 = torch.nn.Conv1d(128, 1024, 1)
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(1024, 512)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(512, 256)
self.fc3 = nn.Linear(256, 9)
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm1d(64)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm1d(128)
self.bn3 = nn.BatchNorm1d(1024)
self.bn4 = nn.BatchNorm1d(512)
self.bn5 = nn.BatchNorm1d(256)
def forward(self, x):
batchsize = x.size()[0]
x = F.relu(self.bn1(self.conv1(x)))
x = F.relu(self.bn2(self.conv2(x)))
x = F.relu(self.bn3(self.conv3(x)))
x = torch.max(x, 2, keepdim=True)[0]
x = x.view(-1, 1024)
x = F.relu(self.bn4(self.fc1(x)))
x = F.relu(self.bn5(self.fc2(x)))
x = self.fc3(x)
iden = Variable(torch.from_numpy(np.array([1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1]).astype(np.float32))).view(1, 9).repeat(
batchsize, 1)
if x.is_cuda:
iden = iden.cuda()
x = x + iden
x = x.view(-1, 3, 3)
return x
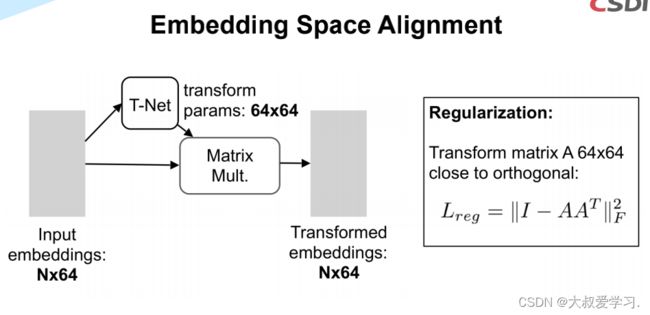
class STNkd(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, k=64):
super(STNkd, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = torch.nn.Conv1d(k, 64, 1)
self.conv2 = torch.nn.Conv1d(64, 128, 1)
self.conv3 = torch.nn.Conv1d(128, 1024, 1)
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(1024, 512)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(512, 256)
self.fc3 = nn.Linear(256, k * k)
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm1d(64)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm1d(128)
self.bn3 = nn.BatchNorm1d(1024)
self.bn4 = nn.BatchNorm1d(512)
self.bn5 = nn.BatchNorm1d(256)
self.k = k
def forward(self, x):
batchsize = x.size()[0]
x = F.relu(self.bn1(self.conv1(x)))
x = F.relu(self.bn2(self.conv2(x)))
x = F.relu(self.bn3(self.conv3(x)))
x = torch.max(x, 2, keepdim=True)[0]
x = x.view(-1, 1024)
x = F.relu(self.bn4(self.fc1(x)))
x = F.relu(self.bn5(self.fc2(x)))
x = self.fc3(x)
iden = Variable(torch.from_numpy(np.eye(self.k).flatten().astype(np.float32))).view(1, self.k * self.k).repeat(
batchsize, 1)
if x.is_cuda:
iden = iden.cuda()
x = x + iden
x = x.view(-1, self.k, self.k)
return x

class PointNetEncoder(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, global_feat=True, feature_transform=False, channel=3):
super(PointNetEncoder, self).__init__()
self.stn = STN3d(channel)
self.conv1 = torch.nn.Conv1d(channel, 64, 1)
self.conv2 = torch.nn.Conv1d(64, 128, 1)
self.conv3 = torch.nn.Conv1d(128, 1024, 1)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm1d(64)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm1d(128)
self.bn3 = nn.BatchNorm1d(1024)
self.global_feat = global_feat
self.feature_transform = feature_transform
if self.feature_transform:
self.fstn = STNkd(k=64)
def forward(self, x):
B, D, N = x.size()
trans = self.stn(x)
x = x.transpose(2, 1)
if D >3 :
x, feature = x.split(3,dim=2)
x = torch.bmm(x, trans)
if D > 3:
x = torch.cat([x,feature],dim=2)
x = x.transpose(2, 1)
x = F.relu(self.bn1(self.conv1(x)))
if self.feature_transform:
trans_feat = self.fstn(x)
x = x.transpose(2, 1)
x = torch.bmm(x, trans_feat)
x = x.transpose(2, 1)
else:
trans_feat = None
pointfeat = x
x = F.relu(self.bn2(self.conv2(x)))
x = self.bn3(self.conv3(x))
x = torch.max(x, 2, keepdim=True)[0]
x = x.view(-1, 1024)
if self.global_feat:
return x, trans, trans_feat
else:
x = x.view(-1, 1024, 1).repeat(1, 1, N)
return torch.cat([x, pointfeat], 1), trans, trans_feat
def feature_transform_reguliarzer(trans):
d = trans.size()[1]
I = torch.eye(d)[None, :, :]
if trans.is_cuda:
I = I.cuda()
loss = torch.mean(torch.norm(torch.bmm(trans, trans.transpose(2, 1) - I), dim=(1, 2)))
return loss
PointNet++ 点云处理任务的代码
PointNet++ 物体形状分类代码
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.utils.data
import torch.nn.functional as F
from pointnet import PointNetEncoder, feature_transform_reguliarzer
class get_model(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, k=40, normal_channel=True):
super(get_model, self).__init__()
if normal_channel:
channel = 6
else:
channel = 3
self.feat = PointNetEncoder(global_feat=True, feature_transform=True, channel=channel)
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(1024, 512)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(512, 256)
self.fc3 = nn.Linear(256, k)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(p=0.4)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm1d(512)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm1d(256)
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
def forward(self, x):
x, trans, trans_feat = self.feat(x)
x = F.relu(self.bn1(self.fc1(x)))
x = F.relu(self.bn2(self.dropout(self.fc2(x))))
x = self.fc3(x)
x = F.log_softmax(x, dim=1)
return x, trans_feat
class get_loss(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, mat_diff_loss_scale=0.001):
super(get_loss, self).__init__()
self.mat_diff_loss_scale = mat_diff_loss_scale
def forward(self, pred, target, trans_feat):
loss = F.nll_loss(pred, target)
mat_diff_loss = feature_transform_reguliarzer(trans_feat)
total_loss = loss + mat_diff_loss * self.mat_diff_loss_scale
return total_loss
PointNet++ 部件分割代码
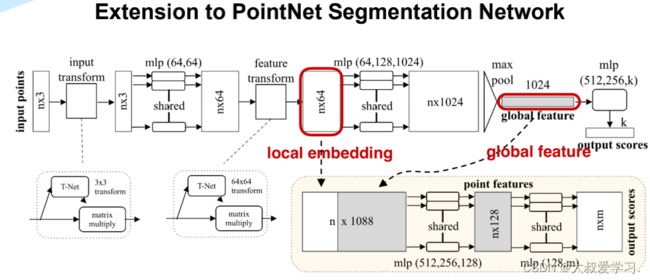
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.parallel
import torch.utils.data
import torch.nn.functional as F
from pointnet import STN3d, STNkd, feature_transform_reguliarzer
class get_model(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, part_num=50, normal_channel=True):
super(get_model, self).__init__()
if normal_channel:
channel = 6
else:
channel = 3
self.part_num = part_num
self.stn = STN3d(channel)
self.conv1 = torch.nn.Conv1d(channel, 64, 1)
self.conv2 = torch.nn.Conv1d(64, 128, 1)
self.conv3 = torch.nn.Conv1d(128, 128, 1)
self.conv4 = torch.nn.Conv1d(128, 512, 1)
self.conv5 = torch.nn.Conv1d(512, 2048, 1)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm1d(64)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm1d(128)
self.bn3 = nn.BatchNorm1d(128)
self.bn4 = nn.BatchNorm1d(512)
self.bn5 = nn.BatchNorm1d(2048)
self.fstn = STNkd(k=128)
self.convs1 = torch.nn.Conv1d(4944, 256, 1)
self.convs2 = torch.nn.Conv1d(256, 256, 1)
self.convs3 = torch.nn.Conv1d(256, 128, 1)
self.convs4 = torch.nn.Conv1d(128, part_num, 1)
self.bns1 = nn.BatchNorm1d(256)
self.bns2 = nn.BatchNorm1d(256)
self.bns3 = nn.BatchNorm1d(128)
def forward(self, point_cloud, label):
B, D, N = point_cloud.size()
trans = self.stn(point_cloud)
point_cloud = point_cloud.transpose(2, 1)
if D > 3:
point_cloud, feature = point_cloud.split(3, dim=2)
point_cloud = torch.bmm(point_cloud, trans)
if D > 3:
point_cloud = torch.cat([point_cloud, feature], dim=2)
point_cloud = point_cloud.transpose(2, 1)
out1 = F.relu(self.bn1(self.conv1(point_cloud)))
out2 = F.relu(self.bn2(self.conv2(out1)))
out3 = F.relu(self.bn3(self.conv3(out2)))
trans_feat = self.fstn(out3)
x = out3.transpose(2, 1)
net_transformed = torch.bmm(x, trans_feat)
net_transformed = net_transformed.transpose(2, 1)
out4 = F.relu(self.bn4(self.conv4(net_transformed)))
out5 = self.bn5(self.conv5(out4))
out_max = torch.max(out5, 2, keepdim=True)[0]
out_max = out_max.view(-1, 2048)
out_max = torch.cat([out_max,label.squeeze(1)],1)
expand = out_max.view(-1, 2048+16, 1).repeat(1, 1, N)
concat = torch.cat([expand, out1, out2, out3, out4, out5], 1)
net = F.relu(self.bns1(self.convs1(concat)))
net = F.relu(self.bns2(self.convs2(net)))
net = F.relu(self.bns3(self.convs3(net)))
net = self.convs4(net)
net = net.transpose(2, 1).contiguous()
net = F.log_softmax(net.view(-1, self.part_num), dim=-1)
net = net.view(B, N, self.part_num)
return net, trans_feat
class get_loss(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, mat_diff_loss_scale=0.001):
super(get_loss, self).__init__()
self.mat_diff_loss_scale = mat_diff_loss_scale
def forward(self, pred, target, trans_feat):
loss = F.nll_loss(pred, target)
mat_diff_loss = feature_transform_reguliarzer(trans_feat)
total_loss = loss + mat_diff_loss * self.mat_diff_loss_scale
return total_loss
PointNet++ 语义分割代码
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.parallel
import torch.utils.data
import torch.nn.functional as F
from pointnet import PointNetEncoder, feature_transform_reguliarzer
class get_model(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_class, with_rgb=True):
super(get_model, self).__init__()
if with_rgb:
channel = 6
else:
channel = 3
self.k = num_class
self.feat = PointNetEncoder(global_feat=False, feature_transform=True, channel=channel)
self.conv1 = torch.nn.Conv1d(1088, 512, 1)
self.conv2 = torch.nn.Conv1d(512, 256, 1)
self.conv3 = torch.nn.Conv1d(256, 128, 1)
self.conv4 = torch.nn.Conv1d(128, self.k, 1)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm1d(512)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm1d(256)
self.bn3 = nn.BatchNorm1d(128)
def forward(self, x):
batchsize = x.size()[0]
n_pts = x.size()[2]
x, trans, trans_feat = self.feat(x)
x = F.relu(self.bn1(self.conv1(x)))
x = F.relu(self.bn2(self.conv2(x)))
x = F.relu(self.bn3(self.conv3(x)))
x = self.conv4(x)
x = x.transpose(2,1).contiguous()
x = F.log_softmax(x.view(-1,self.k), dim=-1)
x = x.view(batchsize, n_pts, self.k)
return x, trans_feat
class get_loss(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, mat_diff_loss_scale=0.001):
super(get_loss, self).__init__()
self.mat_diff_loss_scale = mat_diff_loss_scale
def forward(self, pred, target, trans_feat, weight):
loss = F.nll_loss(pred, target, weight = weight)
mat_diff_loss = feature_transform_reguliarzer(trans_feat)
total_loss = loss + mat_diff_loss * self.mat_diff_loss_scale
return total_loss
if __name__ == '__main__':
model = get_model(13, with_rgb=False)
xyz = torch.rand(12, 3, 2048)
(model(xyz))
PointNet++ Util工具函数代码
Farthest Point Sample 最远点采样
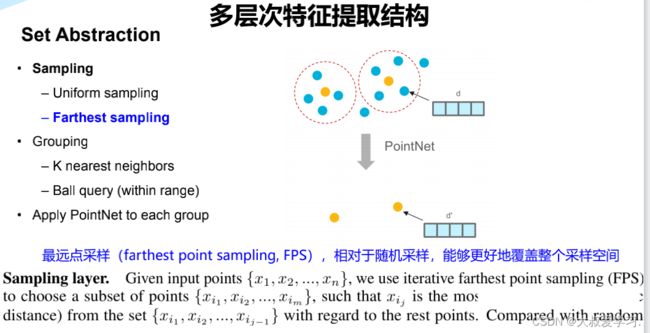
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
from time import time
import numpy as np
def timeit(tag, t):
print("{}: {}s".format(tag, time() - t))
return time()
def pc_normalize(pc):
l = pc.shape[0]
centroid = np.mean(pc, axis=0)
pc = pc - centroid
m = np.max(np.sqrt(np.sum(pc**2, axis=1)))
pc = pc / m
return pc
def square_distance(src, dst):
"""
Calculate Euclid distance between each two points.
src^T * dst = xn * xm + yn * ym + zn * zm;
sum(src^2, dim=-1) = xn*xn + yn*yn + zn*zn;
sum(dst^2, dim=-1) = xm*xm + ym*ym + zm*zm;
dist = (xn - xm)^2 + (yn - ym)^2 + (zn - zm)^2
= sum(src**2,dim=-1)+sum(dst**2,dim=-1)-2*src^T*dst
Input:
src: source points, [B, N, C]
dst: target points, [B, M, C]
Output:
dist: per-point square distance, [B, N, M]
"""
B, N, _ = src.shape
_, M, _ = dst.shape
dist = -2 * torch.matmul(src, dst.permute(0, 2, 1))
dist += torch.sum(src ** 2, -1).view(B, N, 1)
dist += torch.sum(dst ** 2, -1).view(B, 1, M)
return dist
def index_points(points, idx):
"""
Input:
points: input points data, [B, N, C]
idx: sample index data, [B, S]
Return:
new_points:, indexed points data, [B, S, C]
"""
device = points.device
B = points.shape[0]
view_shape = list(idx.shape)
view_shape[1:] = [1] * (len(view_shape) - 1)
repeat_shape = list(idx.shape)
repeat_shape[0] = 1
batch_indices = torch.arange(B, dtype=torch.long).to(device).view(view_shape).repeat(repeat_shape)
new_points = points[batch_indices, idx, :]
return new_points
def farthest_point_sample(xyz, npoint):
"""
Input:
xyz: pointcloud data, [B, N, 3]
npoint: number of samples
Return:
centroids: sampled pointcloud index, [B, npoint]
"""
device = xyz.device
B, N, C = xyz.shape
centroids = torch.zeros(B, npoint, dtype=torch.long).to(device)
distance = torch.ones(B, N).to(device) * 1e10
farthest = torch.randint(0, N, (B,), dtype=torch.long).to(device)
batch_indices = torch.arange(B, dtype=torch.long).to(device)
for i in range(npoint):
centroids[:, i] = farthest
centroid = xyz[batch_indices, farthest, :].view(B, 1, 3)
dist = torch.sum((xyz - centroid) ** 2, -1)
mask = dist < distance
distance[mask] = dist[mask]
farthest = torch.max(distance, -1)[1]
return centroids
Ball Query 球查询
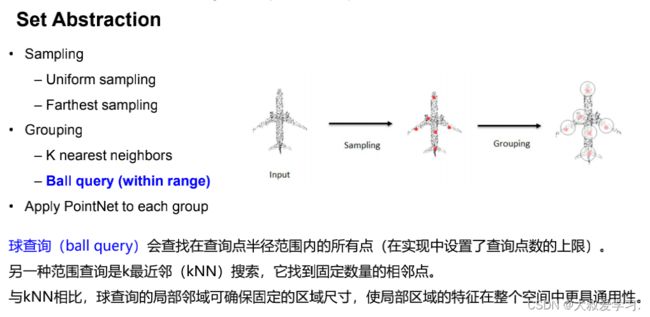
def query_ball_point(radius, nsample, xyz, new_xyz):
"""
Input:
radius: local region radius
nsample: max sample number in local region
xyz: all points, [B, N, 3]
new_xyz: query points, [B, S, 3]
Return:
group_idx: grouped points index, [B, S, nsample]
"""
device = xyz.device
B, N, C = xyz.shape
_, S, _ = new_xyz.shape
group_idx = torch.arange(N, dtype=torch.long).to(device).view(1, 1, N).repeat([B, S, 1])
sqrdists = square_distance(new_xyz, xyz)
group_idx[sqrdists > radius ** 2] = N
group_idx = group_idx.sort(dim=-1)[0][:, :, :nsample]
group_first = group_idx[:, :, 0].view(B, S, 1).repeat([1, 1, nsample])
mask = group_idx == N
group_idx[mask] = group_first[mask]
return group_idx
Sample and Group
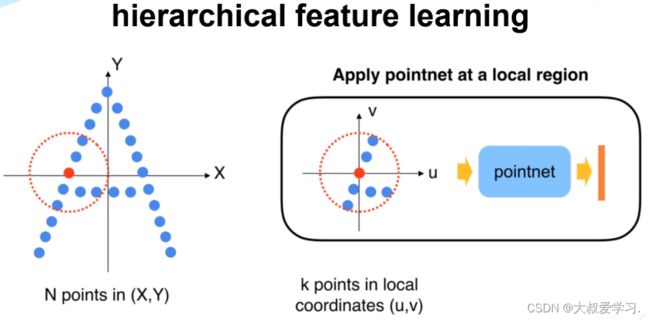
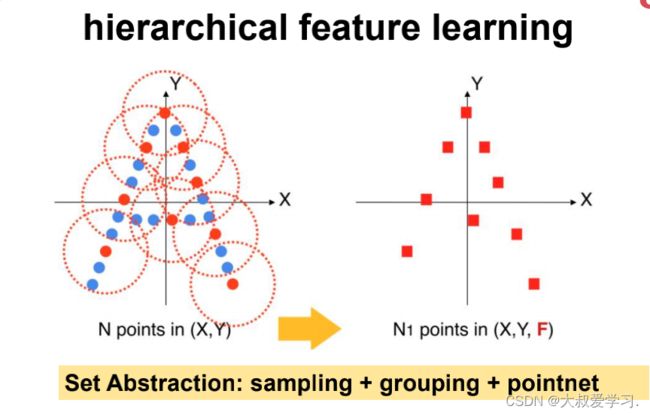
def sample_and_group(npoint, radius, nsample, xyz, points, returnfps=False):
"""
Input:
npoint:
radius:
nsample:
xyz: input points position data, [B, N, 3]
points: input points data, [B, N, D]
Return:
new_xyz: sampled points position data, [B, npoint, nsample, 3]
new_points: sampled points data, [B, npoint, nsample, 3+D]
"""
B, N, C = xyz.shape
S = npoint
fps_idx = farthest_point_sample(xyz, npoint)
torch.cuda.empty_cache()
new_xyz = index_points(xyz, fps_idx)
torch.cuda.empty_cache()
idx = query_ball_point(radius, nsample, xyz, new_xyz)
torch.cuda.empty_cache()
grouped_xyz = index_points(xyz, idx)
torch.cuda.empty_cache()
grouped_xyz_norm = grouped_xyz - new_xyz.view(B, S, 1, C)
torch.cuda.empty_cache()
if points is not None:
grouped_points = index_points(points, idx)
new_points = torch.cat([grouped_xyz_norm, grouped_points], dim=-1)
else:
new_points = grouped_xyz_norm
if returnfps:
return new_xyz, new_points, grouped_xyz, fps_idx
else:
return new_xyz, new_points
def sample_and_group_all(xyz, points):
"""
Input:
xyz: input points position data, [B, N, 3]
points: input points data, [B, N, D]
Return:
new_xyz: sampled points position data, [B, 1, 3]
new_points: sampled points data, [B, 1, N, 3+D]
"""
device = xyz.device
B, N, C = xyz.shape
new_xyz = torch.zeros(B, 1, C).to(device)
grouped_xyz = xyz.view(B, 1, N, C)
if points is not None:
new_points = torch.cat([grouped_xyz, points.view(B, 1, N, -1)], dim=-1)
else:
new_points = grouped_xyz
return new_xyz, new_points
Set Abstraction

class PointNetSetAbstraction(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, npoint, radius, nsample, in_channel, mlp, group_all):
super(PointNetSetAbstraction, self).__init__()
self.npoint = npoint
self.radius = radius
self.nsample = nsample
self.mlp_convs = nn.ModuleList()
self.mlp_bns = nn.ModuleList()
last_channel = in_channel
for out_channel in mlp:
self.mlp_convs.append(nn.Conv2d(last_channel, out_channel, 1))
self.mlp_bns.append(nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channel))
last_channel = out_channel
self.group_all = group_all
def forward(self, xyz, points):
"""
Input:
xyz: input points position data, [B, C, N]
points: input points data, [B, D, N]
Return:
new_xyz: sampled points position data, [B, C, S]
new_points_concat: sample points feature data, [B, D', S]
"""
xyz = xyz.permute(0, 2, 1)
if points is not None:
points = points.permute(0, 2, 1)
if self.group_all:
new_xyz, new_points = sample_and_group_all(xyz, points)
else:
new_xyz, new_points = sample_and_group(self.npoint, self.radius, self.nsample, xyz, points)
new_points = new_points.permute(0, 3, 2, 1)
for i, conv in enumerate(self.mlp_convs):
bn = self.mlp_bns[i]
new_points = F.relu(bn(conv(new_points)))
new_points = torch.max(new_points, 2)[0]
new_xyz = new_xyz.permute(0, 2, 1)
return new_xyz, new_points
class PointNetSetAbstractionMsg(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, npoint, radius_list, nsample_list, in_channel, mlp_list):
super(PointNetSetAbstractionMsg, self).__init__()
self.npoint = npoint
self.radius_list = radius_list
self.nsample_list = nsample_list
self.conv_blocks = nn.ModuleList()
self.bn_blocks = nn.ModuleList()
for i in range(len(mlp_list)):
convs = nn.ModuleList()
bns = nn.ModuleList()
last_channel = in_channel + 3
for out_channel in mlp_list[i]:
convs.append(nn.Conv2d(last_channel, out_channel, 1))
bns.append(nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channel))
last_channel = out_channel
self.conv_blocks.append(convs)
self.bn_blocks.append(bns)
def forward(self, xyz, points):
"""
Input:
xyz: input points position data, [B, C, N]
points: input points data, [B, D, N]
Return:
new_xyz: sampled points position data, [B, C, S]
new_points_concat: sample points feature data, [B, D', S]
"""
xyz = xyz.permute(0, 2, 1)
if points is not None:
points = points.permute(0, 2, 1)
B, N, C = xyz.shape
S = self.npoint
new_xyz = index_points(xyz, farthest_point_sample(xyz, S))
new_points_list = []
for i, radius in enumerate(self.radius_list):
K = self.nsample_list[i]
group_idx = query_ball_point(radius, K, xyz, new_xyz)
grouped_xyz = index_points(xyz, group_idx)
grouped_xyz -= new_xyz.view(B, S, 1, C)
if points is not None:
grouped_points = index_points(points, group_idx)
grouped_points = torch.cat([grouped_points, grouped_xyz], dim=-1)
else:
grouped_points = grouped_xyz
grouped_points = grouped_points.permute(0, 3, 2, 1)
for j in range(len(self.conv_blocks[i])):
conv = self.conv_blocks[i][j]
bn = self.bn_blocks[i][j]
grouped_points = F.relu(bn(conv(grouped_points)))
new_points = torch.max(grouped_points, 2)[0]
new_points_list.append(new_points)
new_xyz = new_xyz.permute(0, 2, 1)
new_points_concat = torch.cat(new_points_list, dim=1)
return new_xyz, new_points_concat
分割中的 Feature Prepogation
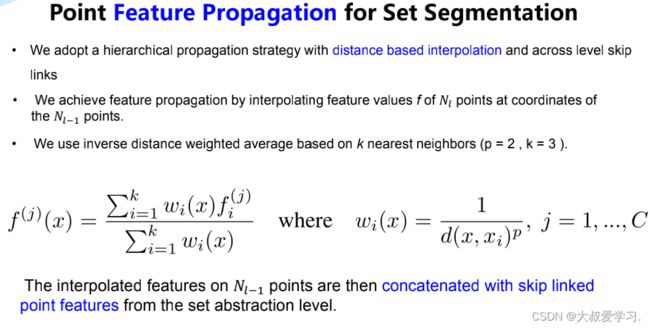
class PointNetFeaturePropagation(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channel, mlp):
super(PointNetFeaturePropagation, self).__init__()
self.mlp_convs = nn.ModuleList()
self.mlp_bns = nn.ModuleList()
last_channel = in_channel
for out_channel in mlp:
self.mlp_convs.append(nn.Conv1d(last_channel, out_channel, 1))
self.mlp_bns.append(nn.BatchNorm1d(out_channel))
last_channel = out_channel
def forward(self, xyz1, xyz2, points1, points2):
"""
Input:
xyz1: input points position data, [B, C, N]
xyz2: sampled input points position data, [B, C, S]
points1: input points data, [B, D, N]
points2: input points data, [B, D, S]
Return:
new_points: upsampled points data, [B, D', N] # 上采样后的点
"""
xyz1 = xyz1.permute(0, 2, 1)
xyz2 = xyz2.permute(0, 2, 1)
points2 = points2.permute(0, 2, 1)
B, N, C = xyz1.shape
_, S, _ = xyz2.shape
if S == 1:
interpolated_points = points2.repeat(1, N, 1)
else:
dists = square_distance(xyz1, xyz2)
dists, idx = dists.sort(dim=-1)
dists, idx = dists[:, :, :3], idx[:, :, :3]
dist_recip = 1.0 / (dists + 1e-8)
norm = torch.sum(dist_recip, dim=2, keepdim=True)
weight = dist_recip / norm
interpolated_points = torch.sum(index_points(points2, idx) * weight.view(B, N, 3, 1), dim=2)
if points1 is not None:
points1 = points1.permute(0, 2, 1)
new_points = torch.cat([points1, interpolated_points], dim=-1)
else:
new_points = interpolated_points
new_points = new_points.permute(0, 2, 1)
for i, conv in enumerate(self.mlp_convs):
bn = self.mlp_bns[i]
new_points = F.relu(bn(conv(new_points)))
return new_points











