MotionPlaning(一)基于搜索的路径规划——A*&JPS
【本文仅作为本人对路径规划学习记录所用】
基于搜索的路径规划——A*&JPS
- DFS vs BFS
- Dijkstra vs A*
- Rviz下进行A*路径搜索
- A-Star
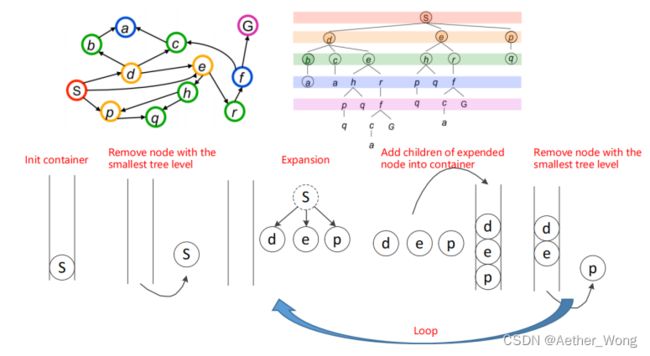
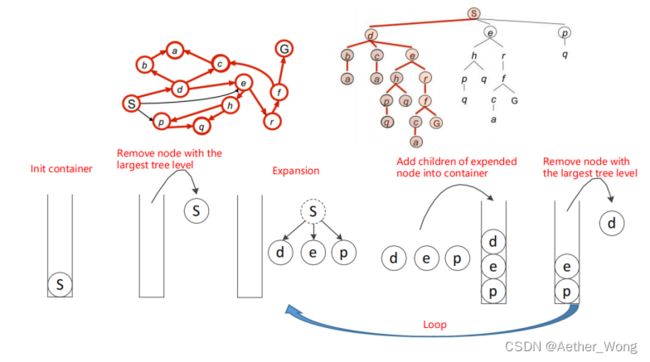
DFS vs BFS
常规的路径搜索分为深度优先搜索和广度优先搜索,区别在于节点的搜索顺序,广度优先搜索弹出最浅的节点,一层一层进行扫描搜索,深度优先搜索则类似于堆栈结构,弹出树状结构最深的节点。目前工程中常采用广度优先搜索。
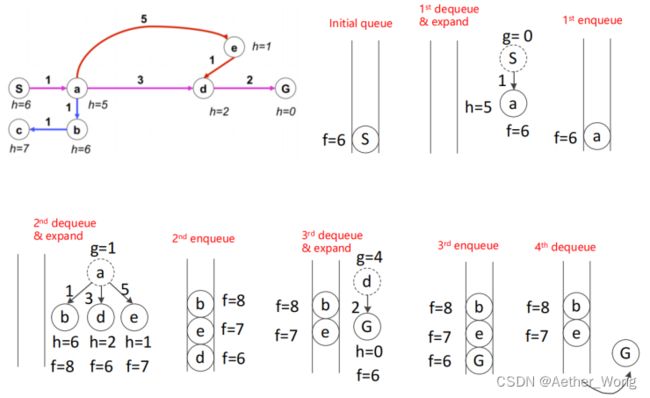
Dijkstra vs A*
最基本的广度优先搜索是在基于节点间cost为0相同的情况,Dijkstra则在此基础上进行改进,相较于BFS区别在于,其弹出的不再是最浅的节点,而是弹出函数g(n)值最小的节点,g(n)代表着节点到起点的cost总和。而A*则是在Dijkstra算法的基础上加入贪心算法,其不同在于弹出准则改为函数f(n)=g(n)+h(n)最小,h(n)值表示预计该节点到达最终目标的cost。

Rviz下进行A*路径搜索
更改随机种子,将地图设立为固定的地图,对比A*算法在不同启发式函数下进行路径规划的情况:
| H1 | H2 | H3 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Run Time(ms) | 0.082 | 0.325 | 0.095 |
| Visited Nodes Size | 289 | 1062 | 381 |
其中H1:Manhattan,H2:Euclidean,H3:Diagnol Distance
欧式距离——以起点和终点为两端的线段的距离;
曼哈顿距离——仅在垂直、水平方向上行进的最短距离;
切比雪夫距离——仅在对角线、水平方向上行进的最短距离。
3种情况皆为同一张地图下运行结果,且终点均设于地图右下角z=0处,依表可简单得出在本地图的条件下,选用Manhattan启发式函数的表现结果最佳,运行时间和访问节点都最少。

A-Star
算法流程图如下:
Created with Raphaël 2.3.0 初始化起点Xs, g(xs)=0且进入Openlist(g(xs)- >id==1), priority queue(g)中其余点g(n)=inf, g(n)- >id==0. g为非空? 从priority queue移除代价最低的点n, n进入ClosedSet (g(n)- >id==-1), 代价f(n)=g(n)+h(n). 扩展节点n(寻找neighbour) n为非Xgoal点? unexpand的neighbour点m g(m)=inf 或g(m)- >id==0? {g(m)=g(n)+Cnm Neighbour->id==1} g(m)>g(n)+Cnm {g(m)=g(n)+Cnm Neighbour- >id==1} yes yes no yes no
对FastLAB提供的A-star 案例进行了简要注释,并对缺失的七个核心部分进行补全:
#include "Astar_searcher.h"
using namespace std;
using namespace Eigen;
bool tie_break = false;
// 初始化-栅格地图
void AstarPathFinder::initGridMap(double _resolution, Vector3d global_xyz_l, Vector3d global_xyz_u, int max_x_id, int max_y_id, int max_z_id)
{
// gl_()u -地图上边界; gl_()l -地图下边界
gl_xl = global_xyz_l(0);
gl_yl = global_xyz_l(1);
gl_zl = global_xyz_l(2);
gl_xu = global_xyz_u(0);
gl_yu = global_xyz_u(1);
gl_zu = global_xyz_u(2);
// 定义-地图的三维长度
GLX_SIZE = max_x_id;
GLY_SIZE = max_y_id;
GLZ_SIZE = max_z_id;
GLYZ_SIZE = GLY_SIZE * GLZ_SIZE;
GLXYZ_SIZE = GLX_SIZE * GLYZ_SIZE;
// resolutio-栅格地图精度
resolution = _resolution;
inv_resolution = 1.0 / _resolution;
// void *memset(void *s, int ch, size_t n);将s中当前位置后面的n个字节(typedef unsigned int size_t)用ch替换并返回 s 。
//请求一个无符号的字符数组,数组的大小为地图的体积
data = new uint8_t[GLXYZ_SIZE];
// data数组 -->0; memset -->初始化函数
memset(data, 0, GLXYZ_SIZE * sizeof(uint8_t));
GridNodeMap = new GridNodePtr ** [GLX_SIZE];
for(int i = 0; i < GLX_SIZE; i++){
GridNodeMap[i] = new GridNodePtr * [GLY_SIZE];
for(int j = 0; j < GLY_SIZE; j++){
GridNodeMap[i][j] = new GridNodePtr [GLZ_SIZE];
for( int k = 0; k < GLZ_SIZE;k++){
// 初始化-所有栅格坐标
Vector3i tmpIdx(i,j,k);
// 初始化-所有实际坐标
Vector3d pos = gridIndex2coord(tmpIdx);
// GridNodeMap-三维指针:传入-栅格坐标&实际坐标; 初始化-所有节点属性-->0
GridNodeMap[i][j][k] = new GridNode(tmpIdx, pos);
}
}
}
}
// 所有节点的属性设置为0,未被访问
void AstarPathFinder::resetGrid(GridNodePtr ptr)
{
ptr->id = 0;
ptr->cameFrom = NULL;
ptr->gScore = inf;
ptr->fScore = inf;
}
// 循环-遍历重置所有节点
void AstarPathFinder::resetUsedGrids()
{
for(int i=0; i < GLX_SIZE ; i++)
for(int j=0; j < GLY_SIZE ; j++)
for(int k=0; k < GLZ_SIZE ; k++)
resetGrid(GridNodeMap[i][j][k]);
}
// 在栅格地图中设置障碍物,进行路径规划
void AstarPathFinder::setObs(const double coord_x, const double coord_y, const double coord_z)
{
if( coord_x < gl_xl || coord_y < gl_yl || coord_z < gl_zl ||
coord_x >= gl_xu || coord_y >= gl_yu || coord_z >= gl_zu )
return;
int idx_x = static_cast( (coord_x - gl_xl) * inv_resolution);//double型-->int型
int idx_y = static_cast( (coord_y - gl_yl) * inv_resolution);
int idx_z = static_cast( (coord_z - gl_zl) * inv_resolution);
data[idx_x * GLYZ_SIZE + idx_y * GLZ_SIZE + idx_z] = 1;
}
// 获得-访问过的所有节点
vector AstarPathFinder::getVisitedNodes()
{
vector visited_nodes;
for(int i = 0; i < GLX_SIZE; i++)
for(int j = 0; j < GLY_SIZE; j++)
for(int k = 0; k < GLZ_SIZE; k++){
if(GridNodeMap[i][j][k]->id != 0) // visualize all nodes in open and close list,所有节点打开,并关闭列表
//if(GridNodeMap[i][j][k]->id == -1) // visualize nodes in close list only,仅显示关闭列表中的节点
visited_nodes.push_back(GridNodeMap[i][j][k]->coord);
}
ROS_WARN("visited_nodes size : %d", visited_nodes.size());
return visited_nodes;
}
// 栅格坐标-->实际坐标
Vector3d AstarPathFinder::gridIndex2coord(const Vector3i & index)
{
Vector3d pt;
pt(0) = ((double)index(0) + 0.5) * resolution + gl_xl;
pt(1) = ((double)index(1) + 0.5) * resolution + gl_yl;
pt(2) = ((double)index(2) + 0.5) * resolution + gl_zl;
return pt;
}
// 实际坐标-->栅格坐标
Vector3i AstarPathFinder::coord2gridIndex(const Vector3d & pt)
{
Vector3i idx;
idx << min( max( int( (pt(0) - gl_xl) * inv_resolution), 0), GLX_SIZE - 1),
min( max( int( (pt(1) - gl_yl) * inv_resolution), 0), GLY_SIZE - 1),
min( max( int( (pt(2) - gl_zl) * inv_resolution), 0), GLZ_SIZE - 1);
return idx;
}
Eigen::Vector3d AstarPathFinder::coordRounding(const Eigen::Vector3d & coord)
{
return gridIndex2coord(coord2gridIndex(coord));
}
// inline--定义一个内联函数,解决函数因频繁调用而消耗栈内存问题。
// 判断-栅格坐标是否为障碍物点(函数内调用-->以实际坐标判断的函数)
inline bool AstarPathFinder::isOccupied(const Eigen::Vector3i & index) const
{
return isOccupied(index(0), index(1), index(2));
}
// 判断-栅格坐标是否为空点(函数内调用-->以实际坐标判断的函数)
inline bool AstarPathFinder::isFree(const Eigen::Vector3i & index) const
{
return isFree(index(0), index(1), index(2));
}
inline bool AstarPathFinder::isOccupied(const int & idx_x, const int & idx_y, const int & idx_z) const
{
return (idx_x >= 0 && idx_x < GLX_SIZE && idx_y >= 0 && idx_y < GLY_SIZE && idx_z >= 0 && idx_z < GLZ_SIZE &&
(data[idx_x * GLYZ_SIZE + idx_y * GLZ_SIZE + idx_z] == 1));
}
inline bool AstarPathFinder::isFree(const int & idx_x, const int & idx_y, const int & idx_z) const
{
return (idx_x >= 0 && idx_x < GLX_SIZE && idx_y >= 0 && idx_y < GLY_SIZE && idx_z >= 0 && idx_z < GLZ_SIZE &&
(data[idx_x * GLYZ_SIZE + idx_y * GLZ_SIZE + idx_z] < 1));
}
// edgeCostSets:节点到目标的距离
// 获取该点周围的所有节点和周围点的edgeCostSets
inline void AstarPathFinder::AstarGetSucc(GridNodePtr currentPtr, vector & neighborPtrSets, vector & edgeCostSets)
{
//Note:此集合中的指针将复制到GridNodeMap
neighborPtrSets.clear();
edgeCostSets.clear();
/*
AstarPathFinder::AstarGetSucc yourself
*/
if(currentPtr == nullptr)
std::cout << "Error: Current pointer is null!" << endl;
Eigen::Vector3i thisNode = currentPtr -> index;
int this_x = thisNode[0];
int this_y = thisNode[1];
int this_z = thisNode[2];
auto this_coord = currentPtr -> coord;
int n_x, n_y, n_z;
double dist; //距离:当前节点到周边节点
GridNodePtr temp_ptr = nullptr; //指针:周边节点
Eigen::Vector3d n_coord;
// 遍历周边节点,获取edgeCostSets
for(int i = -1;i <= 1;++i ){
for(int j = -1;j <= 1;++j ){
for(int k = -1;k <= 1;++k){
if( i == 0 && j == 0 && k == 0)
continue; // 避免该节点
n_x = this_x + i;
n_y = this_y + j;
n_z = this_z + k;
if( (n_x < 0) || (n_x > (GLX_SIZE - 1)) || (n_y < 0) || (n_y > (GLY_SIZE - 1) ) || (n_z < 0) || (n_z > (GLZ_SIZE - 1)))
continue; // 避免索引问题
if(isOccupied(n_x, n_y, n_z))
continue; // 避免障碍节点
// 将指针放入 neighborPtrSets
temp_ptr = GridNodeMap[n_x][n_y][n_z];
if(temp_ptr->id == -1)
continue; // 检查:为何节点可以跨越障碍节点
n_coord = temp_ptr->coord;
if(temp_ptr == currentPtr){
std::cout << "Error: temp_ptr == currentPtr)" << std::endl;
}
if( (std::abs(n_coord[0] - this_coord[0]) < 1e-6) and (std::abs(n_coord[1] - this_coord[1]) < 1e-6) and (std::abs(n_coord[2] - this_coord[2]) < 1e-6 )){
std::cout << "Error: Not expanding correctly!" << std::endl;
std::cout << "n_coord:" << n_coord[0] << " "<coord;
auto node2_coord = node2->coord;
// Heuristics 1: Manhattan
h = std::abs(node1_coord(0) - node2_coord(0) ) +
std::abs(node1_coord(1) - node2_coord(1) ) +
std::abs(node1_coord(2) - node2_coord(2) );
// Heuristics 2: Euclidean
//h = std::sqrt(std::pow((node1_coord(0) - node2_coord(0)), 2 ) +
// std::pow((node1_coord(1) - node2_coord(1)), 2 ) +
// std::pow((node1_coord(2) - node2_coord(2)), 2 ));
// Heuristics 3: Diagnol distance
//double dx = std::abs(node1_coord(0) - node2_coord(0) );
//double dy = std::abs(node1_coord(1) - node2_coord(1) );
//double dz = std::abs(node1_coord(2) - node2_coord(2) );
//double min_xyz = std::min({dx, dy, dz});
//h = dx + dy + dz + (std::sqrt(3.0) -3) * min_xyz; // idea: diagnol is a short-cut, find out how many short-cuts can be realized
//tie_break:为减少同伦轨迹造成的额外邻居节点遍历,用以调高算法速度
if(tie_break){
double p = 1.0 / 25.0;
h *= (1.0 + p);
//std::cout << "Tie Break!" << std::endl;
}
return h;
}
// A-star_searcher
void AstarPathFinder::AstarGraphSearch(Vector3d start_pt, Vector3d end_pt)
{
ros::Time time_1 = ros::Time::now();
//index of start_point and end_point
Vector3i start_idx = coord2gridIndex(start_pt); // 实际坐标转换为栅格坐标存在近似
Vector3i end_idx = coord2gridIndex(end_pt);
goalIdx = end_idx;
//position of start_point and end_point
start_pt = gridIndex2coord(start_idx); // 近似的栅格坐标的中心点
end_pt = gridIndex2coord(end_idx);
//Initialize the pointers of struct GridNode which represent start node and goal node
GridNodePtr startPtr = new GridNode(start_idx, start_pt);
GridNodePtr endPtr = new GridNode(end_idx, end_pt);
//openSet is the open_list implemented through multimap in STL library
openSet.clear();
// currentPtr represents the node with lowest f(n) in the open_list
GridNodePtr currentPtr = NULL;
GridNodePtr neighborPtr = NULL;
//put start node in open set
startPtr -> gScore = 0;
startPtr -> fScore = getHeu(startPtr,endPtr);
//STEP 1: finish the AstarPathFinder::getHeu , which is the heuristic function
startPtr -> id = 1;
startPtr -> coord = start_pt;
// make_pair:无需写出型别,就可以生成一个pair对象;比如std::make_pair(42, '@'),而不必费力写成:std::pair(42, '@')
//todo Note: modified, insert the pointer GridNodeMap[i][j][k] to the start node in grid map
openSet.insert( make_pair(startPtr -> fScore, startPtr) );
/*
*
step 2:新GridNodePtr中起始节点的信息
*
*/
//three dimension pointer GridNodeMap[i][j][k] is pointed to a struct GridNode(Eigen::Vector3i _index, Eigen::Vector3d _coord);
//assign g(xs) = 0, g(n) = inf (already done in initialzation of struct)
//mark start point as visited(expanded) (id 0: no operation, id: 1 in OPEN, id -1: in CLOSE )
// id=1表示已扩展
GridNodeMap[start_idx[0]][start_idx[1]][start_idx[2]] -> id = 1;
vector neighborPtrSets; // 周边节点
vector edgeCostSets;
Eigen::Vector3i current_idx; // record the current index
// this is the main loop
while ( !openSet.empty() ){
/*
*
*
step 3: 将具有最低成本函数的节点从开集移除到闭集
IMPORTANT NOTE!!!
This part you should use the C++ STL: multimap, more details can be find in Homework description
*
*
*/
// openset:待访问节点容器;closed set:访问过节点容器
int x = openSet.begin()->second->index(0);
int y = openSet.begin()->second->index(1);
int z = openSet.begin()->second->index(2);
openSet.erase(openSet.begin());
currentPtr = GridNodeMap[x][y][z];
// 如果节点被访问过;则返回
if(currentPtr->id == -1)
continue;
// 标记id为-1,表示节点已被扩展
currentPtr->id = -1;
// currentPtr = openSet.begin() -> second; // first T1, second T2
// openSet.erase(openSet.begin()); // remove the node with minimal f value
// current_idx = currentPtr->index;
// GridNodeMap[current_idx[0]][current_idx[1]][current_idx[2]] -> id = -1;// update the id in grid node map
// if the current node is the goal
if( currentPtr->index == goalIdx ){
ros::Time time_2 = ros::Time::now();
terminatePtr = currentPtr;
ROS_WARN("[A*]{sucess} Time in A* is %f ms, path cost if %f m", (time_2 - time_1).toSec() * 1000.0, currentPtr->gScore * resolution ); // .toSec() -->转化为秒
return;
}
//get the succetion
AstarGetSucc(currentPtr, neighborPtrSets, edgeCostSets); //STEP 4: finish AstarPathFinder::AstarGetSucc yourself
/*
*
*
STEP 5: Loop:对"n"节点周边"m"节点进行遍历
*
*/
// 遍历周边节点
for(int i = 0; i < (int)neighborPtrSets.size(); i++){
/*
*
*
判断邻居节点是否已经扩展
IMPORTANT NOTE!!!
neighborPtrSets[i]->id = -1 : expanded, equal to this node is in close set
neighborPtrSets[i]->id = 1 : unexpanded, equal to this node is in open set
*
*/
neighborPtr = neighborPtrSets[i];
if(neighborPtr -> id == 0){ //discover a new node, which is not in the closed set and open set
/*
*
*
STEP 6: 对于新节点,将邻节点放入开集并记录
*
*/
// shall update: gScore = inf; fScore = inf; cameFrom = NULL, id, mayby direction
neighborPtr->gScore = currentPtr->gScore + edgeCostSets[i];
neighborPtr->fScore = neighborPtr->gScore + getHeu(neighborPtr,endPtr);
neighborPtr->cameFrom = currentPtr; // todo shallow copy or deep copy
// push node "m" into OPEN
openSet.insert(make_pair(neighborPtr -> fScore, neighborPtr));
neighborPtr -> id = 1;
continue;
}
else if(neighborPtr -> id == 1){ //this node is in open set and need to judge if it needs to update, the "0" should be deleted when you are coding
/*
*
*
STEP 7: 更新并维护开集中的节点,将邻节点放入开集并记录
*
*/
if( neighborPtr->gScore > (currentPtr->gScore+edgeCostSets[i]))
{
neighborPtr -> gScore = currentPtr -> gScore + edgeCostSets[i];
neighborPtr -> fScore = neighborPtr -> gScore + getHeu(neighborPtr,endPtr);
neighborPtr -> cameFrom = currentPtr;
}
continue;
}
else{//this node is in closed set
/*
*
please write your code below
*
*/
continue;
}
}
}
//if search fails
ros::Time time_2 = ros::Time::now();
if((time_2 - time_1).toSec() > 0.1)
ROS_WARN("Time consume in Astar path finding is %f", (time_2 - time_1).toSec() );
}
// 获得A-star的完整路径
vector AstarPathFinder::getPath()
{
vector path;
vector gridPath;
/*
*
*
STEP 8: 从当前节点回溯以获取路径上的所有节点
*
*/
auto ptr = terminatePtr;
while(ptr -> cameFrom != NULL){
gridPath.push_back(ptr);
ptr = ptr->cameFrom;
}
for (auto ptr: gridPath)
path.push_back(ptr->coord);
reverse(path.begin(),path.end()); // reverse:翻转
return path;
}