均值坐标参数化(MVC Parameterization)
欢迎关注更多精彩
关注我,学习常用算法与数据结构,一题多解,降维打击。
均值坐标定义
均值坐标定义
![]()
v 0 是 多 边 形 v 1 v 2 v 3 . . . v n 内 的 一 点 v_0是多边形v_1v_2v_3...v_n内的一点 v0是多边形v1v2v3...vn内的一点
就 会 存 在 均 值 坐 标 ϕ i ( v 0 ) = ω i ∑ j = 1 n ω j 就会存在均值坐标\phi_i(v_0)=\frac {\omega_i}{\sum_{j=1}^n\omega_j} 就会存在均值坐标ϕi(v0)=∑j=1nωjωi
其 中 ω i = t a n ( α i − 1 2 ) + t a n ( α i 2 ) ∣ ∣ v i − v 0 ∣ ∣ 其中\omega_i=\frac {tan \left(\frac {\alpha_{i-1}}{2} \right)+tan \left(\frac {\alpha_{i}}{2} \right)}{||v_i-v_0||} 其中ωi=∣∣vi−v0∣∣tan(2αi−1)+tan(2αi)
使得
v 0 = ∑ i = 1 n ϕ i ( v 0 ) ⋅ v i … … ( 1 ) v_0=\displaystyle \sum_{i=1}^n\phi_i(v_0)\cdot v_i ……(1) v0=i=1∑nϕi(v0)⋅vi……(1)
均值坐标参数化(MVC Parameterization)
该算法与tutte’s embedding 算法的基本过程一样,只是把线性组合的系数换成均值坐标表示。
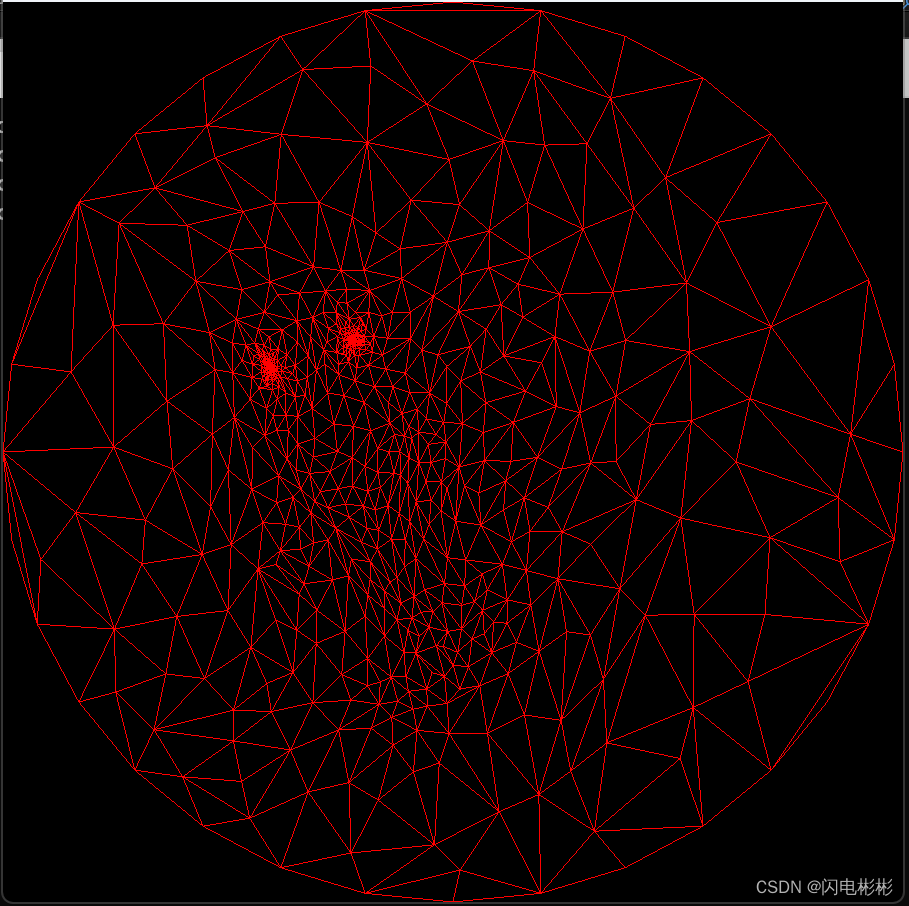
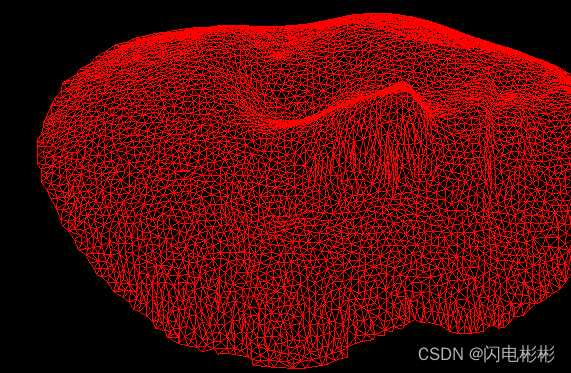
该算法可以处理与圆盘同胚非闭合的三角网格面,他能保证3D与2D是一一映射的。
算法过程
- 先把边界点按照顺序均匀地放置在圆边界上。
- 对于内部的点,vi 是周围顶点的均值坐标线性组合。
v i = ∑ j ∈ Ω ( i ) ϕ j ( v i ) ⋅ v j ( 1 ) , ϕ j ( v i ) 是 顶 均 值 坐 标 表 示 。 v_i = \displaystyle \sum_{j \in \Omega(i)} {\phi_j(v_i)\cdot v_j} (1), \phi_j(v_i)是顶均值坐标表示。 vi=j∈Ω(i)∑ϕj(vi)⋅vj(1),ϕj(vi)是顶均值坐标表示。
n个未知顶点,n个方程刚好解出来。
行列式构建
对 ( 1 ) 式 两 边 都 乘 以 ∑ j ∈ Ω ( i ) ω i j , 再 移 项 , 得 到 对(1)式两边都乘以 \displaystyle \sum_{j\in \Omega(i)}\omega_{ij},再移项, 得到 对(1)式两边都乘以j∈Ω(i)∑ωij,再移项,得到
( ∑ j ∈ Ω ( i ) ω i j ) v i − ∑ j ∈ Ω ( i ) ω i j ⋅ v j = 0 \left(\displaystyle \sum_{j\in \Omega(i)}\omega_{ij}\right)v_i - \displaystyle \sum_{j \in \Omega(i)} {\omega_{ij}\cdot v_j}= 0 ⎝⎛j∈Ω(i)∑ωij⎠⎞vi−j∈Ω(i)∑ωij⋅vj=0
利用上式,在具体实现的时候可以先计算出所有wij(没有连接关系则为0),
然后对于边界点,行列式的值r[i][i]=1, b[i]=(ui, vi)
对 于 非 边 界 点 r [ i ] [ i ] = ( ∑ j ∈ Ω ( i ) ω i j ) 对于非边界点r[i][i]=\left(\displaystyle \sum_{j\in \Omega(i)}\omega_{ij}\right) 对于非边界点r[i][i]=⎝⎛j∈Ω(i)∑ωij⎠⎞
r [ i ] [ j ] = − ω i j , b [ i ] = ( 0 , 0 ) r[i][j]=-\omega_{ij},b[i]=(0,0) r[i][j]=−ωij,b[i]=(0,0)
算法实现
代码链接点击前往
代码链接点击前往
代码链接点击前往
#include"include/PolyMesh/IOManager.h"
#include"include/PolyMesh/PolyMesh.h"
#include 算法效果
本人码农,希望通过自己的分享,让大家更容易学懂计算机知识。
![]()