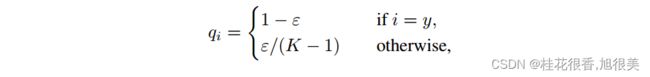label-smoothing
标签平滑(label-smoothing)在one-hot的基础上,添加一个平滑系数ε ,使得最大预测与其它类别平均值之间差距的经验分布更加平滑。主要用于防止过拟合,增强模型的泛化能力。
Pytorch代码实现
import torch
def smooth_one_hot(true_labels: torch.Tensor, classes: int, smoothing=0.0):
"""
if smoothing == 0, it's one-hot method
if 0 < smoothing < 1, it's smooth method
"""
assert 0 <= smoothing < 1
confidence = 1.0 - smoothing
label_shape = torch.Size((true_labels.size(0), classes)) # torch.Size([2, 5])
#with torch.no_grad():
true_dist = torch.empty(size=label_shape, device=true_labels.device) # 空的,没有初始化
true_dist.fill_(smoothing / (classes - 1))
_, index = torch.max(true_labels, 1)
true_dist.scatter_(1, torch.LongTensor(index.unsqueeze(1)), confidence) # 必须要torch.LongTensor()
return true_dist
true_labels = torch.zeros(2, 5)
true_labels[0, 1], true_labels[1, 3] = 1, 1
print('标签平滑前:\n', true_labels)
true_dist = smooth_one_hot(true_labels, classes=5, smoothing=0.05)
print('标签平滑后:\n', true_dist)
'''
Loss = CrossEntropyLoss(NonSparse=True, ...)
. . .
data = ...
labels = ...
outputs = model(data)
smooth_label = smooth_one_hot(labels, ...)
loss = (outputs, smooth_label)
...
'''
数据标签不均衡的另外一种方法:Focal loss
Focal Loss 使模型可以更"放松"地预测事物,而无需80-100%确信此对象是“某物”。简而言之,它给模型提供了更多的自由,可以在进行预测时承担一些风险。这在处理高度不平衡的数据集时尤其重要,因为在某些情况下(例如癌症检测),即使预测结果为假阳性也可接受(高召回),确实需要模型承担风险并尽量进行预测。