Pytorch学习记录(十一):数据增强、torchvision.transforms各函数讲解
常用的数据增强方法
常用的数据增强方法如下:
1.对图片进行一定比例缩放
2.对图片进行随机位置的截取
3.对图片进行随机的水平和竖直翻转
4.对图片进行随机角度的旋转
5.对图片进行亮度、对比度和颜色的随机变化
import sys
sys.path.append('..')
from PIL import Image
from torchvision import transforms as tfs
# 读入一张图片
im = Image.open('./cat.png')
im
随机比例放缩
随机比例缩放主要使用的是 torchvision.transforms.Resize()
第一个参数可以是一个整数,那么图片会保存现在的宽和高的比例,并将更短的边缩放到这个整数的大小,第一个参数也可以是一个 tuple,那么图片会直接把宽和高缩放到这个大小;第二个参数表示放缩图片使用的方法,比如最邻近法,或者双线性差值等,一般双线性差值能够保留图片更多的信息,所以 pytorch 默认使用的是双线性差值。
# 比例缩放
print('before scale, shape: {}'.format(im.size))
new_im = tfs.Resize((100, 200))(im)
print('after scale, shape: {}'.format(new_im.size))
new_im
随机位置截取
torchvision.transforms.RandomCrop(),传入的参数就是截取出的图片的长和宽,对图片在随机位置进行截取,torchvision.transforms.CenterCrop(),同样传入介曲初的图片的大小作为参数,会在图片的中心进行截取。
# 随机裁剪出 100 x 100 的区域
random_im1 = tfs.RandomCrop(100)(im)
random_im1
# 中心裁剪出 100 x 100 的区域
center_im = tfs.CenterCrop(100)(im)
center_im
随机的水平和竖直方向翻转
随机翻转使用的是 torchvision.transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip() 和 torchvision.transforms.RandomVerticalFlip()
# 随机水平翻转
h_filp = tfs.RandomHorizontalFlip()(im)
h_filp
# 随机竖直翻转
v_flip = tfs.RandomVerticalFlip()(im)
v_flip
随机角度旋转
一些角度的旋转仍然是非常有用的数据增强方式,在 torchvision 中,使用 torchvision.transforms.RandomRotation() 来实现,其中第一个参数就是随机旋转的角度,比如填入 10,那么每次图片就会在 -10 ~ 10 度之间随机旋转。
rot_im = tfs.RandomRotation(45)(im)
rot_im
亮度、对比度和颜色的变化
torchvision 中主要使用 torchvision.transforms.ColorJitter() 来实现的,第一个参数就是亮度的比例,第二个是对比度,第三个是颜色。
# 亮度
bright_im = tfs.ColorJitter(brightness=1)(im) # 随机从 0 ~ 2 之间亮度变化,1 表示原图
bright_im
# 对比度
contrast_im = tfs.ColorJitter(contrast=1)(im) # 随机从 0 ~ 2 之间对比度变化,1 表示原图
contrast_im
# 颜色
color_im = tfs.ColorJitter(hue=0.5)(im) # 随机从 -0.5 ~ 0.5 之间对颜色变化
color_im

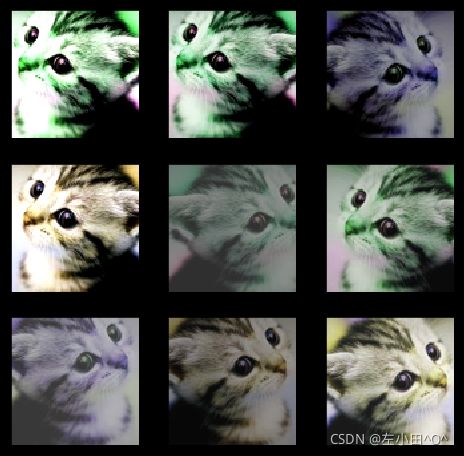
比如先做随机翻转,然后随机截取,再做对比度增强等等,torchvision 里面有个非常方便的函数能够将这些变化合起来,就是torchvision.transforms.Compose(),下面我们举个例子
im_aug = tfs.Compose([
tfs.Resize(120),
tfs.RandomHorizontalFlip(),
tfs.RandomCrop(96),
tfs.ColorJitter(brightness=0.5, contrast=0.5, hue=0.5)
])
nrows = 3
ncols = 3
figsize = (8, 8)
_, figs = plt.subplots(nrows, ncols, figsize=figsize)
for i in range(nrows):
for j in range(ncols):
figs[i][j].imshow(im_aug(im))
figs[i][j].axes.get_xaxis().set_visible(False)
figs[i][j].axes.get_yaxis().set_visible(False)
plt.show()
# coding = utf-8
# @Time : 2020-11-17
# @Author : 郭冰洋
# @File : data_aug.py
# @Desc : 数据增强处理
# @Usual : Compose RandomHflip RandomVflip Reszie RandomCrop Normalize Rotate RandomRotate
from __future__ import division
import cv2
import numpy as np
from numpy import random
import math
from torchvision import transforms
# 所有处理类型
__all__ = ['Compose',# 综合处理多个并写以下的处理,
'RandomHflip', 'RandomUpperCrop', 'Resize', 'UpperCrop', 'RandomBottomCrop',"RandomErasing",
'BottomCrop', 'Normalize', 'RandomSwapChannels', 'RandomRotate', 'RandomHShift',"CenterCrop","RandomVflip",
'ExpandBorder', 'RandomResizedCrop','RandomDownCrop', 'DownCrop', 'ResizedCrop',"FixRandomRotate"]
# 旋转(rotate)
def rotate_nobound(image, angle, center=None, scale=1.):
(h, w) = image.shape[:2]
# if the center is None, initialize it as the center of the image
if center is None:
center = (w // 2, h // 2) # perform the rotation
M = cv2.getRotationMatrix2D(center, angle, scale)
rotated = cv2.warpAffine(image, M, (w, h))
return rotated
# 缩放(scale)
def scale_down(src_size, size):
w, h = size
sw, sh = src_size
if sh < h:
w, h = float(w * sh) / h, sh
if sw < w:
w, h = sw, float(h * sw) / w
return int(w), int(h)
# 固定裁剪(fixed crop)
def fixed_crop(src, x0, y0, w, h, size=None):
out = src[y0:y0 + h, x0:x0 + w]
if size is not None and (w, h) != size:
out = cv2.resize(out, (size[0], size[1]), interpolation=cv2.INTER_CUBIC)
return out
# 随机旋转(random rotate)
class FixRandomRotate(object):
def __init__(self, angles=[0,90,180,270], bound=False):
self.angles = angles
self.bound = bound
def __call__(self,img):
do_rotate = random.randint(0, 4)
angle=self.angles[do_rotate]
if self.bound:
img = rotate_bound(img, angle)
else:
img = rotate_nobound(img, angle)
return img
# 中心裁剪(center crop)
def center_crop(src, size):
h, w = src.shape[0:2]
new_w, new_h = scale_down((w, h), size)
x0 = int((w - new_w) / 2)
y0 = int((h - new_h) / 2)
out = fixed_crop(src, x0, y0, new_w, new_h, size)
return out
# 底部裁剪(bottom crop)
def bottom_crop(src, size):
h, w = src.shape[0:2]
new_w, new_h = scale_down((w, h), size)
x0 = int((w - new_w) / 2)
y0 = int((h - new_h) * 0.75)
out = fixed_crop(src, x0, y0, new_w, new_h, size)
return out
# 旋转约束(rotate bound)
def rotate_bound(image, angle):
# grab the dimensions of the image and then determine the center
h, w = image.shape[:2]
(cX, cY) = (w // 2, h // 2)
M = cv2.getRotationMatrix2D((cX, cY), angle, 1.0)
cos = np.abs(M[0, 0])
sin = np.abs(M[0, 1])
# compute the new bounding dimensions of the image
nW = int((h * sin) + (w * cos))
nH = int((h * cos) + (w * sin))
# adjust the rotation matrix to take into account translation
M[0, 2] += (nW / 2) - cX
M[1, 2] += (nH / 2) - cY
rotated = cv2.warpAffine(image, M, (nW, nH))
return rotated
# 排序(compose)
class Compose(object):
def __init__(self, transforms):
self.transforms = transforms
def __call__(self, img):
for t in self.transforms:
img = t(img)
return img
# 随机旋转(random rotate)
class RandomRotate(object):
def __init__(self, angles, bound=False):
self.angles = angles
self.bound = bound
def __call__(self,img):
do_rotate = random.randint(0, 2)
if do_rotate:
angle = np.random.uniform(self.angles[0], self.angles[1])
if self.bound:
img = rotate_bound(img, angle)
else:
img = rotate_nobound(img, angle)
return img
# 随机亮度增强(random brightness)
class RandomBrightness(object):
def __init__(self, delta=10):
assert delta >= 0
assert delta <= 255
self.delta = delta
def __call__(self, image):
if random.randint(2):
delta = random.uniform(-self.delta, self.delta)
image = (image + delta).clip(0.0, 255.0)
# print('RandomBrightness,delta ',delta)
return image
# 随机对比度增强(random contrast)
class RandomContrast(object):
def __init__(self, lower=0.9, upper=1.05):
self.lower = lower
self.upper = upper
assert self.upper >= self.lower, "contrast upper must be >= lower."
assert self.lower >= 0, "contrast lower must be non-negative."
# expects float image
def __call__(self, image):
if random.randint(2):
alpha = random.uniform(self.lower, self.upper)
# print('contrast:', alpha)
image = (image * alpha).clip(0.0,255.0)
return image
# 随机饱和度增强(random saturation)
class RandomSaturation(object):
def __init__(self, lower=0.8, upper=1.2):
self.lower = lower
self.upper = upper
assert self.upper >= self.lower, "contrast upper must be >= lower."
assert self.lower >= 0, "contrast lower must be non-negative."
def __call__(self, image):
if random.randint(2):
alpha = random.uniform(self.lower, self.upper)
image[:, :, 1] *= alpha
# print('RandomSaturation,alpha',alpha)
return image
# 随机
class RandomHue(object):
def __init__(self, delta=18.0):
assert delta >= 0.0 and delta <= 360.0
self.delta = delta
def __call__(self, image):
if random.randint(2):
alpha = random.uniform(-self.delta, self.delta)
image[:, :, 0] += alpha
image[:, :, 0][image[:, :, 0] > 360.0] -= 360.0
image[:, :, 0][image[:, :, 0] < 0.0] += 360.0
# print('RandomHue,alpha:', alpha)
return image
# 随机色彩通道转换(convert color)
class ConvertColor(object):
def __init__(self, current='BGR', transform='HSV'):
self.transform = transform
self.current = current
def __call__(self, image):
if self.current == 'BGR' and self.transform == 'HSV':
image = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2HSV)
elif self.current == 'HSV' and self.transform == 'BGR':
image = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_HSV2BGR)
else:
raise NotImplementedError
return image
# 色彩通道随机交换(random swap channels)
class RandomSwapChannels(object):
def __call__(self, img):
if np.random.randint(2):
order = np.random.permutation(3)
return img[:,:,order]
return img
# 随机裁剪(random crop)
class RandomCrop(object):
def __init__(self, size):
self.size = size
def __call__(self, image):
h, w, _ = image.shape
new_w, new_h = scale_down((w, h), self.size)
if w == new_w:
x0 = 0
else:
x0 = random.randint(0, w - new_w)
if h == new_h:
y0 = 0
else:
y0 = random.randint(0, h - new_h)
out = fixed_crop(image, x0, y0, new_w, new_h, self.size)
return out
# 随机大小裁剪(random resized crop)
class RandomResizedCrop(object):
def __init__(self, size,scale=(0.49, 1.0), ratio=(1., 1.)):
self.size = size
self.scale = scale
self.ratio = ratio
def __call__(self,img):
if random.random() < 0.2:
return cv2.resize(img,self.size)
h, w, _ = img.shape
area = h * w
d=1
for attempt in range(10):
target_area = random.uniform(self.scale[0], self.scale[1]) * area
aspect_ratio = random.uniform(self.ratio[0], self.ratio[1])
new_w = int(round(math.sqrt(target_area * aspect_ratio)))
new_h = int(round(math.sqrt(target_area / aspect_ratio)))
if random.random() < 0.5:
new_h, new_w = new_w, new_h
if new_w < w and new_h < h:
x0 = random.randint(0, w - new_w)
y0 = (random.randint(0, h - new_h))//d
out = fixed_crop(img, x0, y0, new_w, new_h, self.size)
return out
# Fallback
return center_crop(img, self.size)
# 下裁剪(down crop)
class DownCrop():
def __init__(self, size, select, scale=(0.36,0.81)):
self.size = size
self.scale = scale
self.select = select
def __call__(self,img, attr_idx):
if attr_idx not in self.select:
return img, attr_idx
if attr_idx == 0:
self.scale=(0.64,1.0)
h, w, _ = img.shape
area = h * w
s = (self.scale[0]+self.scale[1])/2.0
target_area = s * area
new_w = int(round(math.sqrt(target_area)))
new_h = int(round(math.sqrt(target_area)))
if new_w < w and new_h < h:
dw = w-new_w
x0 = int(0.5*dw)
y0 = h-new_h
out = fixed_crop(img, x0, y0, new_w, new_h, self.size)
return out, attr_idx
# Fallback
return center_crop(img, self.size), attr_idx
# 缩放裁剪(resized crop)
class ResizedCrop(object):
def __init__(self, size, select,scale=(0.64, 1.0), ratio=(3. / 4., 4. / 3.)):
self.size = size
self.scale = scale
self.ratio = ratio
self.select = select
def __call__(self,img, attr_idx):
if attr_idx not in self.select:
return img, attr_idx
h, w, _ = img.shape
area = h * w
d=1
if attr_idx == 2:
self.scale=(0.36,0.81)
d=2
if attr_idx == 0:
self.scale=(0.81,1.0)
target_area = (self.scale[0]+self.scale[1])/2.0 * area
# aspect_ratio = random.uniform(self.ratio[0], self.ratio[1])
new_w = int(round(math.sqrt(target_area)))
new_h = int(round(math.sqrt(target_area)))
# if random.random() < 0.5:
# new_h, new_w = new_w, new_h
if new_w < w and new_h < h:
x0 = (w - new_w)//2
y0 = (h - new_h)//d//2
out = fixed_crop(img, x0, y0, new_w, new_h, self.size)
# cv2.imshow('{}_img'.format(idx2attr_map[attr_idx]), img)
# cv2.imshow('{}_crop'.format(idx2attr_map[attr_idx]), out)
#
# cv2.waitKey(0)
return out, attr_idx
# Fallback
return center_crop(img, self.size), attr_idx
# 随机水平翻转(random h flip)
class RandomHflip(object):
def __call__(self, image):
if random.randint(2):
return cv2.flip(image, 1)
else:
return image
# 随机垂直翻转(random v flip)
class RandomVflip(object):
def __call__(self, image):
if random.randint(2):
return cv2.flip(image, 0)
else:
return image
# 水平翻转(h flip)
class Hflip(object):
def __init__(self,doHflip):
self.doHflip = doHflip
def __call__(self, image):
if self.doHflip:
return cv2.flip(image, 1)
else:
return image
# 中心裁剪(center crop)
class CenterCrop(object):
def __init__(self, size):
self.size = size
def __call__(self, image):
return center_crop(image, self.size)
# 上裁剪(upper crop)
class UpperCrop():
def __init__(self, size, scale=(0.09, 0.64)):
self.size = size
self.scale = scale
def __call__(self,img):
h, w, _ = img.shape
area = h * w
s = (self.scale[0]+self.scale[1])/2.0
target_area = s * area
new_w = int(round(math.sqrt(target_area)))
new_h = int(round(math.sqrt(target_area)))
if new_w < w and new_h < h:
dw = w-new_w
x0 = int(0.5*dw)
y0 = 0
out = fixed_crop(img, x0, y0, new_w, new_h, self.size)
return out
# Fallback
return center_crop(img, self.size)
# 随机上裁剪(random upper crop)
class RandomUpperCrop(object):
def __init__(self, size, select, scale=(0.09, 0.64), ratio=(3. / 4., 4. / 3.)):
self.size = size
self.scale = scale
self.ratio = ratio
self.select = select
def __call__(self,img, attr_idx):
if random.random() < 0.2:
return img, attr_idx
if attr_idx not in self.select:
return img, attr_idx
h, w, _ = img.shape
area = h * w
for attempt in range(10):
s = random.uniform(self.scale[0], self.scale[1])
d = 0.1 + (0.3 - 0.1) / (self.scale[1] - self.scale[0]) * (s - self.scale[0])
target_area = s * area
aspect_ratio = random.uniform(self.ratio[0], self.ratio[1])
new_w = int(round(math.sqrt(target_area * aspect_ratio)))
new_h = int(round(math.sqrt(target_area / aspect_ratio)))
# new_w = int(round(math.sqrt(target_area)))
# new_h = int(round(math.sqrt(target_area)))
if new_w < w and new_h < h:
dw = w-new_w
x0 = random.randint(int((0.5-d)*dw), int((0.5+d)*dw)+1)
y0 = (random.randint(0, h - new_h))//10
out = fixed_crop(img, x0, y0, new_w, new_h, self.size)
return out, attr_idx
# Fallback
return center_crop(img, self.size), attr_idx
# 随机下裁剪(random down crop)
class RandomDownCrop(object):
def __init__(self, size, select, scale=(0.36, 0.81), ratio=(3. / 4., 4. / 3.)):
self.size = size
self.scale = scale
self.ratio = ratio
self.select = select
def __call__(self,img, attr_idx):
if random.random() < 0.2:
return img, attr_idx
if attr_idx not in self.select:
return img, attr_idx
if attr_idx == 0:
self.scale=(0.64,1.0)
h, w, _ = img.shape
area = h * w
for attempt in range(10):
s = random.uniform(self.scale[0], self.scale[1])
d = 0.1 + (0.3 - 0.1) / (self.scale[1] - self.scale[0]) * (s - self.scale[0])
target_area = s * area
aspect_ratio = random.uniform(self.ratio[0], self.ratio[1])
new_w = int(round(math.sqrt(target_area * aspect_ratio)))
new_h = int(round(math.sqrt(target_area / aspect_ratio)))
#
# new_w = int(round(math.sqrt(target_area)))
# new_h = int(round(math.sqrt(target_area)))
if new_w < w and new_h < h:
dw = w-new_w
x0 = random.randint(int((0.5-d)*dw), int((0.5+d)*dw)+1)
y0 = (random.randint((h - new_h)*9//10, h - new_h))
out = fixed_crop(img, x0, y0, new_w, new_h, self.size)
# cv2.imshow('{}_img'.format(idx2attr_map[attr_idx]), img)
# cv2.imshow('{}_crop'.format(idx2attr_map[attr_idx]), out)
#
# cv2.waitKey(0)
return out, attr_idx
# Fallback
return center_crop(img, self.size), attr_idx
# 随机水平移动(random h shift)
class RandomHShift(object):
def __init__(self, select, scale=(0.0, 0.2)):
self.scale = scale
self.select = select
def __call__(self,img, attr_idx):
if attr_idx not in self.select:
return img, attr_idx
do_shift_crop = random.randint(0, 2)
if do_shift_crop:
h, w, _ = img.shape
min_shift = int(w*self.scale[0])
max_shift = int(w*self.scale[1])
shift_idx = random.randint(min_shift, max_shift)
direction = random.randint(0,2)
if direction:
right_part = img[:, -shift_idx:, :]
left_part = img[:, :-shift_idx, :]
else:
left_part = img[:, :shift_idx, :]
right_part = img[:, shift_idx:, :]
img = np.concatenate((right_part, left_part), axis=1)
# Fallback
return img, attr_idx
# 随机底部裁剪(random bottom crop)
class RandomBottomCrop(object):
def __init__(self, size, select, scale=(0.4, 0.8)):
self.size = size
self.scale = scale
self.select = select
def __call__(self,img, attr_idx):
if attr_idx not in self.select:
return img, attr_idx
h, w, _ = img.shape
area = h * w
for attempt in range(10):
s = random.uniform(self.scale[0], self.scale[1])
d = 0.25 + (0.45 - 0.25) / (self.scale[1] - self.scale[0]) * (s - self.scale[0])
target_area = s * area
new_w = int(round(math.sqrt(target_area)))
new_h = int(round(math.sqrt(target_area)))
if new_w < w and new_h < h:
dw = w-new_w
dh = h - new_h
x0 = random.randint(int((0.5-d)*dw), min(int((0.5+d)*dw)+1,dw))
y0 = (random.randint(max(0,int(0.8*dh)-1), dh))
out = fixed_crop(img, x0, y0, new_w, new_h, self.size)
return out, attr_idx
# Fallback
return bottom_crop(img, self.size), attr_idx
# 底部裁剪(bottom crop)
class BottomCrop():
def __init__(self, size, select, scale=(0.4, 0.8)):
self.size = size
self.scale = scale
self.select = select
def __call__(self,img, attr_idx):
if attr_idx not in self.select:
return img, attr_idx
h, w, _ = img.shape
area = h * w
s = (self.scale[0]+self.scale[1])/3.*2.
target_area = s * area
new_w = int(round(math.sqrt(target_area)))
new_h = int(round(math.sqrt(target_area)))
if new_w < w and new_h < h:
dw = w-new_w
dh = h-new_h
x0 = int(0.5*dw)
y0 = int(0.9*dh)
out = fixed_crop(img, x0, y0, new_w, new_h, self.size)
return out, attr_idx
# Fallback
return bottom_crop(img, self.size), attr_idx
# 大小重置(resize)
class Resize(object):
def __init__(self, size, inter=cv2.INTER_CUBIC):
self.size = size
self.inter = inter
def __call__(self, image):
return cv2.resize(image, (self.size[0], self.size[0]), interpolation=self.inter)
# 边界扩充(expand border)
class ExpandBorder(object):
def __init__(self, mode='constant', value=255, size=(336,336), resize=False):
self.mode = mode
self.value = value
self.resize = resize
self.size = size
def __call__(self, image):
h, w, _ = image.shape
if h > w:
pad1 = (h-w)//2
pad2 = h - w - pad1
if self.mode == 'constant':
image = np.pad(image, ((0, 0), (pad1, pad2), (0, 0)),
self.mode, constant_values=self.value)
else:
image = np.pad(image,((0,0), (pad1, pad2),(0,0)), self.mode)
elif h < w:
pad1 = (w-h)//2
pad2 = w-h - pad1
if self.mode == 'constant':
image = np.pad(image, ((pad1, pad2),(0, 0), (0, 0)),
self.mode,constant_values=self.value)
else:
image = np.pad(image, ((pad1, pad2), (0, 0), (0, 0)),self.mode)
if self.resize:
image = cv2.resize(image, (self.size[0], self.size[0]),interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
return image
# 字节整形转换(type to int)
class AstypeToInt():
def __call__(self, image, attr_idx):
return image.clip(0,255.0).astype(np.uint8), attr_idx
# 字节浮点数转换(type to float)
class AstypeToFloat():
def __call__(self, image, attr_idx):
return image.astype(np.float32), attr_idx
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 正则化(normalize)
class Normalize(object):
def __init__(self,mean, std):
'''
:param mean: RGB order
:param std: RGB order
'''
self.mean = np.array(mean).reshape(3,1,1)
self.std = np.array(std).reshape(3,1,1)
def __call__(self, image):
'''
:param image: (H,W,3) RGB
:return:
'''
# plt.figure(1)
# plt.imshow(image)
# plt.show()
return (image.transpose((2, 0, 1)) / 255. - self.mean) / self.std
# 随机擦除(random erasing)
class RandomErasing(object):
def __init__(self, select,EPSILON=0.5,sl=0.02, sh=0.09, r1=0.3, mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406]):
self.EPSILON = EPSILON
self.mean = mean
self.sl = sl
self.sh = sh
self.r1 = r1
self.select = select
def __call__(self, img,attr_idx):
if attr_idx not in self.select:
return img,attr_idx
if random.uniform(0, 1) > self.EPSILON:
return img,attr_idx
for attempt in range(100):
area = img.shape[1] * img.shape[2]
target_area = random.uniform(self.sl, self.sh) * area
aspect_ratio = random.uniform(self.r1, 1 / self.r1)
h = int(round(math.sqrt(target_area * aspect_ratio)))
w = int(round(math.sqrt(target_area / aspect_ratio)))
if w <= img.shape[2] and h <= img.shape[1]:
x1 = random.randint(0, img.shape[1] - h)
y1 = random.randint(0, img.shape[2] - w)
if img.shape[0] == 3:
# img[0, x1:x1+h, y1:y1+w] = random.uniform(0, 1)
# img[1, x1:x1+h, y1:y1+w] = random.uniform(0, 1)
# img[2, x1:x1+h, y1:y1+w] = random.uniform(0, 1)
img[0, x1:x1 + h, y1:y1 + w] = self.mean[0]
img[1, x1:x1 + h, y1:y1 + w] = self.mean[1]
img[2, x1:x1 + h, y1:y1 + w] = self.mean[2]
# img[:, x1:x1+h, y1:y1+w] = torch.from_numpy(np.random.rand(3, h, w))
else:
img[0, x1:x1 + h, y1:y1 + w] = self.mean[1]
# img[0, x1:x1+h, y1:y1+w] = torch.from_numpy(np.random.rand(1, h, w))
return img,attr_idx
return img,attr_idx
if __name__ == '__main__':
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
class FSAug(object):
def __init__(self):
self.augment = Compose([
AstypeToFloat(),
# RandomHShift(scale=(0.,0.2),select=range(8)),
# RandomRotate(angles=(-20., 20.), bound=True),
ExpandBorder(select=range(8), mode='symmetric'),# symmetric
# Resize(size=(336, 336), select=[ 2, 7]),
AstypeToInt()
])
def __call__(self, spct,attr_idx):
return self.augment(spct,attr_idx)
trans = FSAug()
img_path = '/home/by/Orbit.png'
img = cv2.cvtColor(cv2.imread(img_path),cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
img_trans,_ = trans(img,5)
# img_trans2,_ = trans(img,6)
print (img_trans.max(), img_trans.min())
print (img_trans.dtype)
plt.figure()
plt.subplot(221)
plt.imshow(img)
plt.subplot(222)
plt.imshow(img_trans)
# plt.subplot(223)
# plt.imshow(img_trans2)
# plt.imshow(img_trans2)
plt.show()