HLS+各种接口实现案例(mm_master、mm_slave、pointer、mm_stream interface)
HLS+各种接口实现加案例 mm_master和mm_slave
-
- Pointer_arguments
- Avalon Streaming Interfaces
-
- stream_in
- stream_out
- 使用包信号允许多个流调用站点
- Avalon Memory-Mapped Master Interfaces
-
- Implicit Example
- Explicit Example
- Slave Interfaces
-
- hls_avalon_slave_component
- hls_avalon_slave_register_argument
- slave_memory_argument
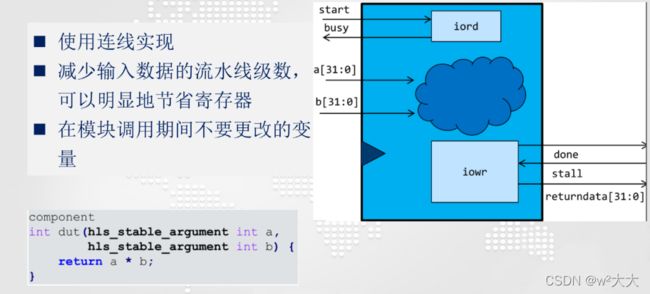
- stable_argument
- HLS编译器标准版组件调用接口参数总结
- Intel HLS编译器标准版组件宏总结
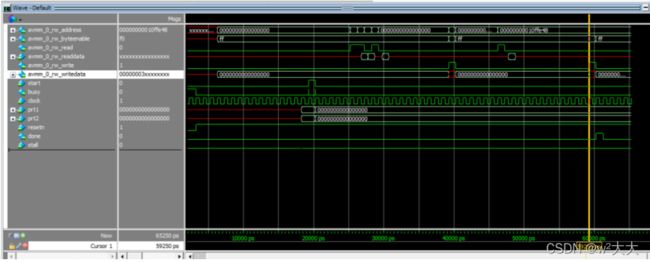
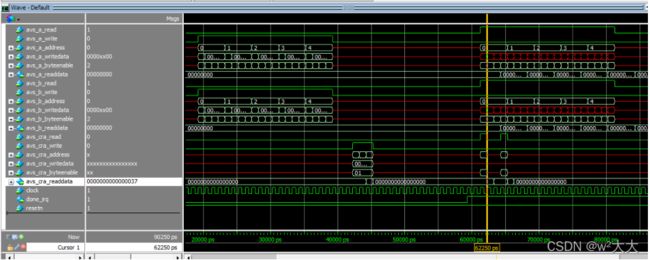
Pointer_arguments
#include 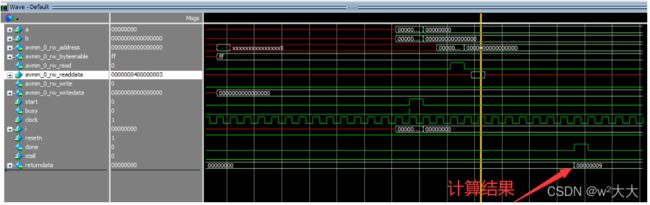
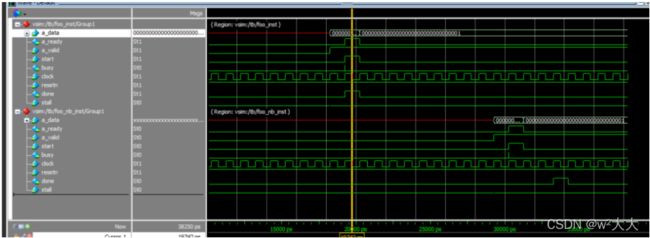
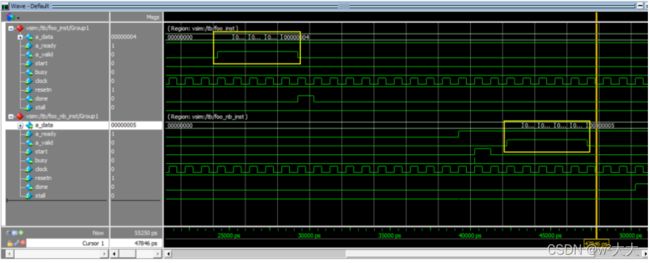
通过字节使能ff 低8bit为有效,为什么是0000000400000003 因为从i=2后的地址读取数据了,但是因为字节使能的原因 ,所以 03 有效与a=3相乘,结果为9

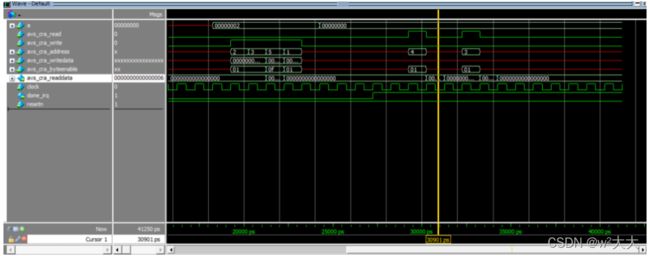
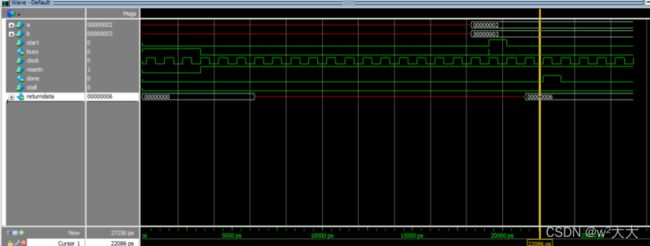
如果组件dut把busy信号拉高,那么调用dut的模块需要把start信号拉高直到busy拉低;如果dut的下游部件把stall信号拉高,那么dut需要将done信号拉高直到stall信号拉低。
Avalon Streaming Interfaces
白嫖知识:
- 阻塞:阻塞调用是指调用结果返回之前,当前线程会被挂起。函数只有在得到结果之后才会返回。
- 非阻塞:非阻塞和阻塞的概念相对应,指在不能立刻得到结果之前,该函数不会阻塞当前线程,而会立刻返回。
- 组件可以具有符合Avalon-ST接口规范的输入和输出流。这些输入和输出流在C源中通过将对ihc::stream_in<>和ihc::stream_out<>对象的引用作为对组件的函数参数来表示。
- 一个组件调用可以从一个流中读取多次。
- 不能从流类派生新类,或将它们封装为其他格式,如结构或数组
- 一个组件可以为一个流有多个读取站点,同样一个组件可以为同一流拥有多个写入站点。
- 在组件中,不能保证不同流的执行顺序,除非流之间存在数据依赖性。
stream_in
#include stream_out
#include 使用包信号允许多个流调用站点

在流接口上公开starttofpacket和endofpacket边带信号,可以被基于读写的包访问
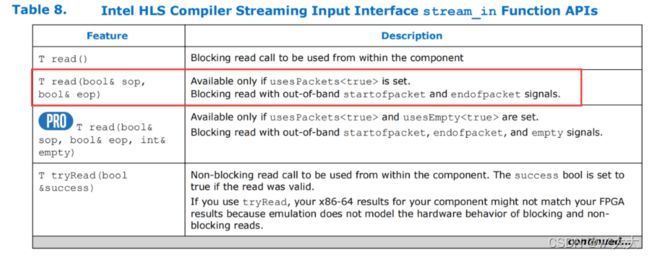
仅当设置了usesPackets时可用。
用带外的starttofpacket和endofpacket信号阻塞读取。
#include Avalon Memory-Mapped Master Interfaces
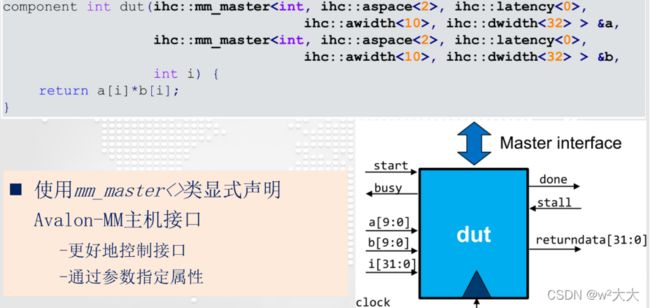
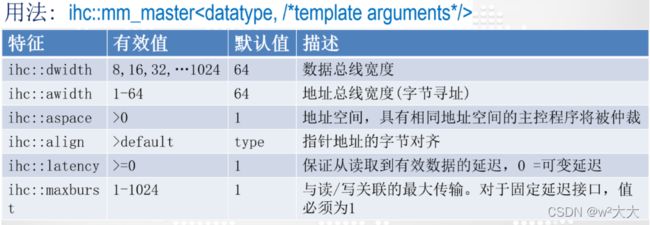
组件可以通过Avalon内存映射与外部内存接口mm_master<>。您可以使用函数指针参数或引用参数隐式指定Avalon MM Master接口,也可以显式使用“HLS/hls .h”头文件中定义的mm_master<>类。
Implicit Example
下面的代码示例仲裁加载和存储指令,这些指令来自组件顶级模块上单个接口的两个指针解引用。这个接口的数据总线宽度为64位,地址宽度为64位,固定延迟为1。
#include Explicit Example
这个示例演示了如何使用显式mm_master类为特定内存接口优化前面的代码片段。mm_master类有一个已定义的模板,它具有以下特征:
- 每个接口都有一个唯一的ID,它推断出两个独立的接口,减少了组件中仲裁的数量。
- 数据总线宽度大于默认的64位宽度。
- 地址总线宽度小于默认的64位宽度。
- 接口的延迟固定为2。
通过定义这些特征,可以声明系统在两个时钟周期之后返回有效的读数据,并且接口在读写时从不停止,但是系统必须能够提供两个不同的内存。一个唯一的空间被期望对应一个唯一的物理内存。如果将具有相同空间的多个Avalon-MM Master接口连接到相同的物理内存,那么Intel HLS编译器无法确保任何内存依赖项的功能正确性。
#include mm(void* ptr, int size, bool use_socket=false);
#if DEBUG_TYPEDEF
Master1 mm_x(x,2*sizeof(int),false);
Master2 mm_y(&y,1*sizeof(int),false);
#else
ihc::mm_master<int,ihc::dwidth<256>,ihc::awidth<32>,ihc::aspace<1>,ihc::latency<2> > mm_x(x,2*sizeof(int),false);
ihc::mm_master<int,ihc::dwidth<256>,ihc::awidth<32>,ihc::aspace<4>,ihc::latency<2> > mm_y(&y,1*sizeof(int),false);
#endif
//调用组件
dut(mm_x,mm_y);
return 0;
}
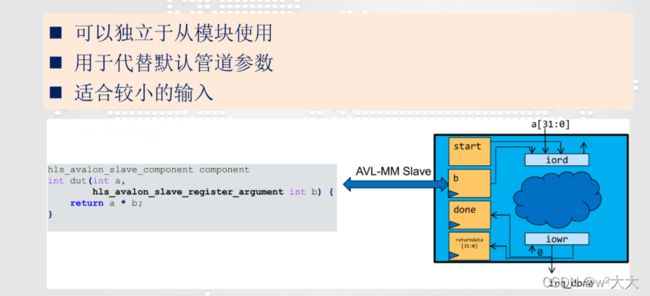
Slave Interfaces
Intel HLS Compiler提供了两种不同类型的从接口,您可以在组件中使用它们。一般来说,较小的标量输入应该使用从寄存器。如果您打算将大数组复制到组件中或从组件中复制出来,那么应该使用从属内存。

hls_avalon_slave_component
#include hls_avalon_slave_register_argument
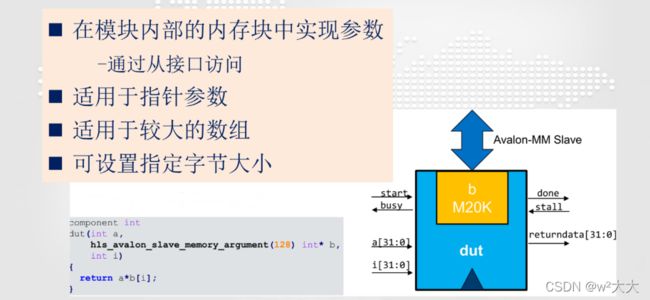
#include slave_memory_argument
#include stable_argument
#include HLS编译器标准版组件调用接口参数总结
Intel HLS编译器标准版组件宏总结
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| hls_conduit_argument | Implement the argument as an input conduit that is synchronous to the component call (start and busy).将参数实现为与组件调用(start和busy)同步的输入管道。 |
| hls_avalon_slave_register_argument | Implement the argument as a register that can be read from and written to over an Avalon-MM slave interface.将参数实现为一个可以通过Avalon-MM从接口读写的寄存器。 |
| hls_avalon_slave_memory_argument | Implement the argument, in on-chip memory blocks, which can be read from or written to over a dedicated slave interface.在片上内存块中实现参数,它可以在专用的从接口上读取或写入。 |
| hls_stable_argument | A stable argument is an argument that does not change while there is live data in the component (that is, between pipelined function invocations).稳定参数是当组件中有实时数据时(即在管道函数调用之间)不发生更改的参数。 |