Android10 HAL模块的实现
一、前言
-
本文的目的
研究HAL模块的实现过程。
-
前期准备
已编译完成Android 10版本源码。 源码下载参照:AOSP源码下载
开发板或者可运行Android 10版本镜像的设备,本文以开发板为例,例子通用。理论上Android 10编译出的库文件及bin文件,在同版本系统的开发板或者设备上都可运行。
二、HAL介绍
-
什么是HAL
在Android系统中,硬件抽象层(
HAL, Hardware Abstraction Layer),向下屏蔽硬件驱动模块的实现细节,向上提供对硬件访问的抽象接口服务。HAL是底层硬件和上层框架直接的接口,框架层通过HAL可以操作硬件设备,HAL的实现在用户空间。 -
为什么需要HAL
Android系统是基于Linux内核进行开发,Linux驱动一般有两种类型:访问硬件寄存器的代码和业务逻辑的代码。对于访问硬件寄存器的代码,都是调用的Linux内核的标准函数进行的标准操作。Linux驱动的业务逻辑部分每个硬件厂商都有自己的实现的方式,对于一些企业或个人并不想将源代码公开。而Linux内核采用GPL协议,GPL协议要求所有使用基于GPL协议的源代码的程序必须开源。
为此,Google在Android层次结构中的系统运行层增加了一个HAL,硬件厂商就可以将自己的核心算法之类的放在HAL层,从而保护各个厂商的利益。
-
HAL架构的种类
-
module架构 (旧架构)
源码对应目录:
hardware/libhardware_legacy谷歌对旧版HAL架构的描述:旧版HAL。其实就是Android8.0之前,一直用的是旧的架构。Android 8.0 开始已不再支持的旧版架构。
Android用户应用程序或者框架层代码由Java实现,Java运行在Dalvik虚拟机中,没有办法直接访问底层硬件,只能通过调用so本地库代码实现,在so本地代码里有对底层硬件操作的代码,如下图所示:

应用层或者框架层Java代码,通过JNI调用C或C++写的so库代码,在so库代码中调用底层驱动,从而实现上层应用操作底层硬件的目的。实现硬件操作的so库为module。这种设计架构虽然满足了Java应用访问硬件的需要,但是,使得我们的代码上下层次间的耦合太高,用户程序或者框架代码必须要去加载module库,如果底层硬件有变化,module要从新编译,上层也要做相应变化,另外,如果多个应用程序同时访问硬件,都去加载module,同一module被多个进程映射多次,会有代码的重入问题。
-
module stub (新架构)
源码对应目录:
hardware/libhardware新的代码架构使用的是module stub方式.Stub是存根或者桩的意思,其实说白了,就是指一个对象代表的意思。上层应用层或者框架层代码加载so库代码,so库代码我们称之为module,在Hal层注册了每个硬件对象的存根stub,当上层需要访问硬件的时候,就从当前注册的硬件对象stub里查找,找到之后stub会向上层module提供该硬件对象的operations interface(操作接口),该操作接口就保存在module中,上层应用或框架层再通过这个module操作接口来访问硬件。其架构如下:
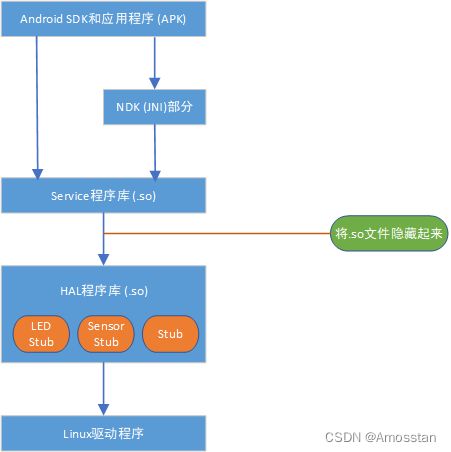
-
新旧架构对比
在Module架构中,本地代码由so库实现,上层直接将so库映射到进程空间,会有代码重入及设备多次打开的问题。新的Stub框架虽然也要加载module库,但是这个module已经不包含操作底层硬件驱动的功能了,它里面保存的只是底层stub提供的操作接口,底层stub扮演了“接口提供者”的角色,当stub第一次被使用时加载到内存,后续再使用时仅返回硬件对象操作接口,不会存在设备多次打开的问题,并且由于多进程访问时返回的只是函数指针,代码并没有重入。
-
-
HAL实现规则(新架构)
-
规则源码定义
头文件定义:
hardware/libhardware/include/hardware/hardware.hC文件定义:
hardware/libhardware/hardware.c -
规则说明
每种硬件对应一个HAL模块,HAL需要满足相应规则,hardware.h中对应三个重要结构体:
struct hw_module_t; struct hw_module_methods_t; struct hw_device_t;结构体hw_module_t代表HAL模块,顶自己定义的HAL模块必须包含一个自定义struct,且结构体内第一个变量必须为 hw_module_t,且模块的tag必须指定为HARDWARE_MODULE_TAG,代表这是HAL模块的结构体。
typedef struct hw_module_t { /** tag must be initialized to HARDWARE_MODULE_TAG */ uint32_t tag; /** * The API version of the implemented module. The module owner is * responsible for updating the version when a module interface has * changed. * * The derived modules such as gralloc and audio own and manage this field. * The module user must interpret the version field to decide whether or * not to inter-operate with the supplied module implementation. * For example, SurfaceFlinger is responsible for making sure that * it knows how to manage different versions of the gralloc-module API, * and AudioFlinger must know how to do the same for audio-module API. * * The module API version should include a major and a minor component. * For example, version 1.0 could be represented as 0x0100. This format * implies that versions 0x0100-0x01ff are all API-compatible. * * In the future, libhardware will expose a hw_get_module_version() * (or equivalent) function that will take minimum/maximum supported * versions as arguments and would be able to reject modules with * versions outside of the supplied range. */ uint16_t module_api_version; #define version_major module_api_version /** * version_major/version_minor defines are supplied here for temporary * source code compatibility. They will be removed in the next version. * ALL clients must convert to the new version format. */ /** * The API version of the HAL module interface. This is meant to * version the hw_module_t, hw_module_methods_t, and hw_device_t * structures and definitions. * * The HAL interface owns this field. Module users/implementations * must NOT rely on this value for version information. * * Presently, 0 is the only valid value. */ uint16_t hal_api_version; #define version_minor hal_api_version /** Identifier of module */ const char *id; /** Name of this module */ const char *name; /** Author/owner/implementor of the module */ const char *author; /** Modules methods */ struct hw_module_methods_t* methods; /** module's dso */ void* dso; #ifdef __LP64__ uint64_t reserved[32-7]; #else /** padding to 128 bytes, reserved for future use */ uint32_t reserved[32-7]; #endif } hw_module_t;结构体hw_module_methods_t代表模块的操作方法列表,它内部只有一个函数指针open,用来打开该模块下的设备。
typedef struct hw_module_methods_t { /** Open a specific device */ int (*open)(const struct hw_module_t* module, const char* id, struct hw_device_t** device); } hw_module_methods_t;结构体hw_device_t代表该模块下的设备,自己定义的HAL模块必须包含一个结构体,且第一个变量必须为hw_device_t。
/** * Every device data structure must begin with hw_device_t * followed by module specific public methods and attributes. */ typedef struct hw_device_t { /** tag must be initialized to HARDWARE_DEVICE_TAG */ uint32_t tag; /** * Version of the module-specific device API. This value is used by * the derived-module user to manage different device implementations. * * The module user is responsible for checking the module_api_version * and device version fields to ensure that the user is capable of * communicating with the specific module implementation. * * One module can support multiple devices with different versions. This * can be useful when a device interface changes in an incompatible way * but it is still necessary to support older implementations at the same * time. One such example is the Camera 2.0 API. * * This field is interpreted by the module user and is ignored by the * HAL interface itself. */ uint32_t version; /** reference to the module this device belongs to */ struct hw_module_t* module; /** padding reserved for future use */ #ifdef __LP64__ uint64_t reserved[12]; #else uint32_t reserved[12]; #endif /** Close this device */ int (*close)(struct hw_device_t* device); } hw_device_t;每个自定义HAL模块还有一个模块名和N个设备名(标识模块下的设备个数,一个模块可以有多个设备)。
最后这个模块定义好之后还必须导出符号HAL_MODULE_INFO_SYM指向这个模块,HAL_MODULE_INFO_SYM定义在hardware.h中值为"HMI"。
/** * Name of the hal_module_info */ #define HAL_MODULE_INFO_SYM HMI
-
三、HAL模块实现步骤
-
LED模块功能简介
主要实现一个LED灯的开关及信息读取功能,当然开关及信息读取的数据用伪代码实现,用于演示功能。
-
实现HAL层LED模块
-
led.h
vim hardware/libhardware/include/hardware/led.h实现代码如下:
#include#include #include /* 定义HAL模块名 */ #define LED_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID "led" /* 定义HAL版本号 */ #define LED_MODULE_API_VERSION_1_0 HARDWARE_MODULE_API_VERSION(0, 1) /* 定义设备名 */ #define HARDEARE_LED "led" /* 自定义HAL模块结构体 */ typedef struct led_module { struct hw_module_t common; } led_module_t; /* 自定义HAL设备结构体 */ typedef struct led_device { struct hw_device_t common; /* LED控制 */ int (*ledControl) (const struct led_device *dev, int status); /* 获取LED状态 */ int (*getLEDStatus) (const struct led_device *dev, int *status); } led_device_t; /* 给外部调用提供打开设备的函数 */ static inline int _led_open(const struct hw_module_t *module, led_device_t **device) { return module->methods->open(module, HARDEARE_LED, (struct hw_device_t **) device); } -
led.c
mkdir -p hardware/libhardware/modules/led vim hardware/libhardware/modules/led/led.c实现代码如下:
#include#include #include #include #include #include #include #define LOG_TAG "LED" #define ALOGD(...) __android_log_print(ANDROID_LOG_DEBUG, LOG_TAG, __VA_ARGS__) static int LED_STATUS = 0; /* LED控制 */ int led_control(const struct led_device *dev, int status) { if (dev == NULL) { ALOGD("Error: device is NULL!!"); return -1; } ALOGD("set led status: %d", status); if (status == 0) { LED_STATUS = 0; } else { LED_STATUS = 1; } return 0; } /* 获取LED状态 */ int get_led_status(const struct led_device *dev, int *status) { if (dev == NULL) { ALOGD("Error: device is NULL!!"); return -1; } *status = LED_STATUS; ALOGD("get led status: %d", *status); return 0; } /* 关闭LED设备 */ static int led_close(hw_device_t *dev) { if (dev == NULL) { return -1; } free(dev); return 0; } /* 打开LED设备 */ static int led_open(const hw_module_t* module, const char __unused *id, hw_device_t** device) { if (device == NULL) { ALOGD("ERROR: device is null"); return -1; } led_device_t *dev = malloc(sizeof(led_device_t)); memset(dev, 0, sizeof(led_device_t)); dev->common.tag = HARDWARE_DEVICE_TAG; dev->common.version = LED_MODULE_API_VERSION_1_0; dev->common.module = (struct hw_module_t*) module; dev->common.close = led_close; dev->ledControl = led_control; dev->getLEDStatus = get_led_status; *device = &(dev->common); return 0; } /* 打开硬件模块中硬件设备的函数 */ static struct hw_module_methods_t led_module_methods = { .open = led_open, }; /* 导出符号HAL_MODULE_INFO_SYM,指向自定义模块 */ led_module_t HAL_MODULE_INFO_SYM = {HAL_MODULE_INFO_SYM .common = { .tag = HARDWARE_MODULE_TAG, .module_api_version = LED_MODULE_API_VERSION_1_0, .hal_api_version = HARDWARE_HAL_API_VERSION, .id = LED_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID, .name = "Demo Led HAL Test", .author = "[email protected]", .methods = &led_module_methods, }, }; -
Android.bp
vim hardware/libhardware/modules/led/Android.bp实现代码如下:
cc_library_shared { name: "led.default", relative_install_path: "hw", proprietary: true, srcs: ["led.c"], header_libs: ["libhardware_headers"], shared_libs: [ "liblog", "libcutils" ], cflags: [ "-Wall", "-Wextra", "-Wno-unused-parameter", "-Wno-unused-function", ], } -
编译
mmm hardware/libhardware/modules/led -
推送
将编译出来的led.default.so推送到/vendor/lib64/hw/目录下。
-
-
实现LED测试模块
-
led_test.c
mkdir -p hardware/libhardware/modules/led/test vim hardware/libhardware/modules/led/test/led_test.c实现代码如下:
#include#include #include #define LOG_TAG "LED_TEST" #define ALOGD(...) __android_log_print(ANDROID_LOG_DEBUG, LOG_TAG, __VA_ARGS__) static int led_test() { const led_module_t *module = NULL; led_device_t *device = NULL; /* 根据HAL层注册信息id,获取相应的模块 */ int ret = hw_get_module(LED_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID, (const struct hw_module_t**)&module); if (!ret) { /* 打开设备 */ ret = _led_open((const struct hw_module_t*)module, &device); } if (ret < 0) { ALOGD("Error: get HAL Test module failed........"); return -1; } /* 获取LED状态 */ int led_status; device->getLEDStatus(device, &led_status); ALOGD("LED status is %d", led_status); /* 设置LED状态 */ device->ledControl(device, 1); ALOGD("set LED status is 1"); /* 设置LED状态 */ device->getLEDStatus(device, &led_status); ALOGD("LED status is %d", led_status); return 0; } int main(int argc, char *argv[]){ ALOGD("############ LED Test start ############"); led_test(); ALOGD("############ LED Test end ############"); return 0; } -
Android.bp
vim hardware/libhardware/modules/led/test/Android.bp实现代码如下:
cc_binary { name: "led_test", proprietary: true, srcs: ["led_test.cpp"], shared_libs: [ "liblog", "libhardware", ], cflags: [ "-Wall", "-Wextra", "-Wno-unused-parameter", "-Wno-unused-function", ], } -
编译
mmm hardware/libhardware/modules/led/test -
推送
将编译出的led_test可执行文件推送到/vendor/bin目录下。
-
-
测试
adb shell后执行led_test,会出现如下打印:
06-29 18:31:04.615 6389 6389 D LED_TEST: ############ LED Test start ############ 06-29 18:31:04.616 6389 6389 D LED : get led status: 0 06-29 18:31:04.616 6389 6389 D LED_TEST: LED status is 0 06-29 18:31:04.616 6389 6389 D LED : set led status: 1 06-29 18:31:04.616 6389 6389 D LED_TEST: set LED status is 1 06-29 18:31:04.616 6389 6389 D LED : get led status: 1 06-29 18:31:04.616 6389 6389 D LED_TEST: LED status is 1 06-29 18:31:04.616 6389 6389 D LED_TEST: ############ LED Test end ############ -
其它
实现LED HAL层代码目录结构如下:
. └── hardware └── libhardware ├── include │ └── hardware │ └── led.h └── modules └── led ├── Android.bp ├── led.c └── test ├── Android.bp └── led_test.cpp 7 directories, 5 files
四、参考
- 为什么要在Android中加入HAL
- Android 系统HAL 简介
- AndroidQ 打通应用层到HAL层—(HAL模块实现)