Xavier NX实现硬解码H264&H265
提示:文章写完后,目录可以自动生成,如何生成可参考右边的帮助文档
文章目录
- 前言
- 一、NX的硬解码?
- 二、测试代码
- 三、软硬解对比
- 四、总结
前言
最近在做一个项目,使用opencv的VideoCapture拉流并把帧送进模型推理,结果发现VideoCapture本身使用的是cpu的软解码,占用了大量的资源,后来就去研究使用设备本身的硬解码资源去分摊cpu的压力。
一、NX的硬解码?
Xavier NX 使用OpenCV+GStreamer实现硬解码
NX的硬解码叫NVDEC,硬编码交NVENC,这两个都是专门的硬件去做的,效率比cpu高很多。这里要多说一句,NX是共享内存,就是gpu,vpu和cpu都是一个内存,不像台式机有专用显存,显存与内存数据格式不一样,需要转换(实测0-2ms),不能拿来直接用。NX就没有这个问题,但是这里我们不讨论这么深的问题,感兴趣的可以私下里去研究下。先上个图,这里需要使用jtop看

注意看红框里面的,如果解码器没有用这个就是OFF,旁边的就是编码器,不在这次讨论范围内。
二、测试代码
首先你要安装了opencv+gstreamer,具体安装方法我会在另一篇文章里面介绍,这里不多说,直接上代码。这里我们使用官方提供的代码
# --------------------------------------------------------
# Camera sample code for Tegra X2/X1
#
# This program could capture and display video from
# IP CAM, USB webcam, or the Tegra onboard camera.
# Refer to the following blog post for how to set up
# and run the code:
# https://jkjung-avt.github.io/tx2-camera-with-python/
#
# Written by JK Jung 这里我不需要显示,所以我把显示代码注释掉了,需要的可自行打开,前提是你需要一个显示页面。再看看jtop
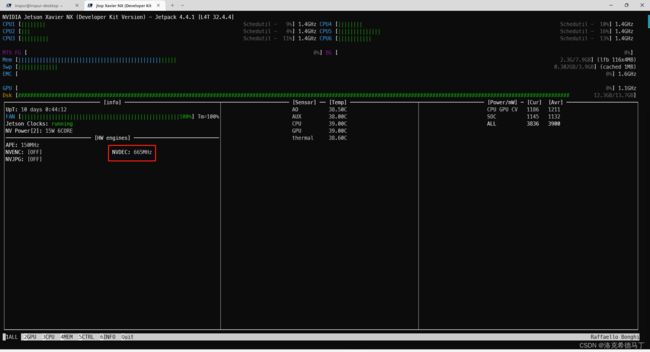
再看看红框里面的,如果有数值,说明硬解码成功了,如果没有那就是你本身的环境装的不对。
补充:这里多说一句,关于怎么提前知道流的信息,我们需要借用ffprobe的指令
ffprobe -show_streams -v quiet -show_format -print_format json -i <url>
{
"streams": [
{
"index": 0,
"codec_name": "hevc",
"codec_long_name": "H.265 / HEVC (High Efficiency Video Coding)",
"profile": "Main",
"codec_type": "video",
"codec_tag_string": "[0][0][0][0]",
"codec_tag": "0x0000",
"width": 1920,
"height": 1080,
"coded_width": 1920,
"coded_height": 1080,
"closed_captions": 0,
"has_b_frames": 2,
"pix_fmt": "yuv420p",
"level": 153,
"color_range": "tv",
"chroma_location": "left",
"refs": 1,
"r_frame_rate": "25/1",
"avg_frame_rate": "0/0",
"time_base": "1/90000",
"start_pts": 3600,
"start_time": "0.040000",
"disposition": {
"default": 0,
"dub": 0,
"original": 0,
"comment": 0,
"lyrics": 0,
"karaoke": 0,
"forced": 0,
"hearing_impaired": 0,
"visual_impaired": 0,
"clean_effects": 0,
"attached_pic": 0,
"timed_thumbnails": 0
}
}
],
"format": {
"filename": "rtsp://10.0.42.30/record_hevc_0",
"nb_streams": 1,
"nb_programs": 0,
"format_name": "rtsp",
"format_long_name": "RTSP input",
"start_time": "0.040000",
"probe_score": 100,
"tags": {
"title": "No Name"
}
}
}
index 就是音视频的索引,我用的这个流是不带声音的,所以只有一个index,一般0是视频,1是音频。codec_name 就是编码格式,你可以先用这个方法获取编码格式再决定选用哪种编码方式,由于H264和H265是最普遍的两种格式,几乎所有的设备都是支持的。所以这里我不介绍其他的了,有兴趣的可自行研究。
其他的参数如帧率,比特率都是可以通过这个命令获取的,rtsp是没有duration的,这个选项不可用,因为流是一直推的,视频文件这个参数是有效的。其它参数请大家自行研究。
三、软硬解对比
由于我需要看硬解码状态所以使用了jtop,jtop对cpu占用还是比较大的,大家可以使用top来看,top对资源占用很少。不过就算这样硬解码的优势还是很明显的。
四、总结
总体来讲是比较简单的,H264和H265两兄弟也基本上能满足日常绝大多数场景的需求了。