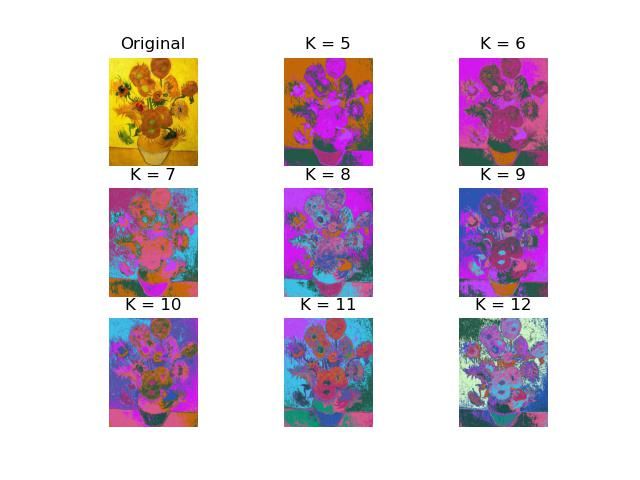
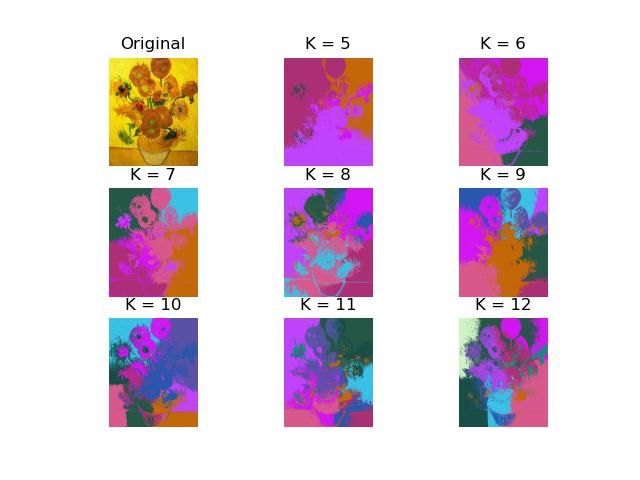
python手动实现图像像素的kmeans聚类(附代码)
1.简介
这篇文章主要是介绍了python使用kmeans算法来对图像中的像素进行聚类。整个kmeans算法为手动实现,不调用sklearn库。一共使用了两种方法,其中方法a.py使用了三通道像素值rgb共三个特征,方法b.py使用了rgb+像素坐标xy共5个特征。
2.kmeans
kmeans步骤共可分为以下步骤:
随机初始化k个聚类中心。
计算所有像素点到聚类中心的距离。
选择最近的聚类中心作为像素点的聚类种类。
根据像素点的聚类种类更新聚类中心。
重复步骤2-4直至聚类中心收敛。
3.代码
部分关键代码:
# 提取图像的像素值
features = []
for y in range(height):
for x in range(width):
features.append(image[y, x, :] / 255)
features = np.array(features)
# 初始化聚类中心
kmeans_centers = features[np.random.choice(len(features), k), :]
kmeans_centers = np.array(kmeans_centers)# 计算所有像素点到聚类中心的距离矩阵
def euclidean_dist(X, Y):
Gx = np.matmul(X, X.T)
Gy = np.matmul(Y, Y.T)
diag_Gx = np.reshape(np.diag(Gx), (-1, 1))
diag_Gy = np.reshape(np.diag(Gy), (-1, 1))
return diag_Gx + diag_Gy.T - 2 * np.matmul(X, Y.T)# 更新聚类中心
new_kmeans_centers = []
for j in range(k):
new_kmeans_centers.append(np.mean(features[segs==j, :], axis=0))
new_kmeans_centers = np.array(new_kmeans_centers)方法a完整代码:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.image as mpimg
if __name__ == '__main__':
# Initialize rgb pixel values for each class in kmeans using specific values
bgr_list = [(0, 0, 255),
(0, 255, 0),
(255, 0, 0),
(128, 128, 255),
(128, 255, 128),
(255, 128, 128),
(128, 0, 255),
(128, 255, 0),
(255, 128, 0),
(0, 128, 255),
(0, 255, 128),
(255, 0, 128)]
# Reading images using matplotlib library
image = mpimg.imread('demo.jpg')
height, width, channel = image.shape
# show original image
plt.figure()
plt.subplot(3, 3, 1)
plt.axis('off')
plt.title('Original')
plt.imshow(image)
# do kmeans segmentation
for i, k in enumerate(range(5, 13, 1)):
# extract bgr features
features = []
for y in range(height):
for x in range(width):
features.append(image[y, x, :] / 255)
features = np.array(features)
# initial segments center using random value in features
kmeans_centers = features[np.random.choice(len(features), k), :]
kmeans_centers = np.array(kmeans_centers)
# update
while True:
# calculate distance matrix
def euclidean_dist(X, Y):
Gx = np.matmul(X, X.T)
Gy = np.matmul(Y, Y.T)
diag_Gx = np.reshape(np.diag(Gx), (-1, 1))
diag_Gy = np.reshape(np.diag(Gy), (-1, 1))
return diag_Gx + diag_Gy.T - 2 * np.matmul(X, Y.T)
dist_matrix = []
for start in range(0, len(features), 1000):
dist_matrix.append(euclidean_dist(features[start:start+1000, :], kmeans_centers))
dist_matrix = np.concatenate(dist_matrix, axis=0)
# dist_matrix = euclidean_dist(features, kmeans_centers)
# get seg class for each sample
segs = np.argmin(dist_matrix, axis=1)
# update new kmeans center
new_kmeans_centers = []
for j in range(k):
new_kmeans_centers.append(np.mean(features[segs==j, :], axis=0))
new_kmeans_centers = np.array(new_kmeans_centers)
# calculate whether converge
if np.mean(abs(kmeans_centers - new_kmeans_centers)) < 0.1:
break
else:
kmeans_centers = new_kmeans_centers
# assign
segs = segs.reshape(height, width)
seg_result = np.zeros((height, width, channel), dtype=np.uint8)
for y in range(height):
for x in range(width):
seg_result[y, x, :] = bgr_list[segs[y, x]]
# show kmeans result
plt.subplot(3, 3, i+2)
plt.title('k={}'.format(k))
plt.axis('off')
plt.imshow(seg_result)
plt.savefig('result_a.jpg')方法b完整代码:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.image as mpimg
if __name__ == '__main__':
# Initialize rgb pixel values for each class in kmeans using specific values
bgr_list = [(0, 0, 255),
(0, 255, 0),
(255, 0, 0),
(128, 128, 255),
(128, 255, 128),
(255, 128, 128),
(128, 0, 255),
(128, 255, 0),
(255, 128, 0),
(0, 128, 255),
(0, 255, 128),
(255, 0, 128)]
# Reading images using matplotlib library
image = mpimg.imread('demo.jpg')
height, width, channel = image.shape
# show original image
plt.figure()
plt.subplot(3, 3, 1)
plt.axis('off')
plt.title('Original')
plt.imshow(image)
# do kmeans segmentation
for i, k in enumerate(range(5, 13, 1)):
# extract bgr and location features
features = []
for y in range(height):
for x in range(width):
features.append(np.concatenate((image[y, x, :] / 255, np.array([y / height, x / width])), axis=0))
features = np.array(features)
# initial segments center using random value in features
kmeans_centers = features[np.random.choice(len(features), k), :]
kmeans_centers = np.array(kmeans_centers)
# update
while True:
# calculate distance matrix
def euclidean_dist(X, Y):
Gx = np.matmul(X, X.T)
Gy = np.matmul(Y, Y.T)
diag_Gx = np.reshape(np.diag(Gx), (-1, 1))
diag_Gy = np.reshape(np.diag(Gy), (-1, 1))
return diag_Gx + diag_Gy.T - 2 * np.matmul(X, Y.T)
dist_matrix = []
for start in range(0, len(features), 1000):
dist_matrix.append(euclidean_dist(features[start:start+1000, :], kmeans_centers))
dist_matrix = np.concatenate(dist_matrix, axis=0)
# dist_matrix = euclidean_dist(features, kmeans_centers)
# get seg class for each sample
segs = np.argmin(dist_matrix, axis=1)
# update new kmeans center
new_kmeans_centers = []
for j in range(k):
new_kmeans_centers.append(np.mean(features[segs==j, :], axis=0))
new_kmeans_centers = np.array(new_kmeans_centers)
# calculate whether converge
if np.mean(abs(kmeans_centers - new_kmeans_centers)) < 0.1:
break
else:
kmeans_centers = new_kmeans_centers
# assign
segs = segs.reshape(height, width)
seg_result = np.zeros((height, width, channel), dtype=np.uint8)
for y in range(height):
for x in range(width):
seg_result[y, x, :] = bgr_list[segs[y, x]]
# show kmeans result
plt.subplot(3, 3, i+2)
plt.title('k={}'.format(k))
plt.axis('off')
plt.imshow(seg_result)
plt.savefig('result_b.jpg')4.结果
完整的代码可以在我的github上找到:lizhiTech/manual_kmeans: python手动实现图像像素的kmeans聚类 (github.com)
或者csdn下载:python手动实现图像像素的kmeans聚类-机器学习文档类资源-CSDN文库
我们也提供包括深度学习、计算机视觉、机器学习等其他方向的其他代码及辅导服务,有需求可以通过csdn私聊或github上的联系方式联系我们。