多维时序 | MATLAB实现SSA-KELM和KELM麻雀算法优化核极限学习机多输入单输出时间序列预测
时序预测 | MATLAB实现SSA-KELM和KELM麻雀算法优化核极限学习机多输入单输出时间序列预测
目录
-
- 时序预测 | MATLAB实现SSA-KELM和KELM麻雀算法优化核极限学习机多输入单输出时间序列预测
-
- 预测效果
- 基本介绍
- 模型描述
- 程序设计
- 学习小结
- 参考资料
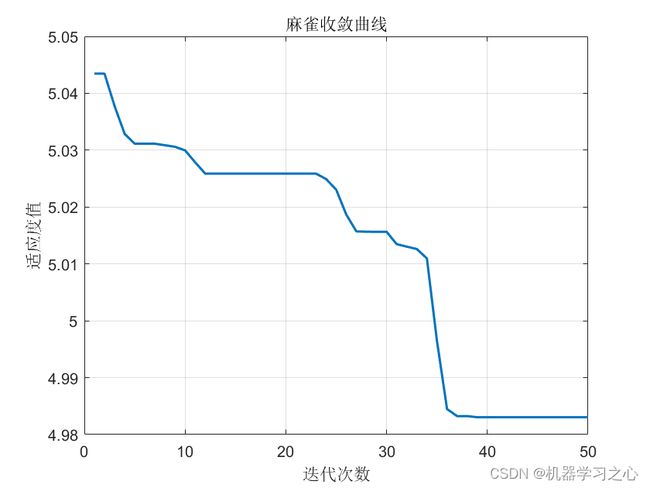
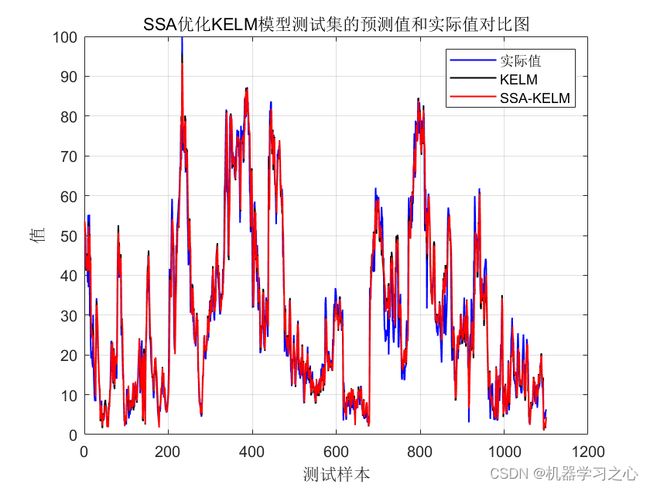
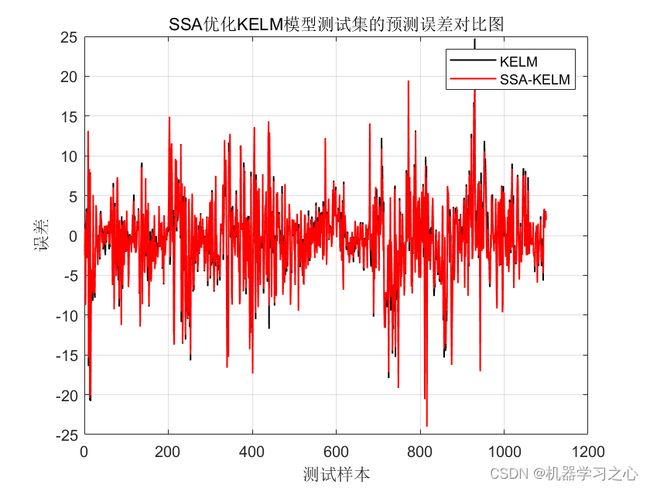
预测效果
基本介绍
MATLAB实现SSA-KELM和KELM麻雀算法优化核极限学习机多输入单输出时间序列预测,运行环境Matlab2018b及以上。核极限学习机(Kernel Based Extreme Learning Machine,KELM)是基于极限学习机(Extreme Learning Machine,ELM)并结合核函数所提出的改进算法,KELM 能够在保留 ELM 优点的基础上提高模型的预测性能。针对时间序列预测, 在单隐层前馈神经网络的基础上, 基于进化计算的优化策略, 提出了一种优化的核极限学习机(optimized kernel extreme learning machine, O-KELM) 方法.麻雀算法优化两个参数,正则化系数 C 和核函数参数 S。命令窗口输出MAE、MAPE、MSE、RMSE和R2。
模型描述
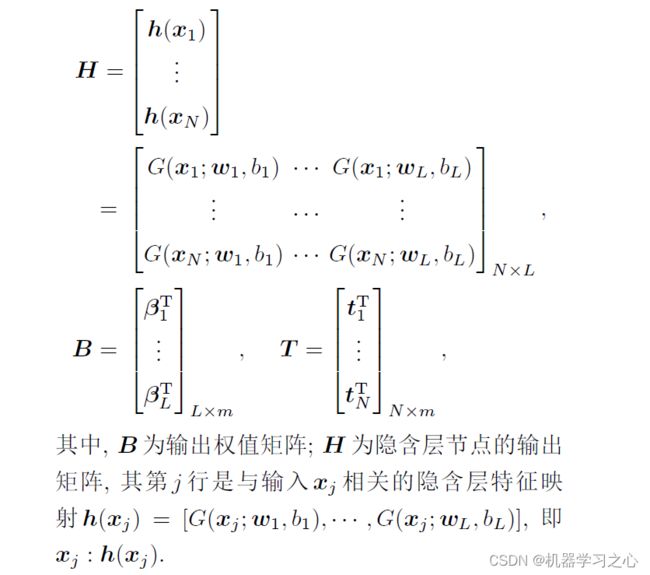
极限学习机(extreme learning machine, ELM)是Huang 等提出的一种基于单隐层前馈神经网络(single-hidden layer feedforward neural networks,SLFNs) 的快速学习方法, 其特点是随机选择SLFNs 的隐含层节点及相应的节点参数, 在训练过程中仅需通过正则化最小二乘算法调节网络的输出权值. 因此, 它能以极快的学习速度获得良好的网络泛化性能.在ELM 的基础上, 当隐含层特征映射未知时, 若以核函数取代, 可形成一种核极限学习机(KELM) 方法, 其优点是无须预先确定隐含层节点的数目. 与ELM 相比, KELM 方法在网络的训练学习过程中, 仅需选择适当的核参数与正则化系数, 通过矩阵运算, 获得网络的输出权值.KELM 是ELM 的非线性延伸, 本节在ELM 的基础上, 给出KELM 的学习方法.对于含有L个隐层节点的SLFNs.
程序设计
- 完整程序和数据下载方式1:同等价值程序兑换;
- 完整程序和数据下载方式2:MATLAB实现SSA-KELM和KELM麻雀算法优化核极限学习机多输入单输出时间序列预测
% 参数初始化
dim=21;
maxgen=30; % 进化次数
sizepop=20; %种群规模
popmax=5;
popmin=-5;
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
P_percent = 0.2; % The population size of producers accounts for "P_percent" percent of the total population size
pNum = round( sizepop * P_percent ); % The population size of the producers
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
for i=1:sizepop
pop(i,:)=5*rands(1,21);
% V(i,:)=rands(1,21);
fitness(i)=fun(pop(i,:),inputnum,hiddennum,outputnum,net,inputn,outputn);
end
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
pFit = fitness;
[ fMin, bestI ] = min( fitness ); % fMin denotes the global optimum fitness value
bestX = pop( bestI, : ); % bestX denotes the global optimum position corresponding to fMin
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%麻雀搜索算法 %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
for t = 1 : maxgen
[ ans, sortIndex ] = sort( pFit );% Sort.
[fmax,B]=max( pFit );
worse= pop(B,:);
r2=rand(1);
if(r2<0.8)
for i = 1 : pNum % Equation (3)
r1=rand(1);
pop( sortIndex( i ), : ) = pop( sortIndex( i ), : )*exp(-(i)/(r1*maxgen));
fitness(sortIndex( i ))=fun(pop(sortIndex( i ),:),inputnum,hiddennum,outputnum,net,inputn,outputn);
end
else
for i = 1 : pNum
pop( sortIndex( i ), : ) = pop( sortIndex( i ), : )+randn(1)*ones(1,dim);
fitness(sortIndex( i ))=fun(pop(sortIndex( i ),:),inputnum,hiddennum,outputnum,net,inputn,outputn);
end
end
[ fMMin, bestII ] = min( fitness );
bestXX = pop( bestII, : );
for i = ( pNum + 1 ) : sizepop % Equation (4)
A=floor(rand(1,dim)*2)*2-1;
if( i>(sizepop/2))
pop( sortIndex(i ), : )=randn(1)*exp((worse-pop( sortIndex( i ), : ))/(i)^2);
else
pop( sortIndex( i ), : )=bestXX+(abs(( pop( sortIndex( i ), : )-bestXX)))*(A'*(A*A')^(-1))*ones(1,dim);
end
fitness(sortIndex( i ))=fun(pop(sortIndex( i ),:),inputnum,hiddennum,outputnum,net,inputn,outputn);
end
c=randperm(numel(sortIndex));
b=sortIndex(c(1:3));
for j = 1 : length(b) % Equation (5)
if( pFit( sortIndex( b(j) ) )>(fMin) )
pop( sortIndex( b(j) ), : )=bestX+(randn(1,dim)).*(abs(( pop( sortIndex( b(j) ), : ) -bestX)));
else
pop( sortIndex( b(j) ), : ) =pop( sortIndex( b(j) ), : )+(2*rand(1)-1)*(abs(pop( sortIndex( b(j) ), : )-worse))/ ( pFit( sortIndex( b(j) ) )-fmax+1e-50);
end
fitness(sortIndex( i ))=fun(pop(sortIndex( i ),:),inputnum,hiddennum,outputnum,net,inputn,outputn);
end
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
for i = 1 : sizepop
if ( fitness( i ) < pFit( i ) )
pFit( i ) = fitness( i );
pop(i,:) = pop(i,:);
end
if( pFit( i ) < fMin )
fMin= pFit( i );
bestX =pop( i, : );
end
end
学习小结
与ELM 方法相比, KELM 方法无需确定隐含层节点的数目, 在ELM 的特征映射函数未知时, 应用核函数的技术, 基于正则化最小二乘算法获取输出权值的解. 因此, KELM 具有更好的逼近精度和泛化能力.
参考资料
[1] https://blog.csdn.net/kjm13182345320/article/details/128577926?spm=1001.2014.3001.5501
[2] https://blog.csdn.net/kjm13182345320/article/details/128573597?spm=1001.2014.3001.5501