MobileNetV3:Searching for MobileNetV3
Searching for MobileNetV3
MobileNet系列;
轻量化网络的集大成者;
(看MobileNet V3之前最好了解MobileNet V1,V2,SENet,MnasNet,NetAdapt,MobileNet V3是集大成者)
发表时间:[Submitted on 6 May 2019 (v1), last revised 20 Nov 2019 (this version, v5)];
发表期刊/会议:Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition;
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/1905.02244;
代码地址:https://github.com/xiaolai-sqlai/mobilenetv3(非官方);
系列论文阅读顺序:
0 摘要
提出下一代MobileNet;
MobileNet V3通过结合NetAdapt算法辅助的硬件NAS和新颖的架构来优化到移动端的CPU上;
(NAS:网络架构搜索,可参考论文"NEURAL ARCHITECTURE SEARCH WITH REINFORCEMENT LEARNING",MobileNet V3是对MnasNet的改进,MnasNet是对NasNet的继承)
本文搜索出两个网络架构:MobileNetV3-Large 和MobileNetV3-Small;
应用于图像分类、目标检测和语义分割任务,均取得好成绩;
1 简介
本文的目标是开发最好的移动端计算机视觉架构,以优化移动设备上的精度和延迟。为了实现这一目标,本文引入了:
- (1)互补搜索技术(complementary search techniques),详情见第4节;
- (2)非线性激活函数,详情见5.2节;
- (3)新型高效网络设计,详情见5.1、5.3节;
- (4)新型高效分割解码器(segmentation decoder),详情见6.4节;
2 相关工作
轻量化模型方面的工作:
- SqueezeNet;
- MobileNetV1;
- MobileNetV2;
- ShuffleNet;
- CondenseNet;
- ShiftNet;
网络架构搜索方面的工作;
3 Efficient Mobile Building Blocks
【1】MobileNet V1引入深度可分离卷积;
【2】MobileNet V2引入线性瓶颈和反向残差结构;

【3】MnasNet在MobileNetV2结构的基础上,在瓶颈结构中引入了SE注意模块;
【4】MobileNet V3结合以上所有,贡献如下:
- 继承V1的深度可分离卷积;
- 继承V2的线性瓶颈和逆残差结构;
- 继承MnasNet的基于SE块的注意力模型;
- (1) 扩展层使用的滤波器数量不同,详情见4.2节;
- (2) 瓶颈层输出的通道数量不同,详情见4.节;
- (3) 重新设计了耗时间的层,详情见5.1节;
- (4) 用h-wish代替ReLU6,详情见5.2节;
- (5) SE模块将通道数压缩为原来的1/4,详情见5.3节;
- (6) 对于SE模块,不再使用sigmoid,而是采用h-sigmoid作为近似,详情见5.2节;

4 Network Search
网络搜索是一个寻找和优化网络架构的强大工具;
MobileNet V3 使用真实平台感知的NAS来搜索全局网络结构,然后使用NetAdapt算法来搜索每一层的卷积核数量;
(翻译一下:NAS进行全局架构搜索,NetAdapt进行局部搜索);
这些技术是互补的,可以结合起来更有效的为给定的硬件平台找到最优模型;
4.1 Platform-Aware NAS for Block-wise Search
标题:
Platform-Aware:用真实移动端平台来衡量效果(准确性、延迟); NAS:Neural Architecture Search
神经网络搜索(不用人力来设计网络 用AI来搜索AI 炼丹 烧钱的魔法); Block-wise
Search:搜索的内容是模块(block);
用相同的MnasNet-A作为最初的大型移动模型,然后在其之上应用NetAdapt和其他优化方法进行优化;
(不同点:使用 w = − 0.15 w = -0.15 w=−0.15代替原文的 w = − 0.07 w = -0.07 w=−0.07);
4.2 NetAdapt for Layer-wise Search
标题:
NetAdapt:用于对各个模块确定之后网络层的微调;
Layer-wise Search:调整的内容是每层的核数量;
NetAdapt技术:
- 1.platform-aware NAS找到的种子网络体系结构开始;
- 2.对于每一步:
- (a) 生成一组新的建议(proposals),每一个建议都表示对架构的修改方法,与上一步相比,至少减少δ个延迟;
- (b) 对于每个建议,使用上一步预训练的模型来填充新的架构,适当的阶段并随机初始化缺失的权重;对 T T T步的每个建议进行微调,得到精度的粗略估计;
- (c ) 根据一些指标来选择最佳方案;
- 3.迭代第2步,直到达到目标延迟;
NetAdapt原文中,度量是使精度变化最小化;
本文:使延迟变化与准确度变化之比最小化;
重复上述过程直到延迟达到预定的目标,然后从头训练新的架构;
两种生成建议(proposals)的方案:
- 减小任意扩展层(expansion layer)的滤波器数量;
- 减少共享相同瓶颈大小的所有块中的瓶颈来保持逆残差连接;
本文实验中采用 T = 10 , 000 , δ = 0.01 ∣ L ∣ T = 10,000,δ = 0.01|L| T=10,000,δ=0.01∣L∣,其中L是延迟;
5 Network Improvements
除了网络搜索,本文还在模型中引进几个新的组件来进一步完善模型;
- 重新设计耗时层-5.1;
- 引入h-swish-5.2;
- SE模块的改变-5.3;
5.1 Redesigning Expensive Layers
重新设计了耗时间的层,将最后一步的平均池化层前移并移除最后一个卷积层;

修改后减少了约11%的延迟,精度几乎没有变化;
5.2 Nonlinearities
nonlinearity定义:
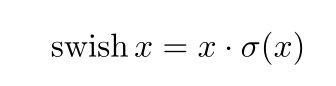
swish可以有效的提升网络的精度,但是sigmoid函数 σ ( x ) σ(x) σ(x)计算量非常大,本文提出了h-swish来解决计算量大的问题:
- 用 R e L U 6 ( x + 3 ) 6 \frac {ReLU6(x+3)} {6} 6ReLU6(x+3)替sigmoid,h-swish代替swish:


动机:效果差不多,但是计算量减少了,降低了延迟;
h-swish代码:
class hswish(nn.Module):
def forward(self, x):
out = x * F.relu6(x + 3, inplace=True) / 6
return out
h-sigmoid代码:
class hsigmoid(nn.Module):
def forward(self, x):
out = F.relu6(x + 3, inplace=True) / 6
return out
- 非线性的代价随着网络的深入而降低(因为每一层激活内存通常在分辨率下降时减半)。在本文的架构中,我们只在模型的后半部分使用h-swish。
表1和表2展示了MobileNet V3的具体的架构;

MobileNetV3-Large代码(pytorch):
class MobileNetV3_Large(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_classes=1000):
super(MobileNetV3_Large, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, 16, kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1, bias=False)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(16)
self.hs1 = hswish()
self.bneck = nn.Sequential(
Block(3, 16, 16, 16, nn.ReLU(inplace=True), None, 1),
Block(3, 16, 64, 24, nn.ReLU(inplace=True), None, 2),
Block(3, 24, 72, 24, nn.ReLU(inplace=True), None, 1),
Block(5, 24, 72, 40, nn.ReLU(inplace=True), SeModule(40), 2),
Block(5, 40, 120, 40, nn.ReLU(inplace=True), SeModule(40), 1),
Block(5, 40, 120, 40, nn.ReLU(inplace=True), SeModule(40), 1),
Block(3, 40, 240, 80, hswish(), None, 2),
Block(3, 80, 200, 80, hswish(), None, 1),
Block(3, 80, 184, 80, hswish(), None, 1),
Block(3, 80, 184, 80, hswish(), None, 1),
Block(3, 80, 480, 112, hswish(), SeModule(112), 1),
Block(3, 112, 672, 112, hswish(), SeModule(112), 1),
Block(5, 112, 672, 160, hswish(), SeModule(160), 1),
Block(5, 160, 672, 160, hswish(), SeModule(160), 2),
Block(5, 160, 960, 160, hswish(), SeModule(160), 1),
)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(160, 960, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=False)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(960)
self.hs2 = hswish()
self.linear3 = nn.Linear(960, 1280)
self.bn3 = nn.BatchNorm1d(1280)
self.hs3 = hswish()
self.linear4 = nn.Linear(1280, num_classes)
self.init_params()
def forward(self, x):
# 表1第一行
out = self.hs1(self.bn1(self.conv1(x)))
# 表1中所有的bneck
out = self.bneck(out)
# 表1倒数第4行
out = self.hs2(self.bn2(self.conv2(out)))
out = F.avg_pool2d(out, 7)
# flatten
out = out.view(out.size(0), -1)
out = self.hs3(self.bn3(self.linear3(out)))
out = self.linear4(out)
return out

MobileNetV3-Small代码实现:
class MobileNetV3_Small(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_classes=1000):
super(MobileNetV3_Small, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, 16, kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1, bias=False)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(16)
self.hs1 = hswish()
self.bneck = nn.Sequential(
Block(3, 16, 16, 16, nn.ReLU(inplace=True), SeModule(16), 2),
Block(3, 16, 72, 24, nn.ReLU(inplace=True), None, 2),
Block(3, 24, 88, 24, nn.ReLU(inplace=True), None, 1),
Block(5, 24, 96, 40, hswish(), SeModule(40), 2),
Block(5, 40, 240, 40, hswish(), SeModule(40), 1),
Block(5, 40, 240, 40, hswish(), SeModule(40), 1),
Block(5, 40, 120, 48, hswish(), SeModule(48), 1),
Block(5, 48, 144, 48, hswish(), SeModule(48), 1),
Block(5, 48, 288, 96, hswish(), SeModule(96), 2),
Block(5, 96, 576, 96, hswish(), SeModule(96), 1),
Block(5, 96, 576, 96, hswish(), SeModule(96), 1),
)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(96, 576, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=False)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(576)
self.hs2 = hswish()
self.linear3 = nn.Linear(576, 1280)
self.bn3 = nn.BatchNorm1d(1280)
self.hs3 = hswish()
self.linear4 = nn.Linear(1280, num_classes)
self.init_params()
def init_params(self):
for m in self.modules():
if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, mode='fan_out')
if m.bias is not None:
init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
elif isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d):
init.constant_(m.weight, 1)
init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
elif isinstance(m, nn.Linear):
init.normal_(m.weight, std=0.001)
if m.bias is not None:
init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
def forward(self, x):
out = self.hs1(self.bn1(self.conv1(x)))
out = self.bneck(out)
out = self.hs2(self.bn2(self.conv2(out)))
out = F.avg_pool2d(out, 7)
out = out.view(out.size(0), -1)
out = self.hs3(self.bn3(self.linear3(out)))
out = self.linear4(out)
return out
5.3 Large squeeze-and-excite
在MnasNet中,SE比率为0或1/4。相反,本文将它们全部替换为扩展层中通道数量的1/4;
发现这样做增加了精度,并且没有明显的延迟成本;
SE模块代码:
class SeModule(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_size, reduction=4):
super(SeModule, self).__init__()
self.se = nn.Sequential(
nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1),
nn.Conv2d(in_size, in_size // reduction, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(in_size // reduction),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(in_size // reduction, in_size, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(in_size),
hsigmoid()
)
def forward(self, x):
return x * self.se(x)
6 实验

代码补充,深度可分离卷积块代码:
class Block(nn.Module):
'''expand + depthwise + pointwise'''
def __init__(self, kernel_size, in_size, expand_size, out_size, nolinear, semodule, stride):
super(Block, self).__init__()
self.stride = stride
self.se = semodule
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_size, expand_size, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=False)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(expand_size)
self.nolinear1 = nolinear
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(expand_size, expand_size, kernel_size=kernel_size, stride=stride, padding=kernel_size//2, groups=expand_size, bias=False)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(expand_size)
self.nolinear2 = nolinear
self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(expand_size, out_size, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=False)
self.bn3 = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_size)
self.shortcut = nn.Sequential()
if stride == 1 and in_size != out_size:
self.shortcut = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_size, out_size, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(out_size),
)
def forward(self, x):
out = self.nolinear1(self.bn1(self.conv1(x)))
out = self.nolinear2(self.bn2(self.conv2(out)))
out = self.bn3(self.conv3(out))
if self.se != None:
out = self.se(out)
out = out + self.shortcut(x) if self.stride==1 else out
return out