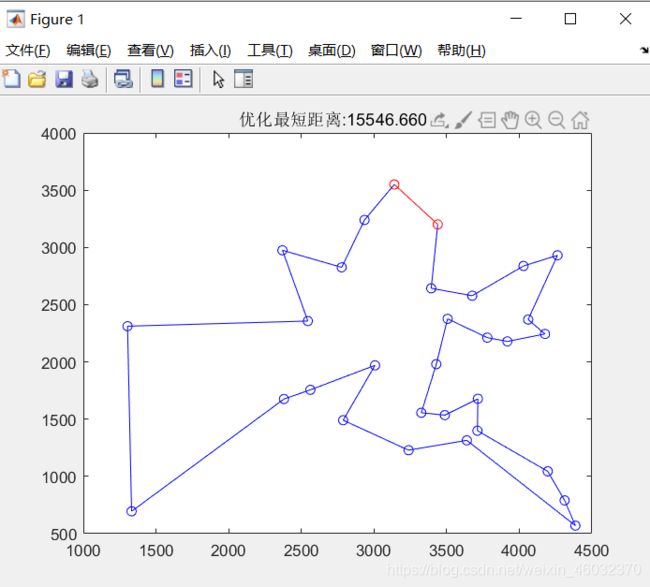
- 2024国赛数学建模-模拟火算法(MATLAB 实现)
V建模忠哥V
2024国赛数学建模算法matlab
模拟退火算法1.1算法原理模拟退火算法的基本思想是从一给定解开始,从邻域中随机产生另一个解,接受Metropolis准则允许目标函数在有限范围内变坏,它由一控制参数t决定,其作用类似于物理过程中的温度T,对于控制参数的每一取值,算法持续进行“产生—判断—接受或舍去”的迭代过程,对应着固体在某一恒定温度下的趋于热平衡的过程,当控制参数逐渐减小并趋于0时,系统越来越趋于平衡态,最后系统状态对应于优化问
- 数学建模强化宝典(7)模拟退火算法
IT 青年
建模强化栈数学建模模拟退火算法编程
前言模拟退火算法(SimulatedAnnealing,SA)是一种基于概率的全局优化算法,它模拟了固体退火过程中的物理现象,通过随机搜索和概率接受机制来寻找问题的全局最优解。以下是对模拟退火算法的详细解析:一、算法起源与背景起源:模拟退火算法的思想最早由N.Metropolis等人在1953年提出,用于研究粒子在金属中的退火过程。1983年,S.Kirkpatrick等人成功地将这一思想引入到组
- 单例模式(Singleton Pattern)
collman
单例模式
概念单例模式(SingletonPattern)是Java中最简单的设计模式之一。这种类型的设计模式属于创建型模式,它提供了一种创建对象的最佳方式。这种模式涉及到一个单一的类,该类负责创建自己的对象,同时确保只有单个对象被创建。这个类提供了一种访问其唯一的对象的方式,可以直接访问,不需要实例化该类的对象。简单实例SingleObject.javapublicclassSingleObject{
- Qt Phonon多媒体框架详解及简单实例分享
dvlinker
C/C++实战专栏qtPhonon多媒体框架
目录1、Phonon简介2、Phonon基本类2.1、VideoPlayer类2.2、MediaObject类2.3、Phonon::createPath()2.4、AudioOutput类2.5、VideoWidgetClass2.6、SeekSlider类2.7、VolumeSlider类3、Phonon完整使用实例4、总结C++软件异常排查从入门到精通系列教程(专栏文章列表,欢迎订阅,持续更
- matlab模拟退火算法
孺子牛 for world
matlab模拟退火算法开发语言
在MATLAB中实现退火算法(也称为模拟退火算法,SimulatedAnnealing,SA)通常涉及几个关键步骤:初始化系统状态、定义能量函数(或成本函数)、模拟退火过程(包括温度下降和状态转移)、以及判断是否达到停止条件。function[best_state,best_energy]=simulatedAnnealing(initial_state,energyFunction,parame
- matlab实现模拟退火算法
孺子牛 for world
matlab模拟退火算法算法
模拟退火算法(SimulatedAnnealing,SA)是一种通用概率优化算法,用于在给定的大搜索空间内寻找问题的近似全局最优解。该算法灵感来源于物理学中固体物质的退火过程,其中温度逐渐降低,粒子逐渐趋于能量最低状态。在MATLAB中实现模拟退火算法,我们首先需要定义目标函数(即我们需要最小化的能量或成本函数),然后设定算法的参数,如初始温度、降温速率、内循环次数(每个温度下的迭代次数)等。以下
- 退火模拟算法c语言程序,模拟退火算法实例(c++ 与 c# 实现)
weixin_39799825
退火模拟算法c语言程序
此片文章主要参考CSDN博主里头的一篇文章,将自己的理解写下来,以方便后期的查阅。一、C++实现1.已知平面上若干点坐标(xi,yi),求平面上一点p(x,y),到这些点的总距离最小。思路:取所有点的均值为目标点。计算全部点与目标点求差值的和,将目标点以一定系数朝着总和的方向移动,得到新的目标点。//求最小距离//限制条件:10.02)//0.02为温度的下限,若温度为temp达到下限,则停止搜索
- 定期存款利率下调
一莲听雨
近日,喜欢闲聊的中老年人聊得热闹的话题是:现在存钱存定期的利率怎么那么低?确有此事!近来多地多家银行定期存款利率纷纷下调,且调整幅度为10个基点,也就是千分之一,还对部分定期存款利率上限进行了小幅调整。举个简单实例来说,我们把1万元定期存银行两年,利息要少20元。这个消息对部分中老年人来说,无疑是不好的消息,因为他们已经习惯了有钱就存银行,就是所谓的“手中有粮,心中不慌”那些从苦日子过来的人,手里
- uni-app介绍基本框架信息及简单实例
2201_75957608
uni-app案例uni-appvue.js前端
Uni-app是一种基于Vue.js的跨平台开发框架,由DCloud公司开发和维护。它允许开发者使用一套代码同时构建多个平台的应用程序,包括iOS、Android、H5、微信小程序、支付宝小程序、百度小程序、字节跳动小程序等。Uni-app的核心思想是“写一次,到处运行”。开发者只需编写一次代码,就可以生成在不同平台上运行的应用程序。这样的开发方式极大地提高了开发效率,减少了开发成本。Uni-ap
- 模拟退火算法
aaa8db431342
学号:17020150083姓名:许学同原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_40562999/article/details/80853354【嵌牛导读】著名的模拟退火算法,它是一种基于蒙特卡洛思想设计的近似求解最优化问题的方法。【嵌牛鼻子】模拟退火算法【嵌牛正文】一点历史——如果你不感兴趣,可以跳过美国物理学家N.Metropolis和同仁在1953年发表研究复杂
- 模拟退火算法(Simulated Annealing, SA)
想做后端的前端
人工智能模拟退火算法算法机器学习
一、简介模拟退火算法来源于固体退火原理,是一种基于概率的算法。将固体加温至充分高的温度,再让其徐徐冷却,加温时,固体内部粒子随温升变为无序状,内能增大,分子和原子越不稳定。而徐徐冷却时粒子渐趋有序,能量减少,原子越稳定。在冷却(降温)过程中,固体在每个温度都达到平衡态,最后在常温时达到基态,内能减为最小。模拟退火算法从某一较高初温出发,伴随温度参数的不断下降,结合概率突跳特性在解空间中随机寻找目标
- Qt QJson 使用
火山上的企鹅
QT数据结构qt开发语言QtJson
文章目录1.简介2.简单实例3.结果1.简介QJson是一个用于Qt应用程序的JSON解析和生成库。JSON(JavaScriptObjectNotation)是一种轻量级的数据交换格式,具有良好的可读性和可扩展性,常用于Web应用程序中。QJson将JSON数据解析为QJsonDocument对象,同时可以将QJsonDocument对象转换为JSON数据。♦常用的QJson类包括:QJsonD
- Sping Cloud Hystrix
花开不合阳春暮
#分布式
SpringCloudHystrix防雪崩利器基于Netflix对应的Hystrix具备的功能:1.服务降级2.依赖隔离3.服务熔断4.监控(HystrixDashboard)服务降级优先核心服务,非核心服务不可用或弱可用通过HystrixCommand注解指定fallbackMethod(回退函数)中具体实现降级逻辑使用RestTemplate的简单实例:1.引入依赖org.springfram
- NX/UG二次开发—其他—矩形套料(排料)简介
恩·艾克斯·红
NX二次开发矩形套料
算法逻辑排料方法+一定时间内获取近似解的算法看了一些论文和博客,一般排料方法采用最低水平线算法排料,再此基础上增加空余区域填充。然后配合遗传学算法||模拟退火算法||蚁群算法||免疫算法等,在一定时间内求得一组最优解。在最简单的水平线算法排料,采用最简单的变异和交叉,结果如下,伴随调整变异和交叉,明显可以提升速度和材料利用率。接下来准备添加空余区域填充,看一下效果。
- 探索PostgreSQL:从基础到实践(简单实例)
Java000I
postgresql数据库
提示:文章写完后,目录可以自动生成,如何生成可参考右边的帮助文档文章目录下载前言一、PostgreSQL是什么?二、使用步骤1.引入库2.读入数据总结下载点击下载提取码888999前言在当今的大数据时代,数据库作为信息的核心存储和管理工具,扮演着举足轻重的角色。在众多数据库管理系统中,PostgreSQL(常简称为PG)以其强大的功能、稳定性和开源的特性,赢得了开发者和数据管理员的青睐。本文旨在为
- c语言怎么取字符串首字母,C语言 字符串首字母转换成大写简单实例
茨小木
c语言怎么取字符串首字母
C语言字符串首字母转换成大写简单实例C语言字符串首字母转换成大写简单实例举例:输入:thisisabook返回:ThisIsABook#include#include#includeintmain(){charinput[]="thisisabook";charoutput[256]={'\0'};inti,len;len=strlen(input);printf("变换前的字符串为:%s\n",
- 用Python实现MD5加密
Lyx-0607
笔记
用Python实现MD5加密用Python实现MD5加密时用到的是hashlib模块,可以通过hashlib标准库使用多种Hash算法,如SHA1、SHA224、SHA256、SHA384、SHA512和MD5算法等。下面是通过调用hashlib模块对字符串进行MD5加密的简单实例:fromhashlibimportmd5defencrypt_md5(s):new_md5=md5()#创建md5对
- 【优化求解】基于模拟退火算法求解通信网频率规划问题matlab代码
matlab科研助手
1简介本文提出一种基于模拟退火算法的无线通信频率规划方法,将目标要布网的覆盖区域划分为若干个小区,划分后的每个小区设置一个对应的发射基站,而每个基站装载一个广播主信道(BCCH信道),根据无线网络设计规划的要求,可以局部或者整体的选择频率复用模式;利用退火算法算法中各种不同设定约束条件来组合设定目标函数f支配方案,并用干扰综合总值E可用于评估频率指配方案的优劣,最终得出最优的频率支配方案,将其指向
- Java动态修改用户Session实战-简单实例准备
java1234_小锋
javajava前端开发语言修改SesssionSession
锋哥原创的Java动态修改用户Session实战:Java动态修改用户Session实战课程_哔哩哔哩_bilibiliJava动态修改用户Session实战课程,管理员可以修改任意一个用户的session信息作者:java1234_小锋站点:www.java1234.vip喜欢的朋友点赞+关注B站支持下哈!,视频播放量839、弹幕量1、点赞数17、投硬币枚数6、收藏人数16、转发人数1,视频作者
- 机器学习系列 - Mean Shift聚类
学海一叶
机器学习算法聚类机器学习python计算机视觉
文章目录前言一、原理前置知识点MeanShift计算步骤二、应用举例-图像分割三、聚类实战-简单实例bandwidth=1bandwidth=2总结前言MeanShift(均值漂移)是基于密度的非参数聚类算法,其算法思想是假设不同簇类的数据集符合不同的概率密度分布,找到任一样本点密度增大的最快方向(最快方向的含义就是MeanShift),样本密度高的区域对应于该分布的最大值,这些样本点最终会在局部
- 新2019计划:python学习-if语句【3】
克里斯托弗的梦想
if语句在编程时,经常需要检查一系列条件,并据此决定采取什么措施。本篇章,主要了解if语句常见的公式,如:单独if语句,if-else语句,if-elif-else语句,if-elif-elif-……else语句等。另外掌握比较数值的符号、检查是否相等、以及多个条件比较、检查特定值是否在列表中、列表是否为空等判断简单实例,比如cars=['audi','bmw','subaru','toyota'
- python-自动化篇-运维-监控-简单实例-道出如何使⽤Python⾃动化数据库备份?
fo安方
#python-自动化篇-运维运维python自动化
使⽤Python⾃动化数据库备份是⼀种有效的⽅式,可以确保数据库数据的安全性和可恢复性。以下是⼀般步骤,说明如何使⽤Python⾃动化数据库备份:选择数据库备份⼯具:⾸先,选择适合数据库类型的备份⼯具。不同的数据库系统有不同的备份⽅法,以下是⼀些常⻅数据库类型以及相应的备份⼯具:(1)MySQL:使⽤mysqldump⼯具或mysqlbackup⼯具进⾏备份。(2)PostgreSQL:使⽤pg_
- 03_Opencv简单实例演示效果和基本介绍
除不掉的灰色
机器学习Opencvopencv人工智能计算机视觉python
视频处理视频分解图片在后面我们要学习的机器学习中,我们需要大量的图片训练样本,这些图片训练样本如果我们全都使用相机拍照的方式去获取的话,工作量会非常巨大,通常的做法是我们通过录制视频,然后提取视频中的每一帧即可!接下来,我们就来学习如何从视频中获取信息ubuntu下摄像头终端可以安装:sudoapt-getinstallcheese然后输入cheese即可打开摄像头实现步骤:1.加载视频2.获取视
- 模拟退火算法(SA)优化BP神经网络
树洞优码
模拟退火算法神经网络算法
模拟退火算法(SA)优化BP神经网络模拟退火算法(SA)可以用于优化神经网络中的参数,包括神经网络的权重和偏置。在优化BP神经网络中,SA可以帮助找到更好的权重和偏置的组合,以提高神经网络的性能。在BP神经网络中,SA主要用于调整网络的权重和偏置。通过SA算法,可以在权衡探索和利用的过程中,更有效地搜索到神经网络的参数组合,以降低误差、提高分类准确率或者加速网络收敛。优化BP神经网络实验结果如下:
- 【Kotlin】协程
风起云涌~
kotlinjava开发语言
1,概述协程是一个轻量级的线程,将调度从系统线程切换拿到用户态,在一定程度上减少了线程切换开销。2,简单实例导入依赖:dependencies{implementation"org.jetbrains.kotlinx:kotlinx-coroutines-core:1.4.2"implementation"org.jetbrains.kotlinx:kotlinx-coroutines-andro
- 2019-03-28派森学习第129天
每日派森
帮师妹装了一晚上tensorflow,按照自己的前天安装的流程总还会报错,在加上她的电脑特别慢,真无语了!今晚学习一会儿模拟退火算法吧,白天都搜索了,一直没有来的及学习。5种启发式算法:1首先要明白全局最小和全局极小值:2模拟退火算法的基本思想:在每一步都有一定概率接受比当前更差的结果,从而有助于跳出局部极小值,找到全局最小值。算法框图
- 【Android】非线性方程的求解寻根
希希雾里
Java数值计算Androidjava数值计算
目录前言:一、Apache-commons-math3介绍二、具体简单实例2.1导入函数类2.2定义函数接口2.3使用求解器2.3.1布伦特法(Brent)2.3.2米勒(Muller)法2.3.3Newton-Raphson法前言:最近在Androidapp实时显示数据上遇到了个问题,就是获取的数据需要进行转换。这里的转换公式为双指数函数,反函数不好转化出一个式子,需要实现非线性方程的求解寻根。
- python-自动化篇-运维-监控-简单实例-道出如何使⽤Python进⾏系统监控?
fo安方
#python-自动化篇-运维运维python自动化
如何使⽤Python进⾏系统监控?使⽤Python进⾏系统监控涉及以下⼀般步骤:选择监控指标:⾸先,确定希望监控的系统指标,这可以包括CPU利⽤率、内存使⽤情况、磁盘空间、⽹络流量、服务可⽤性等。选择监控⼯具:选择适合需求的监控⼯具或库。⼀些常⻅的选择包括:psutil:⼀个Python库,⽤于获取系统资源利⽤率信息,如CPU、内存、磁盘等。Prometheus:⼀个开源监控系统,⽀持多种语⾔,可
- python-自动化篇-运维-监控-简单实例-道出如何使⽤Python进⾏网络监控?
fo安方
#python-自动化篇-运维运维python自动化
如何使⽤Python进⾏⽹络监控?使⽤Python进⾏⽹络监控可以帮助实时监视⽹络设备、流量和服务的状态,以便及时识别和解决问题。以下是⼀般步骤,说明如何使⽤Python进⾏⽹络监控:选择监控⼯具和库:选择适合⽹络监控需求的⼯具和库。以下是⼀些常⻅的⽹络监控任务以及相应的⼯具和库:(1)Ping和ICMP监控:使⽤Python的ping3或pythonping库来执⾏PING测试并检查主机的可达性
- java异步调用简单实例
我的头发哪去了
javapython开发语言
java异步调用简单实例Java中,异步调用是指在调用一个方法后,不等待方法执行完毕而继续执行其他操作,而是通过回调、Future等方式来获取方法的执行结果。在Java中,有多种实现异步调用的方式,包括多线程、线程池、CompletableFuture等。下面是几种常见的异步调用方法的说明和示例代码。多线程:使用多线程可以实现简单的异步调用,可以通过创建新的线程或使用线程池来实现。示例代码://创
- ASM系列六 利用TreeApi 添加和移除类成员
lijingyao8206
jvm动态代理ASM字节码技术TreeAPI
同生成的做法一样,添加和移除类成员只要去修改fields和methods中的元素即可。这里我们拿一个简单的类做例子,下面这个Task类,我们来移除isNeedRemove方法,并且添加一个int 类型的addedField属性。
package asm.core;
/**
* Created by yunshen.ljy on 2015/6/
- Springmvc-权限设计
bee1314
springWebjsp
万丈高楼平地起。
权限管理对于管理系统而言已经是标配中的标配了吧,对于我等俗人更是不能免俗。同时就目前的项目状况而言,我们还不需要那么高大上的开源的解决方案,如Spring Security,Shiro。小伙伴一致决定我们还是从基本的功能迭代起来吧。
目标:
1.实现权限的管理(CRUD)
2.实现部门管理 (CRUD)
3.实现人员的管理 (CRUD)
4.实现部门和权限
- 算法竞赛入门经典(第二版)第2章习题
CrazyMizzz
c算法
2.4.1 输出技巧
#include <stdio.h>
int
main()
{
int i, n;
scanf("%d", &n);
for (i = 1; i <= n; i++)
printf("%d\n", i);
return 0;
}
习题2-2 水仙花数(daffodil
- struts2中jsp自动跳转到Action
麦田的设计者
jspwebxmlstruts2自动跳转
1、在struts2的开发中,经常需要用户点击网页后就直接跳转到一个Action,执行Action里面的方法,利用mvc分层思想执行相应操作在界面上得到动态数据。毕竟用户不可能在地址栏里输入一个Action(不是专业人士)
2、<jsp:forward page="xxx.action" /> ,这个标签可以实现跳转,page的路径是相对地址,不同与jsp和j
- php 操作webservice实例
IT独行者
PHPwebservice
首先大家要简单了解了何谓webservice,接下来就做两个非常简单的例子,webservice还是逃不开server端与client端。我测试的环境为:apache2.2.11 php5.2.10做这个测试之前,要确认你的php配置文件中已经将soap扩展打开,即extension=php_soap.dll;
OK 现在我们来体验webservice
//server端 serve
- Windows下使用Vagrant安装linux系统
_wy_
windowsvagrant
准备工作:
下载安装 VirtualBox :https://www.virtualbox.org/
下载安装 Vagrant :http://www.vagrantup.com/
下载需要使用的 box :
官方提供的范例:http://files.vagrantup.com/precise32.box
还可以在 http://www.vagrantbox.es/
- 更改linux的文件拥有者及用户组(chown和chgrp)
无量
clinuxchgrpchown
本文(转)
http://blog.163.com/yanenshun@126/blog/static/128388169201203011157308/
http://ydlmlh.iteye.com/blog/1435157
一、基本使用:
使用chown命令可以修改文件或目录所属的用户:
命令
- linux下抓包工具
矮蛋蛋
linux
原文地址:
http://blog.chinaunix.net/uid-23670869-id-2610683.html
tcpdump -nn -vv -X udp port 8888
上面命令是抓取udp包、端口为8888
netstat -tln 命令是用来查看linux的端口使用情况
13 . 列出所有的网络连接
lsof -i
14. 列出所有tcp 网络连接信息
l
- 我觉得mybatis是垃圾!:“每一个用mybatis的男纸,你伤不起”
alafqq
mybatis
最近看了
每一个用mybatis的男纸,你伤不起
原文地址 :http://www.iteye.com/topic/1073938
发表一下个人看法。欢迎大神拍砖;
个人一直使用的是Ibatis框架,公司对其进行过小小的改良;
最近换了公司,要使用新的框架。听说mybatis不错;就对其进行了部分的研究;
发现多了一个mapper层;个人感觉就是个dao;
- 解决java数据交换之谜
百合不是茶
数据交换
交换两个数字的方法有以下三种 ,其中第一种最常用
/*
输出最小的一个数
*/
public class jiaohuan1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a =4;
int b = 3;
if(a<b){
// 第一种交换方式
int tmep =
- 渐变显示
bijian1013
JavaScript
<style type="text/css">
#wxf {
FILTER: progid:DXImageTransform.Microsoft.Gradient(GradientType=0, StartColorStr=#ffffff, EndColorStr=#97FF98);
height: 25px;
}
</style>
- 探索JUnit4扩展:断言语法assertThat
bijian1013
java单元测试assertThat
一.概述
JUnit 设计的目的就是有效地抓住编程人员写代码的意图,然后快速检查他们的代码是否与他们的意图相匹配。 JUnit 发展至今,版本不停的翻新,但是所有版本都一致致力于解决一个问题,那就是如何发现编程人员的代码意图,并且如何使得编程人员更加容易地表达他们的代码意图。JUnit 4.4 也是为了如何能够
- 【Gson三】Gson解析{"data":{"IM":["MSN","QQ","Gtalk"]}}
bit1129
gson
如何把如下简单的JSON字符串反序列化为Java的POJO对象?
{"data":{"IM":["MSN","QQ","Gtalk"]}}
下面的POJO类Model无法完成正确的解析:
import com.google.gson.Gson;
- 【Kafka九】Kafka High Level API vs. Low Level API
bit1129
kafka
1. Kafka提供了两种Consumer API
High Level Consumer API
Low Level Consumer API(Kafka诡异的称之为Simple Consumer API,实际上非常复杂)
在选用哪种Consumer API时,首先要弄清楚这两种API的工作原理,能做什么不能做什么,能做的话怎么做的以及用的时候,有哪些可能的问题
- 在nginx中集成lua脚本:添加自定义Http头,封IP等
ronin47
nginx lua
Lua是一个可以嵌入到Nginx配置文件中的动态脚本语言,从而可以在Nginx请求处理的任何阶段执行各种Lua代码。刚开始我们只是用Lua 把请求路由到后端服务器,但是它对我们架构的作用超出了我们的预期。下面就讲讲我们所做的工作。 强制搜索引擎只索引mixlr.com
Google把子域名当作完全独立的网站,我们不希望爬虫抓取子域名的页面,降低我们的Page rank。
location /{
- java-归并排序
bylijinnan
java
import java.util.Arrays;
public class MergeSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a={20,1,3,8,5,9,4,25};
mergeSort(a,0,a.length-1);
System.out.println(Arrays.to
- Netty源码学习-CompositeChannelBuffer
bylijinnan
javanetty
CompositeChannelBuffer体现了Netty的“Transparent Zero Copy”
查看API(
http://docs.jboss.org/netty/3.2/api/org/jboss/netty/buffer/package-summary.html#package_description)
可以看到,所谓“Transparent Zero Copy”是通
- Android中给Activity添加返回键
hotsunshine
Activity
// this need android:minSdkVersion="11"
getActionBar().setDisplayHomeAsUpEnabled(true);
@Override
public boolean onOptionsItemSelected(MenuItem item) {
- 静态页面传参
ctrain
静态
$(document).ready(function () {
var request = {
QueryString :
function (val) {
var uri = window.location.search;
var re = new RegExp("" + val + "=([^&?]*)", &
- Windows中查找某个目录下的所有文件中包含某个字符串的命令
daizj
windows查找某个目录下的所有文件包含某个字符串
findstr可以完成这个工作。
[html]
view plain
copy
>findstr /s /i "string" *.*
上面的命令表示,当前目录以及当前目录的所有子目录下的所有文件中查找"string&qu
- 改善程序代码质量的一些技巧
dcj3sjt126com
编程PHP重构
有很多理由都能说明为什么我们应该写出清晰、可读性好的程序。最重要的一点,程序你只写一次,但以后会无数次的阅读。当你第二天回头来看你的代码 时,你就要开始阅读它了。当你把代码拿给其他人看时,他必须阅读你的代码。因此,在编写时多花一点时间,你会在阅读它时节省大量的时间。让我们看一些基本的编程技巧: 尽量保持方法简短 尽管很多人都遵
- SharedPreferences对数据的存储
dcj3sjt126com
SharedPreferences简介: &nbs
- linux复习笔记之bash shell (2) bash基础
eksliang
bashbash shell
转载请出自出处:
http://eksliang.iteye.com/blog/2104329
1.影响显示结果的语系变量(locale)
1.1locale这个命令就是查看当前系统支持多少种语系,命令使用如下:
[root@localhost shell]# locale
LANG=en_US.UTF-8
LC_CTYPE="en_US.UTF-8"
- Android零碎知识总结
gqdy365
android
1、CopyOnWriteArrayList add(E) 和remove(int index)都是对新的数组进行修改和新增。所以在多线程操作时不会出现java.util.ConcurrentModificationException错误。
所以最后得出结论:CopyOnWriteArrayList适合使用在读操作远远大于写操作的场景里,比如缓存。发生修改时候做copy,新老版本分离,保证读的高
- HoverTree.Model.ArticleSelect类的作用
hvt
Web.netC#hovertreeasp.net
ArticleSelect类在命名空间HoverTree.Model中可以认为是文章查询条件类,用于存放查询文章时的条件,例如HvtId就是文章的id。HvtIsShow就是文章的显示属性,当为-1是,该条件不产生作用,当为0时,查询不公开显示的文章,当为1时查询公开显示的文章。HvtIsHome则为是否在首页显示。HoverTree系统源码完全开放,开发环境为Visual Studio 2013
- PHP 判断是否使用代理 PHP Proxy Detector
天梯梦
proxy
1. php 类
I found this class looking for something else actually but I remembered I needed some while ago something similar and I never found one. I'm sure it will help a lot of developers who try to
- apache的math库中的回归——regression(翻译)
lvdccyb
Mathapache
这个Math库,虽然不向weka那样专业的ML库,但是用户友好,易用。
多元线性回归,协方差和相关性(皮尔逊和斯皮尔曼),分布测试(假设检验,t,卡方,G),统计。
数学库中还包含,Cholesky,LU,SVD,QR,特征根分解,真不错。
基本覆盖了:线代,统计,矩阵,
最优化理论
曲线拟合
常微分方程
遗传算法(GA),
还有3维的运算。。。
- 基础数据结构和算法十三:Undirected Graphs (2)
sunwinner
Algorithm
Design pattern for graph processing.
Since we consider a large number of graph-processing algorithms, our initial design goal is to decouple our implementations from the graph representation
- 云计算平台最重要的五项技术
sumapp
云计算云平台智城云
云计算平台最重要的五项技术
1、云服务器
云服务器提供简单高效,处理能力可弹性伸缩的计算服务,支持国内领先的云计算技术和大规模分布存储技术,使您的系统更稳定、数据更安全、传输更快速、部署更灵活。
特性
机型丰富
通过高性能服务器虚拟化为云服务器,提供丰富配置类型虚拟机,极大简化数据存储、数据库搭建、web服务器搭建等工作;
仅需要几分钟,根据CP
- 《京东技术解密》有奖试读获奖名单公布
ITeye管理员
活动
ITeye携手博文视点举办的12月技术图书有奖试读活动已圆满结束,非常感谢广大用户对本次活动的关注与参与。
12月试读活动回顾:
http://webmaster.iteye.com/blog/2164754
本次技术图书试读活动获奖名单及相应作品如下:
一等奖(两名)
Microhardest:http://microhardest.ite