处理在多标签分类任务中数据不平衡问题——多标签合成少数类过采样技术(Multi label Synthetic Minority Over-sampling Technique,MLSMOTE)
Multi label Synthetic Minority Over-sampling Technique,MLSMOTE
- SMOTE
- MLSMOTE
-
- 少数实例选择Minority Instance Selection:
- 特征向量生成Feature Vector Generation:
- 标签集合生成Label Set Generation:
- MLSMOTE代码(Python)
在处理分类问题时,类别失衡是我们经常遇到的问题,也是经常出现在实际使用场景中的问题。类别失衡会给预测任务带来挑战,并且会导致少数类别的预测效果较差因为大部分机器学习算法的假设场景是类别(数据)平衡的前提。
本文原始链接 MLSMOTE
分类是一种有监督学习技术,是将目标数据分类至提前已经定义好的类别中。大多数有监督学习方法,基于一种正式的设定,其数据对象用特征向量的形式表示,每一个对象唯一对应于一组不相交的类标签(目标)。主要有以下四大类:
- 二分类Binary Classification:在二分类问题中,一个实例对应于一个或者另一个标签。如一个人对应于男生或者女生;
- 多分类问题Mutil-class Classification:在多分类问题中,目标变量包含两个以上不同的值,比如一个人年龄按照区间可以分为儿童、青年、中年、老年等;
- 多标签分类Mutil-label Classification:在多标签分类任务中,目标变量有多个维度,每个维度都是二分类的,即只包含两个不同的值。如,电影类型分类,如果是一个单一的电影可以分为喜剧和戏剧。
- 多维分类:是对多类分类Mutil-class的扩展,目标变量的每个维度都是非二元的non-binary。
SMOTE
在一些分类情况下,与一个类相关联的实例数量远远少于另一个类,这导致了数据不平衡的问题,它极大地影响了我们的机器学习算法的性能。在多标签分类的情况下,标签分布不均匀也会出现这个问题。为了克服数据不平衡的问题,我们使用了各种方法和技术,数据扩充就是其中之一。在本文中,我们讨论了一种常用的不平衡多标签数据扩充方法,即多标签合成方法(Multi label Synthetic Minority Over-sampling Technique,MLSMOTE)。
MLSMOTE是多标签分类中最流行、最有效的数据增强技术之一。顾名思义,它是SMOTE(合成少数过采样技术Synthetic Minority Over-sampling Technique)的扩展或变体。如果你正在阅读这篇文章,我假设你已经熟悉了SMOTE,下面仍然给出一个简短的介绍:
- 选择数据进行过抽样(带有少数类标签的一般数据);
- 选择数据的一个实例;
- 求这个数据点的k个最近邻;
- 随机选择一个与所选数据点相邻k的数据点,在连接这两个数据点的直线上任意位置做一个合成数据点;
- 重复这个过程直到数据平衡。
更多关于SMOTE的细节可以参考这两篇文章:
SMOTE: Synthetic Minority Over-sampling Technique
SMOTE and ADASYN (Handling Imbalanced Data Set)
MLSMOTE
与在SMOTE中一样,我们提供数据并对其进行扩充,以生成选择参考点的同一类的更多样本,但在Multi-label设置中,它失败了,因为数据的每个实例都与各种标签相关联。所以有可能一个包含少数标签的样本也可能包含另一个包含多数标签的样本所以我们也必须为合成数据生成标签。在多标签设置中,我们把大多数标签称为头标签,把少数标签称为尾标签。可以对MLSMOTE中涉及的步骤进行分区。
- 选择要扩充的数据。在多标签数据中更有可能有多个标签是尾标签,因此应该建立适当的标准来选择那些被认为是少数的标签;
- 一旦为所有的尾标签样本选择了数据,我们必须为这些标记数据对应的特征向量生成新的数据;
- 根据与数据相关联的所有标签为新生成的数据生成目标标签。
少数实例选择Minority Instance Selection:
为了生成合成实例,我们需要一些参考点来创建数据,因此在我们应用任何数据增强技术之前,需要选择一个尾标签数据实例。为了选择尾标号,F Charte等给出了两个概念,它们分别为:
- 每个标签的失衡比例Imbalance ratio per label: 它是针对每个标签单独计算的。

其中 ∣ L ∣ |L| ∣L∣和 ∣ N ∣ |N| ∣N∣分别表示标签数和实例数(样本数)。 - 平均失衡率:Mean Imbalance ratio:它被定义为所有标签的IRPL的平均值。
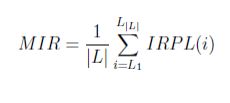
将其IRPL(l) > MIR的每个标签视为尾标签,并将包含该标签的数据的所有实例视为少数实例数据。
特征向量生成Feature Vector Generation:
在这个步骤中,我们知道为什么这个算法被命名为MLSMOTE,因为它使用相同的SMOTE算法为新生成的数据生成特征向量。
标签集合生成Label Set Generation:
在其他多标记数据集尾标记数据的增强技术中,只对特征向量进行增强,对参考数据点的目标变量进行克隆。这种技术完全忽略了关于标签相关性的信息。MLSMOTE提出了三种不同的方法来获得数据的标签相关信息的优势。下面列出了这3种方法:
- 交集Intersection:只有参考数据点和所有相邻数据点上的标签才会在合成数据点上。
- 联合Union:所有在参考数据点或任何相邻数据点中的标签都在合成数据中。
- 排序Ranking:我们计算每个标签出现在参考数据点和相邻数据点的次数,只有这些标签在频率超过考虑实例的一半的合成数据中被考虑。
通过实证研究,证明排序方法是最有效的。
MLSMOTE代码(Python)
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# Importing required Library
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import random
from sklearn.datasets import make_classification
from sklearn.neighbors import NearestNeighbors
def create_dataset(n_sample=1000):
'''
Create a unevenly distributed sample data set multilabel
classification using make_classification function
args
nsample: int, Number of sample to be created
return
X: pandas.DataFrame, feature vector dataframe with 10 features
y: pandas.DataFrame, target vector dataframe with 5 labels
'''
X, y = make_classification(n_classes=5, class_sep=2,
weights=[0.1,0.025, 0.205, 0.008, 0.9], n_informative=3, n_redundant=1, flip_y=0,
n_features=10, n_clusters_per_class=1, n_samples=1000, random_state=10)
y = pd.get_dummies(y, prefix='class')
return pd.DataFrame(X), y
def get_tail_label(df):
"""
Give tail label colums of the given target dataframe
args
df: pandas.DataFrame, target label df whose tail label has to identified
return
tail_label: list, a list containing column name of all the tail label
"""
columns = df.columns
n = len(columns)
irpl = np.zeros(n)
for column in range(n):
irpl[column] = df[columns[column]].value_counts()[1]
irpl = max(irpl)/irpl
mir = np.average(irpl)
tail_label = []
for i in range(n):
if irpl[i] > mir:
tail_label.append(columns[i])
return tail_label
def get_index(df):
"""
give the index of all tail_label rows
args
df: pandas.DataFrame, target label df from which index for tail label has to identified
return
index: list, a list containing index number of all the tail label
"""
tail_labels = get_tail_label(df)
index = set()
for tail_label in tail_labels:
sub_index = set(df[df[tail_label]==1].index)
index = index.union(sub_index)
return list(index)
def get_minority_instace(X, y):
"""
Give minority dataframe containing all the tail labels
args
X: pandas.DataFrame, the feature vector dataframe
y: pandas.DataFrame, the target vector dataframe
return
X_sub: pandas.DataFrame, the feature vector minority dataframe
y_sub: pandas.DataFrame, the target vector minority dataframe
"""
index = get_index(y)
X_sub = X[X.index.isin(index)].reset_index(drop = True)
y_sub = y[y.index.isin(index)].reset_index(drop = True)
return X_sub, y_sub
def nearest_neighbour(X):
"""
Give index of 5 nearest neighbor of all the instance
args
X: np.array, array whose nearest neighbor has to find
return
indices: list of list, index of 5 NN of each element in X
"""
nbs=NearestNeighbors(n_neighbors=5,metric='euclidean',algorithm='kd_tree').fit(X)
euclidean,indices= nbs.kneighbors(X)
return indices
def MLSMOTE(X,y, n_sample):
"""
Give the augmented data using MLSMOTE algorithm
args
X: pandas.DataFrame, input vector DataFrame
y: pandas.DataFrame, feature vector dataframe
n_sample: int, number of newly generated sample
return
new_X: pandas.DataFrame, augmented feature vector data
target: pandas.DataFrame, augmented target vector data
"""
indices2 = nearest_neighbour(X)
n = len(indices2)
new_X = np.zeros((n_sample, X.shape[1]))
target = np.zeros((n_sample, y.shape[1]))
for i in range(n_sample):
reference = random.randint(0,n-1)
neighbour = random.choice(indices2[reference,1:])
all_point = indices2[reference]
nn_df = y[y.index.isin(all_point)]
ser = nn_df.sum(axis = 0, skipna = True)
target[i] = np.array([1 if val>2 else 0 for val in ser])
ratio = random.random()
gap = X.loc[reference,:] - X.loc[neighbour,:]
new_X[i] = np.array(X.loc[reference,:] + ratio * gap)
new_X = pd.DataFrame(new_X, columns=X.columns)
target = pd.DataFrame(target, columns=y.columns)
new_X = pd.concat([X, new_X], axis=0)
target = pd.concat([y, target], axis=0)
return new_X, target
if __name__=='__main__':
"""
main function to use the MLSMOTE
"""
X, y = create_dataset() #Creating a Dataframe
X_sub, y_sub = get_minority_instace(X, y) #Getting minority instance of that datframe
X_res,y_res =MLSMOTE(X_sub, y_sub, 100) #Applying MLSMOTE to augment the dataframe