Linux音频子系统(7) - PCM
- 了解PCM
1.PCM
PCM(Pulse-code modulation)脉冲编码调制,是将模拟信号转化为数字信号的一种方法。声音的转化的过程为,先对连续的模拟信号按照固定频率周期性采样,将采样到的数据按照一定的精度进行量化,量化后的信号和采样后的信号差值叫做量化误差,将量化后的数据进行最后的编码存储,最终模拟信号变化为数字信号。
与音频采样相关的名词:
- Sample : 样本长度. 代表一个声道的音频数据, 大小取决于采样深度, 常见的有8位和16位.
- Channel : 声道数. 常见的有单声道、双声道(立体声)、5.1声道、7.1声道等.
- Frame : 帧, 构成一个完整的声音单元. Frame = Channel * Sample, 例如对于单声道, 它的大小是1Sample, 对于5.1声道, 它的大小是6Sample.
这里帧的概念类似于LCD中的帧, 它是硬件传送的基本单位. 例如I2S每次传输一个完整的帧, 当一帧传输完毕后, 会产生一个硬件中断. - Rate : 采样率, 指采样一帧数据所需的时间. 例如44.1KHz代表采样一帧数据需要1s/44100 = 0.022ms.
- Period : 周期. 当用户空间把音频数据写入RAM后, 底层是用DMA把数据从RAM搬移到I2S的FIFO. DMA每搬移完一段数据后就会产生一次中断,. 我们把DMA搬移这段数据的过程称为一个周期. 这段数据的大小是可以配置的, 因此用户空间可以设置Period的大小, 如果周期设定得较大, 则单次搬移的数据较多, 这意味着单位时间内硬件中断的次数较少, CPU 也就有更多时间处理其他任务, 功耗也更低, 但这样也带来一个显著的弊端——数据处理的时延会增大.
- period_size : 一个周期内的帧数. 它间接决定了周期的大小. 用户空间在设定周期大小时, 给定的参数也是这个帧数.
- period_bytes : 对于DMA硬件来说, 它只关心数据具体有多少字节. period_bytes = period_size * Channels * Sample / 8.
- Buffer : 代表一块RAM, 用户空间与内核通过这块RAM交换数据. DMA也是从这块RAM搬移数据. 一块Buffer内包含多个Period.
- buffer_size : 一块Buffer内帧数, 这块Buffer内包含多个period.
- buffer_bytes : Buffer以字节为单位的大小, 通常在分配RAM时需要该数据. buffer_bytes = buffer_size * Channels * Sample / 8.
PCM两个重要属性:
- 采样率: 单位时间内采样的次数,采样频率越高越高,
- 采样位数: 一个采样信号的位数,也是对采样精度的变现。
人类而言,能接受声音的频率范围是20Hz-20KHz, 所以采样的频率44.1KHz 以及16bit的采样位数就可以有很好的保真能力(CD格式的采样率和采样位数)。
2.PCM中间层
ALSA已经实现了功能强劲的PCM中间层,自己的驱动中只要实现一些底层的需要访问硬件的函数即可。
要访问PCM的中间层代码,首先要包含头文件
每个声卡最多可以包含4个pcm的实例,每个pcm实例对应一个pcm设备文件。pcm实例数量的这种限制源于linux设备号所占用的位大小,如果以后使用64位的设备号,我们将可以创建更多的pcm实例。不过大多数情况下,在嵌入式设备中,一个pcm实例已经足够了。
一个pcm实例由一个playback stream和一个capture stream组成,这两个stream又分别有一个或多个substreams组成。
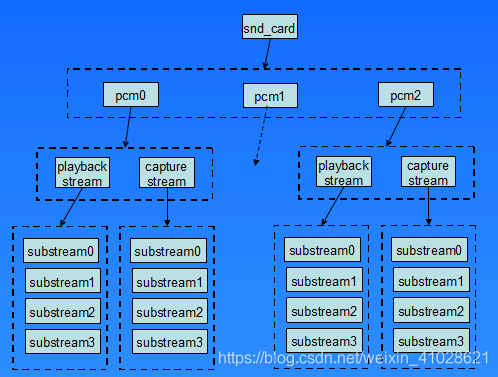
在嵌入式系统中,大多数情况下是一个声卡,一个pcm实例,pcm下面有一个playback和capture stream,playback和capture下面各自有一个substream。
-
一个pcm实例(例如pcm0)是card下的一个逻辑设备, 这个逻辑设备会在用户空间创建两个设备节点.
-
一个pcm实例包含两个stream : playback & capture. 每个stream对应一个设备节点.
-
每个stream下可包含多个substream.
在内核层, 每个substream都有一块自己的Buffer来与用户空间交换音频数据. 从这个角度来看, substream存在的意义貌似是为了分时复用底层的音频硬件.
在用户空间, 每个设备节点可以被open多次, 每次open内核层都会找到一个空闲的substream与之对应, 如果内核层的substream被用完了, 则此次open操作会失败. 这样看来, 用户空间的读、写、控制操作都是针对substream进行的, 这也进一步说明substream可以用来分时复用底层音频硬件.
- snd_pcm是挂在snd_card下面的一个snd_device;
- snd_pcm中的字段:streams[2],该数组中的两个元素指向两个snd_pcm_str结构,分别代表playback stream和capture stream;
- snd_pcm_str中的substream字段,指向snd_pcm_substream结构;
- snd_pcm_substream是pcm中间层的核心,绝大部分任务都是在substream中处理,尤其是他的ops(snd_pcm_ops)字段,许多user空间的应用程序通过alsa-lib对驱动程序的请求都是由该结构中的函数处理。它的runtime字段则指向snd_pcm_runtime结构,snd_pcm_runtime记录这substream的一些重要的软件和硬件运行环境和参数。
3.1.struct snd_pcm (代表一个pcm实例, 也是代表一个pcm逻辑设备)
在ALSA架构下,pcm也被称为设备,所谓的逻辑设备。在linux系统中使用snd_pcm结构表示一个pcm设备。
struct snd_pcm {
struct snd_card *card;
struct list_head list;
int device; /* device number */
unsigned int info_flags;
unsigned short dev_class;
unsigned short dev_subclass;
char id[64];
char name[80];
struct snd_pcm_str streams[2]; //指向它下属的playback stream和capture stream.
struct mutex open_mutex;
wait_queue_head_t open_wait;
void *private_data;
void (*private_free) (struct snd_pcm *pcm);
struct device *dev; /* actual hw device this belongs to */
bool internal; /* pcm is for internal use only */
bool nonatomic; /* whole PCM operations are in non-atomic context */
#if defined(CONFIG_SND_PCM_OSS) || defined(CONFIG_SND_PCM_OSS_MODULE)
struct snd_pcm_oss oss;
#endif
}
3.2.struct snd_pcm_str (代表一个pcm stream)
struct snd_pcm_str {
int stream; /* stream (direction) */
struct snd_pcm *pcm;
/* -- substreams -- */
unsigned int substream_count;
unsigned int substream_opened;
struct snd_pcm_substream *substream;
#if IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_SND_PCM_OSS)
/* -- OSS things -- */
struct snd_pcm_oss_stream oss;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_SND_VERBOSE_PROCFS
struct snd_info_entry *proc_root;
struct snd_info_entry *proc_info_entry;
#ifdef CONFIG_SND_PCM_XRUN_DEBUG
unsigned int xrun_debug; /* 0 = disabled, 1 = verbose, 2 = stacktrace */
struct snd_info_entry *proc_xrun_debug_entry;
#endif
#endif
struct snd_kcontrol *chmap_kctl; /* channel-mapping controls */
struct device dev;
};
- dev : 一个steam对应一个字符设备节点. 这的dev与创建字符设备节点有关.
- substream_count : 该stream下属的substream的个数.
- substream_opened : 有多少个substream已经被用户空间open了. 用户空间可以针对同一个设备节点open多次, 每次open内核层都会选一个空闲的substream与之对应. 如果所有的substream都被opened, 则新的open会失败.
- substream : 用链表的形式串联多个substream.
3.3.struct snd_pcm_file
- 每个被open的substream对应一个snd_pcm_file.
struct snd_pcm_file {
struct snd_pcm_substream *substream;
int no_compat_mmap;
unsigned int user_pversion; /* supported protocol version */
};
3.4.struct snd_pcm_substream
- 代表一个pcm substream. substream的一个重要功能就是要准备一块DMA buffer, 以便与用户空间交换数据.
struct snd_pcm_substream {
struct snd_pcm *pcm;
struct snd_pcm_str *pstr;
void *private_data; /* copied from pcm->private_data */
int number;
char name[32]; /* substream name */
int stream; /* stream (direction) */
struct pm_qos_request latency_pm_qos_req; /* pm_qos request */
size_t buffer_bytes_max; /* limit ring buffer size */
struct snd_dma_buffer dma_buffer;
size_t dma_max;
/* -- hardware operations -- */
const struct snd_pcm_ops *ops;
/* -- runtime information -- */
struct snd_pcm_runtime *runtime;
/* -- timer section -- */
struct snd_timer *timer; /* timer */
unsigned timer_running: 1; /* time is running */
/* -- next substream -- */
struct snd_pcm_substream *next;
/* -- linked substreams -- */
struct list_head link_list; /* linked list member */
struct snd_pcm_group self_group; /* fake group for non linked substream (with substream lock inside) */
struct snd_pcm_group *group; /* pointer to current group */
/* -- assigned files -- */
void *file;
int ref_count;
atomic_t mmap_count;
unsigned int f_flags;
void (*pcm_release)(struct snd_pcm_substream *);
struct pid *pid;
#if IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_SND_PCM_OSS)
/* -- OSS things -- */
struct snd_pcm_oss_substream oss;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_SND_VERBOSE_PROCFS
struct snd_info_entry *proc_root;
struct snd_info_entry *proc_info_entry;
struct snd_info_entry *proc_hw_params_entry;
struct snd_info_entry *proc_sw_params_entry;
struct snd_info_entry *proc_status_entry;
struct snd_info_entry *proc_prealloc_entry;
struct snd_info_entry *proc_prealloc_max_entry;
#ifdef CONFIG_SND_PCM_XRUN_DEBUG
struct snd_info_entry *proc_xrun_injection_entry;
#endif
#endif /* CONFIG_SND_VERBOSE_PROCFS */
/* misc flags */
unsigned int hw_opened: 1;
};
3.5.struct snd_dma_buffer
- 用于描述一块DMA buffer.
struct snd_dma_buffer {
struct snd_dma_device dev; /* device type */
unsigned char *area; /* virtual pointer */
dma_addr_t addr; /* physical address */
size_t bytes; /* buffer size in bytes */
void *private_data; /* private for allocator; don't touch */
};
- area : buffer的虚拟地址, 供CPU访问buffer时使用.
- addr : buffer的物理地址, 供DMA访问buffer时使用.
- bytes : buffer的大小.
3.6.struct snd_pcm_ops
- PCM中间层定义的需要底层驱动实现的接口函数, 相当于interface. 中间层在恰当的时候会回调这些接口函数. 从底层驱动的角度来说, 绝大部分工作就是实现这个ops定义的函数(一般只需实现部分, 其它的中间层都有默认实现. 除非中间层的实现在自己的硬件上用不了, 才需要我们自己实现.), 然后向PCM中间层‘注册’即可.
struct snd_pcm_ops {
int (*open)(struct snd_pcm_substream *substream);
int (*close)(struct snd_pcm_substream *substream);
int (*ioctl)(struct snd_pcm_substream * substream,
unsigned int cmd, void *arg);
int (*hw_params)(struct snd_pcm_substream *substream,
struct snd_pcm_hw_params *params);
int (*hw_free)(struct snd_pcm_substream *substream);
int (*prepare)(struct snd_pcm_substream *substream);
int (*trigger)(struct snd_pcm_substream *substream, int cmd);
snd_pcm_uframes_t (*pointer)(struct snd_pcm_substream *substream);
int (*get_time_info)(struct snd_pcm_substream *substream,
struct timespec *system_ts, struct timespec *audio_ts,
struct snd_pcm_audio_tstamp_config *audio_tstamp_config,
struct snd_pcm_audio_tstamp_report *audio_tstamp_report);
int (*fill_silence)(struct snd_pcm_substream *substream, int channel,
unsigned long pos, unsigned long bytes);
int (*copy_user)(struct snd_pcm_substream *substream, int channel,
unsigned long pos, void __user *buf,
unsigned long bytes);
int (*copy_kernel)(struct snd_pcm_substream *substream, int channel,
unsigned long pos, void *buf, unsigned long bytes);
struct page *(*page)(struct snd_pcm_substream *substream,
unsigned long offset);
int (*mmap)(struct snd_pcm_substream *substream, struct vm_area_struct *vma);
int (*ack)(struct snd_pcm_substream *substream);
};
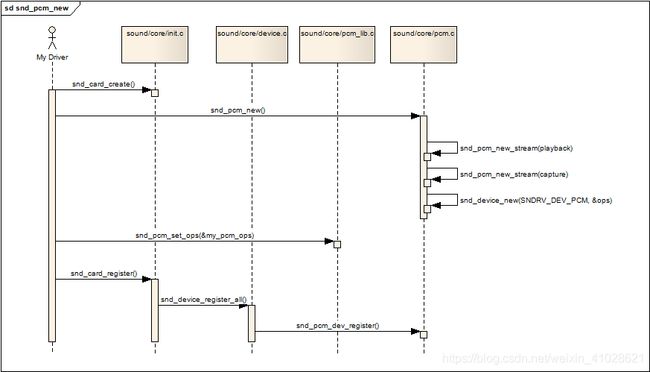
3.7.snd_pcm_new
int snd_pcm_new(struct snd_card *card, const char *id, int device, int playback_count, int capture_count, struct snd_pcm rpcm);
- 参数device 表示目前创建的是该声卡下的第几个pcm,第一个pcm设备从0开始.
- 参数playback_count 表示该pcm将会有几个playback substream.
- 参数capture_count 表示该pcm将会有几个capture substream.
函数实现:
- 构建一个struct snd_pcm数据结构来代表一个PCM实例
- 调用snd_pcm_new_stream(pcm, SNDRV_PCM_STREAM_PLAYBACK, playback_count)构建playback stream, 并创建playback_count个substream.
- 调用snd_pcm_new_stream(pcm, SNDRV_PCM_STREAM_CAPTURE, capture_count)构建capture stream, 并创建capture_count个substream.
- 最后, 调用snd_device_new把这个实例作为一个逻辑设备添加到card->devices链表下.
请注意, 在card被注册之前, 我们需要调用snd_pcm_set_ops为此PCM实例设置回调函数, 因为当用户空间通过设备节点与PCM中间层交互时, PCM中间层需要回调底层驱动实现的ops函数.
3.8.设置pcm操作函数接口
void snd_pcm_set_ops(struct snd_pcm *pcm, int direction, struct snd_pcm_ops *ops);
3.9.PCM字符设备的创建
当card被注册时, 会扫描下属的每个逻辑设备并注册它们, 这里创建的PCM逻辑设备也会在那时进行注册. 当PCM逻辑设备被注册时, ALSA系统层会回调逻辑设备的snd_device_ops. dev_register函数, 也就是snd_pcm_dev_register. 在该回调函数中, 会针对每一个stream调用snd_register_device, 进而在用户空间创建对应的设备节点.
PCM中间层的snd_pcm_f_ops会负责与用户空间交互, 其主要功能包括:
- open / release : 打开或者关闭某substream.
- read / write / mmap : 用户空间与PCM中间层交换音频数据.
- ioctl : 提供各种各样的控制接口.
4.pcm设备创建完成逻辑图

大体上就是一棵树,根节点是card0, 然后子节点是pcm设备,pcm设备分为capture & playback stream, 然后在stream下又分为substrem。