python入门(分享一些自己的学习经验和笔记)
python入门(复制代码,试着运行一下,先体验一下python的魅力)
import turtle
"""
奥运五环的绘制使用库(turtle)
"""
turtle.width(10)
color_list = ['blue', 'black', 'red', 'yellow', 'green']
x_y_list = [(-130, 0), (0, 0), (130, 0), (-65, -50), (65, -50)]
turtle.speed(10)
for i in range(5):
turtle.penup()
turtle.goto(x_y_list[i])
turtle.pendown()
turtle.color(color_list[i])
turtle.circle(50)
turtle.done()
# turtle.width(10)
# turtle.speed(15)
# turtle.penup()
# turtle.backward(130)
# turtle.pendown()
# turtle.color('blue') # 蓝
# turtle.circle(50)
# turtle.penup()
# turtle.forward(130)
# turtle.pendown()
# turtle.color('black') # 黑
# turtle.circle(50)
# turtle.penup()
# turtle.forward(130)
# turtle.pendown()
# turtle.color('red') # 红
# turtle.circle(50)
# turtle.penup()
# turtle.goto(-65, -50)
# turtle.pendown()
# turtle.color('yellow') # 黄
# turtle.circle(50)
# turtle.penup()
# turtle.goto(65, -50)
# turtle.pendown()
# turtle.color('green') # 绿
# turtle.circle(50)
# turtle.done()
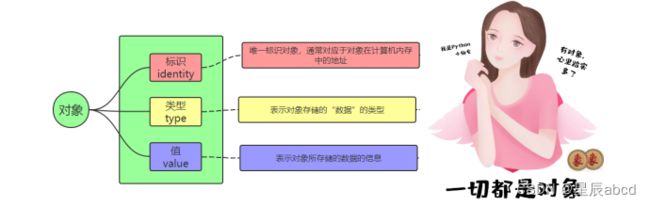
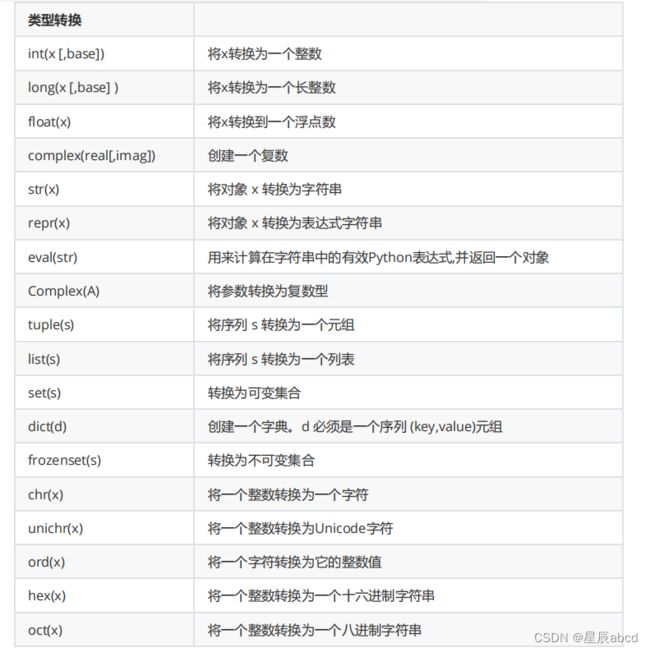
python编程的基本概念
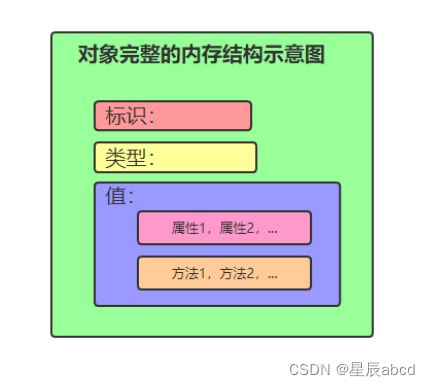
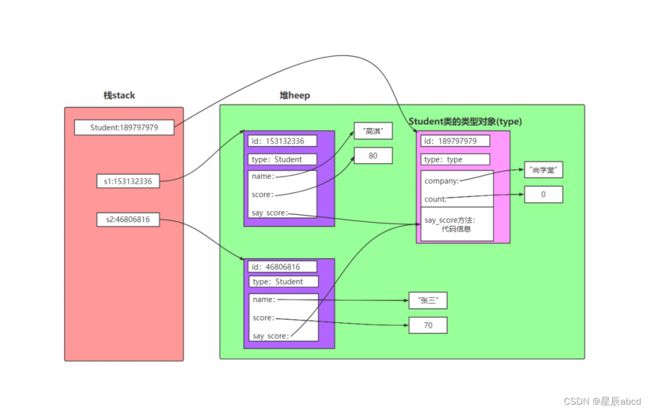
对象的组成id,type, value
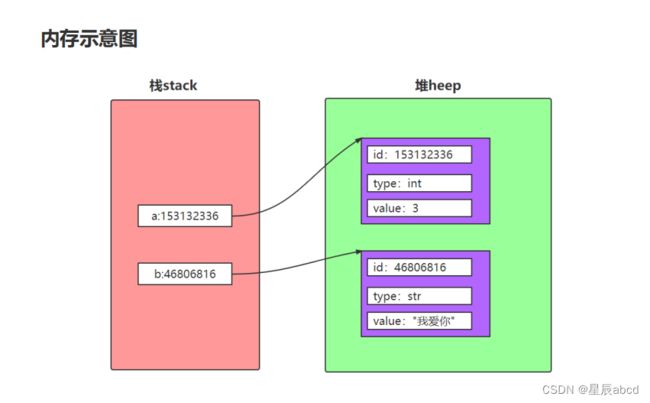
内存示意图
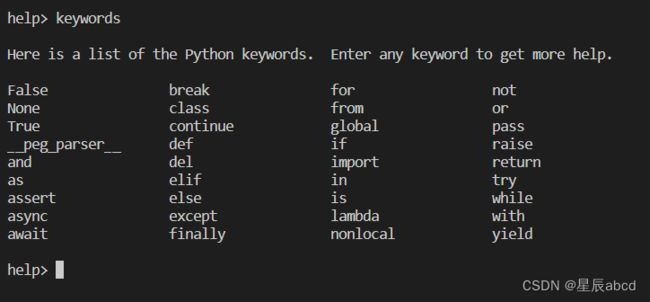
查看python系统关键字,命令行模式下输入help()
round(value) 可以返回四舍五入的值。但不会改变原有值,而是产生新的值
a = 5.5
b = round(a)
print(a)
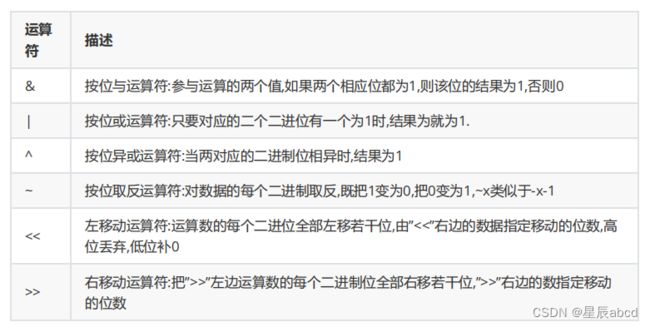
print(b)位运算符
print(3<<2) #左移1位相当于乘以2.左移两位相当于:3*4
print(20>>1) #右移移位相当于除以2‘is’与‘==’的区别
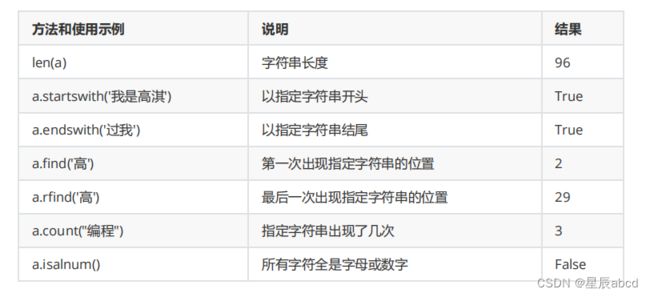
字符串
len()用于计算字符串含有多少字符
a = 'lz520'
print(len(a))
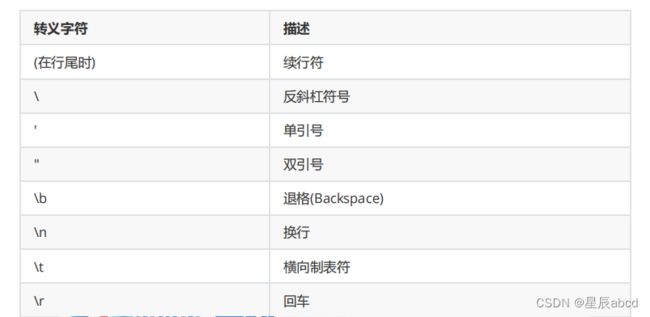
#### 5转义字符
#字符串拼接
#“+”拼接
#join拼接(效率高)
#replace()实现字符串替换
####字符串切片slice操作和索引
a = '123456'
a[start:end:step]
####split()分割和join()合并
#我们可以通过strip()去除字符串首尾指定信息。通过lstrip()去除字符串左边指定信息,rstrip()去除字符串右边指定信息字符串查找
大小写转换
序列
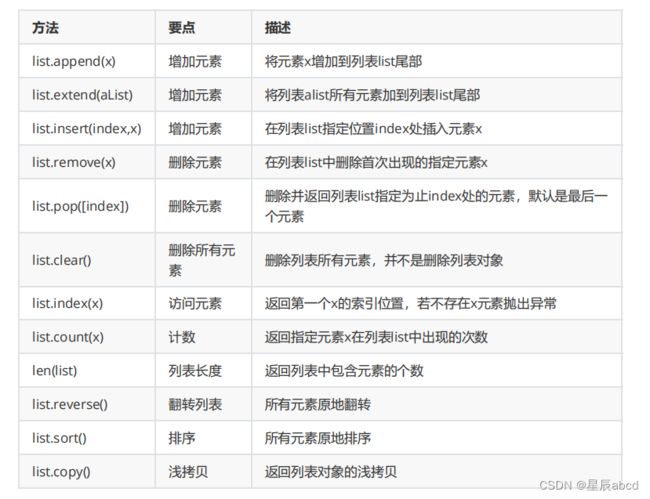
列表 list, 元组 tuple, 字典dict, 集合 set
推导式生成列表
b = [x*2 for x in range(100) if x%9==0] #生成符合条件的列表
#列表添加元素
a = []
a.append(1)
b = [2]
a.extend(b) #不产生新的对象
a.insert(2,100) #(index,value)
#列表元素的删除
a = [1, 2, 3]
del a[1] #[index]
a.pop(1) #默认最后一个元素
a.remove(1) #(value)
#zip(列表1,列表2,...)将多个列表对应位置的元素组合成为元组,并返回这个zip对象字典
#get()
a = {'name': 'lz', 'age': 18}
a.get('name')#通过键得到值
#列出所有的键值对
b = a.items()
#列出所有的键,列出所有的值
k = a.keys()
v = a.values()
#给字典新增“键值对”。如果“键”已经存在,则覆盖旧的键值对;如果“键”不存在,则新增“键值对”
a['name'] = 'wp'
#使用 update() 将新字典中所有键值对全部添加到旧字典对象上。如果 key 有重复,则直接覆盖
#del clear pop 删除元素集合
#元素添加
a = {1, 3, 7}
a.add(9)
#元素的唯一性可以用来去除重复元素元组
a = (5, 6)
b = (x for x in range(10))
# 元组推导式生成是生成器循环与控制语句
# if分支语句
if 表达式:
print("555")
elif 表达式:
print("666")
else:
print("888")
# 循环for和while
# for循环可遍历任何的序列
company = ['Google', 'Apple', 'Facebook', 'Oracle', 'Microsoft']
for x in company:
print(x)三元条件运算符
#条件为真时的值 if (条件表达式) else 条件为假时的值
num = 1
a = x if num == 1 else y
#循环
break #跳出整个循环
continue #跳出单次循环lambda**表达式和匿名函数**
a = lambda x, y : x + y
print(a(10, 20))对象
初始化对象,我们需要定义构造函数 init() 方法。构造方法用于执行“实例对象的初始化工作”,即对象创建后,初始化当前对象的相关属性,无返回值
new() 方法: 用于创建对象,但我们一般无需重定义该方法
#类方法@classmethod直接由类本身调用不需要实例化
#析构方法Python实现自动的垃圾回收,当对象没有被引用时(引用计数为0),由垃圾回收器调用 del() 。
#私有方法属性可通过dir查到_Employee__company
@property 装饰器
#测试@property
class Employee:
def __init__(self,name,salary):
self.name = name
self.__salary = salary
@property #相当于salary属性的getter方法
def salary(self):
print("月薪为{0},年薪为{1}".format(self.__salary, (12*self.__salary)))
return self.__salary
@salary.setter
def salary(self,salary): #相当于salary属性的setter方法
if(0设计模式之单例模式和工厂模式
可以自己动手敲敲熟悉熟悉
# 单例模式
class MySingleton:
__obj = None
__init_flag = True
def __new__(cls, *args, **kwargs):
if cls.__obj is None:
cls.__obj = object.__new__(cls)
return cls.__obj
def __init__(self, name):
if MySingleton.__init_flag:
print("init....")
self.name = name
MySingleton.__init_flag = False
a = MySingleton("aa")
print(a)
b = MySingleton("bb")
print(b)
#工厂模式
class CarFactory:
def createCar(self,brand):
if brand == "奔驰":
return Benz()
elif brand == "宝马":
return BMW()
elif brand == '比亚迪':
return BYD()
else:
return "未知品牌,无法创建"
class Benz:
pass
class BMW:
pass
class BYD:
pass
factory = CarFactory()
c1 = factory.createCar("奔驰")
c2 = factory.createCar("宝马")
print(c1)
print(c2)
#单例模式和工厂模式结合
class MySingleton:
__obj = None
__init_flag = True
def __new__(cls, *args, **kwargs):
if cls.__obj is None:
cls.__obj = object.__new__(cls)
return cls.__obj
def __init__(self, name):
if MySingleton.__init_flag:
print("init....")
self.name = name
MySingleton.__init_flag = False
def createCar(self,brand):
if brand == "奔驰":
return Benz()
elif brand == "宝马":
return BMW()
elif brand == '比亚迪':
return BYD()
else:
return "未知品牌,无法创建"
class Benz:
pass
class BMW:
pass
class BYD:
pass想了解什么是单例模式可参考写文章-CSDN创作中心
工厂模式可参考设计模式之工厂模式(factory pattern) - alpha_panda - 博客园 (cnblogs.com)